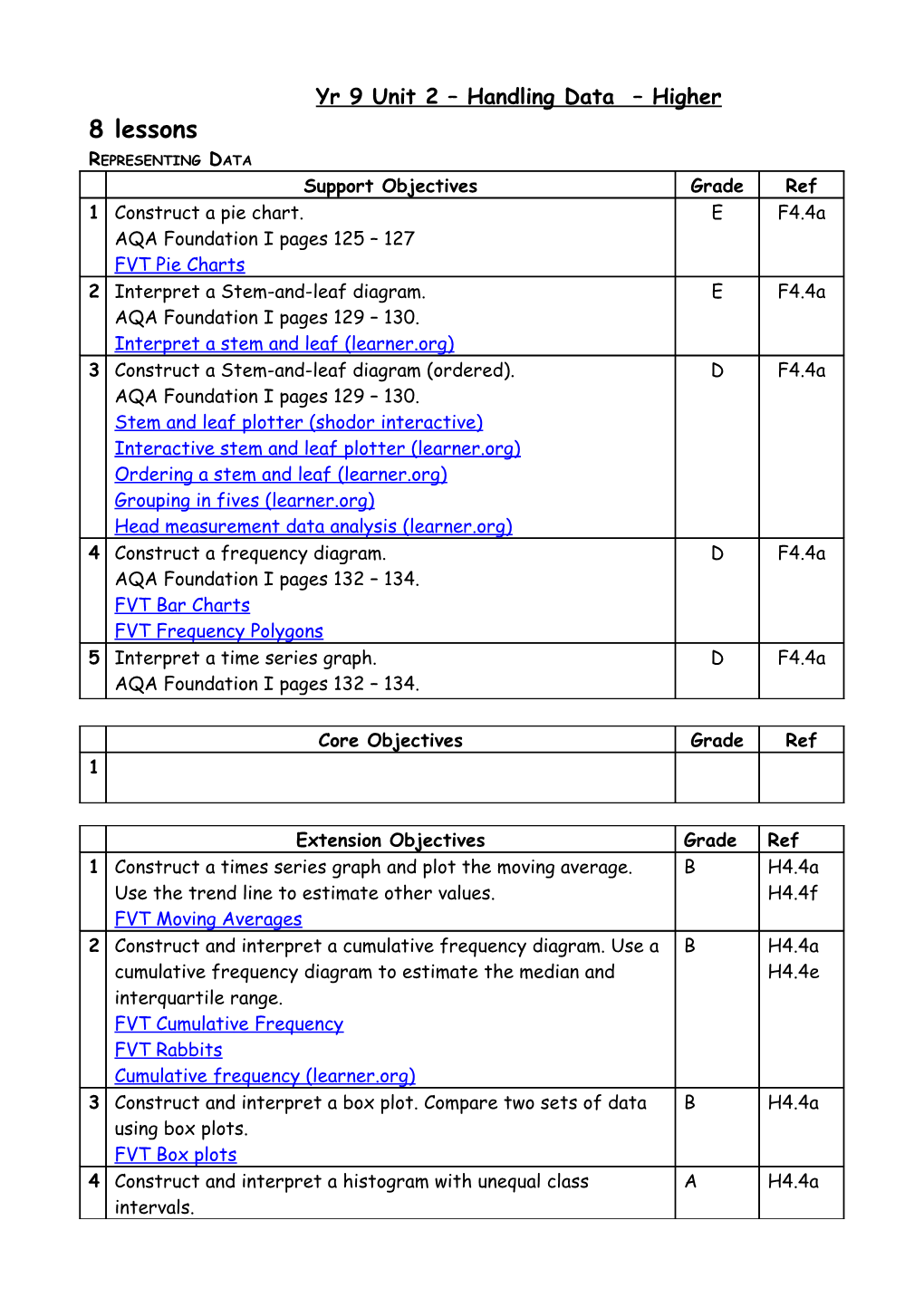
Yr 9 Unit 2 – Handling Data – Higher 8 lessons REPRESENTING DATA Support Objectives Grade Ref 1 Construct a pie chart. E F4.4a AQA Foundation I pages 125 – 127 FVT Pie Charts 2 Interpret a Stem-and-leaf diagram. E F4.4a AQA Foundation I pages 129 – 130. Interpret a stem and leaf (learner.org) 3 Construct a Stem-and-leaf diagram (ordered). D F4.4a AQA Foundation I pages 129 – 130. Stem and leaf plotter (shodor interactive) Interactive stem and leaf plotter (learner.org) Ordering a stem and leaf (learner.org) Grouping in fives (learner.org) Head measurement data analysis (learner.org) 4 Construct a frequency diagram. D F4.4a AQA Foundation I pages 132 – 134. FVT Bar Charts FVT Frequency Polygons 5 Interpret a time series graph. D F4.4a AQA Foundation I pages 132 – 134.
