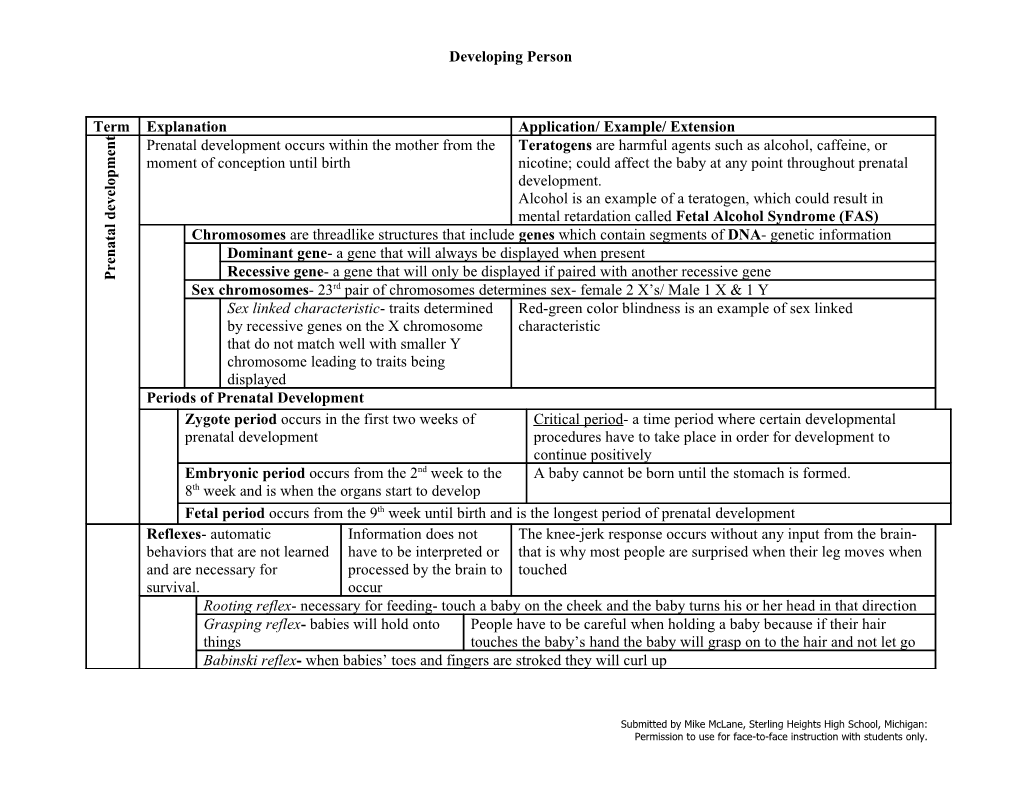
Developing Person
Term Explanation Application/ Example/ Extension t
n Prenatal development occurs within the mother from the Teratogens are harmful agents such as alcohol, caffeine, or e
m moment of conception until birth nicotine; could affect the baby at any point throughout prenatal p
o development. l e
v Alcohol is an example of a teratogen, which could result in e d
mental retardation called Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) l a
t Chromosomes are threadlike structures that include genes which contain segments of DNA- genetic information a
n Dominant gene- a gene that will always be displayed when present e r Recessive gene- a gene that will only be displayed if paired with another recessive gene P
rd
Sex chromosomes- 23 pair of chromosomes determines sex- female 2 X’s/ Male 1 X & 1 Y
Sex linked characteristic- traits determined Red-green color blindness is an example of sex linked
by recessive genes on the X chromosome characteristic
that do not match well with smaller Y
chromosome leading to traits being
displayed
Periods of Prenatal Development
Zygote period occurs in the first two weeks of Critical period- a time period where certain developmental prenatal development procedures have to take place in order for development to continue positively Embryonic period occurs from the 2nd week to the A baby cannot be born until the stomach is formed. 8th week and is when the organs start to develop Fetal period occurs from the 9th week until birth and is the longest period of prenatal development Reflexes- automatic Information does not The knee-jerk response occurs without any input from the brain- behaviors that are not learned have to be interpreted or that is why most people are surprised when their leg moves when and are necessary for processed by the brain to touched survival. occur Rooting reflex- necessary for feeding- touch a baby on the cheek and the baby turns his or her head in that direction Grasping reflex- babies will hold onto People have to be careful when holding a baby because if their hair things touches the baby’s hand the baby will grasp on to the hair and not let go Babinski reflex- when babies’ toes and fingers are stroked they will curl up
Submitted by Mike McLane, Sterling Heights High School, Michigan: Permission to use for face-to-face instruction with students only. Developing Person
n Temperament- researched by Thomas and Chess, who Dogs are born with a temperament- golden retrievers have a r o believed people were born with a specific type of friendly temperament that they are born with and will persist b
w emotional intensity that lasted throughout a person’s life throughout their life e
N Easy temperament- the baby has established eating and sleeping routines, generally happy in mood
e Difficult temperament- intense emotions, no routines in terms of eating, sleeping h t
Slow-to-warm up- shy, withdraws from new situations d
n Maturation- biological growth process that is the result Crawling is going to occur when the baby is physically ready to a
t of the aging process and is not influenced by learning; crawl- it is not going to be influenced by watching mom and dad n e crawling, walking, puberty are a result of the body being crawl m
p physically ready to perform those activities o l
e Vision is the least developed sense at birth v e D Schemas are mental organizations or frameworks that Schemas form from repeatedly doing things over and over, help to interpret and organize information from resulting in performing actions without thinking. For example: experiences tying your shoe, driving home, walking to your next class. Assimilation- interpreting and blending new For example, you already know Remember SS A-same- information into existing schemas how to hit a golf ball, and your golf coach now shows you how shema-ilation/ assimilation to hit the golf ball higher. You is same schema- learning how are assimilating or adding how to hit the ball higher did not to hit the golf ball higher to what change what you already you have already have learned know about golf
