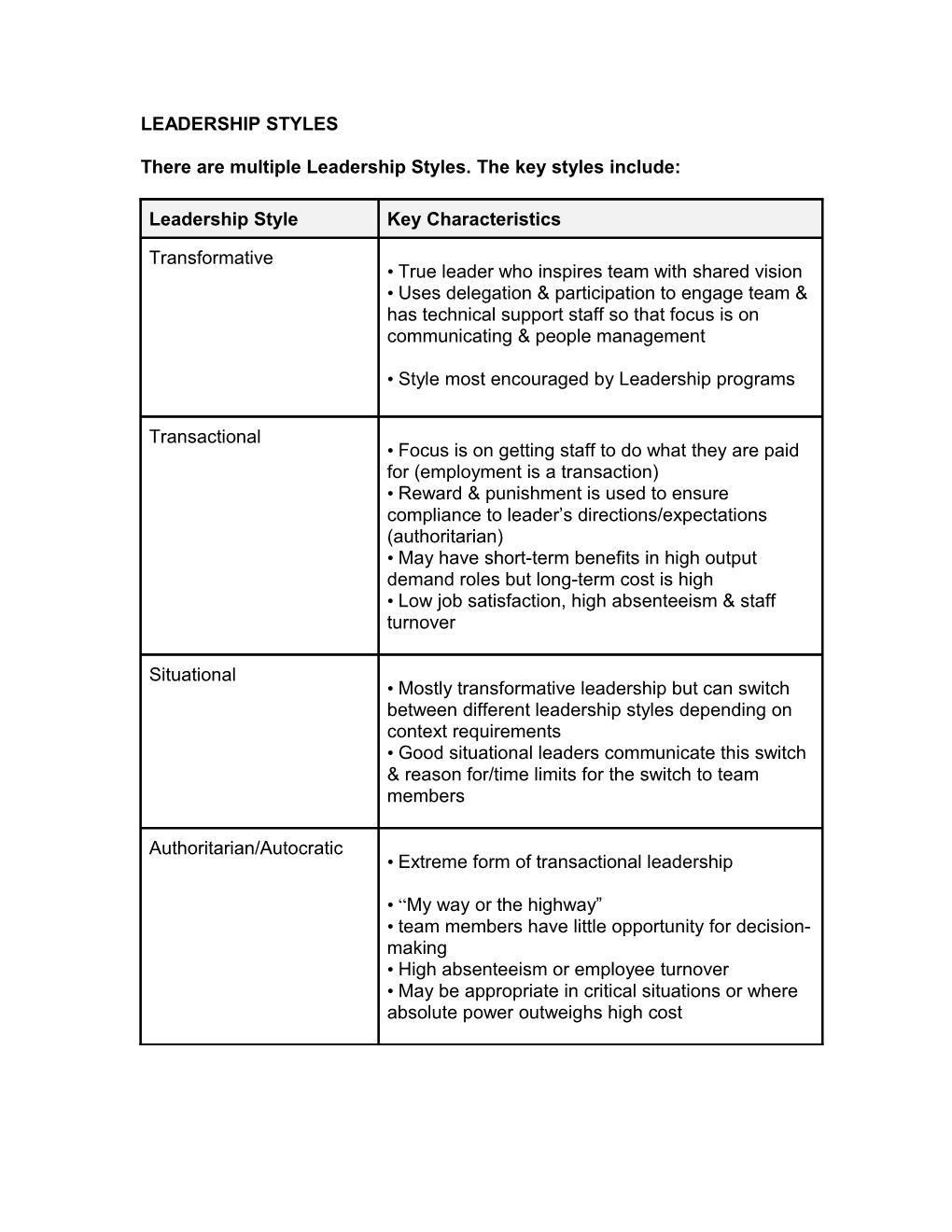
LEADERSHIP STYLES
There are multiple Leadership Styles. The key styles include:
Leadership Style Key Characteristics
Transformative • True leader who inspires team with shared vision • Uses delegation & participation to engage team & has technical support staff so that focus is on communicating & people management
• Style most encouraged by Leadership programs
Transactional • Focus is on getting staff to do what they are paid for (employment is a transaction) • Reward & punishment is used to ensure compliance to leader’s directions/expectations (authoritarian) • May have short-term benefits in high output demand roles but long-term cost is high • Low job satisfaction, high absenteeism & staff turnover
Situational • Mostly transformative leadership but can switch between different leadership styles depending on context requirements • Good situational leaders communicate this switch & reason for/time limits for the switch to team members
Authoritarian/Autocratic • Extreme form of transactional leadership
• “My way or the highway” • team members have little opportunity for decision- making • High absenteeism or employee turnover • May be appropriate in critical situations or where absolute power outweighs high cost Bureaucratic • “By the book” leadership • “If it isn’t a protocol, it isn’t practiced” • Useful for work requiring precise outputs • Limits team members’ capacity for innovation, enterprise and buy-in (unless they like the type of work that is clearly directive)
Charismatic • Leader is highly enthusiastic and motivates others with energy • May be perceived as only source of motivation or inspiration in the team • Team members may feel that without their leader they cannot complete important projects
Democratic/Participative • Invites team members to contribute to decision making, although may make final decision • Very useful in situations where team cohesion is important & job sharing a focus • Change may be slower with participative process but buy-in and outcome likely to be greater • Useful when quality is better than output quantity
Popularist / Laissez-faire • Leaders leave team members to get on with their work: “leave it be” • Useful when team members are highly skilled and proficient, but if feedback on output and achievements (or difficulties) are not provided, lowered engagement or entrenched poor behaviour may result • Popularist leaders are often promoted from within and may ‘leave it be’ to not upset ex-peers/friends • Lack of continual direction or clarity often results Task-orientated • Very task and output focussed • Clearly provides targets, timelines, technical support & advice but little focus on team members as individuals requiring support • Like authoritarian leadership, can lead to increased absenteeism & staff turnover because of lack of staff engagement
People/relations orientated • The opposite of task-orientated • The focus is truly on people management rather
