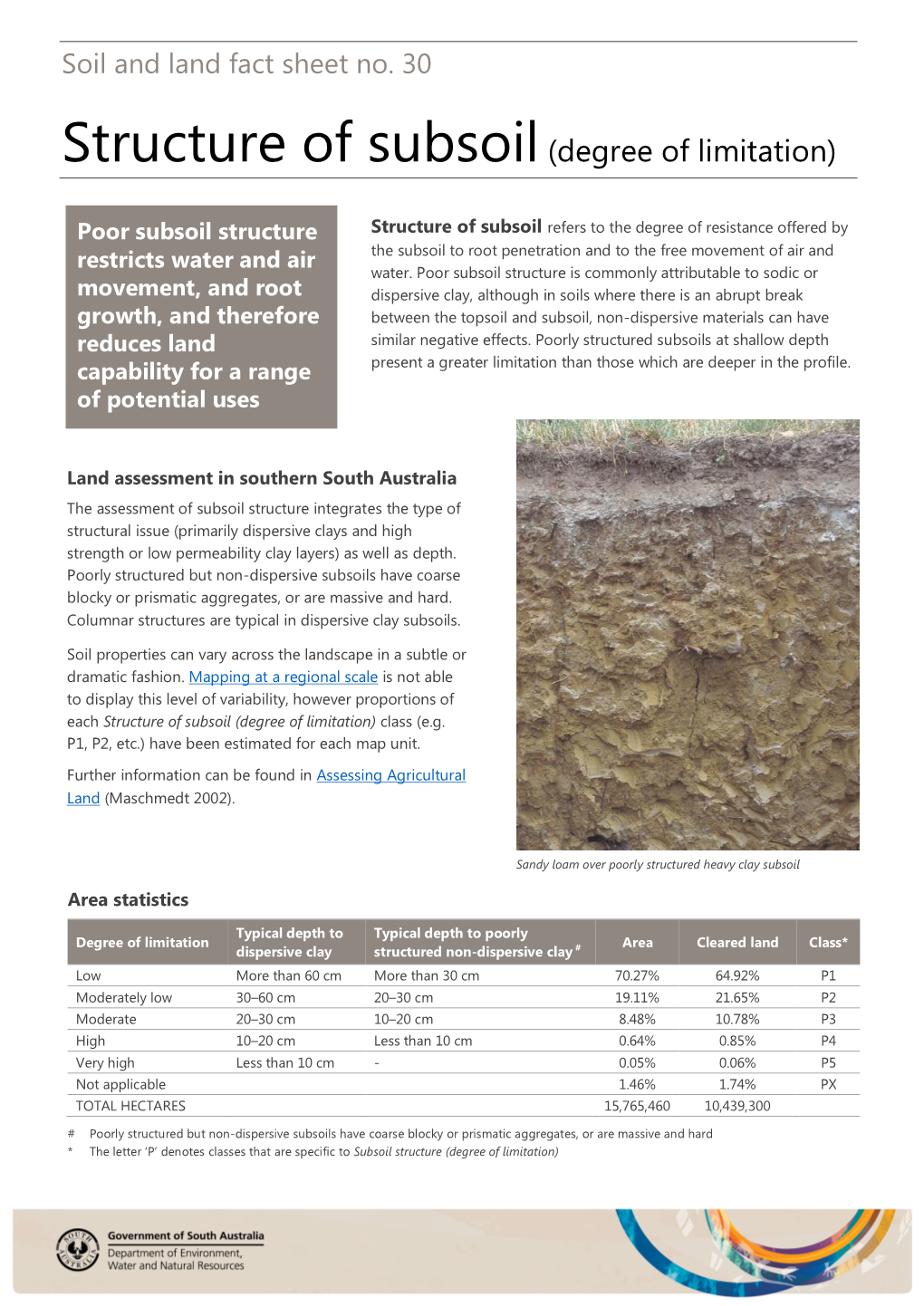
Structure of Subsoil (Degree of Limitation)
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Global Hydrogeology Maps (GLHYMPS) of Permeability and Porosity
UVicSPACE: Research & Learning Repository _____________________________________________________________ Faculty of Engineering Faculty Publications _____________________________________________________________ A glimpse beneath earth’s surface: Global HYdrogeology MaPS (GLHYMPS) of permeability and porosity Tom Gleeson, Nils Moosdorf, Jens Hartmann, and L. P. H. van Beek June 2014 AGU Journal Content—Unlocked All AGU journal articles published from 1997 to 24 months ago are now freely available without a subscription to anyone online, anywhere. New content becomes open after 24 months after the issue date. Articles initially published in our open access journals, or in any of our journals with an open access option, are available immediately. © 2017 American Geophysical Unionhttp://publications.agu.org/open- access/ This article was originally published at: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/2014GL059856 Citation for this paper: Gleeson, T., et al. (2014), A glimpse beneath earth’s surface: Global HYdrogeology MaPS (GLHYMPS) of permeability and porosity, Geophysical Research Letters, 41, 3891–3898, doi:10.1002/2014GL059856 PUBLICATIONS Geophysical Research Letters RESEARCH LETTER A glimpse beneath earth’s surface: GLobal 10.1002/2014GL059856 HYdrogeology MaPS (GLHYMPS) Key Points: of permeability and porosity • Mean global permeability is consistent with previous estimates of shallow crust Tom Gleeson1, Nils Moosdorf 2, Jens Hartmann2, and L. P. H. van Beek3 • The spatially-distributed mean porosity of the globe is 14% 1Department of Civil Engineering, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, 2Institute for Geology, Center for Earth • Maps will enable groundwater in land 3 surface, hydrologic and climate models System Research and Sustainability, University of Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany, Department of Physical Geography, Faculty of Geosciences, Utrecht University, Utrecht, Netherlands Correspondence to: Abstract The lack of robust, spatially distributed subsurface data is the key obstacle limiting the T. -