Submitted by Mike McLane, Sterling Heights High School, Michigan: Permission to use for face-to-face instruction with students only. Developing Person t n Accommodation- new information that An example of accommodation e Remember- the “c” stands for m modifies and changes existing schemas would be if your golf coach change in accommodation and p o came up and told you your golf l this involves changing an e
v swing is incorrect and now e established schema- your golf
D taught you a whole new way to coach is changing the way you e
v hit the golf ball. i hit the golf ball t i n g o C
Jean Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Development
Sensorimotor stage- occurs birth to 2 years; In the sensorimotor stage, If you are playing catch with your
children are learning through their senses and children are acquiring dog and you pretend to throw the
motor skills object permanence, which ball and place it behind your back,
is a continued searching for you may notice that your dog an object that is no longer continues to search the backyard there- this is significant looking for the ball, which is an because it demonstrates example of object permanence the beginnings of memory Preoperational stage- occurs 2-7 years; Animism- belief that inanimate Egocentrism- inability to take children begin to use symbols to represent objects are alive into consideration another things not there- still no logical thought person’s point of view. Lack of reversibility- the inability to reverse the sequence of actions or events- go backwards through a plan Concrete stage- children think logically only Achievement of conservations- Some people believe that about concrete things- things that they can see ability to recognize even though there is a lot of liquid in a in front of them shape changes the amount stays Red Bull can because of the same- ex: tall beaker vs. short, how tall the can is- when in round beaker with same amount of actuality there is not that water much- it just looks like a lot
Submitted by Mike McLane, Sterling Heights High School, Michigan: Permission to use for face-to-face instruction with students only. Developing Person
Formal operational stage- abstract reasoning- During this stage a child starts to learn good morals by comparing is able to form hypothetical thoughts through the positive and negative of a choice; resulting in forming weighing pros and cons of a choice opinions about what is fair or unfair Favorite quote of this stage: “That’s not fair!” Criticism of Piaget’s theory was that he The information-processing model contradicts Piaget’s theory focused too much on age and not on how through suggesting that cognitive development is nonstop and children develop individually and continuous throughout a person’s life uniquely Lev Vygotsky emphasized social interaction in the The more stimulation that a child receives, the more neural development of cognitive abilities- he believed the more communication within the brain will take place, causing more a child is talked to or interacted with by people, the better neurons to be formed, leading to increased brain activity. their cognitive abilities will develop Zone of proximal development- according to A child may feel that he or she is comfortable and capable of Vygotsky is the measurement or indication of completing a task when mom or dad is present. However, once what a child can do alone versus when other mom or dad leaves, the child will often become frustrated or people are around confused. This may occur because when mom or dad are watching, the child feels secure. When they leave, so does the security of knowing someone will be there to help. l Harry Harlow Through his work with monkeys, he Harlow’s experiment had 2 Harlow found that the baby a i c found that attachment- the emotional cages; one cage had a wired- monkeys formed attachments o S
bond between caregiver and another- monkey with a feeding more quickly and effectively
occurs better through contact and apparatus, while the other cage with the warm terry-clothed
warmth, not as much providing food had a monkey wrapped in a monkey rather than the wire- and nourishment warm terry cloth. monkey with a feeding bottle.
