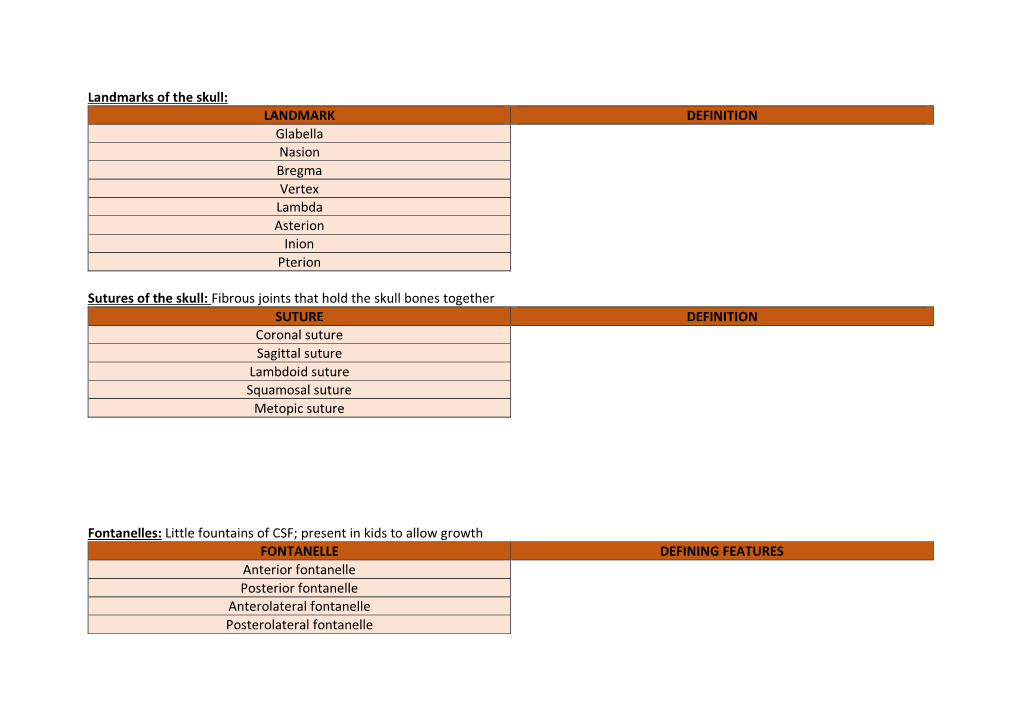
Landmarks of the Skull: LANDMARK DEFINITION Glabella Nasion Bregma Vertex Lambda Asterion Inion Pterion
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Study of Wormian Bones on Dry Human Skull and Its Sexual Dimorphism in the Region of Andhra Pradesh
Original Research Article Study of Wormian Bones on Dry human skull and its sexual dimorphism in the region of Andhra Pradesh Shone Vasudeo Durge Assistant Professor, Dept. of Anatomy, Fathima Institute of Medical Sciences, Ramarajupalli, Andhra Pradesh Corresponding Author: E-mail: [email protected] Abstract This study was aimed at identifying the wormian bone and their overall incidence in respect to their number and location in the region of Andhra Pradesh. Overall incidence of wormian bones was more in female (47.72%) than in male skulls (41.66%). They occurred more frequently at lambdoid suture (38%). Wormian bones along the coronal suture, Bregma and Asterion were seen only in male skulls, while intra-orbital wormian bones and wormian bones at Pterion were seen only in female skulls. This study concludes by stating that, there exists a moderate degree of sexual dimorphism among the wormian bones with respect to overall incidence, number and location. Keywords- Skull, Sexual dimorphism, Wormian bones, Lambda, Asterion. Background knowledge of WBs is important in the diagnosis of Wormian bones, also known as intra-sutural bones, these disorders (Cremin, Goodman, Spranger et al., are extra bone pieces that occur within a suture in the 1982). It was reported that their incidence is well suited cranium. These are irregular isolated bones that appear for comparative studies as an anthropological marker or in addition to the usual centers of ossification of the an indicator of population distance (Gumusburun, cranium and, although unusual, are not rare. They occur Sevim, Katkici et al., 1997). Their knowledge is of most frequently in the course of the lambdoid suture, interest to the human anatomy, physical anthropology which is more tortuous than other sutures. -