Servant • Leadership is achieved because person meets the needs of other team members: often not a formal team leader • Often occurs when team undertakes a project and a team member ‘arises’ as the project leader by value of skills/knowledge/enthusiasm • Useful in many situations, but individual may still be overlooked to become formal leader and this may result in that person’s disengagement or disgruntlement for person
What leadership type are you most often?
Leadership behaviour can be either effective or ineffective.
EFFECTIVE INEFFECTIVE 1. Directing Dominating • Gives people clear directions • Taking control when it is unnecessary, when they are new or interrupting the efforts of others, and inexperienced. overriding other people’s ideas. • Provides explanations and honest feedback to others. • Gives people the information they need to do their jobs.
2. Problem Solving Over-involving • Identifies problems • Meets for the sake of meeting, • Clarifies goals • Discusses issues but does not listen, • Suggests alternatives • Involves people but produces no action. • Chooses the best solution • Monitors implementation • Seeks input from others • Listens to people’s concerns
3. Developing Over-accommodating • Assists members of the group • Tries to be liked by everyone and to keep when they need support. everyone happy. • Provides information or opinions • Agrees with anything and bends over but supports others to develop backwards to be supportive, even when the solutions. requests are inappropriate or do not make • Encourages others to assume sense. responsibility.
4. Delegating Abandoning • Empowers members of the group • Blamed for dumping responsibilities if to make decisions and take action members lack the knowledge or ability to in areas where they have expertise. complete delegated projects themselves. 1 • Members become frustrated by the lack of support and ambiguity.
LEADERSHIP - INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIP
Do unto others as you would do them to you Isadore Sharp Founder, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer
"We demonstrate our beliefs most meaningfully in the way we treat each other and by the example we set for one another. In all our interactions with our guests, customers, business associates and colleagues, we seek to deal with others as we would have them deal with us."
Treat Others with Respect Empathise Honesty & Integrity Goals of business should be your goals Analyse situation and take decision clearly Objective and Business outcomes prevail when taking decisions Open Communication Share workload Privately reprimand but publicly appreciate Plan for future Deal with poor performance Empower Challenge constantly Quick decisions Management – organisation of processes and people, is about doing things right, arranging and telling Leadership – inspiring people to do better, is about doing the right things, nurturing
TEAM LEADERSHIP
. High tolerance to uncertainity . Open to new ideas . Able to see other’s viewpoints . Able to think WIN – WIN . Focus on outcomes and results and not TASKS . Right people in the right seat in the Bus –iness . Identify& develop team member talents . Reward Vs Reprimand . Teach and Coach . Empower