.2 Physics First Semester Exam Practice
These selected problems are to be used as practice. You should review your semester outline for a more complete listing of the topics studied.
1. A scientific fact is……
a) Something you believe is true because you know it. b) An educated guess that has yet to be proven by experiment. c) A synthesis of a collection of data that includes well-tested guesses. d) Close agreement by competent observers of observations of the same phenomena. e) A guess that has been tested over and over again and always found to be true.
2. These values were obtained as the mass of a bar of metal; 8 g, 11 g, 12 g, and 14 g. The known mass is 11 g. The values are……
a) accurate b) precise c) both accurate and precise d) neither accurate nor precise
3. In the process of delivering mail, a postal worker walks 161 m, due east from his truck. He then turns around and walks 194 m, due west. What is the worker’s displacement relative to his truck?
(a) 33 m, due west (c) 194 m, due west (e) 355 m, due west (b) 33 m, due east (d) 252 m, due east
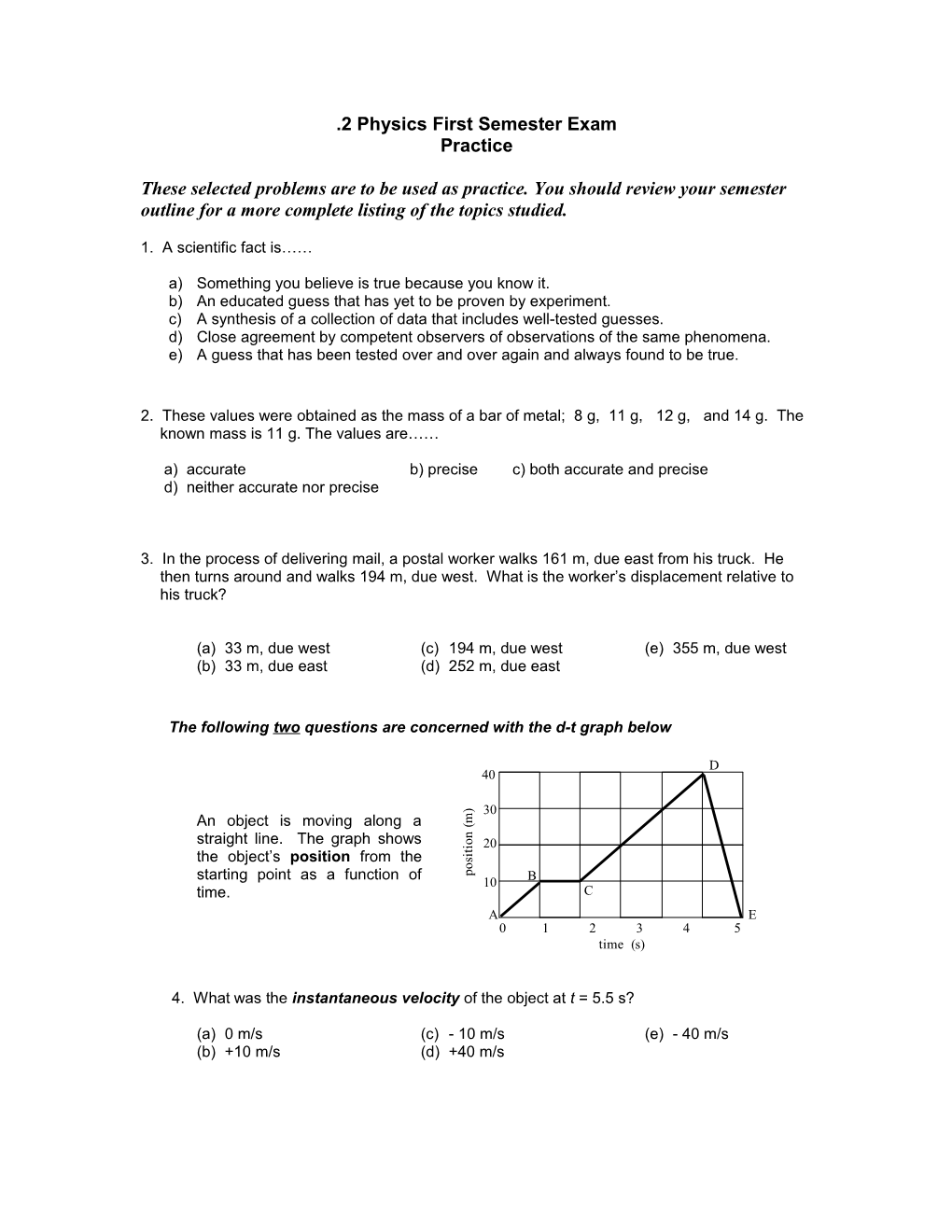
The following two questions are concerned with the d-t graph below
D 40
) 30 m
An object is moving along a (
n
straight line. The graph shows o
i 20 t i
the object’s position from the s o starting point as a function of p 10 B time. C A E 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 time (s)