Port Silt Loam Oklahoma State Soil
PORT SILT LOAM Oklahoma State Soil SOIL SCIENCE SOCIETY OF AMERICA Introduction Many states have a designated state bird, flower, fish, tree, rock, etc. And, many states also have a state soil – one that has significance or is important to the state. The Port Silt Loam is the official state soil of Oklahoma. Let’s explore how the Port Silt Loam is important to Oklahoma. History Soils are often named after an early pioneer, town, county, community or stream in the vicinity where they are first found. The name “Port” comes from the small com- munity of Port located in Washita County, Oklahoma. The name “silt loam” is the texture of the topsoil. This texture consists mostly of silt size particles (.05 to .002 mm), and when the moist soil is rubbed between the thumb and forefinger, it is loamy to the feel, thus the term silt loam. In 1987, recognizing the importance of soil as a resource, the Governor and Oklahoma Legislature selected Port Silt Loam as the of- ficial State Soil of Oklahoma. What is Port Silt Loam Soil? Every soil can be separated into three separate size fractions called sand, silt, and clay, which makes up the soil texture. They are present in all soils in different propor- tions and say a lot about the character of the soil. Port Silt Loam has a silt loam tex- ture and is usually reddish in color, varying from dark brown to dark reddish brown. The color is derived from upland soil materials weathered from reddish sandstones, siltstones, and shales of the Permian Geologic Era. -

