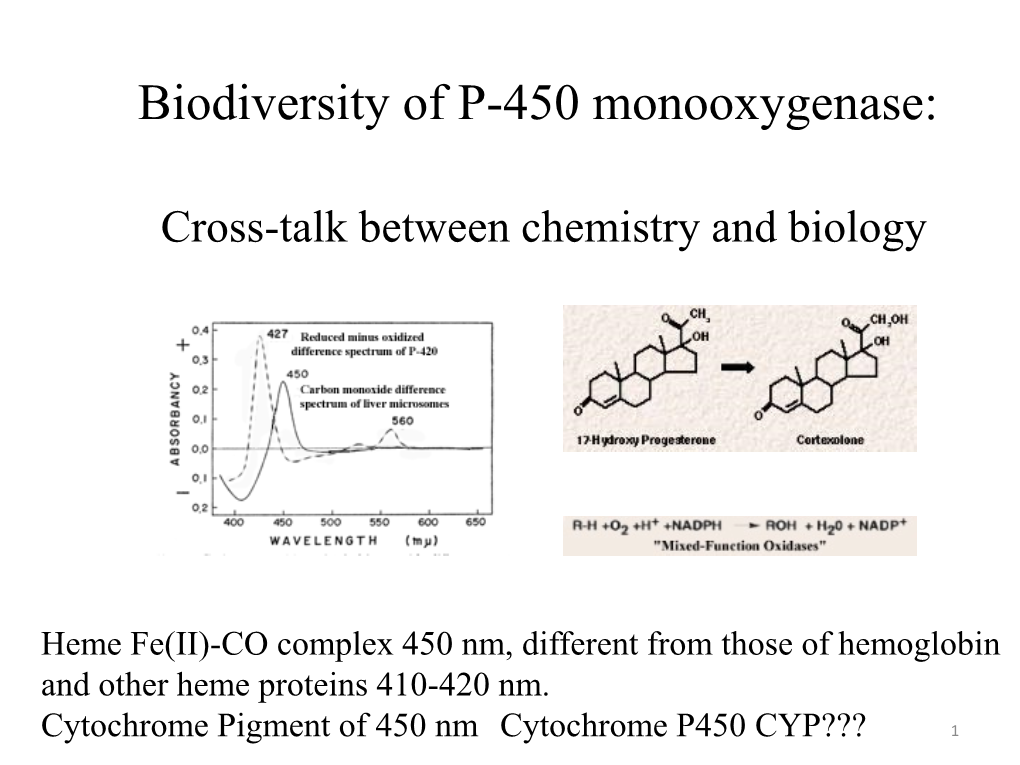
Biodiversity of P-450 Monooxygenase: Cross-Talk Between Chemistry and Biology Toru Shimizu
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

CYP26C1 Is a Hydroxylase of Multiple Active Retinoids and Interacts with Cellular Retinoic Acid Binding Proteins S
Supplemental material to this article can be found at: http://molpharm.aspetjournals.org/content/suppl/2018/02/23/mol.117.111039.DC1 1521-0111/93/5/489–503$35.00 https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.117.111039 MOLECULAR PHARMACOLOGY Mol Pharmacol 93:489–503, May 2018 Copyright ª 2018 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics CYP26C1 Is a Hydroxylase of Multiple Active Retinoids and Interacts with Cellular Retinoic Acid Binding Proteins s Guo Zhong, David Ortiz, Alex Zelter, Abhinav Nath, and Nina Isoherranen Departments of Pharmaceutics (G.Z., N.I.) and Medicinal Chemistry (D.O., A.N.), School of Pharmacy, and Department of Biochemistry, School of Medicine (A.Z.), University of Washington, Seattle, Washington Received October 31, 2017; accepted February 22, 2018 ABSTRACT Downloaded from The clearance of retinoic acid (RA) and its metabolites is believed orientation of retinoids within the CYP26C1 active site. In compar- to be regulated by the CYP26 enzymes, but the specific roles of ison with other CYP26 family members, CYP26C1 was up to CYP26A1, CYP26B1, and CYP26C1 in clearing active vitamin A 10-fold more efficient in clearing 4-oxo-atRA (intrinsic clearance metabolites have not been defined. The goal of this study was to 153 ml/min/pmol) than CYP26A1 and CYP26B1, suggesting that establish the substrate specificity of CYP26C1, and determine CYP26C1 may be important in clearing this active retinoid. In whether CYP26C1 interacts with cellular retinoic acid binding support of this, CRABPs delivered 4-oxo-atRA and atRA for proteins (CRABPs). CYP26C1 was found to effectively metabo- metabolism by CYP26C1. -

