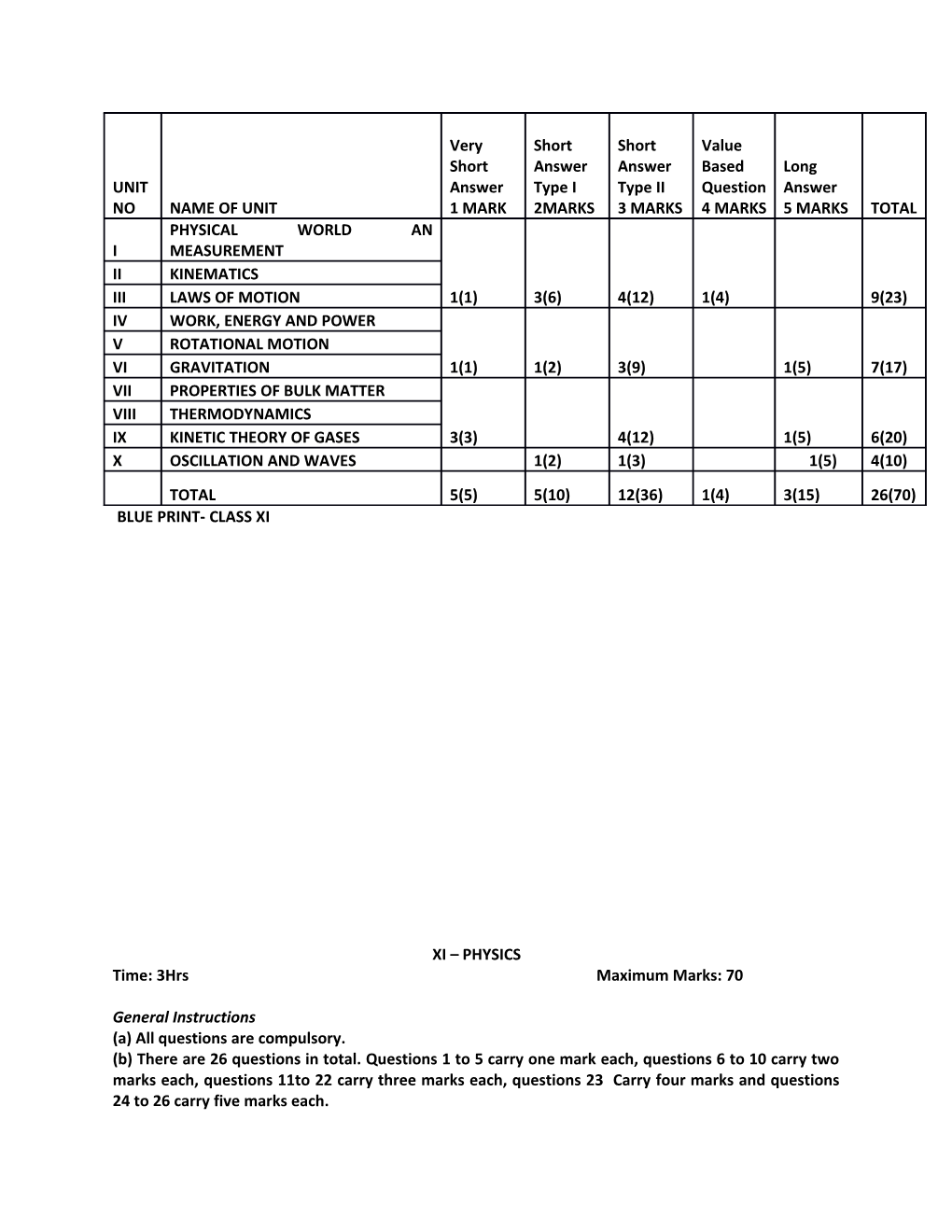
Very Short Short Value Short Answer Answer Based Long UNIT Answer Type I Type II Question Answer NO NAME OF UNIT 1 MARK 2MARKS 3 MARKS 4 MARKS 5 MARKS TOTAL PHYSICAL WORLD AN I MEASUREMENT II KINEMATICS III LAWS OF MOTION 1(1) 3(6) 4(12) 1(4) 9(23) IV WORK, ENERGY AND POWER V ROTATIONAL MOTION VI GRAVITATION 1(1) 1(2) 3(9) 1(5) 7(17) VII PROPERTIES OF BULK MATTER VIII THERMODYNAMICS IX KINETIC THEORY OF GASES 3(3) 4(12) 1(5) 6(20) X OSCILLATION AND WAVES 1(2) 1(3) 1(5) 4(10) TOTAL 5(5) 5(10) 12(36) 1(4) 3(15) 26(70) BLUE PRINT- CLASS XI
XI – PHYSICS Time: 3Hrs Maximum Marks: 70
General Instructions (a) All questions are compulsory. (b) There are 26 questions in total. Questions 1 to 5 carry one mark each, questions 6 to 10 carry two marks each, questions 11to 22 carry three marks each, questions 23 Carry four marks and questions 24 to 26 carry five marks each. (c) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question of two marks, one question of three marks and all three questions of five marks each. You have to attempt only one of the given choices in such questions. (d) Use of calculator is not permitted. (e) You may use the following physical constants wherever necessary. e = 1.6 X 10-19 C c = 3 X 108 m/s h = 6.6 X 10-34 JS µₒ = 4π X 10-7 N/A2 23 kB = 1.38 X 10 J/K -23 NA = 6.023 X 10 /mole -27 mn = 1.6 X 10 Kg
SECTION A
Q1. If ‘slap’ times speed equals power, what is the dimensional formula for slap?
Q2. What is strain? Write dimensional formula for strain.
Q3. Define adiabatic process.
Q4. Which physical quantity is represented by product of moment of inertia and angular velocity?
Q5. State kelvin-plank statement of 2nd law of thermodynamics.
SECTION B
Q6. Calculate the error in density of a cube when its mass is uncertain by +2% and length of its edge is uncertain by +1%.
Q7. Distinguish between g and G? How are they related?
Q8. Derive equations of motion for uniformly accelerated motion using graphical method.
Q9. When a ball is thrown upwards, its momentum first decreases and then increases. Is conservation if linear momentum violated in this process?
OR
A body of mass 2kg is moving with an acceleration of 9.8m/s2.What is the rate of change of its linear momentum?
Q10. Is it possible to design a heat engine of 100% efficiency? Explain.