International Society for Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering
INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR SOIL MECHANICS AND GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING This paper was downloaded from the Online Library of the International Society for Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering (ISSMGE). The library is available here: https://www.issmge.org/publications/online-library This is an open-access database that archives thousands of papers published under the Auspices of the ISSMGE and maintained by the Innovation and Development Committee of ISSMGE. Interaction between structures and compressible subsoils considered in light of soil mechanics and structural mechanics Etude de l’interaction sol- structures à la lumière de la mécanique des sols et de la mécanique des stuctures Ulitsky V.M. State Transport University, St. Petersburg, Russia Shashkin A.G., Shashkin K.G., Vasenin V.A., Lisyuk M.B. Georeconstruction Engineering Co, St. Petersburg, Russia Dashko R.E. State Mining Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia ABSTRACT: Authors developed ‘FEM Models’ software, which allows solving soil-structure interaction problems. To speed up computation time this software utilizes a new approach, which is to solve a non-linear system using a conjugate gradient method skipping intermediate solution of linear systems. The paper presents a study of the main soil-structure calculations effects and contains a basic description of the soil-structure calculation algorithm. The visco-plastic soil model and its agreement with in situ measurement results are also described in the paper. RÉSUMÉ : Les auteurs ont développé un logiciel aux éléments finis, qui permet de résoudre des problèmes d’interactions sol- structure. Pour l’accélération des temps de calcul, une nouvelle approche a été utilisée: qui consiste a résoudre un système non linéaire par la méthode des gradients conjugués, qui ne nécessite pas la solution intermédiaire des systèmes linéaires. -

Controls on Carbon Accumulation and Storage in the Mineral Subsoil Beneath Peat in Lakkasuo Mire, Central Finland
European Journal of Soil Science, June 2003, 54, 279–286 Controls on carbon accumulation and storage in the mineral subsoil beneath peat in Lakkasuo mire, central Finland J. T URUNEN &T.R.MOORE Department of Geography and the Centre for Climate and Global Change Research, McGill University, 805 Sherbrooke Street West, Montre´al, Que´bec H3A 2K6, Canada Summary What processes control the accumulation and storage of carbon (C)in the mineral subsoil beneath peat? To find out we investigated four podzolic mineral subsoil profiles from forest and beneath peat in Lakkasuo mire in central boreal Finland. The amount of C in the mineral subsoil ranged from 3.9 to 8.1 kg mÀ2 over a thickness of 70 cm and that in the organic horizons ranged from 1.8 to 144 kg mÀ2. Rates of increase of subsoil C were initially large (14 g mÀ2 yearÀ1)as the upland forest soil was paludified, but decreased to < 2gmÀ2 yearÀ1 from 150 to 3000 years. The subsoils retained extractable aluminium (Al)but lost iron (Fe)as the surrounding forest podzols were paludified beneath the peat. A stepwise, ordinary least-squares regression indicated a strong relation (R2 ¼ 0.91)between organic C concentration of 26 podzolic subsoil samples and dithionite–citrate–bicarbonate-extractable Fe (nega- tive), ammonium oxalate-extractable Al (positive) and null-point concentration of dissolved organic C (DOCnp)(positive).We examined the ability of the subsoil samples to sorb dissolved organic C from a solution derived from peat. Null-point concentration of dissolved C (DOCnp)ranged from 35 to 83 mg lÀ1, and generally decreased from the upper to the lower parts of the profiles (average E, B and À1 C horizon DOCnp concentrations of 64, 47 and 42 mg l ). -

Soil Test Handbook for Georgia
SOIL TEST HANDBOOK FOR GEORGIA Georgia Cooperative Extension College of Agricultural & Environmental Sciences The University of Georgia Athens, Georgia 30602-9105 EDITORS: David E. Kissel Director, Agricultural and Environmental Services Laboratories & Leticia Sonon Program Coordinator, Soil, Plant, & Water Laboratory TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION .......................................................................................................................................................2 SOIL TESTING...........................................................................................................................................................4 SOIL SAMPLING .......................................................................................................................................................4 SAMPLING TOOLS ......................................................................................................................................................5 SIZE OF AREA TO SAMPLE..........................................................................................................................................5 Traditional Methods.............................................................................................................................................5 Precision Agriculture Methods.............................................................................................................................5 AREAS NOT TO SAMPLE ............................................................................................................................................5 -