Morfofunctional Structure of the Skull
N.L. Svintsytska V.H. Hryn Morfofunctional structure of the skull Study guide Poltava 2016 Ministry of Public Health of Ukraine Public Institution «Central Methodological Office for Higher Medical Education of MPH of Ukraine» Higher State Educational Establishment of Ukraine «Ukranian Medical Stomatological Academy» N.L. Svintsytska, V.H. Hryn Morfofunctional structure of the skull Study guide Poltava 2016 2 LBC 28.706 UDC 611.714/716 S 24 «Recommended by the Ministry of Health of Ukraine as textbook for English- speaking students of higher educational institutions of the MPH of Ukraine» (minutes of the meeting of the Commission for the organization of training and methodical literature for the persons enrolled in higher medical (pharmaceutical) educational establishments of postgraduate education MPH of Ukraine, from 02.06.2016 №2). Letter of the MPH of Ukraine of 11.07.2016 № 08.01-30/17321 Composed by: N.L. Svintsytska, Associate Professor at the Department of Human Anatomy of Higher State Educational Establishment of Ukraine «Ukrainian Medical Stomatological Academy», PhD in Medicine, Associate Professor V.H. Hryn, Associate Professor at the Department of Human Anatomy of Higher State Educational Establishment of Ukraine «Ukrainian Medical Stomatological Academy», PhD in Medicine, Associate Professor This textbook is intended for undergraduate, postgraduate students and continuing education of health care professionals in a variety of clinical disciplines (medicine, pediatrics, dentistry) as it includes the basic concepts of human anatomy of the skull in adults and newborns. Rewiewed by: O.M. Slobodian, Head of the Department of Anatomy, Topographic Anatomy and Operative Surgery of Higher State Educational Establishment of Ukraine «Bukovinian State Medical University», Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor M.V. -

An Anomalous Digastric Muscle in the Carotid Sheath: a Case Report with Its
Short Communication 2020 iMedPub Journals Journal of Stem Cell Biology and Transplantation http://journals.imedpub.com Vol. 4 ISS. 4 : sc 37 ISSN : 2575-7725 DOI : 10.21767/2575-7725.4.4.37 8th Edition of International Conference on Clinical and Medical Case Reports - An anomalous digastric muscle in the carotid sheath: a case report with its embryological perspective and clinical relevance Srinivasa Rao Sirasanagandla Sultan Qaboos University, Oman Abstract Key words: Although infrahyoid muscles show considerable variations in Anterior belly, Posterior belly, Variation, Stylohyoid muscle, My- their development, existence of an anomalous digastric muscle lohyoid muscle, Hyoid bone in the neck was seldom reported. During dissection of trian- Anatomy gles of the neck for medical undergraduate students, we came across an anomalous digastric muscle in the carotid sheath of There is a pair of digastric muscles in the neck, and each digas- left side of neck. It was observed in a middle-aged cadaver at tric muscle has the anterior belly and the posterior belly. The College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Sultan Qaboos Uni- anterior belly is attached to the digastric fossa on the base of versity, Muscat, Oman. Digastric muscle was located within the the mandible close to the midline and runs toward the hyoid carotid sheath between the common and internal carotid arter- bone. The posterior belly is attached to the notch of the mas- ies and internal jugular vein. It had two bellies; cranial belly and toid process of the temporal bone and also runs toward the caudal belly which were connected by an intermediate tendon. -

CLOSURE of CRANIAL ARTICULATIONS in the SKULI1 of the AUSTRALIAN ABORIGINE by A
CLOSURE OF CRANIAL ARTICULATIONS IN THE SKULI1 OF THE AUSTRALIAN ABORIGINE By A. A. ABBIE, Department of Anatomy, University of Adelaide INTRODUCTION While it is well known that joint closure advances more or less progressively with age, there is still little certainty in matters of detail, mainly for lack of adequate series of documented skulls. In consequence, sundry beliefs have arisen which tend to confuse the issue. One view, now disposed of (see Martin, 1928), is that early suture closure indicates a lower or more primitive type of brain. A corollary, due to Broca (see Topinard, 1890), that the more the brain is exercised the more is suture closure postponed, is equally untenable. A very widespread belief is based on Gratiolet's statement (see Topinard, 1890; Frederic, 1906; Martin, 1928; Fenner, 1939; and others) that in 'lower' skulls the sutures are simple and commence to fuse from in front, while in 'higher' skulls the sutures are more complicated and tend to fuse from behind. This view was disproved by Ribbe (quoted from Frederic, 1906), who substituted the generalization that in dolicocephals synostosis begins in the coronal suture, and in brachycephals in the lambdoid suture. In addition to its purely anthropological interest the subject raises important biological considerations of brain-skull relationship, different foetalization in different ethnological groups (see Bolk, 1926; Weidenreich, 1941; Abbie, 1947), and so on. A survey of the literature reveals very little in the way of data on the age incidence of suture closure. The only substantial contribution accessible here comes from Todd & Lyon (1924) for Europeans, but their work is marred by arbitrary rejection of awkward material. -