4. What was the instantaneous velocity of the object at t = 5.5 s?
(a) 0 m/s (c) - 10 m/s (e) - 40 m/s (b) +10 m/s (d) +40 m/s
5. The average velocity of the object from t = 0 s to t = 5 s is (Hint: d / t)
(a) +0 m/s (b) +8 m/s (c) +10 m/s (d) +40 m/s (e) - 40 m/s
The following two questions are concerned with the v-t graph below
20 ) s / 15 m (
y
An object is moving along a straight t 10 i c
line. The graph shows the o l
e 5
object’s velocity as a function of v time. 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 time (s)
6. What is the acceleration of the object in the interval from t = 2 s to t = 3 s?
(a) 0 m/s2 (b) +3.3 m/s2 (c) +10 m/s2 (d) +20 m/s2 (e) +30 m/s2
7. What is the displacement from t = 3 s to t = 5 s?
(a) 5 m (b) 10 m (c) 15 m (d) 20 m (e) 30 m
8. A ball tossed vertically upward rises, reaches its highest point, and then falls back to its starting point. During this time, the acceleration of the ball is always…
a) in the direction of motion b) opposite its velocity
c) directed upward d) directed downward
9. A ball is thrown horizontally from the top of a tall building and is in the air for a period of time before it hits the ground. If it is again thrown horizontally but this time with twice the speed, it will hit the ground..
a) four times as far from the base of the building b) 2 times as far from the base of the building c) the same distance from the base of the building d) at the same time as the first ball 10. Car One is traveling due north and Car Two is traveling (3) due east. After the collision shown, Car One rebounds (2) (4) in the due south direction. Which of the numbered arrows is the only one that can represent the final (1) (5) direction of Car Two?
(a) 1 Two e n
(b) 2 O (c) 3 (d) 4 (e) 5
11. If the radius of the Earth were one half what it is now, and the mass were the same, what would be the value of g?
(a) 39.2 m/s2 (b) 19.6 m/s2 (c) 9.8 m/s2 (d) 4.9 m/s2 (e) 0 m/s2
12. A lunar month is about 28 days. If the moon were closer to Earth than it is now, the lunar month would be..
(a) less than 28 days. (b) more than 28 days. (c) unchanged at 28 days.
13. In the centripetal force lab a student revolves a stopper (mass, ms) around themselves in a horizontal circle of radius, r, with a string weighted by mass, mH. If the radius of the string is increased but the stopper mass and hanging masses are kept the same, what will happen to the speed of the revolving stopper?
(a) It will increase because the stopper has to change direction at a faster rate than before. (b) It will increase because the stopper has to change direction at a slower rate than before. (c) It will increase because the stopper has to change direction at the same rate as before. (d) It will decrease because the stopper has to change direction at a faster rate than before. (e) It will decrease because the stopper has to change direction at a slower rate than before. (f) It will decrease because the stopper has to change direction at the same rate as before. 14. An amusement park ride sometimes called ‘the fly’ is a large cylinder which can rotate. A person stands against the wall, and after the cylinder is rotating at a certain rate the floor drops away. The person remains ‘stuck’ in position against the wall - like a fly.
Which one of the following is the correct free-body force diagram showing all the forces acting on the person when the person is in the position shown above?
15. What is providing the centripetal force that keeps the person moving in a circle?
(a) Friction (b) Gravity (c) Normal (d) Centrifugal
16. If the ride was twice the radius but the person was moving at the same speed what would happen to the centripetal force exerted on the person?
A. It would increase to twice its previous amount B. It would decrease to half its previous amount C. It would increase to √2 its previous amount D. It would decrease to √2 its previous amount E. It wouldn’t change 17. A cannonball shot from a long-barrel cannon travels faster than one shot from a short- barrel cannon because the cannonball receives a greater…
(a) force (c) both (a) and (b) (b) impulse (d) neither (a) and (b)
18. A rocket is fired vertically. At its highest point, it explodes. Which one of the following describes what happens to its total momentum and total kinetic energy as a result of the explosion?
Total momentum Total kinetic energy
A. unchanged increased
B. unchanged unchanged
C. increased increased
D. increased unchanged
19. A car and a truck traveling with equal speeds in opposite directions collide head-on. The truck is more massive than the car.
How will the momentum changes of the vehicles compare in the collision?
A. The car will have the greater momentum change. B. The truck will have the greater momentum change. C The car and truck will have equal but opposite momentum changes. D. One cannot compare momentum changes for an inelastic collision such as this.
20. Two cars travelling at the same speed slam on their breaks and slide to a stop. If Car B has twice the mass of Car A the stopping distance of Car B will be…
A. Half as much as Car A because it has twice the friction force. B. The same as Car A because speed is the deciding factor. C. Twice as much as Car A because it has twice the inertia. D. Four times as much as Car A because kinetic energy depends on the square of the mass. Answers
1. D 2. A 3. A 4. E 5. B 6. A 7. E 8. D 9. D 10. D 11. A 12. A 13. C 14. B 15. C 16. B 17. B 18. A 19. C 20. B