Undrained Pore Pressure Development on Cohesive Soil in Triaxial Cyclic Loading
applied sciences Article Undrained Pore Pressure Development on Cohesive Soil in Triaxial Cyclic Loading Andrzej Głuchowski 1,* , Emil Soból 2 , Alojzy Szyma ´nski 2 and Wojciech Sas 1 1 Water Centre-Laboratory, Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Warsaw University of Life Sciences-SGGW, 02787 Warsaw, Poland 2 Department of Geotechnical Engineering, Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Warsaw University of Life Sciences-SGGW, 02787 Warsaw, Poland * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +48-225-935-405 Received: 5 July 2019; Accepted: 5 September 2019; Published: 12 September 2019 Abstract: Cohesive soils subjected to cyclic loading in undrained conditions respond with pore pressure generation and plastic strain accumulation. The article focus on the pore pressure development of soils tested in isotropic and anisotropic consolidation conditions. Due to the consolidation differences, soil response to cyclic loading is also different. Analysis of the cyclic triaxial test results in terms of pore pressure development produces some indication of the relevant mechanisms at the particulate level. Test results show that the greater susceptibility to accumulate the plastic strain of cohesive soil during cyclic loading is connected with the pore pressure generation pattern. The value of excess pore pressure required to soil sample failure differs as a consequence of different consolidation pressure and anisotropic stress state. Effective stresses and pore pressures are the main factors that govern the soil behavior in undrained conditions. Therefore, the pore pressure generated in the first few cycles plays a key role in the accumulation of plastic strains and constitutes the major amount of excess pore water pressure. Soil samples consolidated in the anisotropic and isotropic stress state behave differently responding differently to cyclic loading. -

The Pore Water Pressure and Settlement Characteristics of Soil Improved by Combined Vacuum and Surcharge Preloading
The Pore Water Pressure and Settlement Characteristics of Soil Improved by Combined Vacuum and Surcharge Preloading Jie Peng, Wen Guang Ji, Neng Li, Hao Ran Jin 1. Key Laboratory for Ministry of Education for Geo-mechanics and Embankment Engineering, Hohai University, Nanjing, 210098, China 2. Geotechnical Research Institute, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China ABSTRACT This study examines the pore water pressure and settlement characteristics of soil improved by combined vacuum and surcharge preloading based on two field tests. It discusses and compares methods of computing settlement and the degree of consolidation between combined vacuum and surcharge preloading and surcharge preloading alone as well. The non- uniform change of in the underground pore water pressure and the change in water depth indicates that the directly effective range of vacuum pumping in this paper should reach 18 m below the surface and that the range of the decline in the pore water pressure during vacuum preloading increases with decreasing depth below the surface. The groundwater table level declines during the process of vacuum preloading, and the restoration of the negative pore water pressure following unloading requires a period of time, as with the dispersion of the positive excess pore water pressure under surcharge preloading. The combination of vacuum and surcharge load can increase both the rate of the soil settlement and the total soil settlement; however, the settlement increment caused by the vacuum load will be less than that caused by the real surcharge load, and the surface settlement of combined vacuum and surcharge preloading is more uniform than that of surcharge preloading. -

Soil Judging Guide
New Hammpshirree Asssociatiionn of Conservaation Disttrriiccttss The New Hampshire SoilSoil JudgingJudging GuideGuide THE NEW HAMPSHIRE SOIL JUDGING GUIDE ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The NH Association of Conservation Districts wishes to acknowledge the following organizations for their support of New Hampshire’s soil judging effort. USDA – Natural Resources Conservation Service Future Farmers of America Students NH Association of Conservation Districts UNH Cooperative Extension Society of Soil Scientists of Northern New England Private Consulting Soil Scientists Conservation District Managers Reprinted September 2001 Revised March 1995 Revised March 1996 2 THE NEW HAMPSHIRE SOIL JUDGING GUIDE ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ..........................................................................................2 Introduction .........................................................................................................4 The Goals of the NH Soil Judging Contest____________________________________________________4 The Use of This Guide ____________________________________________________________________5 PART 1 – Physical Features of the Soil....................................................................6 Soil Profile and Soil Layers ________________________________________________________________6 Texture ________________________________________________________________________________7 Hardpan _______________________________________________________________________________9 Permeability ____________________________________________________________________________9 -