Core Objectives Grade Ref 1
Extension Objectives Grade Ref 1 Construct a times series graph and plot the moving average. B H4.4a Use the trend line to estimate other values. H4.4f FVT Moving Averages 2 Construct and interpret a cumulative frequency diagram. Use a B H4.4a cumulative frequency diagram to estimate the median and H4.4e interquartile range. FVT Cumulative Frequency FVT Rabbits Cumulative frequency (learner.org) 3 Construct and interpret a box plot. Compare two sets of data B H4.4a using box plots. FVT Box plots 4 Construct and interpret a histogram with unequal class A H4.4a intervals. Vocabulary Bar chart Stem-and-leaf diagram Line graph Pictogram Ordered stem-and-leaf diagram Time series Pie chart Back to back stem-and-leaf diagram Histogram Frequency diagram Moving average Box plot Median Lower quartile Continuous data
Ideas for starters *Rehearse vocabulary. *Discuss the collection of information from work/school/family about the following areas: favourite pet/colour/holiday destination. Favourite ice cream/drink/crisps. Favourite book/film/car. Phone network. Mode of transport. Collect information to use for creating various representations-bar chart etc. *Consider different data sets and decide what would be the most appropriate representation and what would be least appropriate. *Working in pairs students should look at and describe each others representations which they must interpret. *Reveal a set of numbers and see how quickly students can put the numbers into a stem and leaf diagram. *Collect examples of line graphs from the media. Which ones are helpful and which ones are deceptive? How can you make information deceptive? *Collect statistics over time and create an on going graph. Use the graph to identify graphs.
HOLS/maths investigations * AQA Foundation I pages 127, 130, 134 * Students must complete the first part of their Statistics Coursework.
ICT links / citizenship * Ferrers VT – Data Handling/Bar Charts * Ferrers VT – Data Handling/Pie Charts * Self-marking Spreadsheets – Data Handling/Pie chart calculations * Self-marking Spreadsheets – Data Handling/Stem and leaf diagrams * Self-marking Spreadsheets – Data Handling/Stem and leaf diagrams 2 * Self-marking Spreadsheets – Data Handling/Interpreting Pie charts * Plenaries – Data Handling/Pie charts
Ideas for plenaries *Give examples of different types of data and ask students to identify whether the data is discrete or continuous- number of cars on the road, height of students, temperature, shoe size etc. *Collect information on how students come to school. This can be used on representing data. * Discuss the collection of information from work/school/family about the following areas: favourite pet/colour/holiday destination. Favourite ice cream/drink/crisps. Favourite book/film/car. Phone network. Mode of transport. Collect information to use for creating various representations-bar chart etc. * Consider different data sets and decide what would be the most appropriate representation and what would be least appropriate. *Working in pairs students should look at and describe each others representations which they must then interpret. *Ask students to create their own data sets, so that they can look at trend lines.
Ideas for homework * AQA Foundation I Homework book. Chapter 10. Numbers 1, 2, 3. * Continue work on Statistics coursework Webmaths Pie Chart Calculations Webmaths Stem and Leaf diagrams Webmaths Box Plots and Averages GCSE Exam Question Pie charts, Bar charts, Stem and Leaf GCSE Exam Question Frequency Polygon and Estimated Mean GCSE Exam Question Cumulative Frequency and Box Plot GCSE Exam Question Moving Averages GCSE Exam Question Histogram and Estimated mean
Ideas for Formative Comments * Make sure you measure the angles accurately when drawing pie charts. * Make sure you include a key when drawing pictograms. * Make sure you include a key when constructing stem and leaf diagrams. * Make sure you line the numbers up in size order in a stem and leaf diagram. * Make sure you leave equal sized gaps between the bars when drawing a bar chart. * Make sure the bars are all the same width when drawing a bar chart.