Morphometric Study of Hypoglossal Canal of Occipital Bone in Dry Skulls of Two States in Southern Nigeria Enaohwo, Taniyohwo.MAMERHI1, Okoro
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 19 No. 04 October’20 Original article: Morphometric study of hypoglossal canal of occipital bone in dry skulls of two states in southern nigeria Enaohwo, Taniyohwo.MAMERHI1, Okoro. Ogheneyebrorue. GODSWILL Abstract: Background: It is observed that the morphologic and morphometric variability of the occipital bone structures may coexist in the same individual or among different subjects of the same or different populations and thus, a sound knowledge of the morphometry of this area can provide important benefits in determining safe surgical zones during surgical procedures. Aim: The present study was aimed at measuring the length (right and left) and width (right and left) of the hypoglossal canal among adult dry skulls of two states in southern Nigeria. Materials and Method: This study adopted the cross sectional study design. A total of eighty (80) hypoglossal canal; right and left were selected by simple random sampling and their length and width were measured with the aid of the digital vernier caliper. Results: The hypoglossal canal length on the right side was seen to be higher compared to the left length of the hypoglossal canal while the right hypoglossal canal width was seen to be higher compared to the left hypoglossal canal width and also observed differences between the right and left sides were statistically significant (P=0.01). Conclusion: There was a statistical significant difference with regard to hypoglossal canal length (right and left) and width (right and left) among the studied population. Keywords: Occipital bone, hypoglossal canal, morphology, variation Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. -

Lab Manual Axial Skeleton Atla
1 PRE-LAB EXERCISES When studying the skeletal system, the bones are often sorted into two broad categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. This lab focuses on the axial skeleton, which consists of the bones that form the axis of the body. The axial skeleton includes bones in the skull, vertebrae, and thoracic cage, as well as the auditory ossicles and hyoid bone. In addition to learning about all the bones of the axial skeleton, it is also important to identify some significant bone markings. Bone markings can have many shapes, including holes, round or sharp projections, and shallow or deep valleys, among others. These markings on the bones serve many purposes, including forming attachments to other bones or muscles and allowing passage of a blood vessel or nerve. It is helpful to understand the meanings of some of the more common bone marking terms. Before we get started, look up the definitions of these common bone marking terms: Canal: Condyle: Facet: Fissure: Foramen: (see Module 10.18 Foramina of Skull) Fossa: Margin: Process: Throughout this exercise, you will notice bold terms. This is meant to focus your attention on these important words. Make sure you pay attention to any bold words and know how to explain their definitions and/or where they are located. Use the following modules to guide your exploration of the axial skeleton. As you explore these bones in Visible Body’s app, also locate the bones and bone markings on any available charts, models, or specimens. You may also find it helpful to palpate bones on yourself or make drawings of the bones with the bone markings labeled. -

A 'Clear View of the N,Eglected Mastoid Aditus
1380 S.A. MEDICAL JOURNAL 11 December 1971 A 'Clear View of the N,eglected Mastoid Aditus G. C. C. BURGER, M.MED. (RAD.D.), Department of Diagnostic Radiology, H. F. Verwoerd Hospital, Pretoria SUMMARY By placing the head with the aditus vertical to the casette an X-ray tomographic cross-section of the aditus The aditus is the central link between the attic and the can be produced, which also allows the integrity of the mastoid antrum. Its patency determines the course of middle fossa floor to be judged with more accuracy than middle ear infections. has been possible in the past. S. Afr. Med. J., 45, 1380 (971). It is possible to make a transverse tomographic 'cut' through the aditus of the ear and at the same time to Fig. 1. Tomographic cross-section of the skull, labelled Fig. 3. Tomographic cross-section of the tympanic cavity with a wire coil insert in a dry skull. with incus in position in a dry skull. Fig. 2. Tomographic cross-section of the aditus in a dry Fig. 4. Tomographic cross-section of aditus in a patient. skull. -Date received: 16 November 1970. 11 Desember 1971 S.-A. MEDIESE TYDSKRIF 1381 demonstrate the thin bony layer which separates it from middle cranial fossa without the advantage of ever seeing the middle cranial fossa (Figs. 1 - 4). its floor in true tangent. One would hesitate to add yet another one to the lono list of radiographic views of the mastoid, but the aditus i;' after all, the passage which controls the course and out ANATOMY come of every inflammatory assault on the middle ear and mastoid. -

