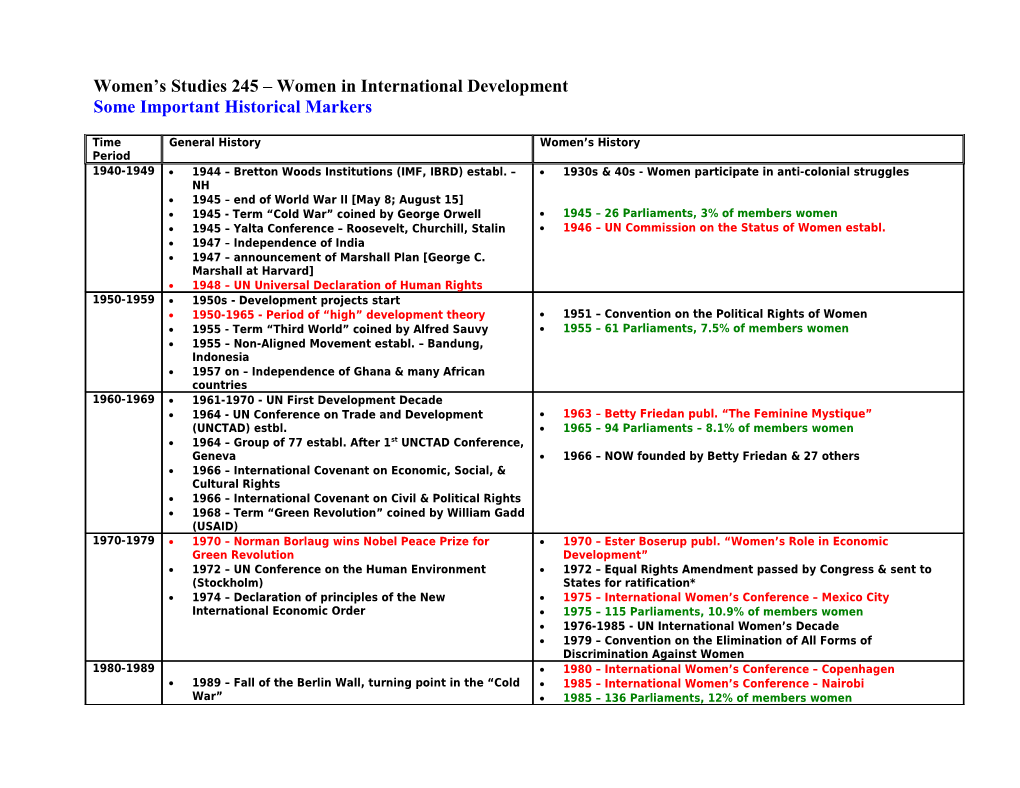
Women’s Studies 245 – Women in International Development Some Important Historical Markers
Time General History Women’s History Period 1940-1949 1944 – Bretton Woods Institutions (IMF, IBRD) establ. – 1930s & 40s - Women participate in anti-colonial struggles NH 1945 – end of World War II [May 8; August 15] 1945 - Term “Cold War” coined by George Orwell 1945 – 26 Parliaments, 3% of members women 1945 – Yalta Conference – Roosevelt, Churchill, Stalin 1946 – UN Commission on the Status of Women establ. 1947 – Independence of India 1947 – announcement of Marshall Plan [George C. Marshall at Harvard] 1948 – UN Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1950-1959 1950s - Development projects start 1950-1965 - Period of “high” development theory 1951 – Convention on the Political Rights of Women 1955 - Term “Third World” coined by Alfred Sauvy 1955 – 61 Parliaments, 7.5% of members women 1955 – Non-Aligned Movement establ. – Bandung, Indonesia 1957 on – Independence of Ghana & many African countries 1960-1969 1961-1970 - UN First Development Decade 1964 - UN Conference on Trade and Development 1963 – Betty Friedan publ. “The Feminine Mystique” (UNCTAD) estbl. 1965 – 94 Parliaments – 8.1% of members women 1964 – Group of 77 establ. After 1st UNCTAD Conference, Geneva 1966 – NOW founded by Betty Friedan & 27 others 1966 – International Covenant on Economic, Social, & Cultural Rights 1966 – International Covenant on Civil & Political Rights 1968 – Term “Green Revolution” coined by William Gadd (USAID) 1970-1979 1970 – Norman Borlaug wins Nobel Peace Prize for 1970 – Ester Boserup publ. “Women’s Role in Economic Green Revolution Development” 1972 – UN Conference on the Human Environment 1972 – Equal Rights Amendment passed by Congress & sent to (Stockholm) States for ratification* 1974 – Declaration of principles of the New 1975 – International Women’s Conference – Mexico City International Economic Order 1975 – 115 Parliaments, 10.9% of members women 1976-1985 - UN International Women’s Decade 1979 – Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women 1980-1989 1980 – International Women’s Conference – Copenhagen 1989 – Fall of the Berlin Wall, turning point in the “Cold 1985 – International Women’s Conference – Nairobi War” 1985 – 136 Parliaments, 12% of members women 1990-1999 1991 – Fall of the USSR 1992 – UN Conf. on Environment & Development (Earth Summit, Rio) 1993 - UN Declaration on the Elimination of All Forms of Violence 1993 – UN Human Rights Conference Against Women 1994 – International Conference on Population and Development 1995 – International Women’s Conference – Beijing 1995 – UN Social Summit 1995 – 176 Parliaments, 11.6% of members women 1996 – FAO World Food Summit 1997 – Framework Convention on Climate Change (Kyoto Protocol) 2000-2009 2004 – Wangari Maathai wins Nobel Peace Prize for Environmental Activism 2005 – 187 Parliaments, 18.7% of members women *The Equal Rights Amendment, first written by suffragist Alice Paul and proposed by the National Women’s Party in 1923, has been introduced in every session of Congress since 1923. After passing in 1972, it was ratified by only 35 of the necessary 38 States before lapsing by the extended deadline of June 30, 1982. [“Equality of rights under the law shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or any State on account of sex”] Women got the vote in the USA in 1920, when the 19th Amendment to the US Constitution was ratified.