Submitted by Mike McLane, Sterling Heights High School, Michigan: Permission to use for face-to-face instruction with students only. Developing Person
Mary Stranger situation Secure attachment- child explores room when mother present, Anisworth 1. Mother and child enter the explores less when mother leaves, shows pleasure when mother room returns. 2. Mother then leaves infant alone Avoidant attachment- form of insecure attachment- child avoids in the playroom mother when mother returns 3. Stranger enters Ambivalent attachment- form of insecure attachment- upset 4. Mother later returns when mother leaves, but when mother returns alternates between clinging to her and rejecting her Konrad Lorenz Imprinting- newborn follows There was an incident where a dog was present when some baby whatever is seen first after birth chicks were just born. Because of imprinting the chicks followed the dog wherever it went. Erik Erikson Trust vs. Mistrust- according to Child abuse and neglect could lead to mistrust and eventually Erikson, trust must occur for insecure attachment attachment to then occur s e
l Diana Baumrind researched the effects of parenting styles on child development y t Authoritative parenting- parents use themselves This style produces children who are independent and mature, S
g as role models, reason with children, emphasize which indicated that the children were instrumentally competent- n i t maturity- also called democratic parenting meaning good children n e Permissive parenting- parents do not take an This style could produce children with problems such as drugs, r a
P interest in child, children do whatever they please trouble with the law as children try to get parents attention, which
they are not getting
Authoritarian parenting- based on power and This style could produce children who experiment with various emphasis on discipline behaviors, as children never have had a chance before to try things
Adolescence is a transitional period between childhood and adulthood.
Process of Primary sex characteristics- Only examples of primary sex characteristics would be the female
Puberty responsible for sexual reproduction ovaries and the male penis
Submitted by Mike McLane, Sterling Heights High School, Michigan: Permission to use for face-to-face instruction with students only. Developing Person e c Secondary sex characteristics- are Secondary sex characteristics are what other people recognize in n e nonreproductive characteristics such terms of classifying a boy or girl as a man or woman c s e
l as facial hair, deepened voice, o
d widening of hips
A Erik Erikson Identity vs. role confusion- during Adolescents experiment with Buying clothes is very similar to this stage adolescents search for different styles of dress, the process of searching for an identity through experimentation music, friends, goals, and identity. When you try on lifestyles; search for an different types of clothes, you end identity that feels natural up buying whichever fits and feels the best. The same is true with finding an identity. Intimacy vs. isolation- during this In order for an adolescent to enter and find success in the stage adolescents and young adults intimacy vs. isolation stage, the adolescent first has to resolve the start to form intimate relationships issue of identity in the identity vs. role confusion stage. If he or she does not know what he or she wants for him or herself, then that person cannot not know what he or she wants from another person in terms of a relationship Jean Piaget Formal operational stage- abstract Adolescents may argue more with parents because they can now reasoning- evaluating pros and cons assess whether or not something is fair. Personal Fable- adolescents believe that nothing wrong An example of personal An example of spotlight effect or bad will happen to them fable would be how certain would be when a girl or boy adolescents live their life- always thinks that people are Spotlight effect, or halo effect- adolescents believe that always through always talking or looking at him or her everyone is always watching them, or concerned with taking chances because they what they are doing or not doing think nothing bad could ever happen to them Morality is the reasoning skills that influence decisions and choices Lawrence Preconventional morality- decisions are Johnny does not pull his sister’s hair only because he does not Kohlberg based on gaining rewards and avoiding want to get grounded. punishment
Submitted by Mike McLane, Sterling Heights High School, Michigan: Permission to use for face-to-face instruction with students only. Developing Person y t
i Conventional morality decisions are Johnny does not pull his sister’s hair because he knows his father l a based on upholding rules and expectations has a rule not to pull hair. r o Postconventional morality decisions are Johnny does not pull his sister’s hair because he personally feels M
based on personal ethical and thoughts that it is wrong and further would not want her to pull his hair.
