RNSG 1327 – Transition to Professional Nursing
Unit IV – Care of the Patient Experiencing Perinatal Cycle Part D - Newborn
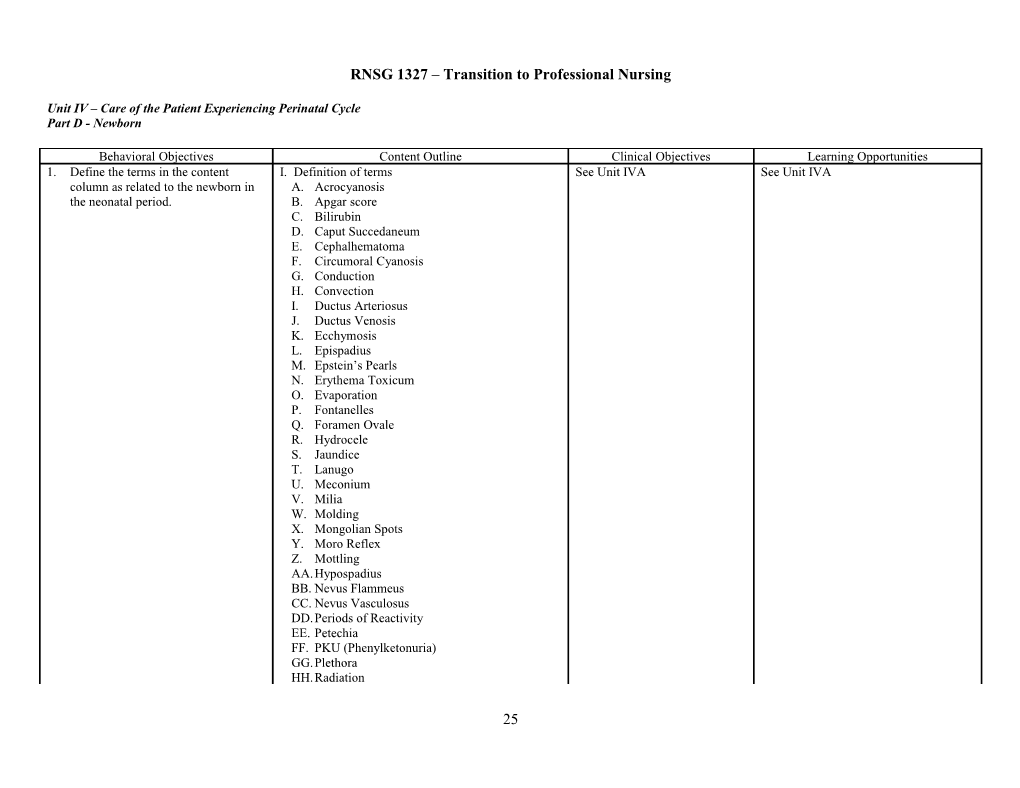
Behavioral Objectives Content Outline Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities 1. Define the terms in the content I. Definition of terms See Unit IVA See Unit IVA column as related to the newborn in A. Acrocyanosis the neonatal period. B. Apgar score C. Bilirubin D. Caput Succedaneum E. Cephalhematoma F. Circumoral Cyanosis G. Conduction H. Convection I. Ductus Arteriosus J. Ductus Venosis K. Ecchymosis L. Epispadius M. Epstein’s Pearls N. Erythema Toxicum O. Evaporation P. Fontanelles Q. Foramen Ovale R. Hydrocele S. Jaundice T. Lanugo U. Meconium V. Milia W. Molding X. Mongolian Spots Y. Moro Reflex Z. Mottling AA.Hypospadius BB. Nevus Flammeus CC. Nevus Vasculosus DD.Periods of Reactivity EE. Petechia FF. PKU (Phenylketonuria) GG.Plethora HH.Radiation
25 RNSG 1327 – Transition to Professional Nursing
Unit IV – Care of the Patient Experiencing Perinatal Cycle Part D - Newborn Behavioral Objectives Content Outline Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities II. Strabismus JJ. Subconjunctival Hemorrhage KK.Surfactant LL. Sutures MM. Talipes Equinovarus NN.Telangiectic Nevi OO. Vernix Caseosa
2. Compare and contrast the changes II. Adaptation to extrauterine life that occur to the newborn during the A. Physiological physical/psychological adaptation to 1. Respiratory extrauterine life. 2. Cardiovascular 3. Hematological 4. Temperature regulation 5. Hepatic changes 6. Gastrointestinal 7. Genitourinary 8. Immunological 9. Neurological & sensory perceptual 10. Behavioral
3. Identify factors influencing the III. Newborn assessment assessment of the newborn. A. Maternal prenatal/intrapartal history B. Initial assessment (at time of birth) 1. Vital signs a. Respiratory rate b. Heart rate c. Temperature 2. Apgar score a. Respiratory effort b. Muscle tone c. Reflex irritability d. Color 3. General appearance a. Posture
26 RNSG 1327 – Transition to Professional Nursing
Unit IV – Care of the Patient Experiencing Perinatal Cycle Part D - Newborn Behavioral Objectives Content Outline Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities
C. Head to toe assessment 1. Vital signs a. Temperature b. Pulse c. Respirations d. Blood pressure 2. Measurements a. Weight b. Length c. Head circumference (FOC) d. Chest circumference e. Abdominal circumference 3. Posture 4. Skin characteristics a. Color b. Texture c. Turgor d. Pigmentation/birthmarks 5. Head a. General appearance, movement b. Molding c. Sutures d. Fontanelles e. Hair 6. Face, eyes, ears, nose, mouth 7. Neck 8. Chest, heart 9. Abdomen/umbilicus 10. Genitals 11. Buttocks & anus 12. Extremities & trunk 13. Neuromuscular 14. Reflexes 15. Gestational Age Assessment a. Neuromuscular maturity
27 RNSG 1327 – Transition to Professional Nursing
Unit IV – Care of the Patient Experiencing Perinatal Cycle Part D - Newborn Behavioral Objectives Content Outline Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities b. Physical maturity