Impaired Hepatic Drug and Steroid Metabolism in Congenital Adrenal
European Journal of Endocrinology (2010) 163 919–924 ISSN 0804-4643 CLINICAL STUDY Impaired hepatic drug and steroid metabolism in congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to P450 oxidoreductase deficiency Dorota Tomalik-Scharte1, Dominique Maiter2, Julia Kirchheiner3, Hannah E Ivison, Uwe Fuhr1 and Wiebke Arlt School of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Centre for Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism (CEDAM), University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, UK, 1Department of Pharmacology, University Hospital, University of Cologne, 50931 Cologne, Germany, 2Department of Endocrinology, University Hospital Saint Luc, 1200 Brussels, Belgium and 3Department of Pharmacology of Natural Products and Clinical Pharmacology, University of Ulm, 89019 Ulm, Germany (Correspondence should be addressed to W Arlt; Email: [email protected]) Abstract Objective: Patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to P450 oxidoreductase (POR) deficiency (ORD) present with disordered sex development and glucocorticoid deficiency. This is due to disruption of electron transfer from mutant POR to microsomal cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes that play a key role in glucocorticoid and sex steroid synthesis. POR also transfers electrons to all major drug- metabolizing CYP enzymes, including CYP3A4 that inactivates glucocorticoid and oestrogens. However, whether ORD results in impairment of in vivo drug metabolism has never been studied. Design: We studied an adult patient with ORD due to homozygous POR A287P, the most frequent POR mutation in Caucasians, and her clinically unaffected, heterozygous mother. The patient had received standard dose oestrogen replacement from 17 until 37 years of age when it was stopped after she developed breast cancer. Methods: Both subjects underwent in vivo cocktail phenotyping comprising the oral administration of caffeine, tolbutamide, omeprazole, dextromethorphan hydrobromide and midazolam to assess the five major drug-metabolizing CYP enzymes. -

Studies on CYP1A1, CYP1B1 and CYP3A4 Gene Polymorphisms in Breast Cancer Patients
Ginekol Pol. 2009, 80, 819-823 PRACE ORYGINALNE ginekologia Studies on CYP1A1, CYP1B1 and CYP3A4 gene polymorphisms in breast cancer patients Badania polimorfizmów genów CYP1A1, CYP1B1 i CYP3A4 u chorych z rakiem piersi Ociepa-Zawal Marta1, Rubiś Błażej2, Filas Violetta3, Bręborowicz Jan3, Trzeciak Wiesław H1. 1 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Poznan University of Medical Sciences 2 Department of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics, 3Department of Tumor Pathology, Poznan University of Medical Sciences Abstract Background: The role of CYP1A1, CYP1B1 and CYP3A4 polymorphism in pathogenesis of breast cancer has not been fully elucidated. From three CYP1A1 polymorphisms *2A (3801T>C), *2C (2455A>G), and *2B variant, which harbors both polymorphisms, the *2A variant is potentially carcinogenic in African Americans and the Taiwanese, but not in Caucasians, and the CYP1B1*2 (355G>T) and CYP1B1*3 (4326C>G) variants might increase breast cancer risk. Although no association of any CYP3A4 polymorphisms and breast cancer has been documented, the CYP3A4*1B (392A>G) variant, correlates with earlier menarche and endometrial cancer secondary to tamoxifen therapy. Objective: The present study was designed to investigate the frequency of CYP1A1, CYP1B1 and CYP3A4 po- lymorphisms in a sample of breast cancer patients from the Polish population and to correlate the results with the clinical and laboratory findings. Material and methods: The frequencies of CYP1A1*2A; CYP1A1*2C; CYP1B1*3; CYP3A4*1B CYP3A4*2 polymorphisms were determined in 71 patients aged 36-87, with primary breast cancer and 100 healthy indi- viduals. Genomic DNA was extracted from the tumor, and individual gene fragments were PCR-amplified. -