Stack Presentation
Challenges in Reconstructing Soils: Building the Foundation for Forest Restoration in Mine Reclamation Sites Shauna Stack, Caren Jones, Jana Bockstette and Simon Landhäusser CLRA/ACRSD 2018 National Conference and AGM University of Alberta, Department of Renewable Resources, Edmonton, AB Boreal Mixedwood Subregion Upland Native trees planted in Reclamation reconstructed soils Reconstructed soils used as capping material Man-made upland features (i.e. lean oil sand overburden) The Aurora Soil Capping Study • Trees were planted in 2012 and their heights were measured each year until 2016 (i.e. 5 years) • Density of 10,000 stems per hectare Measured over the same time period: ▪ Soil nutrients at time of placement ▪ Soil water content ▪ Soil temperature ▪ Precipitation Research Questions How do the following reconstructed soils impact the growth of Trembling Aspen in upland reclamation? Peat FFM Coversoil Type (i.e. Peat, Forest Floor Material, Subsoil Subsoil Subsoil B, Subsoil C) Subsoil Subsoil B C C C OB OB OB OB Peat FFM Subsoil B Subsoil C Research Questions How do the following reconstructed soils impact the growth of Trembling Aspen in upland reclamation? Peat FFM Coversoil Type (i.e. Peat, Forest Floor Material, Subsoil Subsoil Subsoil B, Subsoil C) Subsoil Subsoil B C C C OB OB OB OB Peat Peat FFM FFM Coversoil Placement Depth (i.e. 10cm Peat, 30cm Peat, 10cm FFM, 20cm FFM) Subsoil Subsoil Subsoil Subsoil C C C C OB OB OB OB FFM FFM FFM Subsoil Bm Underlying Subsoil Type (i.e. Subsoils Bm, BC and C) Blended Subsoil Subsoil B/C C -

Recommended Chemical Soil Test Procedures for the North Central Region
North Central Regional Research Publication No. 221 (Revised) Recommended Chemical Soil Test Procedures for the North Central Region Agricultural Experiment Stations of Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, Ohio, Pennsylvania, South Dakota and Wisconsin, and the U.S. Department of Agriculture cooperating. Missouri Agricultural Experiment Station SB 1001 Revised January 1998 (PDF corrected February 2011) Foreword Over the past 30 years, the NCR-13 Soil Testing Agricultural Experiment Stations over the past five and Plant Analysis Committee members have worked decades have been used to calibrate these recom- hard at standardizing the procedures of Soil Testing mended procedures. Laboratories with which they are associated. There NCR-13 wants it clearly understood that the have been numerous sample exchanges and experi- publication of these tests and procedures in no way ments to determine the influence of testing method, implies that the ultimate has been reached. Research sample size, soil extractant ratios, shaking time and and innovation on methods of soil testing should con- speed, container size and shape, and other laboratory tinue. The committee strongly encourages increased procedures on test results. As a result of these activi- research efforts to devise better, faster, less expensive ties, the committee arrived at the recommended pro- and more accurate soil tests. With the high cost of fer- cedures for soil tests. tilizer, and with the many soil related environmental Experiments have shown that minor deviations concerns, it is more important than ever that fertilizer in procedures may cause significant differences in test be applied only where needed and in the amount of results. -

