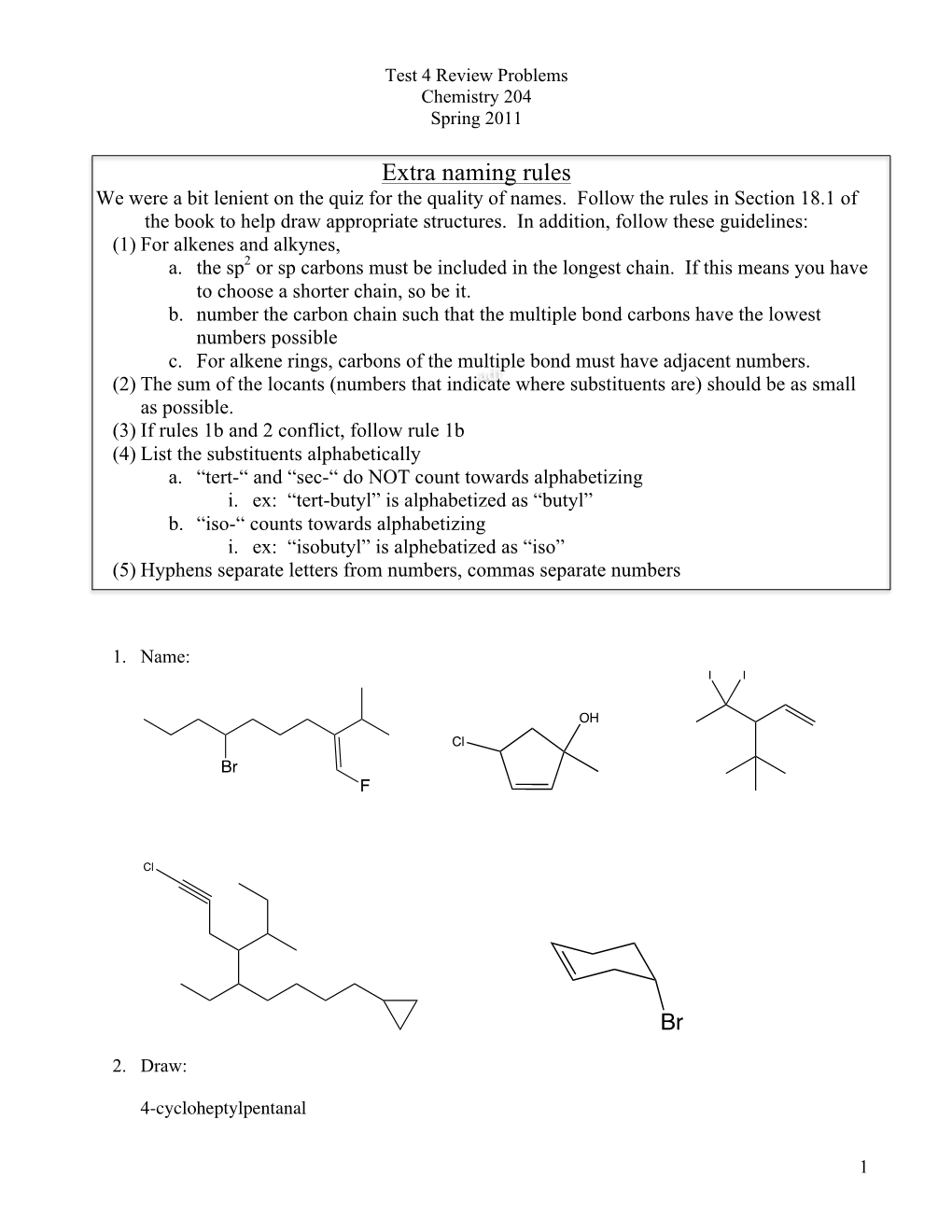
Extra Naming Rules We Were a Bit Lenient on the Quiz for the Quality of Names
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