Pseudoforamina of the Skull Base: a Normal Variant
AJNR:8, July/August 1987 CORRESPONDENCE 737 6. Stimac GK, Solomon MA, Newton TH . CT and MR of angiomatous its relative lucency accounts for the apparent opening of the pseu malformations of the choroid plexus in patients with Sturge-Weber disease. doforamen. AJNR 1986 ;7 :623-627 CT of the region of the foramen magnum in a dried skull also demonstrates the presence of the pseudoforamina (Fig . 3), but only at certain gantry angulations, which vary for each patient. Pseudoforamina of the Skull Base: A Normal Correlation of radiographic features of the pseudoforamina in both Variant dried skull and clinical case material demonstrates the anatomic basis for this normal variant. Recognition of its benign nature is vital to Radiologic evaluation of basal foramina of the skull is frequently a avoid diagnostic error in evaluation of the skull base. critical aspect in the diagnosis of patients with deficits referable to cranial nerves. Commonly encountered normal asymmetries and Robert W. Hurst individual variations often make interpretation difficult. A pseudofor Wayne S. Cail amen in the skull base was initially observed in skull radiographs of Thomas Lee Pope, Jr. several patients and correlated with images of a dried skull. We stress Theodore E. Keats the importance of recognizing pseudoforamina to avoid diagnostic University of Virginia Medical Center confusion and error. Charlottesville, VA 22908 Bilateral, rounded lucent areas with sclerotic margins may be Chris Cimmino visualized on submentovertex or Water's views of the skull base. Mary Washington Hospital Located anteromedially to the hypoglossal canals and directly medial Fredericksburg, VA 22401 to the jugular foramen , these structures may be mistaken for the hypoglossal canal , erosion of the jugular foramen, or other normal REFERENCE structures (Fig . -

MBB: Head & Neck Anatomy
MBB: Head & Neck Anatomy Skull Osteology • This is a comprehensive guide of all the skull features you must know by the practical exam. • Many of these structures will be presented multiple times during upcoming labs. • This PowerPoint Handout is the resource you will use during lab when you have access to skulls. Mind, Brain & Behavior 2021 Osteology of the Skull Slide Title Slide Number Slide Title Slide Number Ethmoid Slide 3 Paranasal Sinuses Slide 19 Vomer, Nasal Bone, and Inferior Turbinate (Concha) Slide4 Paranasal Sinus Imaging Slide 20 Lacrimal and Palatine Bones Slide 5 Paranasal Sinus Imaging (Sagittal Section) Slide 21 Zygomatic Bone Slide 6 Skull Sutures Slide 22 Frontal Bone Slide 7 Foramen RevieW Slide 23 Mandible Slide 8 Skull Subdivisions Slide 24 Maxilla Slide 9 Sphenoid Bone Slide 10 Skull Subdivisions: Viscerocranium Slide 25 Temporal Bone Slide 11 Skull Subdivisions: Neurocranium Slide 26 Temporal Bone (Continued) Slide 12 Cranial Base: Cranial Fossae Slide 27 Temporal Bone (Middle Ear Cavity and Facial Canal) Slide 13 Skull Development: Intramembranous vs Endochondral Slide 28 Occipital Bone Slide 14 Ossification Structures/Spaces Formed by More Than One Bone Slide 15 Intramembranous Ossification: Fontanelles Slide 29 Structures/Apertures Formed by More Than One Bone Slide 16 Intramembranous Ossification: Craniosynostosis Slide 30 Nasal Septum Slide 17 Endochondral Ossification Slide 31 Infratemporal Fossa & Pterygopalatine Fossa Slide 18 Achondroplasia and Skull Growth Slide 32 Ethmoid • Cribriform plate/foramina -