Q11. a) Can a room be cooled by opening the door of a refrigerator in a closed room? Explain. b) Calculate the efficiency of Carnot’s engine working between steam point and ice point.
Q12. What do you mean by banking of roads? Derive an expression for speed at which curve can be negotiated safely along curved roads.
Q13. A physical quantity force is dependent on frequency, mass and radius. Derive physical relation for force using dimensional analysis.
Q14. State and prove work-energy theorem.
Q15.a) Find the torque of force 7i+3j+5k about origin. The force acts on a particle whose position vector is i-j+k. b) How do we find the directin of angular velocity?
Q16. Define S.H.M. Under what conditions is the motion of pendulum simple harmonic? Write the formula for time period of simple pendulum oscillating simple harmonically.
OR
A displacement wave is represented by y=0.25X103sin(500t+0.025hz)
Where y, t and z are in cm, sec. and m respectively.
Deduce:-a)Wave frequency b)wavelength c) Wave speed
Q17.State parallelogram law of vectors. Find analytically magnitude and direction of the resultant of two vectors using parallelogram law of vectors.
Q18.State kepler’s laws of planetary motion. Deduce 2nd law of planetary motion from knowledge of angular momentum.
Q19. i and j are unit vectors along x-axis and y-axis respectively. What is the magnitude and direction of i+j and i-j?
Q20. Define terminal velocity and derive an expression for the same.
Q21. Deduce an expression for pressure exerted by an ideal gas on the walls of a closed container.
Q22. What do you understand by streamline flow of a liquid? Write its two properties.
SECTION D
Q23. While walking through the hills of Shimla, Satish asked his uncle Ramnath if it was possible to measure the height of a distant hill. Ramnath never thought of this earlier. But he decided to find out the possibility of measuring the height of a distant hill. He talked to many of his friends but could not find a satisfactory answer. Then he went to school and consulted a teacher. The teacher explained the method of measurement to Ramnath. Ramnath came home and explained the same to Satish who was very happy and thanked his uncle profusely. a) What according to you are the values dislayed by Ramnath? b) Explain the method of measurement of height of a distant hill?