"3-47-2. 2,720,501 United States Patent Office Patented Oct
Oct. 11, 1955 R. T. VAN NESS 2,720,501 AQUEOUS CONDENSATION PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF POLY WINYL ACETAL RESINS Filed Aug. 10, 1954 ALDEHYDE-f f 27 INVENTOR Robert Terry Van Ness "3-47-2. 2,720,501 United States Patent Office Patented Oct. 11, 1955 2 alcohol groups, and the remainder is polyvinyl butyral. In the attached drawing there is illustrated in a sche 2,720,501 matic fashion a flow sheet representing the process of AQUEOUS CONDENSATIGN PROCESS FOR THE this invention. A solution of polyvinyl alcohol in water PREPARATION OF POLYWNYLACETAL RESNS is prepared in vessel which is fitted with a means for agitating and a means for heating the contents of the Robert Terry Van Ness, Wilmington, Del, assignor to vessel. Polyvinyl alcohol from a storage vessel 3 is E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company, Wimington, added to vessel 1 along with sufficient cold water at a Del, a corporation of Delaware temperature from about 20° C. to 30° C. to form a sus Application August 10, 1954, Serial No. 448,876 10 pension containing about 7 to about 15% solid polyvinyl alcohol. Polyvinyl alcohol is prepared by hydrolyzing 4 Claims. (CI. 260-73) polyvinyl acetate in the presence of an alkaline catalyst or an acid catalyst. Depending upon the polyvinyl ace tate used, the type of hydrolysis catalyst, and the de This invention relates to the preparation of polyvinyl 5 gree to which the hydrolysis is completed, many varieties acetal resins and, more particularly, it relates to a proc of polyvinyl alcohol may be prepared. -

US5147908.Pdf
|||||||||||||||| USOO5147908A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,147,908 Floyd et al. 45) Date of Patent: Sep. 15, 1992 (54) CATIONICPOLYVINYL ALCOHOL BINDER 4,405,375 9/1983 Gibson et al........................ 106/277 ADDITIVE 4,461,858 7/1984 Adelmann ........ ... 524/503 4,528,316 7/1985 Soerens ........ ... 524/503 75) Inventors: William C. Floyd, Chester; Louis R. 4,537,807 8/1985 Chan et al. ............................ 428/74 Dragner, Rock Hill, both of S.C. 4,816,540 3/1989 Onishi .......... ... 527/300 4,837,087 6/1989 Floyd et al. ......................... 428/51 73 Assignee: Sequa Chemicals Inc., Chester, S.C. 4,888,386 12/1989 Huang et al. ... ... 524/503 X (21) Appl. No.: 587,012 4,954,577 9/1990 Dinwald et al. ............... 524/503 X 22 Filed: Sep. 24, 1990 OTHER PUBLICATIONS 51) Int. Cl. ................................................ CO8L 3/04 Zunker, David W.; "Incorporating The Benefits Of 52 U.S. Cl. ........................................ 524/49; 524/55; Polyvinyl Alcohol At the Wet-End Of Papermaking'; 524/503; 525/57; 525/58 1982 Papermakers Conference. 58 Field of Search ..................... 524/503, 49, 55, 57, 524/58 Primary Examiner-Joseph L. Schofer Assistant Examiner-J. M. Reddick 56) References Cited Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Mitchell D. Bittman U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 57 ABSTRACT 3,573,236 3/1971 Barlow .....................r 260/7 3,597,313 8/1971 Williams et al. ... ... 162/67 A cationic polyvinyl alcohol binder additive is prepared 3,600,342 8/97 Nickerson et al. ................... 260/17 suitable for addition in the wet-end of a paper making 3,700,61 0/1972 Nickerson et al. -

Removal of Anionic Dye Congo Red from Aqueous Environment Using
www.nature.com/scientificreports OPEN Removal of anionic dye Congo red from aqueous environment using polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate/ ZSM‑5 zeolite membrane Sabarish Radoor1*, Jasila Karayil2, Jyotishkumar Parameswaranpillai1 & Suchart Siengchin1* In this study, a novel PVA/SA/ZSM‑5 zeolite membrane with good regeneration capacity was successfully prepared by solvent casting technique. The properties of the membranes were assessed by employing diferent characterization techniques such as X‑ray difraction (XRD), Fourier‑transform infrared spectroscopy (FT‑IR), scanning electron microscope (SEM), optical microscopy (OP), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), contact angle and universal testing machine (UTM). XRD, TGA and UTM results revealed that the crystallinity and thermo‑mechanical performance of the membrane could be tuned with zeolite content. The successful incorporation of zeolite into the polymer matrix was confrmed by FT‑IR, SEM and OP analysis. The adsorption ability of the as‑prepared membrane was evaluated with a model anionic dye, Congo red. Adsorption studies show that the removal efciency of the membrane could be tuned by varying zeolite content, initial concentration of dye, contact time, pH and temperature. Maximum dye adsorption (5.33 mg/g) was observed for 2.5 wt% zeolite loaded membrane, at an initial dye concentration of 10 ppm, pH 3 and temperature 30 °C. The antibacterial efciency of the membrane against gram‑positive (Staphylococcus aureus) and gram‑negative bacteria (Escherichia coli) was also reported. The results show that membrane inhibits the growth of both gram‑positive and gram‑negative bacteria. The adsorption isotherm was studied using two models: Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm. The results show that the experimental data ftted well with Freundlich isotherm with a high correlation coefcient (R2 = 0.998). -

