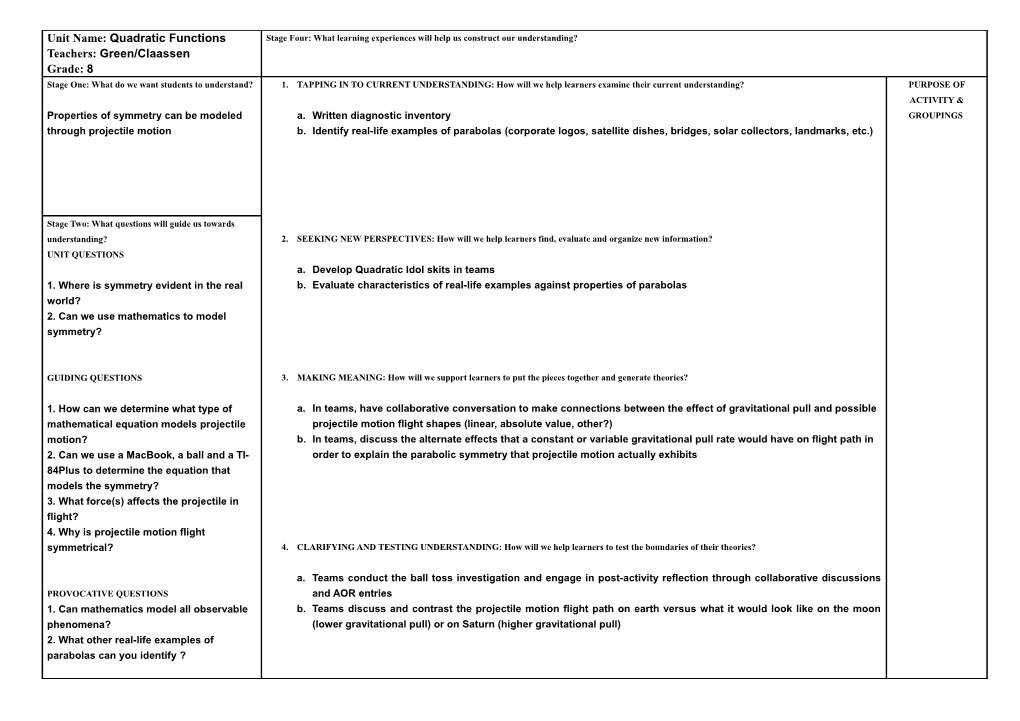
Unit Name: Quadratic Functions Stage Four: What learning experiences will help us construct our understanding? Teachers: Green/Claassen Grade: 8 Stage One: What do we want students to understand? 1. TAPPING IN TO CURRENT UNDERSTANDING: How will we help learners examine their current understanding? PURPOSE OF ACTIVITY & Properties of symmetry can be modeled a. Written diagnostic inventory GROUPINGS through projectile motion b. Identify real-life examples of parabolas (corporate logos, satellite dishes, bridges, solar collectors, landmarks, etc.)
Stage Two: What questions will guide us towards understanding? 2. SEEKING NEW PERSPECTIVES: How will we help learners find, evaluate and organize new information? UNIT QUESTIONS a. Develop Quadratic Idol skits in teams 1. Where is symmetry evident in the real b. Evaluate characteristics of real-life examples against properties of parabolas world? 2. Can we use mathematics to model symmetry?
GUIDING QUESTIONS 3. MAKING MEANING: How will we support learners to put the pieces together and generate theories?
1. How can we determine what type of a. In teams, have collaborative conversation to make connections between the effect of gravitational pull and possible mathematical equation models projectile projectile motion flight shapes (linear, absolute value, other?) motion? b. In teams, discuss the alternate effects that a constant or variable gravitational pull rate would have on flight path in 2. Can we use a MacBook, a ball and a TI- order to explain the parabolic symmetry that projectile motion actually exhibits 84Plus to determine the equation that models the symmetry? 3. What force(s) affects the projectile in flight? 4. Why is projectile motion flight symmetrical? 4. CLARIFYING AND TESTING UNDERSTANDING: How will we help learners to test the boundaries of their theories?
a. Teams conduct the ball toss investigation and engage in post-activity reflection through collaborative discussions PROVOCATIVE QUESTIONS and AOR entries 1. Can mathematics model all observable b. Teams discuss and contrast the projectile motion flight path on earth versus what it would look like on the moon phenomena? (lower gravitational pull) or on Saturn (higher gravitational pull) 2. What other real-life examples of parabolas can you identify ? STUDENT QUESTIONS & MISCONCEPTIONS
1. Quadratic graphs are ‘U’- shaped 2. The dependent variable (y) is limited, not infinite 3. What is graphical ‘end behavior?’ 4. How can equations have more than one solution? 5. How are solutions, roots and zeros, x- intercepts related? 6. How does the quadratic formula relate to graphical solutions? Stage Three: How will we recognize degrees of understanding? ASSESSMENT PLANNER Big Understandings to be assessed: Properties of symmetry can be modeled through projectile motion
CULMINATING ASSESSMENT TASK(S) (Contextual / Understanding): Written unit test including algebraic solutions, graphical representations and application word problems
Knowledge to be assessed Skills to be assessed
1. Using different methods to find the y-intercept, x-intercepts, axis of symmetry and 1. Sketch graphs of quadratic functions showing x- and y-intercepts, axis of symmetry, vertex for quadratic functions vertex and end behavior 2. Draw accurate graphs of quadratic functions 2. Use a variety of methods to find the x-intercepts and vertex of quadratic functions 3. Use the quadratic formula to solve equations including by factoring quadratic equations using x-intercepts, square root method and the q 4. Interpret quadratic graphs for different values of the discriminant quadratic formula 5. Describe transformations of quadratic graphs 3. Use the vertical motion formula to solve real life problems 4. Find values of the discriminant and describe their implications on real and no (imaginary) solutions 5. Sketch graphs using the transformation method 6. Use a graphing calculator to model solutions to quadratic functions, and determine x- intercepts and vertex PRE-ASSESSMENTS for KNOWLEDGE PRE-ASSESSMENTS for SKILLS
1. Written unit diagnostic inventory 1. Written unit diagnostic inventory
FORMATIVE ASSESSMENTS Understanding Tasks Mastery Tasks On-going Assessment Strategies
1. Ball toss team investigation 1. In-class collaborative problem solving and graphing 1. In-class collaborative problem solving and graphing 2. Quadratic Idol skits 2. Guided investigations 2. Guided investigations 3. Written quiz 3. Gizmos and self-assessments 3. Homework problems and selected solutions review 4. Homework problems 4. Action Oriented Reflection (AOR) template entries and follow-up Stage Five: What resources will we need? Resource: Purpose:
1. MacBooks 1. Record and present Quadratic Idol skits 2. Tennis balls, meter sticks, stop watches and TI-84Plus graphing calculators 2. For ball toss teams to model projectile motion and compare stop-watch measured flight time against projectile motion formula solution
Stage Six: How well did we achieve what we set out to achieve? 1. To what extent did the students achieve the target understandings?
2. To what extent did the assessment tasks allow students to demonstrate understanding?
3. To what extent did the learning activities help students build understanding?
4. To what extent did the resources help support students in building understanding?