Identification and Developmental Expression of the Full Complement Of
Goldstone et al. BMC Genomics 2010, 11:643 http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2164/11/643 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Identification and developmental expression of the full complement of Cytochrome P450 genes in Zebrafish Jared V Goldstone1, Andrew G McArthur2, Akira Kubota1, Juliano Zanette1,3, Thiago Parente1,4, Maria E Jönsson1,5, David R Nelson6, John J Stegeman1* Abstract Background: Increasing use of zebrafish in drug discovery and mechanistic toxicology demands knowledge of cytochrome P450 (CYP) gene regulation and function. CYP enzymes catalyze oxidative transformation leading to activation or inactivation of many endogenous and exogenous chemicals, with consequences for normal physiology and disease processes. Many CYPs potentially have roles in developmental specification, and many chemicals that cause developmental abnormalities are substrates for CYPs. Here we identify and annotate the full suite of CYP genes in zebrafish, compare these to the human CYP gene complement, and determine the expression of CYP genes during normal development. Results: Zebrafish have a total of 94 CYP genes, distributed among 18 gene families found also in mammals. There are 32 genes in CYP families 5 to 51, most of which are direct orthologs of human CYPs that are involved in endogenous functions including synthesis or inactivation of regulatory molecules. The high degree of sequence similarity suggests conservation of enzyme activities for these CYPs, confirmed in reports for some steroidogenic enzymes (e.g. CYP19, aromatase; CYP11A, P450scc; CYP17, steroid 17a-hydroxylase), and the CYP26 retinoic acid hydroxylases. Complexity is much greater in gene families 1, 2, and 3, which include CYPs prominent in metabolism of drugs and pollutants, as well as of endogenous substrates. -

New Perspectives of CYP1B1 Inhibitors in the Light of Molecular Studies
processes Review New Perspectives of CYP1B1 Inhibitors in the Light of Molecular Studies Renata Mikstacka 1,* and Zbigniew Dutkiewicz 2,* 1 Department of Inorganic and Analytical Chemistry, Collegium Medicum, Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toru´n,Dr A. Jurasza 2, 85-089 Bydgoszcz, Poland 2 Department of Chemical Technology of Drugs, Pozna´nUniversity of Medical Sciences, Grunwaldzka 6, 60-780 Pozna´n,Poland * Correspondence: [email protected] (R.M.); [email protected] (Z.D.); Tel.: +48-52-585-3912 (R.M.); +48-61-854-6619 (Z.D.) Abstract: Human cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1) is an extrahepatic heme-containing monooxy- genase. CYP1B1 contributes to the oxidative metabolism of xenobiotics, drugs, and endogenous substrates like melatonin, fatty acids, steroid hormones, and retinoids, which are involved in diverse critical cellular functions. CYP1B1 plays an important role in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases, hormone-related cancers and is responsible for anti-cancer drug resistance. Inhibition of CYP1B1 activity is considered as an approach in cancer chemoprevention and cancer chemotherapy. CYP1B1 can activate anti-cancer prodrugs in tumor cells which display overexpression of CYP1B1 in comparison to normal cells. CYP1B1 involvement in carcinogenesis and cancer progression encourages investigation of CYP1B1 interactions with its ligands: substrates and inhibitors. Compu- tational methods, with a simulation of molecular dynamics (MD), allow the observation of molecular interactions at the binding site of CYP1B1, which are essential in relation to the enzyme’s functions. Keywords: cytochrome P450 1B1; CYP1B1 inhibitors; cancer chemoprevention and therapy; molecu- Citation: Mikstacka, R.; Dutkiewicz, lar docking; molecular dynamics simulations Z. New Perspectives of CYP1B1 Inhibitors in the Light of Molecular Studies. -