Crosslinked Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Membranes
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.10 No.3, pp 118-127, 2017 Synthesis and Physical-Chemical Characterization of DEA- Crosslinked Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Membranes María T. Acevedo1*, Alejandra Tapia1, Álvaro Realpe1 1Department of Chemical Engineering, Research Group of Modeling of Particles and Processes, Engineering Faculty, Universidad de Cartagena, Colombia Abstract : In this research, crosslinked PVA was impregnated with 0, 15 and 20% of diethanolamine so as to study the effect of the alkanolamine on the physical-chemical properties which are connected to the CO2 separating process via membranes. Formaldehyde and a porous membrane of polisulfone were used as crosslinking agent and support, respectively. Membranes were characterized by FTIR, SEM-EDS, contact angle, water absorption and porosity measurements. The results suggest that although the water absorption in the bulk of polymer diminished when the percentage of diethnaolamine increased, the surface hydrophilicity and appearance of the membranes were not appreciably affected due to this modification. A favorable balance of properties such as water uptake, the porosity and the superficial hidrophilicity were achieved using the crosslinking and synthesis conditions proposed in this paper, considering the positive effect of those characteristics in the permeability/selectivity of CO2 through the membrane. Keyword : crosslinked PVA, diethanolamine, CO2 separating process, membranes, surface hydrophilicity. Introduction Pollution associated with emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) is one of the preeminent environmental issues [1,2]. The high level of CO2 emission levels is arising from combustion of fossil fuel, accelerated increase in the energy consumption, population and industries, including cement and metal production, which have caused different kinds of devastating effects in particular the increase in global temperature with severe consequences on ecosystems, biodiversity and sea levels [3]. -

Crosslinking of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Via Bis(\Beta-Hydroxyethyl) Sulfone
Polymer Journal, Vol. 36, No. 6, pp. 472—477 (2004) Crosslinking of Poly(vinyl alcohol) via Bis( -hydroxyethyl) Sulfone y Kazuhiro KUMETA,Ã;ÃÃ Ichiro NAGASHIMA,ÃÃ Shigetoshi MATSUI,Ã and Kensaku MIZOGUCHIÃ; ÃDepartment of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Shizuoka University, 3-5-1 Johoku, Hamamatsu 432-8561, Japan ÃÃNitivy Co., 300 Zenzaemon, Fujieda 426-0053, Japan (Received November 4, 2003; Accepted March 29, 2004; Published June 15, 2004) ABSTRACT: Poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) was crosslinked via bis( -hydroxyethyl) sulfone (BHES) at elevated tem- peratures to improve the water resistance. The best conditions for the crosslinking such as temperature, heat-treatment period, and amount of BHES or catalyst were screened out. Water resistance of the crosslinked PVA was characterized in terms of swelling and weight loss in water. The addition of BHES into PVA followed by heating at elevated temper- ature resulted in successful formation of crosslinking structure. The crosslinking occurs above 160 C and takes shorter period at high temperature than low temperature. The crosslinking catalyst, sodium carbonate, acts more effectively at 160 C than at 200 C. The results from thermal analysis using a differential scanning calorimetry revealed that the cat- alyst functions against BHES to lower the temperature for the crosslinking reaction and that even the crosslinked films have the PVA crystalline. The crosslinking procedure using BHES and sodium carbonate is applicable to form ion-ex- change fibers based on PVA with high water resistance. [DOI 10.1295/polymj.36.472] KEY WORDS Poly(vinyl alcohol) / Crosslinking / Thermal Post-treatment / Bis( -hydroxyethyl) Sulfone / PVA is a typical hydrophilic polymer and can be plied heat-treatment methods to crosslinking PVA readily blended with additives such as particles or oth- via glyoxal.3 In this case, the process requires an acid- er polymers. -