Carol Developed a Gilligan believed that a Suzy does not hit her brother In terms of a relationship,
Gilligan morality theory woman’s morality was because she would not want women are always emphasizing
that addressed based on caring and him to be mad at her. the “we”, or “us” On the other
women. upholding relationships hand, males emphasize the “I”, or “me” t n Gender includes the cultural, social, physical, and psychological meaning associated with being male or female e
m Gender role (how you act)- includes behaviors, Think about the definition of a role as the role a person plays in a p o attitudes, and personality traits that describe male or movie- this would include the way a person acts l e v female e
D Gender identity (how you think)- is the If you were asked to describe your identity, it would require you e l psychological feeling of being a male or female to think about who you are o R r e Gender theories d n
e Social learning theory- gender development occurs An example of the social learning theory affecting would be when
G through socially observing, interacting, and modeling a boy watches television and imitates his favorite action hero other people and images while playing with his friends Gender schema theory- involves a person’s mental An example of the gender schema theory would be when a girl representation, or what he or she thinks is female or does not think playing football is ladylike, or a boy thinks that male playing house is not for boys
Submitted by Mike McLane, Sterling Heights High School, Michigan: Permission to use for face-to-face instruction with students only. Developing Person g
n Work and family are central issues of adulthood and a challenge for older people is to balance work and family i g Social clock- is the understanding or feeling that there is Some people feel pressure to be married, or to have children by a A
d a time limit (like certain age) to accomplish specific life certain age. This pressure could come from family, friends, n a goals or tasks cultural or biological restraints, and themselves t l Erik Generativity vs. stagnation- during middle An example of generativity occurs when parents help their u d Erikson to old age people feel a sense to give back or children buy their first house or pay for college. Older people also A
be generous to give their life meaning. If they like to volunteer, for example, at hospitals or voting polls. This
do not have people or things to care for their occurs because volunteering give older people a chance to give
life may feel stagnant or uneventful back, but also feel as though they still have a purpose.
Ego integrity vs. despair- as people approach High school seniors, similar to older people in the ego integrity
the end of their life they may have certain vs. despair stage, approach graduation with certain regrets
regrets as time is starting to come to an end because they soon realize that they no longer have time to do
everything they wanted to during high school. For example:
doing better in school, apologizing to friends
Menopause occurs for women in middle age when the chances of reproduction decline Intelligence Fluid intelligence- based on speed- how Older people have trouble remembering items quickly because fast one is able to come up with an answer their fluid intelligence decreases throughout their life, which is or reasoning why they might not be a good contestant on the game show Jeopardy Crystallized intelligence- accumulated Crystallized intelligence increases as people become older information acquired throughout one’s life because everyday they are able to add information into their long- term memory Alzheimer’s disease- irreversible brain disorder Senile dementia is different than Alzheimer’s disease, as senile characterized by a loss of memory connected to the dementia is the result of a stroke, tumor, or the aging process that deterioration of AcH neurotransmitter. results in loss of memory. Dying: Elizabeth Kuber-Ross explored the issues of People who are terminally ill or people who have lost someone death and grieving, which she described in 5 stages close both experience these stages 1. Denial 4. Depression Every person goes through these stages at different times during 2. Anger 5. Acceptance the grieving process. There is not a set time limit for how long it 3. Bargaining takes a person to grieve
Submitted by Mike McLane, Sterling Heights High School, Michigan: Permission to use for face-to-face instruction with students only. Developing Person
Submitted by Mike McLane, Sterling Heights High School, Michigan: Permission to use for face-to-face instruction with students only.