SECTION E
Q24. Define escape velocity and derive an expression for escape velocity.
OR
(a) Show the variation in value of g with Height and Depth
(b)You are given the following data:-
2 6 8 g=9.81m/s ,RE=6.37X10 m,the distance to the moon ,R=3.84x10 m and the time period of moon’s revolution is 27.3 days.Obtain the mass of earth in two different ways.G=6.67x10- 11Nm2kg.
Q25. State and prove Bernoulli’s theorem.
OR a) Derive an expression for rise of liquid in a capillary tube of radius r. b) Why a liquid does not overflow from a capillary tube of small/shorter height?
Q26. Explain doppler’s effect in sound. Obtain an expression for apparent frequency of sound when source and listener are approaching each other.
OR
Give analytical treatment of formation of standing waves on strings and discuss briefly the normal modes of vibration of strings. MARKING SCHEME
S.NO. EXPECTED ANSWER MARKS 1 [MLT-2] 1 2 Force tending to pull or stretch something to an extreme degree. It is 1 a dimensionless quantity 3. The process that occurs without transfer of heat or matter exchange 1 between system and surroundings. 4. Iω = L 1
5 Correct Definition 1 6. Ρ = M/V = M/L3 , Substitute the values. 2 7. 1. g is acceleration due to gravity while G is a universal gravitational constant. 2. The value of g is 9.8m/s2 while G = 6.67X10-11 2 3. Value of g varies from planet to planet whereas G is fix every where g = GM/R2 8. Derive: 1. V = u+at 2. S = ut + (½)at2 2 3. v2 – u2 = 2as 9. No the law of conservation is not violated in the process because momentum conservation principle is applied only when no external 2 force acts on the system OR F = dp/dt = ma = 2X9.8 = 19.6 N
10. No, if T2 = 0K and T 1 = ∞, are the conditions to get ideal heat engine, which are impossible to attain and hence 100% efficient heat enigine 2 can never be obtained 11 a) No, if refrigerator is working in a closed room with its door closed it is rejecting heat to the air in the room so temperature of room increases. But when door is kept open, heat rejected to the room wil be more than heat taken by 3 refrigerator from room, in this case also temperature of room wil increase. o b) T1 = 100 C = 373K o T2 = 0 C = 273 K
Ƞ = 1 – T2/T1 = 26.81% 12. The raising of the outer edge of curved road above inner edge is known as banking of roads. 3 Correct Derivation 13. F α νa α mb α rc i.e. F = k νambrc 3 [M1L1T-2] = k [T-1]a [M1]b [L1]c Applying principle of homogeneity; a = 2, b = 1, C =1 thus, F = k ν2mr
14. Correct statement and derivation 3 15. (a) Torque = r X F Nm (cross product) (b) Right hand thumb rule or right hand screw rule 3
16. a. The motion which repeats itself after a fixed interval of time is called simple harmonic motion b. If the amplitude of simple pendulum doesnot change then the motion will be simple harmonic
C. T = 2π(l/g)1/2 3
OR
(i) f =/2 =500/2 =250/ Hz 2 (ii) = 2 /R = 2/ 0.025 =8 m (iii) =/ R 1/2 =500/ 0.025 =2x104m/s
17. Statement and correct derivation 3 18. Statement and correct derivation 3 19. To find the magnitude, (I + j)=(I - j) = (12 + 12)1/2 = 21/2 3 To find the direction, Tanθ = 1 Or θ = 45o 20. Highest velocity attainable by an object as it falls through air. Correct derivation for terminal velocity. 3 21. Correct derivation 3 22. Correct Answer 3 23. (a) He is a man of great enthusiasm and strong determination and he is confident in his interaction with people. 4 (b) Triangulation Method 24. Correct Derivation and Statement OR 5 (a) Correct derivation with diagram 2 g = GMe/R
25. Correct Statement and Derivation OR 5 (a) Correct Derivation (b) Correct explanation 26 Correct Derivation and statement 5 OR Correct Derivation