Download Safety Assessment of Polyvinyl Alcohol As Used In
Safety Assessment of Polyvinyl Alcohol as Used in Cosmetics Status: Re-review for Panel Review Release Date: November 15, 2013 Panel Meeting Date: December 9-10, 2013 The 2013 Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel members are: Chairman, Wilma F. Bergfeld, M.D., F.A.C.P.; Donald V. Belsito, M.D.; Ronald A. Hill, Ph.D.; Curtis D. Klaassen, Ph.D.; Daniel C. Liebler, Ph.D.; James G. Marks, Jr., M.D., Ronald C. Shank, Ph.D.; Thomas J. Slaga, Ph.D.; and Paul W. Snyder, D.V.M., Ph.D. The CIR Director is Lillian Gill, DPA. This report was prepared by Christina Burnett, Scientific Analyst/Writer. Cosmetic Ingredient Review 1101 17th Street, NW, Suite 412 ♢ Washington, DC 20036-4702 ♢ ph 202.331.0651 ♢ fax 202.331.0088 ♢ [email protected] Commitment & Credibility since 1976 Memorandum To: CIR Expert Panel Members and Liaisons From: Christina L. Burnett Scientific Writer/Analyst Date: November 15, 2013 Subject: Re-review of Polyvinyl Alcohol In 1998, the CIR Final Report on the safety assessment of polyvinyl alcohol was published with the conclusion “safe as used in cosmetic formulations”. Current uses of polyvinyl alcohol can be found in Table 1. The FDA’s VCRP database indicates that uses have increased from 37 to 225. The majority of the uses are in leave-on products such as eye makeup and skin care products. In 1998, the industry reported the maximum use concentration to be < 25%, with 13% reported for a hydrolyzed version of the ingredient in paste masks (mud packs). Presently, the industry reported a maximum use concentration range of 0.0035% to 15%, with 15% reported in “other” skin care preparation products. -

Basic Physical Properties of PVOH Resin Basic Physical Properties of PVOH Resin
Basic Physical Properties of PVOH Resin Basic Physical Properties of PVOH Resin Table of Contents: 1. Basic Physical Properties of 3. Behavior of PVOH PVOH Aqueous Solution 1-1. Definition of PVOH 3-1. Solubility in Water 1-2. Specific Gravity 3-2. Solubility in Other Solvents 1-3. Refractive Index 3-3. Viscosity of Aqueous Solution 1-4. Second-order Transition Temperature 3-4. Stability of Aqueous Solution 1-5. Crystallinity 3-5. Shear Velocity Dependency of Aqueous Solution 1-6. Melting Point 3-6. Specific Gravity and Refractive Index of Aqueous 1-7. Specific Heat Solution 1-8. Latent Heat of Melting 3-7. pH of Aqueous Solution 1-9. Entropy, enthalpy 3-8. Surface Active Performance 1-10. Heat of Dissolution 3-9. Permeability of Aqueous Solution 1-11. Heat of Combustion 3-10. Contact Angle for Various Plastics 1-12. Thermal Conductivity and Linear Expansion 3-11. Compatibility with Water-soluble Polymers Coefficient 3-12. Dispersive/aggregating Action against Clay Particles 1-13. Thermal Decomposition, Thermal Decomposition 3-13. Influence of Electrolyte Product 3-14. Gellant, Precipitant 1-14. Combustion Characteristics (Limiting Oxygen 3-15. Cloud Point Concentration) 3-16. Biodegradability 1-15. Dust Explosion 2. Microstructure of 4. Physical Properties of PVOH PVOH Film 2-1. Microstructure 4-1. Properties for Water 2-2. Stereoregularity 4-2. Mechanical Properties 2-3. Heterophilic Bonding (1,2-glycol Bonding) 4-3. Gas Permeability 2-4. Terminal Structure 4-4. Resistance to Oil, Resistance to Organic Solvent 2-5. Branching 4-5. Optical Transparency 2-6. Double bond 4-6. -