Cytochrome P450 Enzymes in Oxygenation of Prostaglandin Endoperoxides and Arachidonic Acid
Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Pharmacy 231 _____________________________ _____________________________ Cytochrome P450 Enzymes in Oxygenation of Prostaglandin Endoperoxides and Arachidonic Acid Cloning, Expression and Catalytic Properties of CYP4F8 and CYP4F21 BY JOHAN BYLUND ACTA UNIVERSITATIS UPSALIENSIS UPPSALA 2000 Dissertation for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Faculty of Pharmacy) in Pharmaceutical Pharmacology presented at Uppsala University in 2000 ABSTRACT Bylund, J. 2000. Cytochrome P450 Enzymes in Oxygenation of Prostaglandin Endoperoxides and Arachidonic Acid: Cloning, Expression and Catalytic Properties of CYP4F8 and CYP4F21. Acta Universitatis Upsaliensis. Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from Faculty of Pharmacy 231 50 pp. Uppsala. ISBN 91-554-4784-8. Cytochrome P450 (P450 or CYP) is an enzyme system involved in the oxygenation of a wide range of endogenous compounds as well as foreign chemicals and drugs. This thesis describes investigations of P450-catalyzed oxygenation of prostaglandins, linoleic and arachidonic acids. The formation of bisallylic hydroxy metabolites of linoleic and arachidonic acids was studied with human recombinant P450s and with human liver microsomes. Several P450 enzymes catalyzed the formation of bisallylic hydroxy metabolites. Inhibition studies and stereochemical analysis of metabolites suggest that the enzyme CYP1A2 may contribute to the biosynthesis of bisallylic hydroxy fatty acid metabolites in adult human liver microsomes. 19R-Hydroxy-PGE and 20-hydroxy-PGE are major components of human and ovine semen, respectively. They are formed in the seminal vesicles, but the mechanism of their biosynthesis is unknown. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction using degenerate primers for mammalian CYP4 family genes, revealed expression of two novel P450 genes in human and ovine seminal vesicles. -

Physiologic and Pathophysiologic Roles of Extra Renal Cyp27b1: Case Report T and Review ⁎ Daniel D
Bone Reports 8 (2018) 255–267 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Bone Reports journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bonr Physiologic and pathophysiologic roles of extra renal CYP27b1: Case report T and review ⁎ Daniel D. Bikle , Sophie Patzek, Yongmei Wang Department of Medicine, Endocrine Research Unit, Veterans Affairs Medical Center, University of California San Francisco, United States ARTICLE INFO ABSTRACT Keywords: Although the kidney was initially thought to be the sole organ responsible for the production of 1,25(OH)2D via CYP27b1 the enzyme CYP27b1, it is now appreciated that the expression of CYP27b1 in tissues other than the kidney is Immune function wide spread. However, the kidney is the major source for circulating 1,25(OH)2D. Only in certain granulomatous Cancer diseases such as sarcoidosis does the extra renal tissue produce sufficient 1,25(OH)2D to contribute to the cir- Keratinocytes culating levels, generally associated with hypercalcemia, as illustrated by the case report preceding the review. Macrophages Therefore the expression of CYP27b1 outside the kidney under normal circumstances begs the question why, and in particular whether the extra renal production of 1,25(OH)2D has physiologic importance. In this chapter this question will be discussed. First we discuss the sites for extra renal 1,25(OH)2D production. This is followed by a discussion of the regulation of CYP27b1 expression and activity in extra renal tissues, pointing out that such regulation is tissue specific and different from that of CYP27b1 in the kidney. Finally the physiologic significance of extra renal 1,25(OH)2D3 production is examined, with special focus on the role of CYP27b1 in regulation of cellular proliferation and differentiation, hormone secretion, and immune function. -