D. Behavioral assessment E. Cultural Considerations F. Diagnostic studies 1. Newborn screening test (PKU) 2. Coombs/blood type 3. Hgb/hct 4. Blood glucose
4. Discuss, analysis, planning, IV. Selected nursing diagnoses / implementation/ implementation, and evaluation evaluation of nursing A. Initial care (delivery) management of the newborn. 1. Ineffective airway clearance a. Independent interventions b. Assess ABC’s (airway, breathing, circulation) c. Suction 1. Bulb 2. Deep d. Assess respiratory rate e. Position f. Apgar score g. Stimulate h. Reassess respiratory status frequently i. Collaborative interventions (1) Consult with respiratory therapist (2) Consult with pediatrician j. Evaluation of outcomes: The newborn will have improved airway clearance as exhibited by: (1) Maintaining respiratory rate 30- 60 per minute within 15 minutes of delivery. (2) Absence of retractions, nasal flaring, or use of accessory
28 RNSG 1327 – Transition to Professional Nursing
Unit IV – Care of the Patient Experiencing Perinatal Cycle Part D - Newborn Behavioral Objectives Content Outline Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities muscles within 1-2 hours of delivery
(3) Clear breath sounds within 1-2 hours of delivery 2. Risk for altered body temperature a. Independent interventions (1) Dry the baby (2) Place in controlled environment (radiant warmer) (3) Monitor temperature. b. Evaluation of outcomes: The newborn will have a decreased risk for altered body temperature as exhibited by: (1) Use of radiant warmer the first hours after delivery. (2) Obtaining temperature of 97- 98.8F B. Nursery Care 1. Altered peripheral tissue perfusion a. Independent interventions (1) Assess cardiopulmonary status (2) Maintain patent airway (3) Maintain thermal neutral environment (4) Promote adequate hydration b. Collaborative interventions (1) Administer medications and monitor for desired effects/adverse effects/side effects (a) Vitamin K
29 RNSG 1327 – Transition to Professional Nursing
Unit IV – Care of the Patient Experiencing Perinatal Cycle Part D - Newborn Behavioral Objectives Content Outline Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities
c. Evaluation of outcomes: The newborn will have adequate tissue profusion as exhibited by (1) Stable vital signs within 1-3 hours after delivery (2) Maintenance of temperature 97- 98.6 degrees 2. Altered nutritional/elimination status a. Independent interventions (1) Monitor feeding behavior patterns (formula vs breast feeding) (2) Position after feeding (3) Keep bulb suction available (4) Observe for regurgitation after feeding (5) Measure and document type of feeding, how much taken, and retained (6) Monitor and record output – stool, urine b. Collaborative interventions (1) Glucose monitoring on admission to the nursery (2) Refer to WIC, La Leche League c. Evaluation of outcomes: The newborn will have adequate nutrition/elimination status as exhibited by: (1) Breast feeding every 2-3 hours or bottle feeding 1-2 ounces of formula with minimal regurgitation every 3-4 hours (2) Voiding every 2 hours after first 24 hours of life