Warming Exerts Greater Impacts on Subsoil Than Topsoil CO2 Efflux in A
Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 263 (2018) 137–146 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Agricultural and Forest Meteorology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/agrformet Warming exerts greater impacts on subsoil than topsoil CO2 efflux in a subtropical forest T Weisheng Lina, Yiqing Lia,b, Zhijie Yanga, Christian P. Giardinac, Jinsheng Xiea, Shidong Chena, ⁎ ⁎ Chengfang Lina, , Yakov Kuzyakovd,e,f, Yusheng Yanga, a Key Laboratory for Subtropical Mountain Ecology (Ministry of Science and Technology and Fujian Province Funded), School of Geographical Sciences, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350007, China b College of Agriculture, Forestry and Natural Resource Management, University of Hawaii, Hilo, HI, 96720, USA c Institute of Pacific Islands Forestry, Pacific Southwest Research Station, USDA Forest Service, Hilo, HI, 96720, USA d Department of Soil Science of Temperate Ecosystems, Department of Agricultural Soil Science, University of Gttingen, 37077 Gttingen, Germany e Institute of Physicochemical and Biological Problems in Soil Science, Russian Academy of Sciences, 142290 Pushchino, Russia f Soil Science Consulting, 37077 Gottingen, Germany ARTICLE INFO ABSTRACT Keywords: How warming affects the magnitude of CO2 fluxes within the soil profile remains an important question, with Chinese fir implications for modeling the response of ecosystem carbon balance to changing climate. Information on be- fl CO2 ux lowground responses to warming is especially limited for the tropics and subtropics because the majority of Fine root manipulative studies have been conducted in temperate and boreal regions. We examined how artificial Manipulative warming warming affected CO gas production and exchange across soil profiles in a replicated mesocosms experiment Soil moisture 2 relying on heavily weathered subtropical soils and planted with Chinese fir(Cunninghamia lanceolata). -

Design Guidelines for Horizontal Drains Used for Slope Stabilization
Design Guidelines for Horizontal Drains used for Slope Stabilization WA-RD 787.1 Greg M. Pohll March 2013 Rosemary W.H. Carroll Donald M. Reeves Rishi Parashar Balasingam Muhunthan Sutharsan Thiyagarjah Tom Badger Steve Lowell Kim A. Willoughby WSDOT Research Report Office of Research & Library Services Design Guidelines for Horizontal Drains used for Slope Stabilization Greg M. Pohll, DRI Rosemary W.H. Carroll, DRI Donald M. Reeves, DRI Rishi Parashar, DRI Balasingam Muhunthan, WSU Sutharsan Thiyagarjah, WSU Tom Badger, WSDOT Steve Lowell, WSDOT Kim A. Willoughby, WSDOT 1. REPORT NO. 2. GOVERNMENT ACCESSION 3. RECIPIENTS CATALOG NO NO. WA-RD 787.1 4. TITLE AND SUBTITLE 5. REPORT DATE Design Guidelines for Horizontal Drains used for Slope March 2013 Stabilization 6. PERFORMING ORGANIZATION CODE 7. AUTHOR(S) 8. PERFORMING ORGANIZATION REPORT NO. Greg M. Pohll, Rosemary W.H. Carroll, Donald M. Reeves, Rishi Parashar,Balasingam Muhunthan,Sutharsan Thiyagarjah, Tom Badger, Steve Lowell, Kim A. Willoughby 9. PERFORMING ORGANIZATION NAME AND ADDRESS 10. WORK UNIT NO. Desert Research Institute 2215 Raggio Parkway 11. CONTRACT OR GRANT NO. Reno, NV 89512 GCA6381 12. CO-SPONSORING AGENCY NAME AND ADDRESS 13. TYPE OF REPORT AND PERIOD COVERED Washington State Department of Transportation Final Report 310 Maple Park Ave SE 14. SPONSORING AGENCY CODE Olympia, WA 98504-7372 Research Manager: Kim Willoughby 360.705.7978 15. SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES This study was conducted in cooperation with the U.S. Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration through the pooled fund, TPF-5(151) in cooperation with the state DOT’s of California, Maryland, Mississippi, Montana, New Hampshire, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Texas, Washington and Wyoming.