Transcriptomic Characterization of Fibrolamellar Hepatocellular
Transcriptomic characterization of fibrolamellar PNAS PLUS hepatocellular carcinoma Elana P. Simona, Catherine A. Freijeb, Benjamin A. Farbera,c, Gadi Lalazara, David G. Darcya,c, Joshua N. Honeymana,c, Rachel Chiaroni-Clarkea, Brian D. Dilld, Henrik Molinad, Umesh K. Bhanote, Michael P. La Quagliac, Brad R. Rosenbergb,f, and Sanford M. Simona,1 aLaboratory of Cellular Biophysics, The Rockefeller University, New York, NY 10065; bPresidential Fellows Laboratory, The Rockefeller University, New York, NY 10065; cDivision of Pediatric Surgery, Department of Surgery, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10065; dProteomics Resource Center, The Rockefeller University, New York, NY 10065; ePathology Core Facility, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10065; and fJohn C. Whitehead Presidential Fellows Program, The Rockefeller University, New York, NY 10065 Edited by Susan S. Taylor, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA, and approved September 22, 2015 (received for review December 29, 2014) Fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma (FLHCC) tumors all carry a exon of DNAJB1 and all but the first exon of PRKACA. This deletion of ∼400 kb in chromosome 19, resulting in a fusion of the produced a chimeric RNA transcript and a translated chimeric genes for the heat shock protein, DNAJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfam- protein that retains the full catalytic activity of wild-type PKA. ily B, member 1, DNAJB1, and the catalytic subunit of protein ki- This chimeric protein was found in 15 of 15 FLHCC patients nase A, PRKACA. The resulting chimeric transcript produces a (21) in the absence of any other recurrent mutations in the DNA fusion protein that retains kinase activity. -

Regulation of Vitamin D Metabolizing Enzymes in Murine Renal and Extrarenal Tissues by Dietary Phosphate, FGF23, and 1,25(OH)2D3
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2018 Regulation of vitamin D metabolizing enzymes in murine renal and extrarenal tissues by dietary phosphate, FGF23, and 1,25(OH)2D3 Kägi, Larissa ; Bettoni, Carla ; Pastor-Arroyo, Eva M ; Schnitzbauer, Udo ; Hernando, Nati ; Wagner, Carsten A Abstract: BACKGROUND: The 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25(OH)2D3) together with parathyroid hormone (PTH) and fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) regulates calcium (Ca2+) and phosphate (Pi) homeostasis, 1,25(OH)2D3 synthesis is mediated by hydroxylases of the cytochrome P450 (Cyp) family. Vitamin D is first modified in the liver by the 25-hydroxylases CYP2R1 and CYP27A1 and further acti- vated in the kidney by the 1-hydroxylase CYP27B1, while the renal 24-hydroxylase CYP24A1 catalyzes the first step of its inactivation. While the kidney is the main organ responsible for circulating levelsofac- tive 1,25(OH)2D3, other organs also express some of these enzymes. Their regulation, however, has been studied less. METHODS AND RESULTS: Here we investigated the effect of several Pi-regulating factors including dietary Pi, PTH and FGF23 on the expression of the vitamin D hydroxylases and the vitamin D receptor VDR in renal and extrarenal tissues of mice. We found that with the exception of Cyp24a1, all the other analyzed mRNAs show a wide tissue distribution. High dietary Pi mainly upregulated the hep- atic expression of Cyp27a1 and Cyp2r1 without changing plasma 1,25(OH)2D3. FGF23 failed to regulate the expression of any of the studied hydroxylases at the used dosage and treatment length. -

Synonymous Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Human Cytochrome
DMD Fast Forward. Published on February 9, 2009 as doi:10.1124/dmd.108.026047 DMD #26047 TITLE PAGE: A BIOINFORMATICS APPROACH FOR THE PHENOTYPE PREDICTION OF NON- SYNONYMOUS SINGLE NUCLEOTIDE POLYMORPHISMS IN HUMAN CYTOCHROME P450S LIN-LIN WANG, YONG LI, SHU-FENG ZHOU Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, School of Public Health, Peking University, Beijing 100191, P. R. China (LL Wang & Y Li) Discipline of Chinese Medicine, School of Health Sciences, RMIT University, Bundoora, Victoria 3083, Australia (LL Wang & SF Zhou). 1 Copyright 2009 by the American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. DMD #26047 RUNNING TITLE PAGE: a) Running title: Prediction of phenotype of human CYPs. b) Author for correspondence: A/Prof. Shu-Feng Zhou, MD, PhD Discipline of Chinese Medicine, School of Health Sciences, RMIT University, WHO Collaborating Center for Traditional Medicine, Bundoora, Victoria 3083, Australia. Tel: + 61 3 9925 7794; fax: +61 3 9925 7178. Email: [email protected] c) Number of text pages: 21 Number of tables: 10 Number of figures: 2 Number of references: 40 Number of words in Abstract: 249 Number of words in Introduction: 749 Number of words in Discussion: 1459 d) Non-standard abbreviations: CYP, cytochrome P450; nsSNP, non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphism. 2 DMD #26047 ABSTRACT Non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (nsSNPs) in coding regions that can lead to amino acid changes may cause alteration of protein function and account for susceptivity to disease. Identification of deleterious nsSNPs from tolerant nsSNPs is important for characterizing the genetic basis of human disease, assessing individual susceptibility to disease, understanding the pathogenesis of disease, identifying molecular targets for drug treatment and conducting individualized pharmacotherapy. -