30 RNSG 1327 – Transition to Professional Nursing
Unit IV – Care of the Patient Experiencing Perinatal Cycle Part D - Newborn Behavioral Objectives Content Outline Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities (3) Passage of stool
3. Risk for infection a. Independent interventions (1) Eye care (2) Cord care (3) Circumcision care (4) Skin care/bathing/clothing b. Collaborative interventions (1) Refer to urologist or pediatrician for circumcision c. Evaluation of outcomes: The newborn will have a decreased risk for infection as exhibited by: (1) No evidence of eye, cord, or circumcision infection by discharge (2) No evidence of infection at first newborn checkup 4. Risk for injury a. Independent interventions (1) Maintain bacteriologic, mechanical, & thermal safety (2) Position on side or back (3) Accurate identification (4) Abduction precautions b. Collaborative interventions (1) Administer medications and monitor for desired effects/adverse effects/side effects (a) Antibiotics - Eye - Cord c. Evaluation of outcomes: The newborn will have a decreased risk or injury as exhibited by:
31 RNSG 1327 – Transition to Professional Nursing
Unit IV – Care of the Patient Experiencing Perinatal Cycle Part D - Newborn Behavioral Objectives Content Outline Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities (1) Verbalization by parents of methods of maintaining bacteriologic, mechanical, and thermal safety. (2) Verbalization by parents of rationale for maintaining side lying or back lying position (3) Armbands, footprints and maternal fingerprints (4) Verbalization by parents of abduction precautions 5. Risk for altered parenting a. Independent interventions (1) Facilitate early bonding (2) Identify – armbands, prints (3) Monitor infant response to nurturing activities (4) Monitor sleep/activity patterns (5) Provide tactile/sensory stimulation b. Evaluation of outcome: The newborn will have a decreased risk for altered parenting as exhibited by: (1) Enface interaction between parent and infant (2) No evidence of attachment difficulties 6. Knowledge deficit of newborn care skills a. Independent (1) Bathing (2) Dressing (3) Nutritional needs (4) Follow up care (5) Safety needs (6) Expected behavior patterns (7) Sleep patterns (8) Sensory stimulation
32 RNSG 1327 – Transition to Professional Nursing
Unit IV – Care of the Patient Experiencing Perinatal Cycle Part D - Newborn Behavioral Objectives Content Outline Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities (9) Family adjustments
b. Collaborative interventions (1) Refer to available resources (a) Family planning clinic (b) Well baby clinics (c) La Leche League c. Evaluation of outcomes: The parents will have a decreased knowledge deficit of newborn care skills as evidenced by: (1) Demonstrating bathing & dressing the newborn (2) Demonstrating feeding and holding techniques (3) Verbalization of follow up schedule for well baby check ups and PKU testing (4) Verbalization of safety measures
N/AND/Transition/RNSG 1327 Unit IV D/Newborn Reviewed 03/12 Reviewed 03/13
33