Ectocranial Suture Closure in Pan Troglodytes and Gorilla Gorilla: Pattern and Phylogeny James Cray Jr.,1* Richard S
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 136:394–399 (2008) Ectocranial Suture Closure in Pan troglodytes and Gorilla gorilla: Pattern and Phylogeny James Cray Jr.,1* Richard S. Meindl,2 Chet C. Sherwood,3 and C. Owen Lovejoy2 1Department of Anthropology, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA 15260 2Department of Anthropology and Division of Biomedical Sciences, Kent State University, Kent, OH 44242 3Department of Anthropology, The George Washington University, Washington, DC 20052 KEY WORDS cranial suture; synostosis; variation; phylogeny; Guttman analysis ABSTRACT The order in which ectocranial sutures than either does with G. gorilla, we hypothesized that this undergo fusion displays species-specific variation among phylogenetic relationship would be reflected in the suture primates. However, the precise relationship between suture closure patterns of these three taxa. Results indicated that closure and phylogenetic affinities is poorly understood. In while all three species do share a similar lateral-anterior this study, we used Guttman Scaling to determine if the closure pattern, G. gorilla exhibits a unique vault pattern, modal progression of suture closure differs among Homo which, unlike humans and P. troglodyte s, follows a strong sapiens, Pan troglodytes,andGorilla gorilla.BecauseDNA posterior-to-anterior gradient. P. troglodytes is therefore sequence homologies strongly suggest that P. tr og lodytes more like Homo sapiens in suture synostosis. Am J Phys and Homo sapiens share a more recent common ancestor Anthropol 136:394–399, 2008. VC 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc. The biological basis of suture synostosis is currently Morriss-Kay et al. (2001) found that maintenance of pro- poorly understood, but appears to be influenced by a liferating osteogenic stem cells at the margins of mem- combination of vascular, hormonal, genetic, mechanical, brane bones forming the coronal suture requires FGF and local factors (see review in Cohen, 1993). -

Macewen'striangle
European Journal of Molecular & Clinical Medicine ISSN 2515-8260 Volume 07, Issue 5, 2020 MacEwen’sTriangle- A Review Dr. Bhaskaran Sathyapriya, Professor, Department of Anatomy, Sree Balaji Dental College & Hospital, Bharath Institute of Higher Education & Research, Chennai Chandrakala B1, Govindarajan Sumathy2, Syed FazilHasan 3, Priyadharshini.M3, Srilakshmi.B 3,Bhaskaran Sathyapriya* 1. Senior Lecturer, Department of Anatomy, Sree Balaji Dental College & Hospital, Bharath Institute of Higher Education & Research, Chennai. 2. Professor and Head, Department of Anatomy, Sree Balaji Dental College & Hospital, Bharath Institute of Higher Education & Research, Chennai. 3. Graduate student, Sree Balaji Dental College and Hospital, Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research *Professor, Department of Anatomy, Sree Balaji Dental College & Hospital, Bharath Institute of Higher Education & Research, Chennai. Abstract In the temporal bone, between the posterior wall of the external acoustic meatus and the posterior root of the zygomatic process is the area called the suprameatal triangle, suprameatal pit, mastoid fossa, foveolasuprameatica, or Mac Ewen's triangle, through which an instrument may be pushed into the mastoid antrum..In the adult, the antrum lies approximately 1.5 to 2 cm deep to the suprameatal triangle. This is an important landmark when performing a cortical mastoidectomy. The triangle lies deep to the cymba conchae.The sex determination of unknown human skulls can be evaluated by using the measurement of the area formed by the xerographic projection of 3craniometric points related to the mastoid process: the porion, asterion, and mastoidale points. Keywords: MacEwen's triangle,mastoidectomy,suprameatal spine,Mastoid antrum ,sex determination,zygomatic process,mastoid process. Introduction MacEwen's triangle is a very important surgical landmark for the mastoid antrum or the largest mastoid air cell.[9] It is also known as Suprameatal triangle or Mastoid fossa.[4] The suprameataltrigone plays a big role in the aspect of clinics. -

Topographical Anatomy and Morphometry of the Temporal Bone of the Macaque
Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 1, pp. 13–22 Copyright © 2009 Via Medica O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E ISSN 0015–5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Topographical anatomy and morphometry of the temporal bone of the macaque J. Wysocki 1Clinic of Otolaryngology and Rehabilitation, II Medical Faculty, Warsaw Medical University, Poland, Kajetany, Nadarzyn, Poland 2Laboratory of Clinical Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Institute of Physiology and Pathology of Hearing, Poland, Kajetany, Nadarzyn, Poland [Received 7 July 2008; Accepted 10 October 2008] Based on the dissections of 24 bones of 12 macaques (Macaca mulatta), a systematic anatomical description was made and measurements of the cho- sen size parameters of the temporal bone as well as the skull were taken. Although there is a small mastoid process, the general arrangement of the macaque’s temporal bone structures is very close to that which is observed in humans. The main differences are a different model of pneumatisation and the presence of subarcuate fossa, which possesses considerable dimensions. The main air space in the middle ear is the mesotympanum, but there are also additional air cells: the epitympanic recess containing the head of malleus and body of incus, the mastoid cavity, and several air spaces on the floor of the tympanic cavity. The vicinity of the carotid canal is also very well pneuma- tised and the walls of the canal are very thin. The semicircular canals are relatively small, very regular in shape, and characterized by almost the same dimensions. The bony walls of the labyrinth are relatively thin.