Human Cytochrome P450 CYP2A13
[CANCER RESEARCH 60, 5074–5079, September 15, 2000] Human Cytochrome P450 CYP2A13: Predominant Expression in the Respiratory Tract and Its High Efficiency Metabolic Activation of a Tobacco-specific Carcinogen, 4-(Methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone1 Ting Su, Ziping Bao, Qing-Yu Zhang, Theresa J. Smith, Jun-Yan Hong,2 and Xinxin Ding2 Wadsworth Center, New York State Department of Health, Albany, New York 12201 [T. S., Q-Y. Z., X. D.]; School of Public Health, State University of New York at Albany, Albany, New York [T. S., X. D.]; and Environmental and Occupational Health Sciences Institute, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, Piscataway, New Jersey 08854 [Z. B., T. J. S., J-Y. H.] ABSTRACT However, heterologously expressed CYP2A7 showed no catalytic activity (17, 18). CYP2A13 cDNA has not been isolated previously; The human CYP2A subfamily comprises three genes, CYP2A6, the reported protein sequence was deduced from the predicted coding CYP2A7, and CYP2A13. CYP2A6 is active toward many carcinogens and region of a CYP2A13 genomic clone (1). On the basis of its sequence is the major coumarin 7-hydroxylase and nicotine C-oxidase in the liver, whereas CYP2A7 is not functional. The function of CYP2A13 has not been features that resemble the nonfunctional CYP2A7 and CYP2A6v1 (a characterized. In this study, a CYP2A13 cDNA was prepared by RNA- genetic variant of CYP2A6) proteins, the CYP2A13 protein was PCR from human nasal mucosa and was translated using a baculovirus predicted to be nonfunctional in coumarin 7-hydroxylation (1). Be- expression system. In a reconstituted system, the expressed CYP2A13 was cause the deduced amino acid sequence of CYP2A13 shares a 95.4% more active than CYP2A6 in the metabolic activation of hexamethylphos- identity with that of CYP2A6 (1), antibodies and chemical probes for phoramide, N,N-dimethylaniline, 2-methoxyacetophenone, and N-nitro- CYP2A6 may interact with CYP2A13. -

A Bayesian Approach to Mediation Analysis Predicts 206 Causal Target Genes in Alzheimer’S Disease
bioRxiv preprint first posted online Nov. 14, 2017; doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/219428. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not peer-reviewed) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity. All rights reserved. No reuse allowed without permission. Title A Bayesian approach to mediation analysis predicts 206 causal target genes in Alzheimer’s disease Authors Yongjin Park+;1;2, Abhishek K Sarkar+;3, Liang He+;1;2, Jose Davila-Velderrain1;2, Philip L De Jager2;4, Manolis Kellis1;2 +: equal contribution. 1: Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA 2: Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA, USA 3: Department of Human Genetics, University of Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA 4: Department of Neurology, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, USA MK: [email protected] Abstract Characterizing the intermediate phenotypes, such as gene expression, that mediate genetic effects on complex dis- eases is a fundamental problem in human genetics. Existing methods utilize genotypic data and summary statistics to identify putative disease genes, but cannot distinguish pleiotropy from causal mediation and are limited by overly strong assumptions about the data. To overcome these limitations, we develop Causal Multivariate Mediation within Extended Linkage disequilibrium (CaMMEL), a novel Bayesian inference framework to jointly model multiple medi- ated and unmediated effects relying only on summary statistics. We show in simulation that CaMMEL accurately distinguishes between mediating and pleiotropic genes unlike existing methods. We applied CaMMEL to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and found 206 causal genes in sub-threshold loci (p < 10−4).