Polyvinyl Butyral B-08HX Resin
distributed by: Request Quote or Samples Polyvinyl Butyral B-08HX CHANG CHUN GROUP Technical Data Sheet Effective date: 2015/08/10 Version : 1.0, Page 1/1 Characteristics CCP PVB B-08HX is a polyvinyl butyral resin with a medium solution viscosity. CCP PVB B-08HX is manufactured from the condensation reaction of Polyvinyl Alcohol and n-butyraldehyde. B-08HX is a thermoplastic resin, which is soluble in most organic solvents with excellent film forming capability, strong adhesion to glass, metal, plastic, leather and wood. CCP B-08HX is a white free flowing granule or powder and non-toxic to humans and animals. Specification Item value Unit Remark Butyral content 76 – 82 wt% Hydroxyl content 18.0 – 21.0 wt% Acetyl content ≦2 wt% Solution viscosity was determined in 10% by weight in Viscosity 120 – 180 cps ethanol/toluene = 1/1 at 20°C, using Brookfield viscometer Free Acid ≦0.05 wt% Volatile ≦3 wt% Application Additional Data Typical applications for B-08HX are - wash primer, Specific gravity : 1.05~1.10 paint, ceramic binder, coating and adhesive. Due to Bulk density : 0.25 – 0.40 g/cm³ for powder free hydroxyl groups, B08HX can be used as a Glass transition temperature : ca. 71 °C reactive component or as a co-binder in two-pack Melting Point : 135 – 185°C systems. For example, B08HX can be crosslinked Molecular weight : 52,000 – 62,000 g/mole with phenolic, epoxies, melamine, isocyanate resin. Degree of Polymerization : 800 - 900 Package CCP PVB B-08HX is packed in 10 kg, multi-ply paper bags. -

Biodegradation Studies of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Corn Starch Blend Films in Solid and Solution Media
Journal of Physical Science, Vol. 22(2), 15–31, 2011 15 Biodegradation Studies of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Corn Starch Blend Films in Solid and Solution Media N. A. Azahari, N. Othman* and H. Ismail School of Materials and Mineral Resources Engineering, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Engineering Campus, 14300 Nibong Tebal, Seberang Perai Selatan, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia *Corresponding author: [email protected] Abstract: In this study, polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH)/corn starch (CS) blend films were prepared using the solution casting method. The biodegradability of the films was investigated based on enzymatic absorbency in water and an acidic solution as well as by burial in soil and compost. The tensile properties were examined using a tensile test. The structure of the film was characterised by scanning electron microscopy. Compared to a film without corn starch, the films containing corn starch were found to be more highly biodegradable by enzymes as well as in soil and compost. However, the results from the tensile and elongation at break tests showed that as the corn starch content increased, the strength decreased. The morphology study revealed the distribution of corn starch in the PVOH. Keywords: PVOH/CS blend film, biodegradation, enzymatic, acidic solution, compost burial Abstrak: Dalam kajian ini, polivinil alcohol (PVOH)/kanji jagung (CS) campuran filem telah disediakan dengan menggunakan kaedah larutan pengacuan. Biodegradasi filem dianalisa berdasarkan kuantiti enzim dalam air dan larutan berasid serta oleh perkuburan di dalam tanah dan kompos. Ciri-ciri tegangan telah diperiksa menggunakan ujian tegangan. Struktur filem adalah bercirikan oleh imbasan mikroskop electron. Berbanding dengan filem tanpa kanji jagung, filem-filem yang mengandungi kanji jagung telah didapati lebih tinggi terbiodegradasikan oleh enzim serta perkuburan di dalam tanah dan kompos. -

Active Biodegradable Polyvinyl Alcohol–Hemicellulose/Tea Polyphenol Films with Excellent Moisture Resistance Prepared Via Ultrasound Assistance for Food Packaging
coatings Article Active Biodegradable Polyvinyl Alcohol–Hemicellulose/Tea Polyphenol Films with Excellent Moisture Resistance Prepared via Ultrasound Assistance for Food Packaging Yining Wang 1, Jinhui Li 1, Xin Guo 1, Haisong Wang 1 , Fang Qian 2,* and Yanna Lv 1,3,* 1 School of Light Industry and Chemical Engineering, Dalian Polytechnic University, Dalian 116034, China; [email protected] (Y.W.); [email protected] (J.L.); [email protected] (X.G.); [email protected] (H.W.) 2 School of Food Science and Technology, Dalian Polytechnic University, Dalian 116034, China 3 State Key Laboratory of Pulp and Paper Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China * Correspondence: [email protected] (F.Q.); [email protected] (Y.L.); Tel.: +86-0411-8632-3509 (Y.L.) Abstract: Poor water-vapor barriers and mechanical properties are common problems of biobased films. To maintain food quality, the barrier and its strength performance need to be improved. Tea polyphenols (TP) are a natural active substance, and their benzene ring structure provides a barrier for them as a film material. Films that incorporate TP also have enriched functionalities, e.g., as antioxidants. Here, active poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA)-hemicellulose (HC)/TP films with good moisture resistance and antioxidant capacity were prepared via ultrasound assistance. The effects of TP incorporation and ultrasonication on the physical, antioxidant, and micromorphological Citation: Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; properties of the films were investigated. Results showed that the addition of TP improved the Wang, H.; Qian, F.; Lv, Y. Active thermal stability and water-vapor permeability (WVP) of the composite films. -

Cloning, Expression, Characterization and Immobilization of Carbonyl Reductase from Candida Parapsilosis
Cloning, expression, characterization and immobilization of carbonyl reductase from Candida parapsilosis Von der Fakultät für Mathematik, Informatik und Naturwissenschaften der Rheinisch- Westfälischen Technischen Hochschule Aachen zur Erlangung des akademischen Grades einer Doktorin der Naturwissenschaften genehmigte Dissertation vorgelegt von Master of Science Monideepa Bhattacharjee aus Dibrugarh, Indien Berichter: Universitätsprofessor Dr.-Ing. Winfried Hartmeier Universitätsprofessor Dr. rer. nat. Klaus Wolf Tag der mündlichen Prüfung: 08.06.2006 Diese Dissertation ist auf den Internetseiten der Hochschulbibliothek online verfügbar. Table of Contents I Table of Contents Table of Contents ......................................................................................................................I Glossary of Abbreviations and Symbols ..............................................................................IV 1 Introduction ...................................................................................................................... 1 1.1 Chirality and biocatalysis........................................................................................... 1 1.2 Alcohol dehydrogenases ............................................................................................ 2 1.3 Carbonyl reductase from Candida parapsilosis......................................................... 2 1.4 Versatility of CPCR to other alcohol dehydrogenases............................................... 4 1.5 Secondary alcohol dehydrogenase -

Material Safety Data Sheet
SAFETY DATA SHEET 1. Identification Product identifier LPS® NoFlash Other means of identification Part Number 04016 Recommended use An aggressive non-flammable solvent blend for the removal of dirt, moisture, dust, flux and oxides from the internal components of electronic or precision equipment such as circuit boards, and the internal components of electronic devices used in factories and other industrial settings. Recommended restrictions None known. Manufacturer/Importer/Supplier/Distributor information Manufacturer Manufacturer Company name ITW Pro Brands Address 4647 Hugh Howell Rd. Tucker, GA 30084 Country (U.S.A.) Tel: +1 770-243-8800 In Case of Emergency 1-800-424-9300 (inside U.S.) +001 703-527-3887 (outside U.S.) Website www.lpslabs.com E-mail [email protected] 2. Hazard(s) identification Physical hazards Gases under pressure Liquefied gas Health hazards Acute toxicity, oral Category 4 Skin corrosion/irritation Category 2 Serious eye damage/eye irritation Category 2A Carcinogenicity Category 2 Reproductive toxicity Category 1B Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure Category 3 respiratory tract irritation Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure Category 3 narcotic effects Specific target organ toxicity, repeated Category 2 exposure Environmental hazards Not classified. OSHA defined hazards Not classified. Label elements Signal word Danger Hazard statement Contains gas under pressure; may explode if heated. Harmful if swallowed. Causes skin irritation. Causes serious eye irritation. May cause respiratory irritation. May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Suspected of causing cancer. May damage fertility or the unborn child. May cause damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure. Precautionary statement Prevention Obtain special instructions before use. Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood.