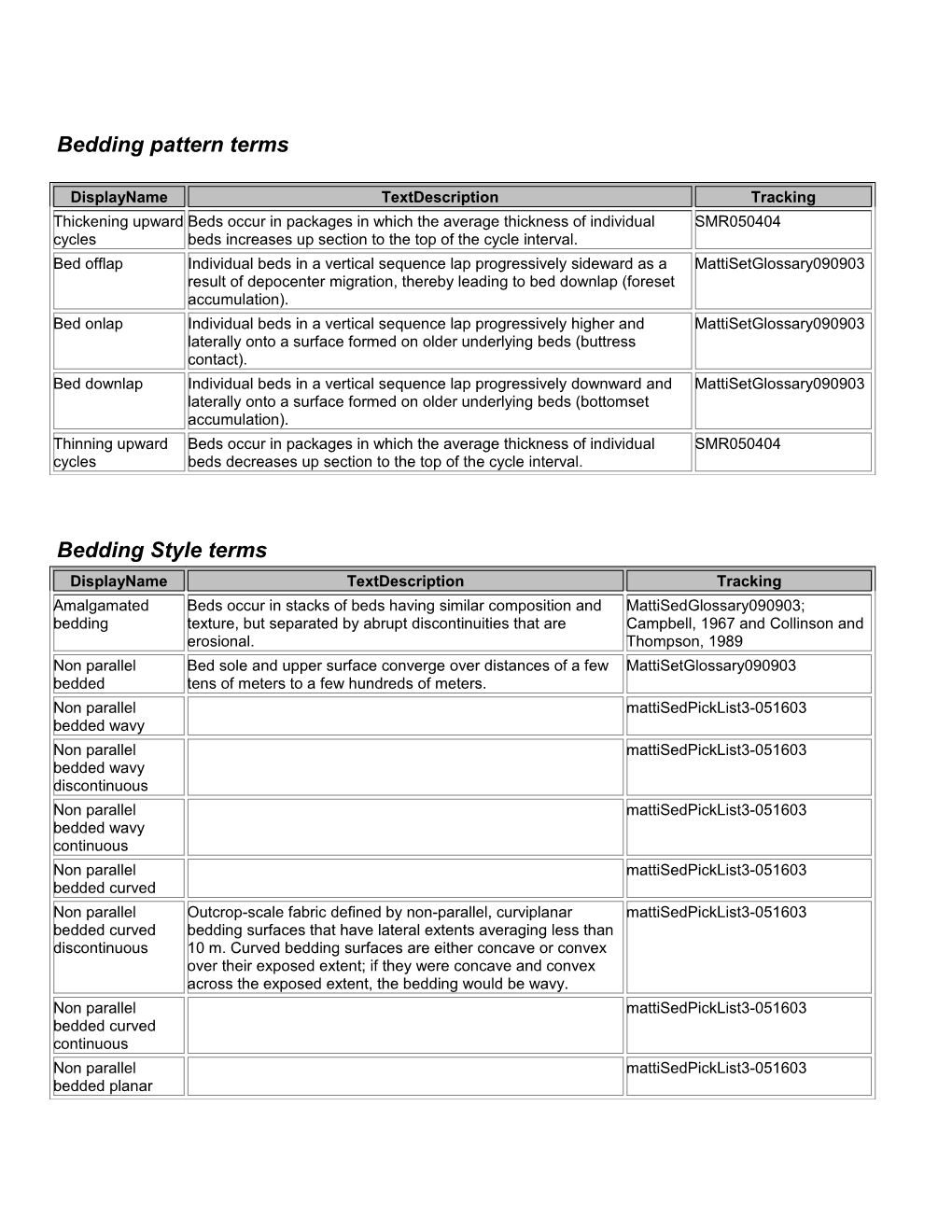
Bedding pattern terms
DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Thickening upward Beds occur in packages in which the average thickness of individual SMR050404 cycles beds increases up section to the top of the cycle interval. Bed offlap Individual beds in a vertical sequence lap progressively sideward as a MattiSetGlossary090903 result of depocenter migration, thereby leading to bed downlap (foreset accumulation). Bed onlap Individual beds in a vertical sequence lap progressively higher and MattiSetGlossary090903 laterally onto a surface formed on older underlying beds (buttress contact). Bed downlap Individual beds in a vertical sequence lap progressively downward and MattiSetGlossary090903 laterally onto a surface formed on older underlying beds (bottomset accumulation). Thinning upward Beds occur in packages in which the average thickness of individual SMR050404 cycles beds decreases up section to the top of the cycle interval.
Bedding Style terms DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Amalgamated Beds occur in stacks of beds having similar composition and MattiSedGlossary090903; bedding texture, but separated by abrupt discontinuities that are Campbell, 1967 and Collinson and erosional. Thompson, 1989 Non parallel Bed sole and upper surface converge over distances of a few MattiSetGlossary090903 bedded tens of meters to a few hundreds of meters. Non parallel mattiSedPickList3-051603 bedded wavy Non parallel mattiSedPickList3-051603 bedded wavy discontinuous Non parallel mattiSedPickList3-051603 bedded wavy continuous Non parallel mattiSedPickList3-051603 bedded curved Non parallel Outcrop-scale fabric defined by non-parallel, curviplanar mattiSedPickList3-051603 bedded curved bedding surfaces that have lateral extents averaging less than discontinuous 10 m. Curved bedding surfaces are either concave or convex over their exposed extent; if they were concave and convex across the exposed extent, the bedding would be wavy. Non parallel mattiSedPickList3-051603 bedded curved continuous Non parallel mattiSedPickList3-051603 bedded planar DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Non parallel mattiSedPickList3-051603 bedded planar continuous Non parallel mattiSedPickList3-051603 bedded planar discontinuous Fissil bedding Bedding parting surfaces separated by < 2mm (on average) SMR over exposed outcrop (base on Jackson, 1997). Channelate Bed sole forms an erosional channel into underlying beds. MattiSetGlossary090903 bedding Parallel bedded Bed sole and upper surface are parallel for many tens to MattiSetGlossary090903 hundreds of meters. Parallel bedded mattiSedPickList3-051603 planar Parallel bedded mattiSedPickList3-051603 planar continuous Parallel bedded mattiSedPickList3-051603 planar discontinuous Parallel bedded mattiSedPickList3-051603 wavy Parallel bedded mattiSedPickList3-051603 wavy continuous Parallel bedded mattiSedPickList3-051603 wavy discontinuous Parallel bedded mattiSedPickList3-051603 curved Parallel bedded mattiSedPickList3-051603 curved discontinuous Parallel bedded mattiSedPickList3-051603 curved continuous
Bedding thickness terms DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Sedimentary Terms for average thickness of bedding layers (individual mattiSedPickList3-051603; bedding layer sedimentation units) within a geologic unit. SMR050304 thickness medium bedded Sedimentation units (strata) average 10-30 cm thick. mattiSedPickList3-051603; (modified from Ingram, 1954; see Campbell, 1967 and Collinson and Thompson, 1989) DisplayName TextDescription Tracking non bedded No apparent stratificaton in geologic unit. mattiSedPickList3-051603; (modified from Ingram, 1954; see Campbell, 1967 and Collinson and Thompson, 1989) thin bedded Sedimentation units (strata) average 3-10 cm thick. mattiSedPickList3-051603; (modified from Ingram, 1954; see Campbell, 1967 and Collinson and Thompson, 1989) very thin bedded Sedimentation units (strata) average 1-3 cm thick. mattiSedPickList3-051603; (modified from Ingram, 1954; see Campbell, 1967 and Collinson and Thompson, 1989) laminated Sedimentation units (strata) average < 1 cm thick in mattiSedPickList3-051603; (modified geologic unit.. from Ingram, 1954; see Campbell, 1967 and Collinson and Thompson, 1989) very thick bedded Sedimentation units (strata) average >100 cm thick. mattiSedPickList3-051603; (modified from Ingram, 1954; see Campbell, 1967 and Collinson and Thompson, 1989) thick bedded Sedimentation units (strata) average 30-100 cm thick. mattiSedPickList3-051603; (modified from Ingram, 1954; see Campbell, 1967 and Collinson and Thompson, 1989) sedimentary Terminology to describe the average thickness of rock mattiSedPickList3-051603; (modified bedding parting between bedding parting surfaces in a sedimentary rock. from Ingram, 1954; see Campbell, thickness Parting surfaces commonly coincide with bed boundaries 1967 and Collinson and Thompson, and contribute to the recognition of stratification. 1989) Fissile parting Parting surfaces spaced 1- 3 mm on average. mattiSedPickList3-051603; (modified from Ingram, 1954; see Campbell, 1967 and Collinson and Thompson, 1989) Platy parting Parting surfaces spaced 3-10 mm on average. mattiSedPickList3-051603; (modified from Ingram, 1954; see Campbell, 1967 and Collinson and Thompson, 1989) Massive parting Parting surfaces spaced >100 cm on average. mattiSedPickList3-051603; (modified from Ingram, 1954; see Campbell, 1967 and Collinson and Thompson, 1989) Flaggy parting Parting surfaces spaced 1-3 cm on average. mattiSedPickList3-051603; (modified from Ingram, 1954; see Campbell, 1967 and Collinson and Thompson, 1989) Blocky bedding Bedding parting surfaces spaced 10-30 cm on average. mattiSedPickList3-051603; (modified parting from Ingram, 1954; see Campbell, 1967 and Collinson and Thompson, 1989) Papery parting Parting surfaces spaced <1 mm on average. mattiSedPickList3-051603; (modified from Ingram, 1954; see Campbell, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking 1967 and Collinson and Thompson, 1989) Slabby parting Parting surfaces spaced 3-10 cm on average. mattiSedPickList3-051603; (modified from Ingram, 1954; see Campbell, 1967 and Collinson and Thompson, 1989)
Colors DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Black Foster RGB: 222222, MundieRGB: 131313. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 2.5PB1/0. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (all) 2.5PB0.8/0 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Blackish Blue Foster RGB: 202830, MundieRGB: 161A1E. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (10BG-9B,9B- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5PB,5-9PB) 9.8B1.3/1.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Blackish Green Foster RGB: 1A2421, MundieRGB: 141613. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (8GY-3G,3- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9G,9G-10BG) 10G1/1.4 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Blackish Purple Foster RGB: 291E29, MundieRGB: 1D1018. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 0.8RP1/1.6. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (9PB-3P,3-9P,9P-3RP,3-9RP,9RP- John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 1R) 0.8RP0.9/1.6 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Blackish Red Foster RGB: 2E1D21, MundieRGB: 1F0E11. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 3.9R1/1.7. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (1-6R) 3.9R0.8/1.7 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Bluish Black Foster RGB: 202428, MundieRGB: 151719. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: Purplish Blue. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (10BG-9B,9B-5PB,5-9PB) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 9.6B1.1/0.8 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Bluish Gray Foster RGB: 81878B, MundieRGB: 7D746D. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (10BG-9B,9B- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5PB,5-9PB) 8.9B5.5/0.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Bluish White Foster RGB: E9E9ED, MundieRGB: F9DFCF. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: conversion better; #CFDFF9 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. transposed but too dark. Munsell Chart Span John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription Centroid: (10BG-9B,9B-5PB,5-9PB) errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted 9.2B9.1/1.2 Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brilliant Blue Foster RGB: 4997D0, MundieRGB: 4285B4. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: Syn celestial blue. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (9B-5PB,5-7PB) 1.6PB5.9/9.4 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brilliant Bluish Foster RGB: 00A693, MundieRGB: 009B76. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Foster Notes: 2.9BG6/7.9673. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (9G-10BG) 2.9BG6/9.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brilliant Green Foster RGB: 3EB489, MundieRGB: 47A76A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9G) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6.2G6.5/8.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brilliant Foster RGB: 239EBA, MundieRGB: 2A8D9C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Greenish Blue Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (10BG-9B) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.6B5.9/7.7 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brilliant Foster RGB: E9E450, MundieRGB: FFDC33. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Greenish Yellow Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9Y,9Y-2GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9.8Y8.8/9.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brilliant Orange Foster RGB: FD943F, MundieRGB: FFB841. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: guess 4YR7/12; 4YR9/2.9 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. #FFDEC9 as indicated here is very light. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (2-7YR) 4YR9/12 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brilliant Orange Foster RGB: FFC14F, MundieRGB: FFB02E. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellow Foster Notes: 0.1Y8.1/10.08. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (7-8YR,8YR-1Y) 0.1Y8.1/10.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brilliant Purple Foster RGB: D399E6, MundieRGB: DD80CC. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9P) 6P7/11 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brilliant Purplish Foster RGB: 6C79B8, MundieRGB: 62639B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Blue Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9PB) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7.3PB5.1/9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brilliant Purplish Foster RGB: FFC8D6, MundieRGB: FF97BB. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Pink Foster Notes: 6RP8.5/5.3. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (9P-3RP,3-9RP) 6RP8.5/11 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brilliant Violet Foster RGB: 7E73B8, MundieRGB: 755D9A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9.9PB5.1/9.4 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brilliant Yellow Foster RGB: FADA5E, MundieRGB: FFCF40. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-7Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.4Y8.7/8.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brilliant Yellow Foster RGB: BDDA57, MundieRGB: CED23A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (2-8GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.9GY8.2/9.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brilliant Foster RGB: 83D37D, MundieRGB: 8CCB5E. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellowish Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (8GY-3G) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 0.3G7.7/8.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brownish Black Foster RGB: 28201C, MundieRGB: 140F0B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 7.8YR1/0.9 Orange Yellow. National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-8YR,8YR- John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 1Y,1-4Y) 7.8YR0.6/0.9 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brownish Gray Foster RGB: 5B504F, MundieRGB: 503D33. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-8YR,8YR- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 1Y,1-4Y) 5.65R3.4/0.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brownish Foster RGB: AE6938, MundieRGB: B15124. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Orange Foster Notes: Brown. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (2-7YR) 4.1YR5/8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Brownish Pink Foster RGB: C2AC99, MundieRGB: CD9A7B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: Reddish Orange. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (5-8YR) 7YR7.1/2.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Blue Foster RGB: 00304E, MundieRGB: 002137. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 2.2PB1.7/5.353; syn. navy blue. National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9B-5PB,5-7PB) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 2.2PB1.7/5.5 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Bluish Gray Foster RGB: 51585E, MundieRGB: 464544. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (10BG-9B,9B- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5PB,5-9PB) 0.3PB3.6/1.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Bluish Foster RGB: 004B49, MundieRGB: 013A33. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Foster Notes: 4.9BG2.7/4.4886. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (9G-10BG) 4.9BG2.7/5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Brown Foster RGB: 422518, MundieRGB: 35170C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-8YR) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5.3YR1.6/3.4 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Gray Foster RGB: 555555, MundieRGB: 49423D. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (all) 2.5PB3.5/0 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Grayish Foster RGB: 36454F, MundieRGB: 2C3337. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Blue Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (10BG-9B,9B- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5PB,5-9PB) 9.2B2.7/2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Grayish Foster RGB: 3E322C, MundieRGB: 32221A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-8YR) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5.5YR2/1.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Grayish Foster RGB: 3A4B47, MundieRGB: 313830. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Foster Notes: (not dark greenish yellowish National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. green or dark grayish yellowish green. Munsell John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription Chart Span Centroid: (8GY-3G,3-9G,9G-10BG) errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted 1BG2.9/1.8 Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Grayish Foster RGB: 363527, MundieRGB: 2B2517. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Olive Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (4-9Y,9Y-2GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9.7Y2/1.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Grayish Foster RGB: 31362B, MundieRGB: 27261A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Olive Green Foster Notes: Yellowish Green. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (2-8GY) 5.4GY2/1.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Grayish Foster RGB: 50404D, MundieRGB: 452D35. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purple Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P,3- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9P,9P-3RP,3-9RP,9RP-1R) 0.5RP2.8/2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Grayish Foster RGB: 543D3F, MundieRGB: 482A2A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Red Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-6R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2.9R2.7/2.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Grayish Foster RGB: 43302E, MundieRGB: 371F1C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Reddish Brown Foster Notes: Orange. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (6-9R,9R-1YR,1-3YR) 9R2/2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Grayish Foster RGB: A18F60, MundieRGB: A47C45. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellow Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-7Y) 3.8Y5.9/4 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Grayish Foster RGB: 483C32, MundieRGB: 3D2B1F. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellowish Brown Foster Notes: Yellow. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (8YR-1Y) 8.8YR2.5/1.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Green Foster RGB: 1B4D3E, MundieRGB: 203A27. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9G) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6.6G2.8/4.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Greenish Foster RGB: 004958, MundieRGB: 003841. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Blue Foster Notes: 3.7B2.7/4.4696. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (10BG-9B) 3.7B2.7/5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Greenish Foster RGB: 4E5755, MundieRGB: 45433B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Gray Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (4GY-8GY,8GY- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 3G,3G-9G,9G-10BG) 1.5BG3.5/0.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Greenish Foster RGB: 98943E, MundieRGB: 9B8127. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellow Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9Y,9Y-2GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9.4Y5.9/6.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Olive Foster RGB: 403D21, MundieRGB: 362C12. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (4-9Y,9Y-2GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 8.9Y2.4/3.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Olive Foster RGB: 3B3121, MundieRGB: 302112. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Brown Foster Notes: Greenish Yellow. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (1-4Y) 2Y1.9/2.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Olive Foster RGB: 2B3D26, MundieRGB: 232C16. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (2-8GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 8GY2.2/3.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Orange Foster RGB: BE8A3D, MundieRGB: C37629. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellow Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-8YR,8YR-1Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9.3YR6/7.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Pink Foster RGB: C08081, MundieRGB: C76864. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9RP-1R,1-6R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2.7R5.9/6.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Purple Foster RGB: 563C5C, MundieRGB: 472A3F. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6.3P2.8/4.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Purplish Foster RGB: 252440, MundieRGB: 1A162A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Blue Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9PB) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 8PB1.3/4.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Purplish Foster RGB: 5D555B, MundieRGB: 564042. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Gray Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P,3- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9P,9P-3RP,3-9RP,9RP-1R) 1RP3.6/1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Purplish Foster RGB: C17E91, MundieRGB: C76574. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Pink Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9RP) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6.4RP5.9/7 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Purplish Foster RGB: 673147, MundieRGB: 5B1E31. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Red Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9RP,9RP-1R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7.1RP2.7/6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Red Foster RGB: 722F37, MundieRGB: 681C23. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-9R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.0R2.8/6.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Reddish Foster RGB: 3E1D1E, MundieRGB: 321011. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (6-9R,9R-1YR,1- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 3YR) 9.6R1.3/3.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Reddish Foster RGB: 5C504F, MundieRGB: 523C36. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Gray Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-9R,9R-1YR) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6R3.4/1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Reddish Foster RGB: 9E4732, MundieRGB: 9B2F1F. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Orange Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9R,9R-1YR,1- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2YR) 9.3R4/9.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Reddish Foster RGB: 5D3954, MundieRGB: 4F273A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purple Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9P-3RP) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 1.3RP2.8/4.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Violet Foster RGB: 2F2140, MundieRGB: 22132B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 1.4P1.3/4.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Yellow Foster RGB: AB9144, MundieRGB: B07D2B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-7Y) 3.9Y6/6.4 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Yellowish Foster RGB: 4B3621, MundieRGB: 3F2512. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (8YR-1Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9.4YR2.3/3.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Yellowish Foster RGB: 355E3B, MundieRGB: 304B26. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (8GY-3G) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 0.6G3.5/5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Dark Yellowish Foster RGB: C48379, MundieRGB: CC6C5C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Pink Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (6-8R) 7R6/6.1 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Blue Foster RGB: 00416A, MundieRGB: 002F55. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 2.8PB2.5/6.817; syn. royal blue. National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9B-5PB,5-7PB) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 2.8PB2.5/7.9 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Bluish Foster RGB: 00443F, MundieRGB: 00382B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Green Foster Notes: 2.8BG2.4/4.478. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (9G-10BG) 2.8BG2.4/8.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Brown Foster RGB: 593319, MundieRGB: 4D220E. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (2-8YR) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5.6YR2.4/5.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Green Foster RGB: 00543D, MundieRGB: 004524. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 5.1G3/5.7915. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (3-9G) 5.1G3/8.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Greenish Foster RGB: 2E8495, MundieRGB: 007BA7. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Blue Foster Notes: guess 2.8B5/6. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (10BG-9B) 5B5/13 see #167 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription #176 see #135 #167 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Greenish Foster RGB: 9B9400, MundieRGB: 9F8200. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellow Foster Notes: 9.2Y5.9/8.7896. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (7-9Y,9Y-2GY) 9.2Y5.9/9.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Olive Foster RGB: 232F00, MundieRGB: 142300. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Foster Notes: 4GY1.5/3.886. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (2-8GY) 4GY1.5/11 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Orange Foster RGB: BE6516, MundieRGB: C34D0A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (2-7YR) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.1YR5.1/11.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Orange Foster RGB: C98500, MundieRGB: D76E00. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellow Foster Notes: 8.6YR6/11.0455. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (7-8YR,8YR-1Y) 8.6YR6/12.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Pink Foster RGB: E4717A, MundieRGB: F3545E. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9RP-1R,1-6R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2.1R6/11.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Purple Foster RGB: 602F6B, MundieRGB: 531A50. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6.3P2.7/9.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Purplish Foster RGB: 272458, MundieRGB: 1A153F. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Blue Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9PB) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7.8PB1.5/8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Purplish Foster RGB: DE6FA1, MundieRGB: EB5284. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Pink Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9P-3RP,3-9RP) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.4RP6/12.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Purplish Foster RGB: 78184A, MundieRGB: 6F0035. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Red Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9RP,9RP-1R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7.3RP2.6/10.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Red Foster RGB: 841B2D, MundieRGB: 7B001C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-9R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5.1R2.8/10.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Reddish Foster RGB: 56070C, MundieRGB: 490005. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (6-9R,9R-1YR,1- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2YR) 1.6YR1.5/8.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Reddish Foster RGB: AA381E, MundieRGB: A91D11. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Orange Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9R,9R-1YR,1- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2YR) 9.2R3.9/12.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Reddish Foster RGB: 702963, MundieRGB: 641349. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purple Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9P-3RP) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 1RP2.8/9.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Violet Foster RGB: 32174D, MundieRGB: 240935. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 1.1P1.2/8.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Yellow Foster RGB: AF8D13, MundieRGB: B57900. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-7Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 3.7Y5.9/9.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Yellow Foster RGB: 467129, MundieRGB: 425E17. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (2-8GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7.4GY4.2/7.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Yellowish Foster RGB: 654522, MundieRGB: 593315. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (8YR-1Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 8.8YR3.1/5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Yellowish Foster RGB: 00622D, MundieRGB: 00541F. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Foster Notes: 0.9G3.5/8.0245. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (8GY-3G) 0.9G3.5/9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Deep Yellowish Foster RGB: E66761, MundieRGB: F64A46. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Pink Foster Notes: #e66721> my error: not National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. #E66721. Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (4-7R) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 5.5R5.8/12.1 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Blue Foster RGB: 536878, MundieRGB: 4A545C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: Syn. slate blue. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (10BG-9B,9B-5PB,5-9PB) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 0.2PB4.2/3 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Brown Foster RGB: 635147, MundieRGB: 5A3D30. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-8YR) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5.5YR3.5/1.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Green Foster RGB: 5E716A, MundieRGB: 575E4E. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (8GY-3G,3- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9G,9G-10BG) 8.8G4.5/1.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Foster RGB: B9B57D, MundieRGB: C4A55F. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Greenish Yellow Foster Notes: Olive. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (7-9Y,9Y-2GY) 9Y7.2/3.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Olive Foster RGB: 5B5842, MundieRGB: 52442C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (4-9Y,9Y-2GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 8Y3.6/2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Olive Foster RGB: 515744, MundieRGB: 48442D. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (2-8GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.6GY3.5/2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Pink Foster RGB: C4AEAD, MundieRGB: CF9B8F. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9RP-1R,1R-6R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2.6R7.2/2.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Purple Foster RGB: 796878, MundieRGB: 72525C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P,3- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9P,9P-3RP,3-9RP,9RP-1R) 8.1P4.5/2.7 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Purplish Foster RGB: 4C516D, MundieRGB: 413D51. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Blue Foster Notes: Violet. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (5-9PB) 6.9PB3.4/3.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Purplish Foster RGB: C3A6B1, MundieRGB: CC9293. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Pink Foster Notes: Purplish Red. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (9P-3RP,3-9RP) 3.7RP7/3.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Purplish Foster RGB: 915F6D, MundieRGB: 8C4852. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Red Foster Notes: Neutral. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (3-9RP,9RP-1R) 7RP4.5/5.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Red Foster RGB: 905D5D, MundieRGB: 8C4743. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-8R) 4R4.4/4.8 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Reddish Foster RGB: 674C47, MundieRGB: 5E3830. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (6-9R,9R-1YR,1- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 3YR) 9R3.4/2.4 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Reddish Foster RGB: B4745E, MundieRGB: B85D43. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Orange Foster Notes: Reddish Brown. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (8-9R,9R-1YR,1-3YR) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 0.4YR5.4/6.2 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Reddish Foster RGB: 836479, MundieRGB: 7D4D5D. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purple Foster Notes: Purplish Pink. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (9P-3RP) 1RP4.5/4.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Violet Foster RGB: 554C69, MundieRGB: 46394B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: Purple. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (9PB-3P) 1.2P3.3/3.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Yellow Foster RGB: C2B280, MundieRGB: CEA262. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-9Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.4Y7.2/3.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Yellow Foster RGB: 8F9779, MundieRGB: 90845B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Foster Notes: Olive Green; (not grayish National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. yellowish green. Munsell Chart Span Centroid: John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription (9Y-2GY,2-8GY) 4.4GY6/2.3 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Foster RGB: 7E6D5A, MundieRGB: 785840. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellowish Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (8YR-1Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9.5YR4.6/2.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Grayish Foster RGB: C7ADA3, MundieRGB: D39B85. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellowish Pink Foster Notes: Brownish Pink. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (6-9R,9R-1YR,1-5YR) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 1.3YR7.2/2.4 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Greenish Black Foster RGB: 1E2321, MundieRGB: 181513. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: Bluish Green. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (4GY-8GY,8GY-3G,3G-9G,9G- John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 10BG) 8.7G1/0.7 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Greenish Gray Foster RGB: 7D8984, MundieRGB: 7A7666. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (4GY-8GY,8GY- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 3G,3G-9G,9G-10BG) 7.5G5.5/1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Greenish White Foster RGB: DFEDE8, MundieRGB: F5E6CB. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: better. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (4GY-8GY,8GY-3G,3G-9G,9G-10BG) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 10G9.2/0.8 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Blue Foster RGB: 70A3CC, MundieRGB: 6C92AF. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: Syn. sky blue. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (9B-5PB,5-7PB) 1.6PB6.4/6.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Bluish Foster RGB: B4BCC0, MundieRGB: BEADA1. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Gray Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (10BG-9B,9B- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5PB,5-9PB) 8.2B7.5/1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Bluish Foster RGB: 66ADA4, MundieRGB: 669E85. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9G-10BG) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.6BG6.5/4.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Brown Foster RGB: A67B5B, MundieRGB: A86540. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-8YR) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5.4YR5.4/4.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Brownish Foster RGB: 8E8279, MundieRGB: 8B6D5C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Gray Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (2-8YR,8YR- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 1Y,1-4Y) 7YR5.4/1.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Gray Foster RGB: B9B8B5, MundieRGB: C2A894. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (all) 6.7Y7.4/0.2 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Grayish Foster RGB: 958070, MundieRGB: 946B54. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (5-8YR) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6.4YR5.4/2.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Grayish Foster RGB: 8C8767, MundieRGB: 8B734B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Olive Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (4-9Y,9Y-2GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7.85Y5.5/2.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Grayish Foster RGB: AF868E, MundieRGB: B27070. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purplish Red Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9RP,9RP-1R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7.8RP5.9/4.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Grayish Foster RGB: AD8884, MundieRGB: B17267. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Red Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-8R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5.3R5.9/3.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Grayish Foster RGB: 977F73, MundieRGB: 966A57. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Reddish Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-5YR) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2.9YR5.4/2.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Grayish Foster RGB: AE9B82, MundieRGB: B48764. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellowish Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (8YR-1Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9.7YR6.4/2.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Green Foster RGB: 6AAB8E, MundieRGB: 719B6E. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9G) 6G6.4/5.1 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Greenish Foster RGB: 66AABC, MundieRGB: 649A9E. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Blue Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (10BG-9B) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.5B6.5/5.4 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Greenish Foster RGB: B2BEB5, MundieRGB: BAAF96. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Gray Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (4GY-8GY,8GY- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 3G,3G-9G,9G-10BG) 3G7.5/0.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Greenish Foster RGB: EAE679, MundieRGB: FFDE5A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellow Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9Y,9Y-2GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9.8Y8.9/7 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Olive Foster RGB: 867E36, MundieRGB: 846A20. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (4-9Y,9Y-2GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 8.2Y5.1/5.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Olive Foster RGB: 967117, MundieRGB: 945D0B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-4Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2.1Y4.9/7.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Olive Gray Foster RGB: 8A8776, MundieRGB: 887359. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (4-9Y,9Y-2GY,2- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4GY) 6.9Y5.5/1.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Orange Foster RGB: FAB57F, MundieRGB: FFA161. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (2-7YR) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.8YR7.8/7.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Orange Foster RGB: FBC97F, MundieRGB: FFB961. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellow Foster Notes: see #35. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (7-8YR,8YR-1Y) 9.4YR8.3/6.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Pink Foster RGB: F9CCCA, MundieRGB: FFBCAD. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9RP-1R,1-6R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2.6R8.5/4 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Purple Foster RGB: B695C0, MundieRGB: BA7FA2. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6.2P6.5/6.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Purplish Foster RGB: 8791BF, MundieRGB: 837DA2. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Blue Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9PB) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7.3PB6/6.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Purplish Foster RGB: BFB9BD, MundieRGB: C8A99E. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Gray Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P,3- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9P,9P-3RP,3-9RP) 0.3RP7.5/1.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Purplish Foster RGB: EFBBCC, MundieRGB: FFA8AF. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Pink Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9P-3RP,3-9RP) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.6RP8/5.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Reddish Foster RGB: A87C6D, MundieRGB: AA6651. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (8-9R,9R-1YR,1- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 3YR) 0.5YR5.5/4.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Reddish Foster RGB: B784A7, MundieRGB: BB6C8A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purple Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9P-3RP) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 0.7RP6/6.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Violet Foster RGB: 8C82B6, MundieRGB: 876C99. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 0.5P5.6/7.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Yellow Foster RGB: F8DE7E, MundieRGB: FFD35F. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-7Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.3Y8.8/6.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Yellow Foster RGB: C9DC89, MundieRGB: DCD36A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (2-8GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5GY8.4/5.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Yellowish Foster RGB: C19A6B, MundieRGB: BB8B54. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-8YR,8YR-1Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 8.7YR6.5/5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Yellowish Foster RGB: 93c592, MundieRGB: 007ba7. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Foster Notes: #9AB973 in color dictionary; National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. #007BA7 see #167 #170. Munsell Chart Span John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription Centroid: (8GY-3G) 0.7G7.4/5.2 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Light Yellowish Foster RGB: F4C2C2, MundieRGB: FFB28B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Pink Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (6-9R,9R-1YR,1- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7YR) 1.9YR8.2/4.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Medium Gray Foster RGB: 848482, MundieRGB: 817066. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (all) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 3.3GY5.4/0.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Blue Foster RGB: 436B95, MundieRGB: 395778. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: Syn. cerulean blue. Munsell National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Chart Span Centroid: (9B-5PB,5-7PB) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 3PB4.3/6.8 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Bluish Foster RGB: 317873, MundieRGB: 2F6556. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9G-10BG) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.6BG4.5/5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Brown Foster RGB: 6F4E37, MundieRGB: 673923. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-8YR) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5.6YR3.5/3.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Green Foster RGB: 3B7861, MundieRGB: 386646. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9G) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6.3G4.5/5.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Foster RGB: 367588, MundieRGB: 30626B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Greenish Blue Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (10BG-9B) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.7B4.5/5.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Foster RGB: B9B459, MundieRGB: C4A43D. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Greenish Yellow Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9Y,9Y-2GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9.5Y7.1/6.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Olive Foster RGB: 665D1E, MundieRGB: 5E490F. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (4-9Y,9Y-2GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7.6Y3.8/5.4 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Olive Foster RGB: 6C541E, MundieRGB: 64400F. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-4Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2.7Y3.6/5.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Olive Foster RGB: 4A5D23, MundieRGB: 434B1B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (2-8GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5.7GY3.6/4.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Foster RGB: D99058, MundieRGB: E8793E. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Orange Foster Notes: Brownish Orange. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (2-7YR) 4.6YR6.5/8.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Foster RGB: E3A857, MundieRGB: F7943C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Orange Yellow Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-8YR,8YR-1Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 8.7YR7.2/8.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Pink Foster RGB: DEA5A4, MundieRGB: EE9086. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9RP-1R,1-6R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2.8R7.2/5.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Purple Foster RGB: 86608E, MundieRGB: 7F4870. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6.6P4.5/7.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Foster RGB: 4E5180, MundieRGB: 423C63. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purplish Blue Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9PB) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7.9PB3.5/6.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Foster RGB: D597AE, MundieRGB: E28090. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purplish Pink Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9P-3RP,3-9RP) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.6RP6.8/6.7 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Foster RGB: A8516E, MundieRGB: A73853. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purplish Red Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9RP,9RP-1R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7.1RP4.5/9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Red Foster RGB: AB4E52, MundieRGB: AB343A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-7R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 3.8R4.4/9.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Foster RGB: 79443B, MundieRGB: 712F26. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Reddish Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (6-9R,9R-1YR,1- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 3YR) 9R3.4/5.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Foster RGB: CB6D51, MundieRGB: D35339. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Reddish Orange Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9R,9R-1YR,1- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2YR) 9.3R5.5/9.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Foster RGB: 915C83, MundieRGB: 8C4566. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Reddish Purple Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9P-3RP) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 0.8RP4.5/7 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Violet Foster RGB: 604E81, MundieRGB: 543964. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 1.4P3.6/7 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Yellow Foster RGB: C9AE5D, MundieRGB: D79D41. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-7Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 3.8Y7.1/6.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Yellow Foster RGB: 8A9A5B, MundieRGB: 8B8940. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (2-8GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.8GY6/5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Foster RGB: 826644, MundieRGB: 7D512D. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellowish Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (8YR-1Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9.5YR4.4/3.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Foster RGB: 679267, MundieRGB: 657F4B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellowish Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (8GY-3G) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 0.5G5.5/4.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Moderate Foster RGB: D9A6A9, MundieRGB: EE9374. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellowish Pink Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (6-9R,9R-1YR,1- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7YR) 0.7YR7.2/4.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Olive Black Foster RGB: 25241D, MundieRGB: 121910. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: Yellow Green. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (4-9Y,9Y-2GY,2-4GY) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 9Y1.1/0.9 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Olive Gray Foster RGB: 57554C, MundieRGB: 4D4234. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (4-9Y,9Y-2GY,2- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4GY) 8.1Y3.5/0.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Pale Blue Foster RGB: 91A3B0, MundieRGB: 919192. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: Syn. alice blue. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (10BG-9B,9B-5PB,5-9PB) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 0.6PB6.5/2.6 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Pale Green Foster RGB: 8DA399, MundieRGB: 8D917A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (8GY-3G,3- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9G,9G-10BG) 7.6G6.4/1.7 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Pale Greenish Foster RGB: EBE8A4, MundieRGB: FFDF84. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellow Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9Y,9Y-2GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9.5Y9/4.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Pale Orange Foster RGB: FAD6A5, MundieRGB: FFCA86. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellow Foster Notes: Yellowish Brown. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (7-8YR,8YR-1Y) 9.2YR8.7/4.4 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Pale Pink Foster RGB: EAD8D7, MundieRGB: FFCBBB. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9RP-1R,1-6R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2.0R8.7/2.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Pale Purple Foster RGB: AA98A9, MundieRGB: AE848B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P,3- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9P,9P-3RP,3-9RP,9RP-1R) 7.9P6.4/3.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Pale Purplish Foster RGB: 8C92AC, MundieRGB: 8A7F8E. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Blue Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (5-9PB) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7PB6/3.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Pale Purplish Foster RGB: E8CCD7, MundieRGB: FDBDBA. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Pink Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9P-3RP,3-9RP) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 3.7RP8.4/3.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Pale Reddish Foster RGB: AA8A9E, MundieRGB: AC7580. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purple Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9P-3RP) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 1.3RP6/4.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Pale Violet Foster RGB: 9690AB, MundieRGB: 957B8D. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 1.3P6/4 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Pale Yellow Foster RGB: F3E5AB, MundieRGB: FFDB8B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-7Y) 4.7Y9/3.8 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Pale Yellow Foster RGB: DADFB7, MundieRGB: F0D698. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Foster Notes: (not pale yellowish green. National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9Y-2GY,2-8GY) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 3.4GY8.7/2.4 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Pale Yellowish Foster RGB: ECD5C5, MundieRGB: FFC8A8. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Pink Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (6-9R,9R-1YR,1- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 8YR) 4.2YR8.6/2.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Pinkish Gray Foster RGB: C1B6B3, MundieRGB: C8A696. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: Red. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (1-9R,9R-1YR,1-7YR) 9.8R7.4/1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Pinkish White Foster RGB: EAE3E1, MundieRGB: F9DBC8. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-9R,9R-1YR,1- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7YR) 5.8R9/0.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Purplish Black Foster RGB: 242124, MundieRGB: 1B1116. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 9.54P1/0.6 Reddish Purple. National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P,3- John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 9P,9P-3RP,3-9RP,9RP-1R) 9.54P0.9/0.6 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Purplish Gray Foster RGB: 8B8589, MundieRGB: 88706B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P,3- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9P,9P-3RP,3-9RP,9RP-1R) 1RP5.5/0.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Purplish White Foster RGB: E8E3E5, MundieRGB: FADBC8. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: better. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (9PB-3P,3-9P,9P-3RP,3-9RP) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 2.5RP9/0.8 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Reddish Black Foster RGB: 282022, MundieRGB: 1E1112. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 2R1/0.9 Yellowish Pink. Munsell National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Chart Span Centroid: (1-9R,9R-1YR) 2R0.9/0.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Reddish Gray Foster RGB: 8F817F, MundieRGB: 8B6C62. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-9R,9R-1YR,1- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2YR) 7R5.4/1.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Blue Foster RGB: 0067A5, MundieRGB: 00538A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 2.9PB4.1/9.935; syn. bright blue. National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9B-5PB,5-7PB) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 2.9PB4.1/10.4 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Bluish Foster RGB: 007A74, MundieRGB: 006D5B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Foster Notes: 4.6B4.5/6.1853. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (9G-10BG) 4.6BG4.5/8.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Brown Foster RGB: 80461B, MundieRGB: 753313. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (2-8YR) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.6YR3.5/7.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Green Foster RGB: 007959, MundieRGB: 006B3C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 5.8G4.4/7.0657. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (3-9G) 5.8G4.4/8.7 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Greenish Foster RGB: 007791, MundieRGB: 00677E. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Blue Foster Notes: 4.9B4.5/6.6453. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (10BG-9B) 4.9B4.5/8.4 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Greenish Foster RGB: BEB72E, MundieRGB: CCA817. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellow Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9Y,9Y-2GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9.2Y7.2/9.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Olive Foster RGB: 404F00, MundieRGB: 0A4500. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Foster Notes: 4GY3/6.304. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (2-8GY) 4GY3/11 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Orange Foster RGB: ED872D, MundieRGB: FF6F1A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (2-7YR) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.3YR6.5/12.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Orange Foster RGB: EAA221, MundieRGB: FF8E0D. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellow Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-8YR,8YR-1Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9.1YR7.1/11.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Pink Foster RGB: EA9399, MundieRGB: FD7B7C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9RP-1R,1-4R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 1.2R6.9/8.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Purple Foster RGB: 875692, MundieRGB: 803E75. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6.5P4.3/9.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Purplish Foster RGB: 545AA7, MundieRGB: 474389. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Blue Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9PB) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 8PB4/10.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Purplish Foster RGB: E68FAC, MundieRGB: F6768E. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Pink Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9P-3RP,3-9RP) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5.6RP6.8/9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Purplish Foster RGB: B3446C, MundieRGB: B32851. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Red Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9RP,9RP-1R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7.3RP4.4/11.4 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Red Foster RGB: BC3F4A, MundieRGB: BF2233. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-7R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4R4.4/12.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Reddish Foster RGB: 882D17, MundieRGB: 7F180D. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9R-1YR,1-2YR) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 0.3YR3.1/9.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Reddish Foster RGB: D9603B, MundieRGB: FFB961. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Orange Foster Notes: #E54326 in color dictionary; see National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. #70. Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9R,9R- John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 1YR,1-2YR) 9.3R5.4/12.2 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Reddish Foster RGB: 9E4F88, MundieRGB: 9A366B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purple Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9P-3RP) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 1.3RP4.4/10.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Violet Foster RGB: 604E97, MundieRGB: 53377A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 0.2P3.7/10.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Yellow Foster RGB: D4AF37, MundieRGB: E59E1F. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-7Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 3.7Y7.2/9.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Yellow Foster RGB: 7E9F2E, MundieRGB: 7F8F18. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (2-8GY) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5.4GY6/8.7 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Yellowish Foster RGB: 996515, MundieRGB: 95500C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Brown Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-8YR,8YR-1Y) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 8.8YR4.6/8.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Yellowish Foster RGB: 44944A, MundieRGB: 478430. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (8GY-3G) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 0.4G5.4/8.7 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Strong Yellowish Foster RGB: F99379, MundieRGB: FF7A5C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Pink Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (4-9R,9R-1YR,1- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2YR) 8.4R7/9.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Dark Bluish Foster RGB: 002A29, MundieRGB: 001D18. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Green Foster Notes: 3.6BG1.2/3.033 Greenish Blue. National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9G-10BG) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 3.6BG1.2/4 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Dark Green Foster RGB: 1C352D, MundieRGB: 16251C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9G) 8G1.8/3 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Dark Foster RGB: 002E3B, MundieRGB: 022027. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Greenish Blue Foster Notes: 5B1.5/3.453 Blue. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (10BG-9B) 5B1.5/3.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Dark Foster RGB: 301934, MundieRGB: 230D21. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purple Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9P) 6.9P1/4.5 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Dark Foster RGB: 38152C, MundieRGB: 28071A. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purplish Red Foster Notes: 6.6RP1/4.8. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (3-9RP,9RP-1R) 6.6RP0.9/4.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Dark Red Foster RGB: 3F1728, MundieRGB: 320A18. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-6R) 2R1.2/4.8 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Dark Foster RGB: 341731, MundieRGB: 270A1F. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Reddish Purple Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9P-3RP) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 1.5RP1/4.8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Dark Foster RGB: 173620, MundieRGB: 132712. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellowish Green Foster Notes: Green. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (8GY-3G) 0.3G1.8/4.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Deep Foster RGB: 401A4C, MundieRGB: 320B35. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purple Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9P) 5P1.5/8 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Deep Foster RGB: 54133B, MundieRGB: 470027. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purplish Red Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9RP,9RP-1R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6.8RP1.7/8 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Deep Red Foster RGB: 5C0923, MundieRGB: 4F0014. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (1-9R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6.5R1.7/8.4 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Deep Foster RGB: 54194E, MundieRGB: 470736. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Reddish Purple Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9P-3RP) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 0.9RP1.9/8.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Deep Foster RGB: 003118, MundieRGB: 002800. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellowish Green Foster Notes: 10GY1.5/4.649. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (8GY-3G) 10GY1.5/11 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Light Blue Foster RGB: A1CAF1, MundieRGB: A6BDD7. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: Syn. baby blue. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (9B-5PB,5-7PB) 2.7PB7.9/6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Light Bluish Foster RGB: 96DED1, MundieRGB: A0D6B4. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9G-10BG) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 4.4BG8.3/4.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Light Green Foster RGB: 8ED1B2, MundieRGB: 98C793. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9G) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6.5G7.8/4.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Light Foster RGB: 9CD1DC, MundieRGB: A3C6C0. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Greenish Blue Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (10BG-9B) 4B8/4 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Light Foster RGB: D5BADB, MundieRGB: E3A9BE. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Purple Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6.5P7.8/5.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Light Foster RGB: B3BCE2, MundieRGB: BAACC7. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purplish Blue Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9PB) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7.4PB7.6/5.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Light Violet Foster RGB: DCD0FF, MundieRGB: EEBEF1. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 2P8.5/5.9. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (9PB-3P) 2P8.5/7 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Light Foster RGB: B6E5AF, MundieRGB: C6DF90. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellowish Green Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (8GY-3G) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 0.2G8.6/4.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Pale Blue Foster RGB: BCD4E6, MundieRGB: C1CACA. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: Syn. cloud blue. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (10BG-9B,9B-5PB,5-9PB) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 1.5PB8.3/3.3 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Pale Green Foster RGB: C7E6D7, MundieRGB: D8DEBA. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (8GY-3G,3-9G) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7.3G8.8/1.9 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Pale Purple Foster RGB: D6CADD, MundieRGB: E6BBC1. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P,3-9P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 5.5P8.2/3.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Pale Foster RGB: C0C8E1, MundieRGB: CBBAC5. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purplish Blue Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (5-9PB) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7PB8/3.7 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Very Pale Violet Foster RGB: C4C3DD, MundieRGB: D8B1BF. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 9.7PB7.9/3.7 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Blue Foster RGB: 00A1C2, MundieRGB: 007CAD. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: guess 5B6/8.291 0,161,194; syn. National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. ultramarine. Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9B- John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 5PB,5-7PB) 5B5/14 see #167 #170 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Bluish Foster RGB: 008882, MundieRGB: 00836E. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Foster Notes: 5BG5/6.8. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (9G-10BG) 5BG5/13 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Green Foster RGB: 008856, MundieRGB: 007D34. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 3.2G4.9/8.546. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (3-9G) 3.2G4.9/11.1 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Greenish Foster RGB: 0085A1, MundieRGB: 007BA7. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Blue Foster Notes: 5B5/7.29; #00A77B transposed, National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. but too green. Munsell Chart Span Centroid: John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription (10BG-9B) 5B5/13 see #170 #176 see #135 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted #170 Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Greenish Foster RGB: DCD300, MundieRGB: F4C800. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellow Foster Notes: 9.1Y8.2/11.3795. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (7-9Y,9Y-2GY) 9.1Y8.2/12 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Orange Foster RGB: F38400, MundieRGB: FF6800. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 4.1YR6.5/13.9295. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (2-7YR) 4.1YR6.5/15 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Orange Foster RGB: F6A600, MundieRGB: FF8E00. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Yellow Foster Notes: 8.6YR7.3/12.7364. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (7-8YR,8YR-1Y) 8.6YR7.3/15.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Pink Foster RGB: FFB5BA, MundieRGB: FF7E93. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 1R8/6.65. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (9RP-1R,1-4R) 1R8/13 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Purple Foster RGB: 9A4EAE, MundieRGB: 943391. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9P) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 6P4.5/14.0 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Purplish Foster RGB: 30267A, MundieRGB: 20155E. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Blue Foster Notes: (not very purplish blue. Munsell National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Chart Span Centroid: (7-9PB) 7.8PB2/12.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Purplish Foster RGB: CE4676, MundieRGB: D5265B. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Red Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (3-9RP,9RP-1R) National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 7.6RP4.9/13.6 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Red Foster RGB: BE0032, MundieRGB: C10020. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 5R3.9/15.3215. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (1-9R) 5R3.9/15.4 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Reddish Foster RGB: E25822, MundieRGB: F13A13. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Orange Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-9R,9R-1YR,1- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 2YR) 9.8R5.4/14.5 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Reddish Foster RGB: 870074, MundieRGB: 7E0059. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Purple Foster Notes: 1RP3/13.823. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (9P-3RP) 1RP3/14 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Violet Foster RGB: 9065CA, MundieRGB: 884BAE. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (9PB-3P) 2P5/14 National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Yellow Foster RGB: F3C300, MundieRGB: FFB300. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: 3.3Y8/11.9424. Munsell Chart National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Span Centroid: (1-7Y) 3.3Y8/14.3 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Yellow Foster RGB: 8DB600, MundieRGB: 93AA00. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Foster Notes: 5.4GY6.8/11.1473; (not vivid National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. yellowish green see #129. Munsell Chart Span John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription Centroid: (2-8GY) 5.4GY6.8/11.2 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Yellowish Foster RGB: 27A64C, MundieRGB: 379931. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Green Foster Notes: see #115. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (8GY-3G) 1.1G5.9/11.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Vivid Yellowish Foster RGB: FFB7A5, MundieRGB: FF845C. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Pink Foster Notes: 8R8/6.21. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (4-9R,9R-1YR,1-2YR) 8R8/13 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. White Foster RGB: F2F3F4, MundieRGB: FFC9D7. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: better. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (all) 2.5PB9.5/0.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Yellowish Gray Foster RGB: BFB8A5, MundieRGB: CAA885. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Foster Notes: Olive Brown. Munsell Chart Span National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. Centroid: (7-8YR,8YR-1Y,1-9Y,9Y-2GY,2-4GY) John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription 3.8Y7.4/1.4 errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted. Yellowish White Foster RGB: F0EAD6, MundieRGB: FFE2B7. Color centroids K.L. Kelly and D.B. Judd, 1976, Munsell Chart Span Centroid: (7-8YR,8YR- National Bur. Standards, Spec. Publ. 440, 189 p. 1Y,1-9Y,9Y-2GY,2-4GY) 4.5Y9.2/1.2 John Foster, Texas Precancel Club: Fix transcription errors from NBS Spec. Publ. 440; reconverted Munsell values to RGB; values outside RGB gamut adjusted.
Consolidation degree terms DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Consolidated Particulate constituents of a compound material adhere to each other SMR101703 strongly enough that the aggregate can be considered a solid material in its own right.. Consolidation Vocabulary for specifying degree of consolidatioin of an Earth SMR Vocabulary degree terms material. organization terms Consolidation not In normative descriptions, indicates that consolidation state is not a no tracking record specified determining factor in identification. assigned consolidation state No data to determine consoliation state. no tracking record unknown assigned Indurated Requires blasting or heavy equipment to loosen; Relative density 0.9- mattiSedPickList3-051603 1.0 (NADMSLTTs 2004 after Bowles, 1984). Synonomous with lithified. Rings to blow of hammer.. Loosely Easily shoveled, can be indented with fingers; Relative density 0.2-0.4 SLTTsBowles DisplayName TextDescription Tracking consolidated (NADMSLTTs 2004, after Bowles, 1984, slightly modified by SMR). Moderately Shoveled with difficulty (NADMSLTTs 2004, after Bowles, 1984). SLTTsBowles consolidated moderately Multiple blows with standard rock hammer (< 1kg) are required to mattiSedPickList3-051603; indurated break rock.. SMR050304 slightly indurated Rock can be broken with single blow from standard rock hammer (< 1 mattiSedPickList3-051603; kg mass). SMR050304 Unconsolidated Particulate constituents of a compound material do not adhere to each SMR101703 other strongly enough that the aggregate can be considered a solid in its own right.. Variable induration Material is lithified, but induration varies at scale of description. SMR Very Loosely Easily indented with fingers; Relative density 0.0-0.2 (NADMSLTTs no tracking record consolidated 2004 after Bowles, 1984). assigned Well consolidated Requires pick to loosen for shoveling; relative density 0.7-0.9 SLTTsBowles (NADMSLTTs 2004 after Bowles, 1984). well indurated Particles in the rock are strongly bound together such that rock mattiSedPickList3-051603; surface can only be broken with great difficulty using standard rock SMR050304 hammer (< 1kg mass)..
DNAG stratigraphic eras DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Top GSA DNAG time scale Unknown Used for Unknown ages GSA DNAG time scale Phanerozoic GSA DNAG time scale Cenozoic GSA DNAG time scale Quaternary GSA DNAG time scale recent (=late Holocene) GSA DNAG time scale Holocene GSA DNAG time scale late Holocene GSA DNAG time scale middle Holocene GSA DNAG time scale early Holocene GSA DNAG time scale Pleistocene (Calabrian) GSA DNAG time scale Late Pleistocene GSA DNAG time scale Middle Pleistocene GSA DNAG time scale Early Pleistocene GSA DNAG time scale Tertiary GSA DNAG time scale Neogene GSA DNAG time scale Pliocene GSA DNAG time scale Late Pliocene (Piacenzian) GSA DNAG time scale DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Early Pliocene (Zanclean) GSA DNAG time scale Miocene GSA DNAG time scale Late Miocene GSA DNAG time scale Messinian GSA DNAG time scale Tortonian GSA DNAG time scale Middle Miocene GSA DNAG time scale Serravallian GSA DNAG time scale Langhian GSA DNAG time scale Early Miocene GSA DNAG time scale Burdigalian GSA DNAG time scale Aquitanian GSA DNAG time scale Paleogene GSA DNAG time scale Oligocene GSA DNAG time scale Late Oligocene (Chattian) GSA DNAG time scale Early Oligocene (Rupelian) GSA DNAG time scale Eocene GSA DNAG time scale Late Eocene (Priabonian) GSA DNAG time scale Middle Eocene GSA DNAG time scale Bartonian GSA DNAG time scale Lutetian GSA DNAG time scale Early Eocene (Ypresian) GSA DNAG time scale Paleocene GSA DNAG time scale Late Paleocene (Selandian) GSA DNAG time scale Thanetian GSA DNAG time scale Early Paleocene (Danian) GSA DNAG time scale Mesozoic GSA DNAG time scale Cretaceous GSA DNAG time scale Late Cretaceous GSA DNAG time scale Maastrichtian GSA DNAG time scale Campanian GSA DNAG time scale Santonian GSA DNAG time scale Coniacian GSA DNAG time scale Turonian GSA DNAG time scale Cenomanian GSA DNAG time scale Early Cretaceous GSA DNAG time scale DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Albian GSA DNAG time scale Aptian GSA DNAG time scale Neocomian GSA DNAG time scale Barremian GSA DNAG time scale Hauterivian GSA DNAG time scale Valanginian GSA DNAG time scale Berriasian GSA DNAG time scale Jurassic GSA DNAG time scale Late Jurassic GSA DNAG time scale Tithonian GSA DNAG time scale Kimmeridgian GSA DNAG time scale Oxfordian GSA DNAG time scale Middle Jurassic GSA DNAG time scale Callovian GSA DNAG time scale Bathonian GSA DNAG time scale Bajocian GSA DNAG time scale Aalenian GSA DNAG time scale Early Jurassic GSA DNAG time scale Toarcian GSA DNAG time scale Pliensbachian GSA DNAG time scale Sinemurian GSA DNAG time scale Hettangian GSA DNAG time scale Triassic GSA DNAG time scale Late Triassic GSA DNAG time scale Norian GSA DNAG time scale Carnain GSA DNAG time scale Middle Triassic GSA DNAG time scale Ladinian GSA DNAG time scale Anisian GSA DNAG time scale Early Triassic GSA DNAG time scale Scythian GSA DNAG time scale Paleozoic GSA DNAG time scale Permian GSA DNAG time scale Late Permian GSA DNAG time scale Tatarian GSA DNAG time scale DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Kazanian (Ufimian) GSA DNAG time scale Early Permian GSA DNAG time scale Kungurian GSA DNAG time scale Artinskian GSA DNAG time scale Sakmarian (Asselian) GSA DNAG time scale Carboniferous GSA DNAG time scale Pennsylvanian (Late Carboniferous) GSA DNAG time scale Gzelian (Kasimovian, Stephanian) GSA DNAG time scale Moscovian GSA DNAG time scale Bashkirian GSA DNAG time scale Westphalian GSA DNAG time scale Namurian GSA DNAG time scale Mississippian (Early Carboniferous) GSA DNAG time scale Serpukhovian GSA DNAG time scale Visean GSA DNAG time scale Tournaisian GSA DNAG time scale Devonian GSA DNAG time scale Late Devonian GSA DNAG time scale Famennian GSA DNAG time scale Frasnian GSA DNAG time scale Middle Devonian GSA DNAG time scale Givetian GSA DNAG time scale Eifelian GSA DNAG time scale Early Devonian GSA DNAG time scale Emsian GSA DNAG time scale Siegenian GSA DNAG time scale Gedinnian GSA DNAG time scale Silurian GSA DNAG time scale Late Silurian GSA DNAG time scale Pridolian GSA DNAG time scale Ludlovian GSA DNAG time scale Early Silurian GSA DNAG time scale Wenlockian GSA DNAG time scale Llandoverian GSA DNAG time scale Ordovician GSA DNAG time scale DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Late Ordovician GSA DNAG time scale Ashgillian GSA DNAG time scale Caradocian GSA DNAG time scale Middle Ordovician GSA DNAG time scale Llandeilan GSA DNAG time scale Llanvirnian GSA DNAG time scale Early Ordovician GSA DNAG time scale Arenigian GSA DNAG time scale Tremadocian GSA DNAG time scale Cambrian GSA DNAG time scale Late Cambrian GSA DNAG time scale Trempealeauan GSA DNAG time scale Franconian GSA DNAG time scale Dresbachian GSA DNAG time scale Middle Cambrian GSA DNAG time scale Early Cambrian GSA DNAG time scale Precambrain GSA DNAG time scale Proterozic GSA DNAG time scale Late Proterozoic GSA DNAG time scale Middle Proterozoic GSA DNAG time scale Early Proterozoic GSA DNAG time scale Archean GSA DNAG time scale Late Archean GSA DNAG time scale Middle Archean GSA DNAG time scale Early Archean GSA DNAG time scale
Earth material composition terms Same as geologic unit composition terms, but without chemical classification terms included in that vocabulary DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Quartz-feldspar- Rock for which the sum of modal quartz+feldspar+ mica + aluminous mineral is SMR, pelitic >=70%. SLTTM1.0 Semi-pelitic Rock for which the sum of modal quartz+feldspar+ mica + aluminous mineral is SMR, >=70%, and quartz+ feldspar < 60%.. SLTTM1.0 Calcareous-semi- Rock for which the sum of modal quartz+feldspar+ mica + aluminous mineral is SMR, pelitic >=70%, and quartz+ feldspar < 60% and carbonate + calcsilicate minerals > 10%. SLTTM1.0 DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Quartzo-feldspathic Rock for which the sum of modal quartz+feldspar+ mica + aluminous mineral is SMR, >=70%, and quartz + feldspar (sensu Robertson, 1999) >60%.. SLTTM1.0 Calcareous Rock consists of 10%-50% carbonate or calcsilicate minerals, and micaceous or SMR, quartzo-feldspathic aluminous minerals form <40% of non-(carbonate or calcsilicate) minerals and quartz SLTTM1.0 forms <60% of the non-carbonate + calcsilicate minerals. Quartzose Material consists of >=75% quartz. SMR, SLTTM1.0 Calcareous- Rock consists of 10%-50% carbonate or calcsilicate minerals, and micaceous or SMR, quartzose aluminous minerals form <40% of non-(carbonate or calcsilicate) minerals, and SLTTM1.0 quartz forms >=75% of the non-(carbonate + calcsilicate) minerals. Pelitic Rock for which the sum of modal quartz+feldspar+ mica + aluminous mineral is SMR, >=70%, and aluminous mineral + mica content is >=40%.. SLTTM1.0 Calcareous-pelitic Rock consists of 10%-50% carbonate or calcsilicate minerals, and micaceous or SMR, aluminous minerals form >=40% of non-(carbonate or calcsilicate) minerals. SLTTM1.0 Greisen Hydrothermal rock consisting of >70% quartz + muscovite or lepodilite, with SMR, accessory (>1%) topaz or tourmaline (or other flourine-bearing phase). In a hierarchy SLTTM1.0 based purely on description, would be a kind of semi-pelitic rock (10-40% aluminous minerals; <60% quartz+feldspar) or quartz-feldspathic (<40% aluminous and >60% quartz + feldspar). Mono mineralic Rock that consists of >75% of a single mineral species. SMR, SLTTM1.0 Serpentinite material consists of >75% serpentine. SMR, composition SLTTM1.0 Ferromagnesian Rock with >40% dark ferromagnesian minerals. Standard term defined by Bates and SMR, Jackson (1987) to mean 'containing iron and magnesium'. SLTTM1.0 Eclogite Composition term for material that consists of >75% garnet (almandine-pyrope) and SMR, composition sodic pyroxene (omphacite). SLTTM1.0 Ultramafic Material consists of >90% ferromagnesian minerals.. SMR, SLTTM1.0 Mafic Rock consists of >=40% and <90% ferromagnesian minerals. SMR, SLTTM1.0 Amphibolite Rock consisting of >=40% dark-colored amphibole, in which more than half of the SMR, non-amphibole mineral is plagioclase, and quartz < 5%. SLTTM1.0 Impure calcsilicate Rock consists of >50% calcsilicate or carbonate minerals and relative proportion of SMR, or carbonate calcsilicate and carbonate minerals is unknown or not specified. SLTTM1.0 Calcsilicate Composition term that denotes a rock that consists of >=50% calcsilicate or SMR, carbonate minerals and carbonate minerals <= calcsilicate minerals in mineral mode. SLTTM1.0 Epidositic Rock consisting of >75% epidote, and >50% of non-epidote mineral is quartz. SMR, SLTTM1.0 Metacarbonate Rock consists of >50% calcsilicate or carbonate minerals and carbonate minerals > SMR, calcsilicate minerals in mineral mode. Meta prefix is to distinguish usage with SLTTM1.0 metamorphic as opposed to sedimentary rock.. Marble Rock in which carbonate minerals form > 75% of rock. SMR, SLTTM1.0 Dolomite marble Carbonate minerals form > 75% of rock, and dolomite forms >75% of carbonate SMR, minerals.. SLTTM1.0 Calcite marble Carbonate minerals form > 75% of rock, and calcite forms >75% of carbonate SMR, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking minerals.. SLTTM1.0 Special Mineral composition that doesn't fit in any other defined composition class. A modal SMR, composition mineral description is essential. Material consists of <40% ferromagnesian minerals SLTTM1.0 and <50% carbonate + calcsilicate minerals and <70% Q+Fs + mica + aluminous minerals.
Earth material or geologic unit genesis. Example vocabularies are the same here DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Genesis Genetic history of rock can not be determined. Generally SMR060104 indeterminant indicates rock is too fine-grained and out of context to be able to infer igneous, sedimentary, or composite origin. Genesis unknown or Null value for genesis. Use in normative descriptions to indicate SMR060104 not specified any value is allowed; in occurrence descriptions indicates that there are insufficient data to specify genesis.. Anthropogenic Genesis that includes at least one event that requires human SMR060104 genesis participation. Composite process Earth materials formed in a single event (thus not Composite SMR060104 genesis event genesis) that involves some combination of igneous, sedimentary, cataclastic, metamorphic, or shock-related processes that better represents the origin of the material than classification into one of those genetic classes. Volcaniclastic Genesis by combination of extrusive igneous activity and SMR060104 genesis sedimentary transport and deposition.. Sedimentary genesis Genesis that includes deposition or precipitation of material at SLTTS_1.00_072904 the Earth’s surface. Includes nonbiogenic sedimentary genesis and biogenic sedimentary genesis. Igneous genesis Genesis with 'crystallization from magma' as a genetic event in SMR_synchronizeWith_NADM- the genesis sequence. C1 Extrusive igneous Formation by crystallization of magma on the surface of the SMR_synchronizeWith_NADM- genesis Earth.. C1 Subaerial Extrusive genesis by extrusive igneous activity on land. SMR060104 Genesis Subaqueous Genesis by extrusive igneous activity beneath water. SMR060104 Extrusive Genesis Intrusive igneous Formation of rock by crystallization of magma within the earth.. SMR_synchronizeWith_NADM- genesis C1 Composite event SMR_synchronizeWith_NADM- genesis C1 Metamorphic SMR060104 genesis Metasomatic or Rock was formed by solid-state mineralogical and chemical SMR060404, Based on hydrothermal changes in response to hot, mineral-rich waters. SLTTM1.0 genesis Metasedimentary Denotes that rock has original rock formation by sedimentary SMR060104 genesis genesis, followed by metamorphism. DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Metaigneous Denotes that rock originated by igneous genesis, and was then SMR060104 genesis metamorphosed. Metavolcanic Denotes that rock originated by volcanic genesis, and was then SMR060104 genesis metarmorphosed. Metaplutonic Denotes that rock originated by plutonic igneous genesis, and SMR060104 genesis was then metamorphosed. Metamorphic melting Genesis by melting through high-temperature contact SMR, SLTTM1.0 genesis metamorphism or friction-related heat generation.. Cataclastic genesis Genesis dominated by brittle deformation that occurred after the SMR060404, Based on formation of the protolith. Cataclastic rocks are commonly SLTTM1.0 associated with faults. Shock metamorphic Genesis that includes shock metamorphism, usually associated SMR060104 genesis with impact by an extraterrestrial object.
Earth material fabric terms DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Clast A depositional fabric in which the sand- and gravel-size particles MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 supported touch at point contacts and form a supporting framework, with any fabric fine matrix merely occupying the interstices between the coarser grains. Imbricated Fabric defined by long axis of tabular clasts stacked like shingles to SMR092603 Clast fabric define a surface that makes a small angle with the bedding surface. Matrix A depositional fabric in which finer-grained clastic particles support MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 supported the sediment mass while coarser-grained particles-float in the matrix fabric with minimal point contacts between them. The result is a distinctive bimodal or multi-modal grain-size distribution. Depositional mattiSedPickList3-051603 fabric not preserved Obliterated by (DELETE? structure would be bioturbated). mattiSedPickList3-051603 bioturbation Obliterated by mattiSedPickList3-051603 recrystallization Obliterated by mattiSedPickList3-051603 grain overgrowths massive The depositional fabric of a sedimentation unit is structureless-i.e., mattiSedPickList3-051603 sedimentary the fabric lacks any form of geometry or particle organization such as fabric lamination, cross lamination, and size grading. Massive does not refer to the character or thickness of bedding. granoblastic Fabric characterized by mosaic of equidimensional, anhedral grains; SMR, base on Best, 1982 fabric inequant grains, if present, are randomly oriented; grain boundaries apporach bubble-like configuration (crystalloblastic), with dihedral angles between faces commonly near 120 degrees. Poikiliblastic Metamorphic fabric in which large crystals of one phase contain based on Bates & Jackson, texture numerous small crystals of other phases. [NGMDB note: This is a 1997 fabric because it is defined based on the relationships between particles.]. DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Foliation A penetrative planar fabric in a rock.. SMR Foliation Foliation in a metamorphic rock with a granoblastic texture. Fabric SMR crystalloblastic elements may be layering or aligned tabular crystals or crystal aggregates.. Schistosity Planar foliation defined by aligned planar or tabular mineral grains, in SMR which the shape of the grains is related to the crystal habit of the mineral, not deformation of grain shape.. laminated Foliation defined by compositional segregation, in which the layers SMR differentiated are less than 1 cm thick.. foliation Foliation Layering defined by mineralogical variations in a rock body, SMR compositional commonly associated with layers that have sharp boundaries. Also layering known as gneissic foliation. Foliation Layering defined by mineralogical variations in a rock body, SMR compositional commonly associated with layers that have sharp boundaries. Origin layering of compositional variations interpreted to be result of solid-state mineral reactions in rock body (metamorphic segregation).. segregation Foliation vague Compositional layering and of uncertain origin.. formed by subtle SMR_DI25DatabaseDevelop compositional mineralogical or textural variations, with gradational layer boundaries ment layering Foliation Layering defined by mineralogical variations in a rock body, SMR compositional commonly associated with layers that have sharp boundaries. layering Compositional variations are result of melt segregation during high- migmatitic grade metamorphism; some layers have magmatic/igneous mineralogy. Foliation Layering defined by mineralogical variations in a rock body, SMR compositional commonly associated with layers that have sharp boundaries. layering Layering is relict of compositional variations in protolith, typically inherited from heterogeneous sedimentary or volcanic rock.. protolith Foliation Vague layering defined by subtle compositional and textural SMR nebulitic variations. The descriptor nebulitic is from migmatite terminology, and the term fabric is associated with high-grade metamorphic rocks intermediate between igneous and metamorphic. Distinction from textural and compositional layering varieties is not clearly defined .. Mylonitic Generic mylonitic shape fabric; defined by shape of deformed SMR foliation mineral grains or aggregates of mineral grains; greater than 10% generic TRIG matrix. Mylonitic Ultramylonitic foliation; greater than 90% of rock is matrix due to SMR foliation tectonic grain size reduction processes. ultramylonite Mylonitic Protomylonitic foliation; 10-50% of rock is matrix due to tectonic grain SMR foliation size reduction processes. protomylonite Mylonitic Foliation defined by shape of deformed, originally equant grains, in SMR foliation weak which aspect ratio of deformed grains is generally less than 3 to 1 grain shape (longest to shortest axis). fabric Mylonitic Foliation defined by aligned tectonically flattened mineral grains, and SMRDI21DataSetSetup foliation well planar or tabular grains rotated to parallel foliation, as well as developed s cleavage along slip or shear surfaces. Intermediate fabric in mylonite DisplayName TextDescription Tracking tectonite series.. foliation Mylonitic Mylonitic foliation; 50-90% of rock is matrix due to tectonic grain size SMR foliation reduction processes. mylonite weak shape Planar foliation defined by aligned mineral grains, in cases where SMR fabric less than 50% of rock consists of mineral grains defining the foliation. Shape of mineral grains due to crystal habit, deformation, some combination of these or not specified.. Weak Planar foliation defined by aligned mineral grains whose crystal habit SMR_DI25DatabaseDevelop schistosity imparts the tabular shape defining the foliation, in cases where less ment than 50% of rock consists of mineral grains defining the foliation.. Cleavage A planar tectonic foliation in a rock characterized by a tendency for SMR the rock to break parallel to the foliation.. Cleavage slaty Continuous planar foliation defined by aligned fine to very-fine SMR grained phylosilicate mineral grains. Grades into schistosity as grain size increases. [synonomous with fissility]. Cleavage Superclass for a cleavage that is overprinted on an older foliation. SMRDataBaseDevelopment generic crenulation Cleavage A crenulation cleavage in which the cleavage domains have discrete SMRDataBaseDevelopment spaced boundaries. crenulation Cleavage Cleavage defined by long, thin limbs of crenulation folds of pre- SMR continuous existing foliation, in which the boundaries between cleavage domains crenulation and lithons are gradational. Both the crenulation foliation and the crenulated foliation are easily visible. Grades to spaced crenulation cleavage as boundaries of cleavage domains become sharp, and transposed foliations as crenulation foliation obscures the crenulated foliation.. Cleavage close Spaced cleavage in sandstone or phyllosilicate-poor rock, defined by SMR disjunct partings of uncertain origin, and does not crenulate an existing cleavage. (sometimes called 'fracture cleavage'). Cleavage domains have no apparent thickness, and are spaced less than 5 cm on average. Domainal if cleavage is clearly developed in some parts of outcrop but not in others.. Cleavage Cleavage typically in phyllosilicate-poor rock, in which the cleavage SMR spaced disjunct domains have no apparent thickness, and are spaced between 5 cm close joints and 25 cm, and do not crenulate an older foliation. Cleavage domains are regularly spaced, and penetrative on a 1-10 m scale.. Foliation A planar tectonic foliation defined by fabric elements that indicate SMR generic more than one origin for the foliation.. composite Composite Layering interpreted to have originated as sedimentary bedding that SMR foliation has been transposed as a result of metamorphism and deformation; layering sedimentary top direction indicators are present. transposed bedding w tops Composite Mylonite with continuous compositional layering greater than 5 mm OverhaulClassificationConce foliation thick. Continuous means individual layers can be traced more than 1 pts071300 gneissic m. mylonitic DisplayName TextDescription Tracking foliation Composite Composite fabric in which a cleavage is developed parallel to SMR foliation bedding. generic cleavage parallel to bedding Composite Layering interpreted to have originated as sedimentary bedding that SMR foliation has been transposed as a result of metamorphism and deformation. layering transposed bedding Joints Parting surfaces in rock that occur in crudely parallel orientation, SMR spaced >25 cm on average if in a very regular joint set. Spacing is more variable and alignment of surfaces is cruder that cleavage.. Lineation Lineation defined by small-scale wrinkles, typically of phylosillicate SMRCartoRepresentationCle crenulation minerals, on another surface, typically a cleavage or schistosity. Use anupForDI8 instead of intersection lineation if the wrinkles are the measured feature and the intersecting planar feature is not apparent. Lineation, Fabric defined by aligned elongate (prolate) fabric elements for which SMR shape, generic the alignment is due to tectonic processes (i.e. post depositional for tectonic sedimentary rocks, post crystallization for igneous rocks, or any lineation related to metamorphism). lineation Lineation defined by elongate (prolate) fabric elements in which the SMR stretch shape alignment of the fabric elements, and the formation of prolate fabric mylonitic elements, is due to crystal plastic deformation processes. lineation Mylonitic lineation for which the sense of shear relative to the SMRDI21DataSetSetup mylonitic containing foliation is known. stretch shape directed Mineral Lineation defined by aligned elongate crystals of one or more SMR lineation minerals with a prismatic crystal habit. lineation Mineral lineation defined by aligned hornblende crystals. SMR mineral hornblende lineation Mineral lineation defined by aligned elongate biotite aggregates in a SMR mineral biotite foliation surface. Biotite does not have an elongate (prismatic, acicular) mineral habit, so production of lineation must reflect elongate aggregates of biotite crystals.. lineation Mineral lineation defined by aligned sillimanite crystals.. SMR mineral sillimanite Lineation Lineation defined by the intersection of bedding surfaces and SMR intersection cleavage surfaces. bedding cleavage lineation Lineation defined by the intersection of two tectonic foliations. SMR intersection Sn Sn+1 intersertal Interstices between plagioclase crystals forming framework of an SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert1 texture igneous rock are filled with glass, cryptocrystalline material, or non- 954 granular deuteric or secondary minerals, such as serpentine, DisplayName TextDescription Tracking nontronite, chlorite, calcite, zeolite or sodalite.. poikilitic Grains of various minerals in random orientation are completely SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert1 enclosed within large optically consitnuous crystals of different 954 composition.Enclosing crystal is typically anhedral.. graphic texture Quartz is intergrown with alkali feldspar, quartz commonly cuneiform, SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert1 on background of feldspar. A type of poikilitic texture larger crystals 954BatesJackson1987 have a fairly regular geometric outline and orientation. Quartz commonly occupies tirangular areas. Intergrowth may involve other minerals. Ophitic texture Lathes of plagioclase in a matrix of coarse subhedral pyroxene such SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert1 that the feldspar laths appear to be largelo or entirely cnclosed in 954 pyroxene. Length of plagioclase laths is less than diameter of pyroxene grains.. Diktytaxitic Abundant, closely spaced, minute, angular cavities between laths of SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert1 texture feldspar of random orientation; cavities bear no definitie relation th 954 ethe arrangement of enclosing feldspar. Feldspar bordering cavities are of same size and composition as in the areas between the cavities. Felted texture Holocrystalline matrix of rock consists of tightly appressed microlite SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert1 generally of feldspar.. 954 Trachytic Felted texture in which microlite is disposed in a sub-parallel, aligned SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert1 texture manner, and interstices are occupied by mirco or crypto-crystalline 954 material. Myrmekitic Minute worm-like or finger like bodies of quartz enclosed in sodic SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert1 texture plagioclase. 954 Subophitic Laths of plagioclase in a matrix of coarse subhedral pyroxene such SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert1 texture that the feldspar laths appear to be largely enclosed in pyroxene. 954 Length of plagioclase laths is greater than diameter of pyroxene grains.. intergranular Framework of feldspar crystals contains ferromagnesian mineral SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert1 texture grains in angular interstices between crystals. 954 hyaloophitic Lathes of plagioclase in a matrix of glass such that the feldspar laths no tracking record assigned texture appear to be largely or entirely enclosed in glass. Igneous sieve Large spongy crystals formed by crystallization from magma that SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert1 texture contain abundant inclusions. 954 Bostonitic Irregular interlocking laths of alkali feldspar arranged in crudely SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert1 texture divertent groups. 954
Fault movement sense terms DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Normal slip no tracking record assigned Reverse slip no tracking record assigned Left slip no tracking record assigned Right slip no tracking record assigned Left normal oblique slip no tracking record assigned Right normal oblique slip no tracking record assigned DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Left reverse oblique slip no tracking record assigned Right reverse oblique slip no tracking record assigned
Fault movement types DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Strike slip no tracking record assigned Oblique slip no tracking record assigned Dip slip no tracking record assigned Thrust no tracking record assigned Low-angle normal no tracking record assigned
Frequency qualifier terms DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Always Denotes a relationship where the subject is Always present. jac 3-23 Common Denotes a relationship that is commonly present. jac Never Denotes a relationship where the subject never occurs. jac 3-23 Sometimes Denotes a relationship where the subject is sometimes present. jac 3-23 Rare Denotes a relationship where the subject is rarely present. jac 3-23
Genetic boundary types DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Contact depositional Contact at which a sedimentary or volcanic rock has been SMR deposited on another rock body; timing relationship across the contact known. angular unconformity Contact between stratified rocks across which the orientation of SMR050404 contact bedding is discordant. Denotes period of tilting of strata and erosion before deposition of the younger stratigraphic unit. Nonconformable Contact between sedimentary rocks at which some time interval SMR011905SBWashImport contact separates rocks above and below the contact. channelized contact Contact between geologic units at which the older unit has SLTT_SMR undergone some erosion to produce channels cut into the surface outcrop of the unit before deposition of the younger geologic unit, which must be a sedimentary rock.. Paraconformable no tracking record assigned contact conformable Depositional contact across which there is no evidence of elapsed SLTT_SMR depositional contact geologic time.. Contact, not classified Contact between rock bodies that is not a fault.. SMR DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Contact, nature Contact between rock bodies, the nature of which is ambiguous SMR ambiguous based on field observation or available data.. Contact, gradational Gradational contact; use for depositional or alteration contacts SMR between a unit X and a unit Y, or which the thickness of the boundary zone between rock that is clearly X and rock that is clearly Y is greater than 3m.. gradational contact, Gradational contact between brecciated and non-brecciated SMR brecciation zones rocks. sedimentary facies Gradational contact between different facies in sedimentary SMR transition rocks; boundaries are commonly zones of interbedding with progressively more of one or the other facies.. gradational contact Gradational contact between igneous rocks; typically between SMR between igneous rocks phases within a pluton.. gradational contact, Gradational contact in metamorphic rocks between rocks of SMR metamorphic facies different metamorphic facies. gradational contact, Gradational contact between rocks displaying different styles of SMRDI21DataSetSetup alteration zones alteration. Contact, intrusive Contact at which an igneous rock has intruded an older rock SMR body. Contact, hypothetical Contact existence hypothesized based on some insufficient SMR information, but not field checked. Intraformational Mappable contacts within a formation, such as flow boundaries; SMR contact not a marker bed..
Geologic unit composition terms DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Igneous rock Terms specifying chemical character of SMRNGMDBScienceLanguageOrganization0503 chemical terms igneous rocks based on whole rock chemistry. Alkalic Chemical modifier that indicates that the total SMR_NGMDB;FromJohnsonLithClass6Definitions of alkali oxides (Na20+K20) exceeds that of Ca0 at a silica content less than 51% (undersaturated). Subaluminous Aluminum oxide within 10 percent of sum of SMR_NGMDB;FromJohnsonLithClass6Definitions Na and K oxide. Peraluminous Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) greater than sum of SMR_NGMDB;FromJohnsonLithClass6Definitions Na, K and Ca oxide. Peralkaline Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) is less than sum of K SMR_NGMDB;FromJohnsonLithClass6Definitions and Na oxide. Metaluminous Chemical composition term used for igneous SMR_NGMDB;FromJohnsonLithClass6Definitions rocks, denoting that content of aluminum oxide is greater than sodium oxide plus potassium oxide, but aluminum oxide less than sum of Na, K and Ca oxide. Metamorphic rock Terms for classifying general chemical SMRNGMDBScienceLanguageOrganization0503 mineralogical character of metamorphic rocks based on composition terms mineralogical characteristics; based on NADM DisplayName TextDescription Tracking SLTT metamorphic rocks. Quartz-feldspar- Rock for which the sum of modal SMR, SLTTM1.0 pelitic quartz+feldspar+ mica + aluminous mineral is >=70%. Semi-pelitic Rock for which the sum of modal SMR, SLTTM1.0 quartz+feldspar+ mica + aluminous mineral is >=70%, and quartz+ feldspar < 60%.. Calcareous-semi- Rock for which the sum of modal SMR, SLTTM1.0 pelitic quartz+feldspar+ mica + aluminous mineral is >=70%, and quartz+ feldspar < 60% and carbonate + calcsilicate minerals > 10%. Quartzo-feldspathic Rock for which the sum of modal SMR, SLTTM1.0 quartz+feldspar+ mica + aluminous mineral is >=70%, and quartz + feldspar (sensu Robertson, 1999) >60%.. Calcareous Rock consists of 10%-50% carbonate or SMR, SLTTM1.0 quartzo-feldspathic calcsilicate minerals, and micaceous or aluminous minerals form <40% of non- (carbonate or calcsilicate) minerals and quartz forms <60% of the non-carbonate + calcsilicate minerals. Quartzose Material consists of >=75% quartz. SMR, SLTTM1.0 Calcareous- Rock consists of 10%-50% carbonate or SMR, SLTTM1.0 quartzose calcsilicate minerals, and micaceous or aluminous minerals form <40% of non- (carbonate or calcsilicate) minerals, and quartz forms >=75% of the non-(carbonate + calcsilicate) minerals. Pelitic Rock for which the sum of modal SMR, SLTTM1.0 quartz+feldspar+ mica + aluminous mineral is >=70%, and aluminous mineral + mica content is >=40%.. Calcareous-pelitic Rock consists of 10%-50% carbonate or SMR, SLTTM1.0 calcsilicate minerals, and micaceous or aluminous minerals form >=40% of non- (carbonate or calcsilicate) minerals. Greisen Hydrothermal rock consisting of >70% quartz + SMR, SLTTM1.0 muscovite or lepodilite, with accessory (>1%) topaz or tourmaline (or other flourine-bearing phase). In a hierarchy based purely on description, would be a kind of semi-pelitic rock (10-40% aluminous minerals; <60% quartz+feldspar) or quartz-feldspathic (<40% aluminous and >60% quartz + feldspar). Mono mineralic Rock that consists of >75% of a single mineral SMR, SLTTM1.0 species. Serpentinite material consists of >75% serpentine. SMR, SLTTM1.0 composition Ferromagnesian Rock with >40% dark ferromagnesian SMR, SLTTM1.0 DisplayName TextDescription Tracking minerals. Standard term defined by Bates and Jackson (1987) to mean 'containing iron and magnesium'. Eclogite Composition term for material that consists of SMR, SLTTM1.0 composition >75% garnet (almandine-pyrope) and sodic pyroxene (omphacite). Ultramafic Material consists of >90% ferromagnesian SMR, SLTTM1.0 minerals.. Mafic Rock consists of >=40% and <90% SMR, SLTTM1.0 ferromagnesian minerals. Amphibolite Rock consisting of >=40% dark-colored SMR, SLTTM1.0 amphibole, in which more than half of the non- amphibole mineral is plagioclase, and quartz < 5%. Impure calcsilicate Rock consists of >50% calcsilicate or SMR, SLTTM1.0 or carbonate carbonate minerals and relative proportion of calcsilicate and carbonate minerals is unknown or not specified. Calcsilicate Composition term that denotes a rock that SMR, SLTTM1.0 consists of >=50% calcsilicate or carbonate minerals and carbonate minerals <= calcsilicate minerals in mineral mode. Epidositic Rock consisting of >75% epidote, and >50% of SMR, SLTTM1.0 non-epidote mineral is quartz. Metacarbonate Rock consists of >50% calcsilicate or SMR, SLTTM1.0 carbonate minerals and carbonate minerals > calcsilicate minerals in mineral mode. Meta prefix is to distinguish usage with metamorphic as opposed to sedimentary rock.. Marble Rock in which carbonate minerals form > 75% SMR, SLTTM1.0 of rock. Dolomite marble Carbonate minerals form > 75% of rock, and SMR, SLTTM1.0 dolomite forms >75% of carbonate minerals.. Calcite marble Carbonate minerals form > 75% of rock, and SMR, SLTTM1.0 calcite forms >75% of carbonate minerals.. Special Mineral composition that doesn't fit in any other SMR, SLTTM1.0 composition defined composition class. A modal mineral description is essential. Material consists of <40% ferromagnesian minerals and <50% carbonate + calcsilicate minerals and <70% Q+Fs + mica + aluminous minerals. Composition not Composition not specified. SMR specified Silicic Qualitative composition term for apparently SMR, SLTTM1.0 siliceous aphanitic rocks; should be considered to mean "appears to consist largely of quartz and feldspar". Does not denote igneous origin (contrast with Bates and Jackson, 1987). Calcareous Qualitiative composition term, means that rock SMR, SLTTM1.0 DisplayName TextDescription Tracking reacts to form bubbles when hydrochloric acid is applied. Argillic Chemical composition term for apparently clay- SMR, SLTTM1.0 rich aphanitic material. Ferruginous Indicates a material that contains between 10 SMR, from MattiSLTTSed050604 and 49 percent iron minerals (hematite, magnetite, siderite...). From sedimentary science language composition modifiers.
Geologic unit morphology terms DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Metamorphic rock Terminology for describing geometry (shape) of metamorphic rock bodies. no tracking record body form terms assigned layer Sedimentary body geometry characterized by generally thin character SMR051604 relative to the lateral extent of the body (on order of 1:100). Thin bodys of lesser extent are likely to be thought of as lenses. A dike is a layer-like body of igneous rock tthat cuts across leayering/or foliation in country rock. Rock body Rock body geometry is irregular and can not be characterized using SMR060104 geometry irregular terminology. Rock body Rock body geometry is not specified. SMR 072204 geometry not specified Igneous rock body Terminology for describing geometry (shape) of igneous rock bodies. no tracking record form terms assigned Intrusive rock body no tracking record form terms assigned laccolith form no tracking record assigned Stock form no tracking record assigned Sill form no tracking record assigned Dike form no tracking record assigned Extrusive body Overlap with geomorphic terms must be avoided. Use extrusive body form no tracking record form terms terms for bodies of volcanic rock that are preserved in the rock record, such assigned that their original geomorphic expression has been buried.. Cone no tracking record assigned Ejecta blanket no tracking record assigned Dome b. Comment: no tracking record assigned Body Morphology No description of body form. no tracking record not described assigned DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Sedimentary Body Terminology for describing geometry (shape) of sedimentary rock bodies. no tracking record Geometry Terms assigned Blanket Thin, laterally extensive rock body. no tracking record assigned Ribbon Body of sedimentary rock that is ribbon like, that is stratigraphically thin, long no tracking record in one horizontal direction, and narrow in a perpendicular direction.. assigned Channel Lens with convex downward lower surface, near planar upper surface. mattiSedPickList3- 051603 Prism Body of sedimentary rock that is long in one dimension, and thins rapidly in a no tracking record perpendicular direction. assigned Mound Lense like body of rock, lateral extent less than 100m, generally flat at no tracking record bottom, with stratigraphic pinch out of beds along upper sides. assigned Lense Lens-like body of of rock, lateral extent greater than 100m. no tracking record assigned
Geologic unit outcrop character terms DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Surface Terms for specifying the degree of development of desert MattiSLTTSed050604 pavement terms pavement, a " stony surface generally composed of a layer of angular or subrounded gravels one or two stones thick sitting on a mantle of finer stone-free material" (Dixon, 1994b, p. 74).. Strong pavement Clast concentrations consist of interlocking mosaic, yielding MattiSLTTSed050604 a pavemented surface that resists all but the strongest efforts to disrupt it; underlying Av horizon well developed. very slight Incipient clast concentration relative to un-pavemented MattiSLTTSed050604 pavement surfaces; no interlocking of clasts. moderate Clast concentrations consist of weakly interlocking mosaics, MattiSLTTSed050604 pavement yielding a surface that can be disrupted easily by a pick but resists disruption by hand; underlying Av horizon moderately developed. no pavement No concentration of surface clasts. MattiSLTTSed050604 slight pavement Clast concentrations show incipient interlocking; easily MattiSLTTSed050604 disrupted by hand; underlying Av horizon weakly developed. Soil stage The degree (intensity) of soil-profile development for a MattiSLTTSed050604 classification given soil, usually in comparison with the development of another soil. Birkeland refers to this as "ranking on a relative scale, based on the properties of a sequence of soils in the area". Definition (from Birkeland, 1999, p. 19-20, adapted from Retallack, 1993). pedogenesis Some soil profile developement can be recognized and mattiSedPickList3-051603 developed described. Silicic soils Soil that contains pedogenic silica. mattiSedPickList3-051603 duripan A subsurface soil horizon that is cemented by illuvial silica, mattiSedPickList3-051603 usually opal or microcrystalline forms of silica, to the degree DisplayName TextDescription Tracking that less than 50 percent of the volume of air-dry fragments will slake in water or HCl Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. 196). carbonate- Soil stage index for carbonate-bearing soils in arid and SLTTsGilesMachette bearing soil stage semiarid climatic regimes, Giles and others (1966, 1981; classification extended by Machette, 1985). Stage III+ In gravelly parent material most clasts have thick carbonate no tracking record assigned carbonate coats; matrix particles continuously coated with carbonate or pores plugged by carbonate; cementation more or less continuous; >40% CaCO3. In fine-grained parent material most grains are coated with carbonate; most pores plugged; >40% CaCO3.. Stage I In gravelly parent material clast coatings are thin and no tracking record assigned carbonate discontinuous; some filaments; matrix can be calcareous next to stones; about 4% CaCo3. In fine-grained material a few filaments or coatings on sand grains are observed; <4% CaCo3. Stage V Laminar layer and platy structure are strongly expressed; no tracking record assigned carbonate incipient brecciation and pisolith formation (thin, multiple layers of carbonate surrounding particles). Stage IV Upper part of K horizon is nearly pure cemented carbonate no tracking record assigned carbonate (75-90% CaCO3) and has a weak platy structure due to the weakly expressed laminar depositional layers of carbonate; the rest of the horizon is plugged with carbonate (50-75% CaCO3). Stage VI Brecciation and re-cementation of pedogenic carbonate no tracking record assigned carbonate material with laminar layer and platy structure, as well as pisoliths (thin, multiple layers of carbonate surrounding particles), are common. Stage III In gravelly parent material, the soil horizon has 50-90% K no tracking record assigned carbonate fabric with carbonate forming an essentially continuous medium; color mostly white; carbonate-rich layers more common in upper part; about 20-25% CaCO3. In fine- grained material many nodules are present, and carbonate coats so many grains that over 90% of horizon is white; carbonate-rich layers more common in upper part; about 20% CaCO3. Stage I+ In gravelly parent material many or all clast coatings are no tracking record assigned carbonate thin and continuous. In fine-grained material carbonate filaments are common.. Stage II+ In gravelly parent material, same as stage II, except no tracking record assigned carbonate carbonate in matrix is more pervasive, In fine-grained material nodules are common; 50-90% of matrix is whitened; about 15% CaCO3 in whole sample.. Stage II In gravelly parent material clast coatings are continuous; no tracking record assigned carbonate local cementation of few to several clasts; matrix is loose and calcareous enough to give somewhat whitened appearance. In fine-grained material contains few to common nodules; matrix between nodules is slightly whitened by carbonate (15—50% by area), and the latter DisplayName TextDescription Tracking occurs in veinlets and as filaments; some matrix can be non-calcareous; about 10-15% CaCO3 in whole sample, 15-75% in nodules. Non carbonate Classification of soil development from Giles et al., 1981 SLTTsGilesMachette soil stage and Machette,1985. classificaton very weakly Soil has an A horizon with or without a Cox horizon. MattiSLTTSed050604 developed soil profile moderately Soil has an A/Bt/Cox, A/E, Bs/Cox, or A/Bt/Bk/Cox horizon SLTTsGilesMachette developed soil sequence. The Bt, E, Bs, and Bk horizons meet the criteria profile for argillic, albic, spodic, and calcic horizons. Carbonate accumulations would display stage II morphology (of Giles and others, 1981 and Machette, 1985). weakly Soil has an A/Bw/Cox and/or Bk horizon. Accumulation of MattiSLTTSed050604 developed soil pedogenic constituents is not sufficient to qualify the profile horizons as argillic, spodic, or calcic. If carbonate horizons are present, morphology is probably stage I (of Giles and others, 1981 and Machette, 1985). Strongly Profile similar to moderately developed profile, with the SLTTsGilesMachette developed soil following exceptions: the B horizon in the strongly profile developed profile is generally thicker and redder, contains more clay, and has a more strongly developed structure; if carbonates are present, they would form a K horizon (stage III and higher morphology of Giles and others, 1981 and Machette, 1985). no pedogenic Soil profile never developed on surface of deposit. mattiSedPickList3-051603 development Surface soil Surface soil has been removed by erosion; relict pedogenic mattiSedPickList3-051603 stripped away carbonate may be present.. Surface The degree to which the upper surface of unconsolidated MattiSLTTSed050604 dissection terms sedimentary material has been degraded and incised by erosion after the unit has been abandoned by the geologic processes that formed it. moderately Upper surface is degraded by gullying, but between 2/3 and MattiSLTTSed050604 dissected 1/3 of the original genetic surface area remains. very slightly Upper surface is degraded by gullying, but >90% of the MattiSLTTSed050604 dissected original genetic surface area remains. highly dissected Upper surface is so degraded by gullying that <1/3 of the MattiSLTTSed050604 original genetic surface area remains. extremely Upper surface is so degraded by gullying that no evidence MattiSLTTSed050604 dissected of the original genetic surface morphology and texture remains. This is the ridge-and-ravine condition of Bull (1991). slightly dissected Upper surface is degraded by gullying, but more than 2/3 of MattiSLTTSed050604 the original genetic surface area remains. no dissection Original depositional/genetic surface of unit is preserved.. SMR, based on MattiSLTTSed050604 undissected Upper surface is not degraded by gullying. MattiSLTTSed050604 DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Outcrop Surface Typical character of rock outcrop considered on a OverhaulClassificationConcepts071300 Character decimeter to meter scale, generally having to do with the shape of the rock outcrop.. ledge forming Outcrops with vertical faces less than or equal to 5 m high. SMR rib forming Forms bold outcrops that do not follow slope contours (iso SMR elevation lines). alternating ledge Outcrops alternate between slopes and vertical faces less SMR and slope than 5 m high. forming cliff forming Tends to form outcrops with near vertical faces greater than SMR 5 m high.. slope forming Forms extensive subdued slopes between wide-spaced SMR prominent outcrops or between other geologic-map units. blocky Forms angular, block-like outcrops.. SMR massive blocky Forms blocky outcrops with rock faces > 10 m high... SMR bouldery hills Outcrops tend to be bouldery hills, with some exposed rock SMR 081303 faces; typical of many granites in the desert. Boulders greated than 1 m in diameter are common on surface.. Massive rounded Forms rounded, bouldery outcrops, with exposed rock SMR outcrop surfaces greater than 10 m high.. recessive Poorly exposed, forming slopes, saddles, and flat areas, SMR commonly with extensive colluvial or soil cover.. regolith landform Low relief deeply weathered outcrop.. SMR Steep rubbly hills Typical desert hills, with scattered outcrop, thin soil, few SMR 081303 dramatic distinctive geomorphic features. Mostly angular Forms steep hills with jagged profiles, ourcrops and blocks SMR 081303 outcrop rubbly in rubble tend to be angular or jagged. Typical of strongly hills indurated or well-layered, steeply dipping rocks. mostly rounded Rock forms steep rounded hills, with abundant colluvial smr 081503, phx NW descriptions outcrop rubbly rubble. Boulders greater than 1 m in diameter on surface hills are sparse..
Geologic unit part role terms DisplayName TextDescription Tracking interlayered Lithosome in igneous or metamorphic geologic unit that occurs as layers alternating with SMR090104 lithosome other constituents. irregular Lithosome in mixed/heterogeneous lithodemic unit that occurs in irregular bodies within SMR090104 lithosome unit. Stratigraphic Geologic unit part that occupies a particular stratigraphic position within the geologic SMR090104 part unit.. facies Geologic unit constituent is a lateral variant of a lithostratigraphic unit, or a variant of a SMR090104 lithodemic unit. Represents a particular body of rock -- a non-stratigragphic subdivision of a lithostratigraphic or lithodemic unit that is a geologic unit itself (although may be too small to be mapped at the scale of mapping). dominant Lithosome forms most or all of geologic unit; other geologic unit parts are incidental to or SMR090104 DisplayName TextDescription Tracking lithosome contained within this lithosome.. interbedded Lithosome in lithostratigraphic unit that occurs interbedded with other constituents on SMR090104 lithosome the outcrop (m) scale or larger. geologic unit Lithosome in a geologic unit that is generally interstitial to other constituents, e.g. in a SMR 081303 matrix mass wasting deposit, melange, tuff breccia.. marker horizon A mappable layer of material within a rock body that is so thin relative to its horizontal SMR050404 extent that is is treated as a single surface at the scale of description.. marker bed Geologic unit is a laterally continuous stratigraphic marker within another unit. SMR090104 inclusion Geologic unit part that occurs as non-stratigraphic bodies with generally discrete SMR090104 boundaries of older material incoporated into a geologic unit during formation of the unit, e.g. exotic blocks in melange, blocks in tuff breccia, xenoliths in igneous rock.. xenolith Blocks in intrusive igneous matrix, cm to meter scale.. SMR090104 blocks Geologic unit constituent is present as masses with generally sharp boundaries and SMR 081303 block-like geometry within a matrix of some other material emplaced by processes at the earth's surface--e.g. volcanic eruption or mass wasting.. pendants Geologic unit constituent forms inclusions too large to be considered as lithologic SMR090104 constituents (range from 10's of cm to 100's of meters) in an igneous rock.. tectonic block Geologic unit constituent occurs as discrete masses with faulted boundaries, emplaced SMR090104 into the unit by tectonic processes inside the earth, e.g. blocks in tectonic melange..
Geologic unit rank terms. The standard ranks from the stratigraphic codes are included here. Because this terminology is always uses in a local sense, it is not especially useful for defining levels of generalization for map display—formations in one area may be thinner than members in another area. For purposes of specifying level of map generalization, a more useful ranking might be developed that is quantitiative w.r.t. to the thickness, outcrop area, or estimated volume of the unit. DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Rank not Geologic unit rank not specified. SMR specified 072204 Supergroup A group of stratigraphic groups. Regional-scale unit (500,000 scale or more general) SMR Group A group of formations; appropriate to 1:100000 to 1:500000. SMR Formation Base level unit of geologic mapping appropriate for 1:24000 to 1:100000 scale SMR depiction. Member A part of a formation; apropriate for mapping more detailed than 1:24000. SMR Bed an individual, identifiable bed in a stratigraphic sequence treated as a mappable unit; SMR commonly shown as a line (degenerate volume).
Geologic structures within geologic units DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Vein Sheet-like body of hydrothermally deposited mineral material. SMR Vein mineralized shear Superclass for veins that are formed by mineralization along a SMR faulted zone, as degenerate polygon rock-body boundary. DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Vein mineral fill Superclass for veins that are formed by a solid mineral fill (like a SMR dike), as a degenerate polygon rock-body boundary. channelized contact Contact between geologic units at which the older unit has SLTT_SMR undergone some erosion to produce channels cut into the surface outcrop of the unit before deposition of the younger geologic unit, which must be a sedimentary rock.. Fossil structure Structure in rock resulting from incorporation of a living organism SMR into a rock, or resulting from activity of living organisms on non- lithified material.. Sedimentary Structure A structure in sedimentary material formed at any point of its life SLTTs cycle before it becomes a rock. A sedimentary structure can be one of the following: (1) structures that intrinsically reflect the conditions of sediment deposition (e.g., transportation and deposition of sediment); (2) structures formed during penecontemporaneous modification of sediment shortly after its accumulation, and intrinsically reflecting depositional conditions (e.g., downslope slumping, biologic activity); (3) structures representing modification of sediment while it is soft and weak, but not intrinsically related to depositional conditions (e.g., dewatering, loading); (4) structures formed during diagenesis and lithification (e.g., concretionary nodules, dissolution voids).. Secondary A sedimentary structure "...that originated subsequently to the MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 sedimentary structure deposition...of the rock in which it is found...; esp. an epigenetic sedimentary structure, such as a concretion or nodule produced by chemical action, or a sedimentary dike formed by infilling- Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. 576). Includes deformation structures, dissolution structures, hardground structures, and epigenetic-growth structures. Dissolution structures A general term for a secondary sedimentary structure formed MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 where soluble material has been partly or wholly removed by dissolution, thereby creating a void space into which adjacent and superjacent sedimentary material can collapse or subside by plastic failure. Includes collapse breccias, solution breccias, and stylolites. Stylolite A type of dissolution structure consisting of "a surface or contact, MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 usually occurring in homogeneous carbonate rocks and more rarely in sandstones and quartzites, that is marked by an irregular and interlocking penetration of the two sides....As usually seen in cross section, it resembles a suture or the tracing of a stylus. Stylolites are supposedly formed diagenetically by differential vertical movement under pressure, accompanied by solution" Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 632). brecciation non Non-tectonic breccia structure in sedimentary rock interpreted to be SMR tectonic the product of secondary processes modifying already lithified sedimentary rock.. dissolution breccia A type of dissolution structure consisting of -a collapse breccia MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 formed where soluble material has been partly or wholly removed by dissolution, thereby allowing the overlying rock to fall or settle and become fragmented- Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. DisplayName TextDescription Tracking 606). Collapse breccia "A type of dissolution structure consisting of -a breccia formed by MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 the collapse of rock overlying an opening, as by foundering of the roof of a cave...." Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 126). fenestrae "A term used by Tebbutt et al. (1965, p. 4) for a shrinkage pore, or MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 primary or 'penecontemporaneous gap in rock framework larger than the grain-supported interstices.' It may be an open space in the rock, or be completely or partly filled with secondarily introduced sediment or cement" Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 231). calcite fracture fill SMR calcite blebs SMR secondary deformation A general term for secondary structures caused by the plastic MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 structure deformation or fluidization of accumulated sediment in response to hydrostatic, gravitational, geochemical, and physical processes not intrinsically related to the depositional environment. Sand dike A secondary deformation structure formed by "a sedimentary dike MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 consisting of sand that has been squeezed or injected upward into a fissure" Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. 565). Termed sand sills where injected laterally. Shrinkage crack A secondary sedimentary structure synonymous with syneresis MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 crack--A subaqueous shrinkage crack formed by the loss of pore water from clays or shrinkage of swelling-clay mineral lattices due to changes in salinity of surrounding water- Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. 645). Fluid escape structure "A secondary deformation structure that is a general category of MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 sedimentary feature produced by the escape of fluids from a bed of sediment after deposition" Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 243). Fluid-escape structures include dish structures, pillar structures, sand and mud volcanoes, and sheet structures.. Sheet structure MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 Sand and mud volcano MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 Pillar structure MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 Tepee structure A secondary deformation structure formed by "a disharmonic MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 sedimentary structure consisting of a fold which in cross section resembles a chevron, an 'inverted depressed V', or the profile of a peaked dwelling of the North American Indians. It is believed to be an early diagenetic structure formed at the margins of large polygons produced by expansion of surface sediments (Assereto and Kendall, 1977)- Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 656). Convolute stratification A secondary deformation structure consisting of "...a structure MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 showing marked crumpling or complicated folding of the laminae of a rather well-defined sedimentation unit." (Reineck and Singh, 1980, p. 87)."Convolute bedding and convolute lamination are size- related terms for similar features, the former at the scale of decimeters or bigger, the latter at the scale of centimeters. However, the terms are used loosely ....The structure involves folding of lamination, commonly into upright cuspate forms with DisplayName TextDescription Tracking sharp anticlines and more gentle synclines....It usually is possible to trace laminae through the folds....Convolution involves plastic deformation of partially liquefied sediment soon after deposition." (Collinson and Thompson, 1989, p. 154). "It seems certain that convolute bedding can be produced in more than one way. However, we feel that liquefaction of a sediment is the most important factor in the genesis of convolute lamination" (Reineck and Singh, 1980, p. 89) "Sedimentary structure, secondary, deformation, fluid escape. A secondary deformation structure that is a general category of sedimentary feature produced by the escape of fluids from a bed of sediment after deposition" Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 243). Fluid-escape structures include dish structures, pillar structures, sand and mud volcanoes, and sheet structures. Sedimentary structure MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 secondary deformation fluid escape dish structure Load and founder Secondary deformation structures that consist of rounded, lobate, MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 structures sack-like protrusions of sand or other coarse-grained clastic sediment that extend downward into fine-grained mudrock, in some cases to the point of detachment and foundering of the protrusion (extracted from Glossary of Geology definition of load cast; Jackson, 1997, p. 373). -The basic mechanism of formation is gravity acting on beds which were unstable due to their high porosity and lack of compaction and coherence, and to differences in density between the beds....[A] combination of density inversion and temporary weakness leads to the sinking of one bed into the other....- Collinson and Thompson, 1989, p. 147). Representative examples include: ball-and-pillow structure, flame structure, and load casts. Ball and pillow A secondary load-and-founder structure consisting of. MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 structure Flame structure A secondary load-and-founder structure consisting of “...wave- or MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 flame-shaped plumes of mud that have been squeezed irregularly upward into an overlying layer. It is probably formed by load casting accompanied by horizontal slip or drag” Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. 238, in NADMSLTTs 2004) Load cast “A sole mark, usually measuring lees than a meter in any direction, MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 consisting of a swelling in the shape of a slight bulge, a deep or shallow rounded sack, a highly irregular protuberance, or a bulbous, mammillary. or papilliform protrusion of sand or other coarse clastics, extending downward into finer-grained, softer, and originally hydroplastic underlying material, such as wet clay, mud, or peat, that contained an initial depression. It is produced by the exaggeration of the depression as a result of unequal settling and compaction of the overlying material and by the partial sinking of such material into the depression....” Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. 373, in NADMSLTTs 2004) Epigenetic growth A general term for secondary structures formed during epigenesis MattiSLTTSed050604 structures by growth of minerals. They range in size from centimeters (nodules and concretions) to basin-wide dimensions (duricrusts). DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Epigenetic cavity filling A type of epigenetic-growth structure: A general term for mineral MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 aggregates that fill or partly fill open spaces in sedimentary materials. The open spaces may be primary pores or may be fenestrae created by secondary processes. Stromatactis A type of cavity-filling epigenetic-growth structure: -A sedimentary MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 structure characterized by a horizontal or nearly flat bottom, up to about 10 cm in diameter, and an irregular or convex-upward upper surface, consisting of sparry calcite cement....They have been interpreted as fillings of original cavities caused by the burial and decay of soft-bodied but rigid frame-building organisms...although they may represent syngenetic voids- (Glossary of Geology, Jackson, 1997, p. 630). Epigenetic cavity filling A type of cavity-filling epigenetic-growth structure: A primary pore MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 vug or secondary dissolution space that is partly or wholly filled with sediment or epigenetic minerals. Typically developed in carbonate rocks, but may occur in any sedimentary material. Geopetal structure A type of cavity-filling epigenetic-growth structure: "A common MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 structure in limestones where a cavity contains sediment in the lower part and cement (usually calcite) in the upper part. These structures are like spirit levels and can be used to deduce the way- up of the rocks and the horizontal at the time of deposition" (Glossary of Geology, Jackson, 1997, p. 266). Epigenetic growth A type of epigenetic-growth structure: "A large euhedral or MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 structure sand crystal subhedral crystal (as of barite, gypsum, and esp. calcite) loaded with detrital-sand inclusions (up to 60%), developed by growth in sand during cementation. Crystals or crystal clusters...may grow poikilitically encasing sandy matrix" (Glossary of Geology, Jackson, 1997, p. 565). Epigenetic growth Epigenetic growth structure of unknown type. MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 structure type unknown Epigenetic replacement A type of epigenetic-growth structure: A general term for secondary MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 displacive growth structures that form by epigenetic mineral growth, thereby replacing structure and (or) displacing pre-existing sedimentary particles. In the extreme, such growth may bind pre-existing sediment into hard, extensive concretionary aggregates. Replacement A type of replacement-displacive epigenetic-growth structure: "A MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 displacive nodule small, irregularly rounded knot, mass, or lump of a mineral or mineral aggregate, normally having a warty or knobby surface and no internal structure, and usually exhibiting a contrasting composition from the enclosing sediment or rock matrix in which it is embedded; e.g., a nodule of pyrite in a coal bed, a chert nodule in limestone, or a phosphatic nodule in marine strata" (Glossary of Geology, Jackson, 1997, p. 435). Epigenetic replacement A type of replacement-displacive epigenetic-growth structure: "A MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 displacive concretion hard, compact mass or aggregate of mineral matter, normally subspherical but commonly oblate, disk-shaped, or irregular with odd or fantastic outlines; formed by precipitation about a nucleus or center, such as a leaf,bone, shell, or fossil, in the pores of sedimentary or volcanic rock, and usually of a composition widely different from that of the rock in which it is found....Most concretions were formed during diagenesis, and many (especially DisplayName TextDescription Tracking in limestone and shale) shortly after sediment deposition" (Glossary of Geology, Jackson, 1997, p. 132). Collinson and Thompson (1989, p. 164-165) indicate that concretions can form by (1) primary pore filling, (2) displacive nodule growth, (3) nodule growth by replacement, and (4) concretions due to cavity infill (geopetal structures and stromatactis). Cone in cone structure A type of replacement-displacive epigenetic-growth structure: -A MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 minor sedimentary structure in thin, generally calcareous layers of some shales and in outer parts of some large concretions...; it resembles a set of concentric, right circular cones fitting one into another in inverted positions (base upward, apex downward), commonly separated by clay films, and consisting usually of fibrous calcite and rarely of siderite or gypsum....The structure appears to be due to pressure aided by crystallization and weathering (solution) along intersecting conical shear zones- (Glossary of Geology, Jackson, 1997, p. 630). Duricrust A type of replacement-displacive epigenetic-growth structure: -A MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 general term for a hard crust on the surface of, or layer in the upper horizons of, a soil in a semiarid climate. It is formed by the accumulation of soluble minerals deposited by mineral-bearing waters that move upward by capillary action and evaporate during the dry season- Glossary of Geology, Jackson, 1997, p. 196). silcrete soil horizon Silcretes are very hard layers of silica-enriched materials formed mattiSedPickList3-051603; beneath the surface in soils, unconsolidated sediments, and http://www.tec.army.mil/resear permeable rocks. These materials range from silica-cemented sand ch/products/desert_guide/lsms and gravel to an amorphous matrix enriched with small silica heet/lssilc.htm particles. There is little agreement as to their classification and origin. A minimum silica (SiO2) content of 85 percent by weight has been proposed by Summerfield (1983a [1]) to distinguish silcretes from other duricrusts. Although not restricted to arid regions, silcrete zones are found in many deserts, and they are most extensive and prominent topographic features in Australian deserts. Silcrete tends to form roughly horizontal, highly resistant layers generally less than 5 m thick. When exposed by erosion, silcrete forms highly resistant cap rocks of scarps ("breakaways" in Australia). These cap rocks resemble quartzite. Many talus slopes and gravel plains in areas of exposed silcrete consist of silcrete fragments eroded from the cap rock. Buried silcrete layers thicker than 3 m are rare, and they are generally not laterally continuous over large areas. In the Kalahari Desert of southern Africa, they occur widely as layers within sandy surface deposits, and they are also found along old, dry river courses such as the Molopo River (Summerfield, 1983b [2]). These buried silcrete layers can be virtually impenetrable.. Calcrete A type of calcareous duricrust: A general term for calcium MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 carbonate layers, crusts, and nodules that form hard discontinuous to continuous masses in sedimentary materials. The calcium carbonate is -...precipitated from solution and re-deposited through the agency of infiltrating waters, or deposited by the escape of carbon dioxide from vadose water- (modified from the Glossary of Geology, Jackson, 1997, p. 91). Although the Glossary of Geology indicates a pedogenic origin for calcrete, SLTTS_1.0 uses the term DisplayName TextDescription Tracking only to indicate a secondary feature, without specifying an origin. Ferricrete "A ferruginous duricrust" (Glossary of Geology, Jackson, 1997, p. MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 232): A general term for secondary ferruginous layers, crusts, and nodules that form hard discontinuous to continuous masses in terrigenous-clastic sedimentary materials. calcite stringers SMR Mottled hh. Comment: SMR SMR calcite vug fill SMR Sedimentary A type of secondary sedimentary structure: A general term for MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 hardground sedimentary substrates that are hardened without undergoing burial diagenesis or subaerial exposure. Typically such hardgrounds develop in carbonate sediment to yield limestone hardgrounds, but they also can develop in clay-rich sediment that is calcareous. Submarine hardground A type of sedimentary hardground consisting of "a limestone which MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 has been cemented on the seafloor. The hardground surface may be encrusted, discolored, case-hardened, bored, and solution- ridden. It implies a gap in sedimentation and may be preserved stratigraphically as an unconformity" Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 290). Beachrock "A type of sedimentary hardground consisting of -a friable to well- MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 cemented sedimentary rock, formed in the intertidal zone in a tropical or subtropical region, consisting of sand or gravel (detrital and/or skeletal) cemented with calcium carbonate" Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 59). Linear structure with Superclass for all sorts of sedimentary lineations. Paleocurrent OverhaulClassificationConcep sedimentary origin indicators will be sub types of this super class.. ts071300 Biogenic Sedimentary A primary sedimentary structure that is biogenic in origin, SLTTs Structure consisting of tracks, trails, burrows, and other disturbances left in the sediment by body fossils as a result of their living activities. Radially symmetrical mattiSedPickList3-051603 mark biogenic structure Axial vertical radially radially symmetrical mark, biogenic sedimentary structure. mattiSedPickList3-051603 symmetrical marks Multi rayed, axial mattiSedPickList3-051603 vertical radially symmetrical marks Five rayed axial vertical mattiSedPickList3-051603 radially symmetrical marks Biogenic mark mattiSedPickList3-051603 structure, no axial vertical structure Multi rayed, radially mattiSedPickList3-051603 symmetrical biogenic mark structure Algal Structure Sedimentary structures formed by the activity of algae. OverhaulClassificationConcep ts071300 DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Algal lamination Milimeter scale layering in sedimentary material interpreted to be SLTT_SMR related to growth of algae. Cryptalgal lamination fine, crinkly lamination; structures formed by the interaction of StrotherCryptalgal microbial growth with sedimentary deposition. As filaments of cyanobacteria grow toward the light, for example, the sticky, mucilagenous sheaths that surround these bacteria, trap and bind sediment into discrete structures. Algal lamination in SLTTs laterally linked columnar head Spreiten mattiSedPickList3-051603 Branched spreiten mattiSedPickList3-051603 Spiral spreiten mattiSedPickList3-051603 U shaped spreiten mattiSedPickList3-051603 Tunnels and shafts mattiSedPickList3-051603 biogenic tunnel or shaft mattiSedPickList3-051603 diameter uniform biogenic tunnel or shaft mattiSedPickList3-051603 diameter uniform U shaped biogenic tunnel or shaft mattiSedPickList3-051603 diameter uniform horizontal biogenic tunnel or shaft mattiSedPickList3-051603 diameter uniform Vertical biogenic tunnel or shaft mattiSedPickList3-051603 diameter uniform Regularly branching biogenic tunnel or shaft mattiSedPickList3-051603 diameter variable biogenic track structure mattiSedPickList3-051603 Bioturbation structure Burrows, tracks, and traces of biogenic origin that are very densely mattiSedPickList3-051603 distributed and interpenetrating, leading to a diffuse or swirled sedimentary fabric within which individual biogenic structures are difficult to distinguish (modified from Collinson and Thompson, 1989, p. 172). completely bioturbated Original depositional fabric completely obliterated (modified from mattiSedPickList3-051603 Hallsworth and Knox (1999, p. 27-28), who credit Reineck (1967), Drosser and Bottjer (1986, 1989, 1991), and Pemberton and others (1992). Pouch biogenic mattiSedPickList3-051603 structure Transverse ornament mattiSedPickList3-051603 pouch biogenic structure DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Smooth surface pouch mattiSedPickList3-051603 biogenic structure biogenic trail structure NADMSLTTs 2004 mattiSedPickList3-051603 Overlapping trail mattiSedPickList3-051603 biogenic structure Simple Overlapping mattiSedPickList3-051603 trail structure Overlapping Bilobed mattiSedPickList3-051603 trail structure Freely winding trail mattiSedPickList3-051603 biogenic structure Freely winding Bilobed mattiSedPickList3-051603 trail structure Freely winding Trilobed mattiSedPickList3-051603 trail Simple Freely winding mattiSedPickList3-051603 trail structure Net pattern biogenic mattiSedPickList3-051603 structure Penecontemporaneous An inorganic structure formed shortly after the deposition of mattiSedPickList3-051603 sedimentary structure sediment, usually involving deformation (shape change) or disruption of the sediment mass, and intrinsically related to depositional conditions. Salt crystal Imprint A penecontemporaneous sedimentary structure consisting of an mattiSedPickList3-051603 imprint formed by solution of a soluble salt crystal (derived from Glossary of Geology definition of salt-crystal cast; Jackson, 1997, p. 563). Can sometimes form casts on the lower surfaces of beds. Desiccation Mudcrack "A penecontemporaneous sedimentary structure consisting of an mattiSedPickList3-051603 irregular fracture in a crudely polygonal pattern, formed by the shrinkage of clay, silt, or mud, generally in the course of drying under the influence of atmospheric conditions" Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 422). Icewedge Casts and mattiSedPickList3-051603 Polygons Icewedge polygon A penecontemporaneous sedimentary structure consisting of "a MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 large nonsorted polygon characterized by borders of intersecting ice wedges, found only in permafrost regions and formed by contraction of frozen ground. The fissured borders delineating the polygon may be ridges...or shallow troughs....In plan the pattern tends to be three- to six-sided" Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. 317). Ice wedge cast A penecontemporaneous sedimentary structure consisting of a MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 "sedimentary structure formed by the filing of the space formerly occupied by an ice wedge that had melted" Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. 317). Raindrop Impression "A penecontemporaneous sedimentary structure synonymous with MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 rain print--A small, shallow crater-like print surrounded by a slightly raised rim, formed in soft, fine sand, silt, or clay...by the impact of a DisplayName TextDescription Tracking falling raindrop, and sometimes preserved on the bedding planes of sedimentary rocks or as casts on the underside of...beds" Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 530). Fenestral Structures mattiSedPickList3-051603 Olistostrome A sedimentary deposit consisting of a chaotic mass of intimately mattiSedPickList3-051603 mixed heterogeneous materials (such as blocks and muds) that accumulated by submarine gravity sliding or slumping of unconsolidated sediment- Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 445).. Deformed Cross A penecontemporaneous sedimentary structure consisting of mattiSedPickList3-051603 Stratification oversteepened or overturned foresets that occur "...within single sets. The deformation ranges from foresets that dip more steeply than the angle of rest in the upper parts of sets (oversteepened) to extensive overturning of foresets into recumbent folds. The overfolding is always in the direction of the original foreset dip.... [Oversteepening and overturning develop in response to] a shear force acting on the upper surface of a bedform, and in the same direction of the current that produced the bedform...." (Collinson and Thompson, 1989, p. 153-154).. Synsedimentary Fault A penecontemporaneous sedimentary structure consisting of a MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 surface or narrow zone of discrete slip separating blocks of internally coherent sediment, with displacement ranging from centimeters to hundreds of meters (Collinson and Thompson, 1989, p. 157). Also see Growth fault. Slump Fold "A penecontemporaneous sedimentary structure consisting of -an MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 intraformational fold produced by slumping of soft sediments" Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 530). Slumping is a response to local depositional-slope conditions. Slump Scar A penecontemporaneous sedimentary structure consisting of a MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 pull-away scarp from which a submarine slump has detached and across which younger sediment is draped (Collinson and Thompson, 1989, p.158).. Slump Block "A penecontemporaneous sedimentary structure consisting of "the MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 mass of material torn away as a coherent unit during slumping…" Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 600). Syngenetic An inorganic sedimentary structure formed during the genesis of MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 sedimentary structure sedimentation units and sedimentary bedforms or caused by the scouring action of fluids, and intrinsically reflecting conditions of the sedimentary environment.. sedimentary A syngenetic depositional structure occurring within a bed or mattiSedPickList3-051603 depositional structures lamina, originating from migration of a sedimentary bedform. internal to beds Primary Sedimentary SMR 062803 Fabric Clast supported fabric A depositional fabric in which the sand- and gravel-size particles MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 touch at point contacts and form a supporting framework, with any fine matrix merely occupying the interstices between the coarser grains. Imbricated Clast fabric Fabric defined by long axis of tabular clasts stacked like shingles to SMR092603 DisplayName TextDescription Tracking define a surface that makes a small angle with the bedding surface. Matrix supported fabric A depositional fabric in which finer-grained clastic particles support MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 the sediment mass while coarser-grained particles-float in the matrix with minimal point contacts between them. The result is a distinctive bimodal or multi-modal grain-size distribution. Depositional fabric not mattiSedPickList3-051603 preserved massive sedimentary The depositional fabric of a sedimentation unit is structureless-i.e., mattiSedPickList3-051603 fabric the fabric lacks any form of geometry or particle organization such as lamination, cross lamination, and size grading. Massive does not refer to the character or thickness of bedding. lamination A type of syngenetic depositional structure (internal) where the mattiSedPickList3-051603 depositional fabric has discrete to diffuse planar structure created by layers and (or) grains that are oriented parallel to bedding planes. planar lamination A type of syngenetic depositional structure (internal) where the based on def's in depositional fabric has discrete to diffuse planar structure created mattiSedGlos1-0 060103; smr by lamina that are oriented parallel to bedding planes. Lamina are "The thinnest recognizable unit layer of original deposition in a sediment or sedimentary rock...; specif. such a sedimentary layer less than 1 cm in thickness (Otto, 1938, p. 575)" Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. 355). Also see Campbell (1967, p. 16- 20). "A lamina can be regarded as the smallest megascopic layer in a sedimentary sequence....[It] is relatively uniform in composition...[and] is generally not megascopic internally layered." (Reineck and Singh, 1980, p. 96). varve lamination A type of lamination consisting of diffuse to distinct planar fabric mattiSedPickList3-051603 developed in mudstones and mud due to the alignment of clay minerals. convolute lamination Mm-scale layering in sedimentary rocks that is in irregular, non- SLTTs systematic folds, generally with cm-scale amplitude and wavelength.. cross stratification Laminae or layers oriented at an angle to the bounding surfaces of mattiSedPickList3-051603 a bed. Classified into cross bedding and cross lamination if the thickness of layers is known. Cross bedding A type of cross stratification consisting of inclined layers greater MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 than or equal to 1 cm thick. Cross lamination A type of cross stratification consisting of inclined laminae less MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 than1 cm thick. tabular cross mattiSedPickList3-051603 stratification Small scale tabular mattiSedPickList3-051603 cross stratification Small scale tabular mattiSedPickList3-051603 flaser bedding herringbone cross mattiSedPickList3-051603 lamination Small scale tabular mattiSedPickList3-051603 dune cross lamination DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Small scale tabular mattiSedPickList3-051603 climbing ripple cross lamination Small scale tabular mattiSedPickList3-051603 ripple cross lamination Small scale tabular mattiSedPickList3-051603 lenticular bedding large scale tabular mattiSedPickList3-051603 cross stratification large scale tabular mattiSedPickList3-051603 scour channel cross stratification large scale tabular mattiSedPickList3-051603 dune cross stratification large scale tabular mattiSedPickList3-051603 sand wave cross stratification large scale tabular mattiSedPickList3-051603 foreset layer trough cross mattiSedPickList3-051603 stratification large scale trough mattiSedPickList3-051603 cross stratification large scale trough mattiSedPickList3-051603 foreset layer large scale trough dune mattiSedPickList3-051603 cross stratification large scale trough sand mattiSedPickList3-051603 wave cross stratification large scale trough mattiSedPickList3-051603 scour channel cross stratification large scale hummocky mattiSedPickList3-051603 cross bedding Small scale trough mattiSedPickList3-051603 cross stratification Small scale trough mattiSedPickList3-051603 dune cross lamination Small scale trough mattiSedPickList3-051603 flaser bedding Small scale trough mattiSedPickList3-051603 climbing ripple cross lamination Small scale trough mattiSedPickList3-051603 ripple cross lamination DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Small scale trough mattiSedPickList3-051603 herringbone cross lamination Small scale trough mattiSedPickList3-051603 lenticular bedding Scour and fill structure A small-scale scour channel developed in a sedimentary sequence MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 as the result of channel migration. Can be filled with material either coarser grained or finer grained than enclosing host sediment. Burrow mottled Burrows, tracks, and traces of biogenic origin are common and MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 distinct (modified from Collinson and Thompson, 1989, p. 172). graded bedding See bedding, graded, and also graded bedding, normal and graded mattiSedPickList3-051603 bedding, reverse. normal graded bedding mattiSedPickList3-051603 reverse graded mattiSedPickList3-051603 bedding Bedding Outcrop-scale fabric defined by layering that results from the MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 successive stacking of sedimentation units, each of which generally formed under uniform depositional conditions (see discussions by Otto, 1938; McKee and Weir, 1953; Campbell, 1967; Reineck and Singh, 1980; Collinson and Thompson, 1989). Has properties of parallel or non-parallel surfaces; planar, curviplanar, or wavy surfaces; discontinuous or continous surfaces, clarity of development (crude, well-defined). Subtype terms identify commonly used combinations of properties. Large scale cross Outcrop scale fabric defined by cross-bedded relationships SMR, proposed modification bedding involving individual beds in sets.. of SLTT Parallel Bedding Bedding fabric defined by non-parallel bedding surfaces. MattiSedPickList082903 Erosional channel A syngenetic erosional structure consisting of a trough-shaped MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 structure depression scoured downward into older earth materials by streamflows, wave action, storm surges, density currents, etc.; range from decimeters to many hundreds of meters in scale. Where appropriate, erosion channels can be classified either as (1) penecontemporaneous channels scoured into previously deposited material or (2) channels scoured into older material along a hardground that may mark an unconformity. Water erosion Sedimentary structures resulting from the erosion of sediment by mattiSedPickList3-051603; structures moving water. SMR050304 Swash marks A type of syngenetic erosional structure consisting of "A thin MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 delicate wavy or arcuate line or very small ridge on a beach, marking the farthest advance of a wave uprush. It is convex landward, and consists of fine sand...." Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 643). Rill marks A type of syngenetic erosional structure consisting of "A small, MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 dendritic channel, groove, or furrow formed on the surface of beach mud or sand by a wave-generated rill or by a retreating tide" Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 550). Scour marks A syngenetic erosional sedimentary structure. "A current mark MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 produced by the cutting or scouring action of a current of water flowing over the bottom" Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. DisplayName TextDescription Tracking 574). Obstacle Scour Current -...a scour mark produced by the interaction of an obstacle on the MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 Crescent bed and a current flowing around it- Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 442). The mark typically consists of crescent or horseshoe shaped ridges around an object on the base of a bed. transverse scours "A scour mark whose long axis is transverse to the main direction MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 of the current" Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 676). Transverse scours are small features that are morphologically transitional with flutes (Reineck and Singh, 1980, p. 74). flute marks A type of scour mark consisting of an elongate depression scoured mattiSedPickList3-051603 in cohesive sediment by random eddy scour or by current eddies produced behind an obstacle. The marks range in length from a few cm to as much as 50 cm. They are elongate parallel to current flow, have a bulbous depression at the upstream end, and shallow and flare out downcurrent. Usually expressed as casts on the base of sand beds (Collinson and Thompson, 1989; Boggs, 2001). Gutter cast A type of scour mark consisting of "A down-bulge on the bottom of MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 a sedimentary bed, of great length (usually one meter or more) compared with its width and depth (a few centimeters to several decimeters)" Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 287). According to Collinson and Thompson (1989, p. 43) they are U or V shaped isolated elongate ridges that project downward into underlying finer grained sediment from an otherwise flat bedding plane in vertical profile. obstacle scours mattiSedPickList3-051603 longitudinal ridges and A type of scour mark consisting of "...structures made up of closely mattiSedPickList3-051603 furrows spaced continuous ridges alternating with furrows, arranged parallel to the current. Regularly spaced ridges are separated by furrows a few millimeters to several centimeters apart. Ridges make the continuous structure" (Reineck and Singh, 1980, p. 75). Wind erosion mattiSedPickList3-051603 structures sand tail A type of syngenetic erosional structure, found on the upper mattiSedPickList3-051603 surface of a bedding unit, formed by wind erosion. (NADMSLTTs 2004) Sole mark "A general descriptive term applied to a directional structure or to a MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 small, wave like, mainly convex irregularity or penetration found on the underside of a bed of sandstone or siltstone along its contact with a finer-grained layer....The term usually refers to a filling of a primary sedimentary structure, e.g., a crack, track, groove. or other depression, formed on the surface of the underlying mud by such agents as currents, organisms, and unequal loading, and preserved as a sole cast after the underlying material has consolidated and weathered away...."Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. 605). Tool marks mattiSedPickList3-051603 Groove A type of tool mark consisting of "A long, straight narrow MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 depression, with an almost uniform depth and cross section, on a sedimentary surface...produced by a simultaneous rectilinear advance of objects propelled by a continuous current" Glossary of DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 283). chevron marks mattiSedPickList3-051603 skip marks A type of tool mark consisting of "One of a linear series of regularly MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 spaced, crescent-shaped tool marks produced by an object that intermittently impinged on or skipped along the bottom of a stream" Glossary of Geology, (Jackson, 1997, p. 597). Collinson and Thompson (1989, p. 46) indicate that skip marks represent repeated bouncing of the same tool above the bed. prod marks mattiSedPickList3-051603 bounce marks mattiSedPickList3-051603 Bedding surface Planar structure defined by primary depositional features reflecting based on def's in parting slope of original depositional surface. Bedding surfaces are mattiSedGlos1-0 060103; smr depositional surfaces that reveal the principal rock layering or bedding. They are produced during periods of nondeposition or abrupt change in depositional conditions, and erosion commonly accompanies nondeposition- (Campbell, 1967, p. 12). sedimentary bedding A type of syngenetic depositional structure formed on the upper MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 parting lineation surface of a sedimentation unit. Consists of parallel ridges and grooves a few millimeters wide on the upper surface of lamina and beds, parallel to the direction of current flow (extracted from Glossary of Geology, Jackson, 1997, p. 468). Ripple mark mattiSedPickList3-051603 Asymmetric ripple mark "A ripple mark having an asymmetric profile in cross section, MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 characterized by a short steep slope facing downcurrent and a long gentle slope facing upcurrent" Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. 41). rhomboid ripple "An aqueous current ripple mark characterized by diamond-shaped mattiSedPickList3-051603 tongues of sand arranged in a reticular pattern....each has one acute angle (formed by two steep sides) pointing downcurrent, and another acute angle (formed by the gentle side extending into the re-entrant angle of the steep sides of two tongues of the following [forms]) pointing upcurrent- Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997,p. 547). Arranged in rows parallel to flow, out-of-phase.. oscillation ripple mark A symmetric ripple mark with a sharp, narrow, relatively straight mattiSedPickList3-051603 crest between broadly rounded troughs, formed by the orbital or to- and-fro motion of water agitated by oscillatory waves- Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. 455). catenary bedform mattiSedPickList3-051603 linguoid bedform A bedform having a tongue-shaped outline, with the bulbous end of MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 the form oriented downcurrent; rows arranged parallel to flow are out-of-phase (Allen, 1968). The form has an opposite orientation to that of a lunate bedform. cuspate bedform Linguoid bedforms that are arranged in phase, in rows parallel to MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 flow (Allen, 1968, p. 66). lunate bedform "A type of [bedform] in which the crest lines are strongly curved MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 and open out downcurrent; the form is similar to a barchan and has the opposite orientation to that of a linguoid [bedform]" Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. 380). DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Ripple and dune mattiSedPickList3-051603 bedforms ripple bedform A small-scale sedimentary bedform having height of 5 cm above MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 the bed surface.. dune bedform A large-scale sedimentary bedform having height greater than 5 cm mattiSedPickList3-051603 above the bed surface. Massive metamorphic Rock is massive, lacking foliation. SMR fabric granoblastic fabric Fabric characterized by mosaic of equidimensional, anhedral SMR, base on Best, 1982 grains; inequant grains, if present, are randomly oriented; grain boundaries apporach bubble-like configuration (crystalloblastic), with dihedral angles between faces commonly near 120 degrees. Poikiliblastic texture Metamorphic fabric in which large crystals of one phase contain based on Bates & Jackson, numerous small crystals of other phases. [NGMDB note: This is a 1997 fabric because it is defined based on the relationships between particles.]. Planar penetrative Foliation. Planar structure in a rock body defined by physical SMR tectonic structure components that is related to deformation subsequent to solidification of the rock. Planar is used in the sense that the surface can be thought of as a plane in some sufficiently small neighborhood of any particular point on the surface. Penetrative denotes that the fabric elements defining the structure are repeated at distances so small, compared with the scale of the whole…that they can be considered to pervade it uniformly and be present at every point (paraphrase of Turner and Weiss, 1963, p. 21). Foliation A penetrative planar fabric in a rock.. SMR Foliation Foliation in a metamorphic rock with a granoblastic texture. Fabric SMR crystalloblastic elements may be layering or aligned tabular crystals or crystal aggregates.. Schistosity Planar foliation defined by aligned planar or tabular mineral grains, SMR in which the shape of the grains is related to the crystal habit of the mineral, not deformation of grain shape.. laminated differentiated Foliation defined by compositional segregation, in which the layers SMR foliation are less than 1 cm thick.. Foliation compositional Layering defined by mineralogical variations in a rock body, SMR layering commonly associated with layers that have sharp boundaries. Also known as gneissic foliation. Foliation compositional Layering defined by mineralogical variations in a rock body, SMR layering mineral commonly associated with layers that have sharp boundaries. segregation Origin of compositional variations interpreted to be result of solid- state reactions in rock body (metamorphic segregation).. Foliation vague Compositional layering and of uncertain origin.. formed by subtle SMR_DI25DatabaseDevelop compositional layering mineralogical or textural variations, with gradational layer ment boundaries Foliation compositional Layering defined by mineralogical variations in a rock body, SMR layering migmatitic commonly associated with layers that have sharp boundaries. Compositional variations are result of melt segregation during high- grade metamorphism; some layers have magmatic/igneous mineralogy. DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Foliation compositional Layering defined by mineralogical variations in a rock body, SMR layering inherited from commonly associated with layers that have sharp boundaries. protolith Layering is relict of compositional variations in protolith, typically heterogeneous sedimentary or volcanic rock.. Foliation nebulitic Vague layering defined by subtle compositional and textural SMR variations. The descriptor nebulitic is from migmatite terminology, and the term fabric is associated with high-grade metamorphic rocks intermediate between igneous and metamorphic. Distinction from textural and compositional layering varieties is not clearly defined .. Mylonitic foliation Generic mylonitic shape fabric; defined by shape of deformed SMR generic mineral grains or aggregates of mineral grains; greater than 10% TRIG matrix. Mylonitic foliation Ultramylonitic foliation; greater than 90% of rock is matrix due to SMR ultramylonite tectonic grain size reduction processes. Mylonitic foliation Protomylonitic foliation; 10-50% of rock is matrix due to tectonic SMR protomylonite grain size reduction processes. Mylonitic foliation weak Foliation defined by shape of deformed, originally equant grains, in SMR grain shape fabric which aspect ratio of deformed grains is generally less than 3 to 1 (longest to shortest axis). Mylonitic foliation well Foliation defined by aligned tectonically flattened mineral grains, SMRDI21DataSetSetup developed s tectonite and planar or tabular grains rotated to parallel foliation, as well as foliation cleavage along slip or shear surfaces. Intermediate fabric in mylonite series.. Mylonitic foliation Mylonitic foliation; 50-90% of rock is matrix due to tectonic grain SMR mylonite size reduction processes. weak shape fabric Planar foliation defined by aligned mineral grains, in cases where SMR less than 50% of rock consists of mineral grains defining the foliation. Shape of mineral grains due to crystal habit, deformation, some combination of these or not specified.. Weak schistosity Planar foliation defined by aligned mineral grains whose crystal SMR_DI25DatabaseDevelop habit imparts the tabular shape defining the foliation, in cases ment where less than 50% of rock consists of mineral grains defining the foliation.. Cleavage A planar tectonic foliation in a rock characterized by a tendency for SMR the rock to break parallel to the foliation.. Cleavage slaty Continuous planar foliation defined by aligned fine to very-fine SMR grained phylosilicate mineral grains. Grades into schistosity as grain size increases. [synonomous with fissility]. Cleavage generic Superclass for a cleavage that is overprinted on an older foliation. SMRDataBaseDevelopment crenulation Cleavage spaced A crenulation cleavage in which the cleavage domains have SMRDataBaseDevelopment crenulation discrete boundaries. Cleavage continuous Cleavage defined by long, thin limbs of crenulation folds of pre- SMR crenulation existing foliation, in which the boundaries between cleavage domains and lithons are gradational. Both the crenulation foliation and the crenulated foliation are easily visible. Grades to spaced crenulation cleavage as boundaries of cleavage domains become sharp, and transposed foliations as crenulation foliation obscures DisplayName TextDescription Tracking the crenulated foliation.. Cleavage close Spaced cleavage in sandstone or phyllosilicate-poor rock, defined SMR disjunct by partings of uncertain origin, and does not crenulate an existing cleavage. (sometimes called 'fracture cleavage'). Cleavage domains have no apparent thickness, and are spaced less than 5 cm on average. Domainal if cleavage is clearly developed in some parts of outcrop but not in others.. Cleavage spaced Cleavage typically in phyllosilicate-poor rock, in which the cleavage SMR disjunct close joints domains have no apparent thickness, and are spaced between 5 cm and 25 cm, and do not crenulate an older foliation. Cleavage domains are regularly spaced, and penetrative on a 1-10 m scale.. Foliation generic A planar tectonic foliation defined by fabric elements that indicate SMR composite more than one origin for the foliation.. Composite foliation Layering interpreted to have originated as sedimentary bedding SMR layering transposed that has been transposed as a result of metamorphism and bedding w tops deformation; sedimentary top direction indicators are present. Composite foliation Mylonite with continuous compositional layering greater than 5 mm OverhaulClassificationConcep gneissic mylonitic thick. Continuous means individual layers can be traced more than ts071300 foliation 1 m. Composite foliation Composite fabric in which a cleavage is developed parallel to SMR generic cleavage bedding. parallel to bedding Composite foliation Layering interpreted to have originated as sedimentary bedding SMR layering transposed that has been transposed as a result of metamorphism and bedding deformation. Joints Parting surfaces in rock that occur in crudely parallel orientation, SMR spaced >25 cm on average if in a very regular joint set. Spacing is more variable and alignment of surfaces is cruder that cleavage.. Composite tectonic Tectonic structure that is an aggregation of other structures. SMRBasedOnNADMC1Work1 structure 202 Shear displacement Collection of fault surfaces, folds, and fabrics that represent a no tracking record assigned zone spatially extended zone of related geologic deformation. Name based on GEON structure group 10/04. Symmetric fold Fold near enough to symmetric that a vergence can not be SMR determined;. CCW asymmetric fold Asymmetrical fold, with counter-clockwise vergence viewed down SMR dip. Equivalent to 'S' fold.. Synform Fold that closes downward related to earth surface. no tracking record assigned Syncline Fold that opens upward relative to earth and has older rocks inside SMRDataBaseDevelopment the fold.. Discrete linear tectonic Discrete linear structure defined by physical components that are SMR050404 structure the product of tectonic processes. Linear is used in the sense that the structure can be represented as a line in some sufficiently small neighborhood of any point on the structure.. Boudin neck Linear structure defined by an elongate zone of thinning or fracture SMR separating two boudin.. mullions SMR DisplayName TextDescription Tracking lineation groove or Lineation in which fabric elements are grooves or striations in a SMR striae in surface surface. Fabric elements are penetrative within the surface, but absent in adjacent rock body. Lineation groove or Linear structure, penetrative grooves or striae in a surface, for SMR_DI25DatabaseDevelop striae directed which a direction of movement is specified. slickenside lineation.. ment Linear penetrative Lineation. Penetrative linear structure in a rock body defined by SMR tectonic structure fabric elements that are defined by physical components that are the product of tectonic processes. Linear is used in the sense that the orientation of the structure can be represented as a line in some sufficiently small neighborhood of any point in the material containig the fabric. Penetrative denotes that the fabric elements defining the structure are repeated at distances so small, compared with the scale of the whole…that they can be considered to pervade it uniformly and be present at every point (paraphrase of Turner and Weiss, 1963, p. 21). Lineation crenulation Lineation defined by small-scale wrinkles, typically of phylosillicate SMRCartoRepresentationClea minerals, on another surface, typically a cleavage or schistosity. nupForDI8 Use instead of intersection lineation if the wrinkles are the measured feature and the intersecting planar feature is not apparent. Lineation, shape, Fabric defined by aligned elongate (prolate) fabric elements for SMR generic tectonic which the alignment is due to tectonic processes (i.e. post depositional for sedimentary rocks, post crystallization for igneous rocks, or any lineation related to metamorphism). lineation stretch shape Lineation defined by elongate (prolate) fabric elements in which the SMR mylonitic alignment of the fabric elements, and the formation of prolate fabric elements, is due to crystal plastic deformation processes. lineation mylonitic Mylonitic lineation for which the sense of shear relative to the SMRDI21DataSetSetup stretch shape directed containing foliation is known. Mineral lineation Lineation defined by aligned elongate crystals of one or more SMR minerals with a prismatic crystal habit. lineation mineral Mineral lineation defined by aligned hornblende crystals. SMR hornblende lineation mineral biotite Mineral lineation defined by aligned elongate biotite aggregates in SMR a foliation surface. Biotite does not have an elongate (prismatic, acicular) mineral habit, so production of lineation must reflect elongate aggregates of biotite crystals.. lineation mineral Mineral lineation defined by aligned sillimanite crystals.. SMR sillimanite Lineation intersection Lineation defined by the intersection of bedding surfaces and SMR bedding cleavage cleavage surfaces. lineation intersection Lineation defined by the intersection of two tectonic foliations. SMR Sn Sn+1 Discrete surface Geologic structure that bounds a 3 dimensional volume, and are SMR050404 tectonic structure the product of tectonic processes. Surface has an identity property.. Seam pseudotachylite Discrete, thin layer filled with pseudotachylite (metamorphic glass SMR produced by faulting). Ductile shear zone Generic ductile shear zone or high strain zone, considered as a SMRDataBaseDevelopment DisplayName TextDescription Tracking discrete planar feature; may be mylonitic, or delineated by deformed marker layers or objects.. Ductile Shear zone Ductile shear zone, measured as a discrete feature, for which the SMRDataBaseDevelopment directed sense of shear is known. Nature of zone is described through association of measurement with text description. Top direction for zone is in positive direction of cross product of (Azimuth vector X Slip vector). Azimuth is reported using right hand rule based on that tops determination. Dip is positive if slip vector rakes greater than or equal to 0 and less than 90 measured from azimuth direction, dip is negative if slip vector rake is less than 0 and greater than or equal to 90.. Shear zone A sheet-like zone of distributed deformation, lacking an obvious SMR unclassified discrete slip surface, across which less-deformed bodies of rock have been displaced relative to each other. Boundaries are typically gradational at or near the scale of observation.. Shear Zone mylonitic Shear zone that consists of mylonitic rock.. SMR Shear zone cataclastic Shear zone that consists of cataclastic rock. SMR050404 Shear Zone fault gouge Shear zone that consists of gouge.. SMR Shear Zone brecciated Shear zone that consists of breccia. SMR Seam high strain Discrete, thin layer of deformed rock produced by shearing during SMR relative displacement of rocks adjacent to zone. A small-scale fault, generally not mappable at the scale of observation. Has sharp boundaries, as opposed to shear zones, which have gradational boundaries.. Seam mylonite High-strain seam in which the deformed rock within the seam is SMR mylonitic rock.. seam mylonite directed Mylonite seam for which the sense of shear is known. Nature of SMR_DI25DatabaseDevelop foliation is described through association of measurement with rock ment description. Top direction for seam is in positive direction of cross product of (Azimuth vector X Slip vector). Azimuth is reported using right hand rule based on that tops determination. Dip is positive if slip vector rakes greater than or equal to 0 degrees and less than 90 degrees measured from azimuth direction. Dip is negative if slip vector rake is less than 0 degrees and greater than or equal to 90.. Seam cataclasitic rock High-strain seam in which the deformed rock within the seam is SMR cataclasitic rock (cataclasite, breccia, or gouge). Structure not specified Structure not specified; use in descriptions to indicate any structure SMR is allowed.. Igneous structure Geologic structure formed by igneous process. SMR 081303 Irregular discrete Discrete geologic structure formed by igneous process that is not SMR igneous structure characterized by its geometrical orientation in space.. amygdules Vesicle filled with deuteric or secondary mineral. SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert19 54 Miarolitic cavity Irregular cavity, into which subhedral or euhedral crystals project. SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert19 Crystals projecting into miarolitic cavities are generally larger than 54 those of the surrounding rock, often with different composition.. Vesicles Spherical, ovoid, arcuate, or irregular cavities in igneous rock SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert19 formed by expanding gas. 54 DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Discrete linear Linear structure with identity criteria (possible to define entire OverhaulClassificationConcep structure with igneous structure as one object), interpreted to have igneous origin. ts071300 origin Massive Igneous Fabric in ignous rock that does not have a planar or linear SMRNGMDBImplementation1 Fabric character. 23003 intersertal texture Interstices between plagioclase crystals forming framework of an SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert19 igneous rock are filled with glass, cryptocrystalline material, or non- 54 granular deuteric or secondary minerals, such as serpentine, nontronite, chlorite, calcite, zeolite or sodalite.. poikilitic Grains of various minerals in random orientation are completely SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert19 enclosed within large optically consitnuous crystals of different 54 composition.Enclosing crystal is typically anhedral.. graphic texture Quartz is intergrown with alkali feldspar, quartz commonly SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert19 cuneiform, on background of feldspar. A type of poikilitic texture 54BatesJackson1987 larger crystals have a fairly regular geometric outline and orientation. Quartz commonly occupies tirangular areas. Intergrowth may involve other minerals. Ophitic texture Lathes of plagioclase in a matrix of coarse subhedral pyroxene SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert19 such that the feldspar laths appear to be largelo or entirely 54 cnclosed in pyroxene. Length of plagioclase laths is less than diameter of pyroxene grains.. Diktytaxitic texture Abundant, closely spaced, minute, angular cavities between laths SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert19 of feldspar of random orientation; cavities bear no definitie relation 54 th ethe arrangement of enclosing feldspar. Feldspar bordering cavities are of same size and composition as in the areas between the cavities. Felted texture Holocrystalline matrix of rock consists of tightly appressed microlite SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert19 generally of feldspar.. 54 Trachytic texture Felted texture in which microlite is disposed in a sub-parallel, SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert19 aligned manner, and interstices are occupied by mirco or crypto- 54 crystalline material. Myrmekitic texture Minute worm-like or finger like bodies of quartz enclosed in sodic SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert19 plagioclase. 54 Subophitic texture Laths of plagioclase in a matrix of coarse subhedral pyroxene such SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert19 that the feldspar laths appear to be largely enclosed in pyroxene. 54 Length of plagioclase laths is greater than diameter of pyroxene grains.. intergranular texture Framework of feldspar crystals contains ferromagnesian mineral SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert19 grains in angular interstices between crystals. 54 hyaloophitic texture Lathes of plagioclase in a matrix of glass such that the feldspar no tracking record assigned laths appear to be largely or entirely enclosed in glass. Igneous sieve texture Large spongy crystals formed by crystallization from magma that SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert19 contain abundant inclusions. 54 Bostonitic texture Irregular interlocking laths of alkali feldspar arranged in crudely SMR_WilliamsTurnerGilbert19 divertent groups. 54 Foliation primary Penetrative planar fabric interpreted to be the product of igneous SMR igneous processes, formed in the rock while melt was still present.. Flow foliation Foliation defined by features interpreted to be due to flow in a body SMR DisplayName TextDescription Tracking of magma or lava. Includes flow banding in lava, and foliation defined by aligned crystals in a phaneritic igneous rock.. Foliation textural Layering defined by grain size/ grain shape variations resulting SMR layering from crystallization processes in igneous rock, most commonly observed in pegmatite/aplite dikes or bodies, and in Laramide leucogranites of Wilderness suite in Arizona.. Eutaxitic foliation Foliation defined by flattened pumice clasts or glass shards and SMR aligned elongate lithic fragments in a welded tuff. Denotes interpretation that foliation formed during compaction and welding of tuff.. Cumulate foliation Cumulate foliation in igneous rocks, standard on-site measurement SMR of planar foliation, upright. Discrete surface Surface in igneous rock with identity criteria (possible to define OverhaulClassificationConcep igneous structure whole structure as a single object), interpreted to have igeous ts071300 origin, formed in rock while melt was still present.. Dike A sheet-like body of intrusive igneous rock that cuts across bedding SMR102003 base on or foliation (if present) in host rock. Dike is also a kind of BatesJackson1987 degenerate volume geologic surface.. Intermediate dike Dike in which intrusive rock has intermediate composition. SMR Pegmatite dike Dike in which intrusive rock is pegmatite.. SMR Cumulate layer Discrete layers defined by mineral segregations interpreted to be SMR the result of gravitational separation in a magma.. Schlieren Discontinuous surfaces typically defined by concentrations of dark SMR minerals in a granitoid rock; may be delineated by any mineralogical or textural variation, generally curviplanar, discontinuous traces. Sill Sheet like body of intrusive igneous rock that is generally SMR102003 base on concordant to planar structure in host rock. BatesJackson1987 Igneous Flow band Non-penetrative layering in igneous rock interpreted to reflect SMR shearing during flow in melted rock. Lineation igneous Lineation defined by alignment of elongate features; alignment is SMR generic result of flow in lava or magma. Linear feature Super class for linear features indicating transport direction in SMRDI21DataSetSetup indicating transport welded tuff.. direction in welded tuff Lineation igneous Lineation in igneous rock defined by aligned crystals where there is SMR aligned crystal evidence that the crystal alignment is related to deformation before the rock was solidified.. Lineation igneous grain Lineation in an igneous rock, usually welded tuff, defined by no tracking record assigned shape orientation elongate objects in the rock (usually pumice pads, also elongate crystals). Descriptive--elogation may be due to deformation or to rotation/alignment of originally elongate (prolate ellipsoid) objects in the rock.. Geologic unit weathering character terms DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Surface varnish Terminology for specifying degree of development of rock varnish on mattiSedPickList3-051603 terms clasts on an outcrop surface.. moderate varnish Surface of clast is covered with brown, generally dull colored varnish; SMR, based on texture of underlying rock partially to largely obscured; some varnish is MattiSLTTSed050604 dark and shiny.. no varnish Surfaces of clasts show no darkening due to varnish development. SMR, based on MattiSLTTSed050604 slight varnish Surfaces of clasts show incipient development of orange and brown SMR, based on varnish, texture of rock beneath incipient varnish is clearly visible.. MattiSLTTSed050604 intense varnish Surfaces of clasts are completely covered by dark brown to black, SMR, based on generally shiny varnish; texture of underlying rock completely MattiSLTTSed050604 obscured.. Clast weathering Terminology for describing the degree of weathering of the surfaces of mattiSedPickList3-051603 terminology clasts. Clast weathering Terms for distinguishing degree of weathering intensity of clasts in SMR Vocabulary degree terms sedimentary surficial deposits. Classification is based on degree of organization terms weathering of clasts that were originally indurated material. extremely Strongly weathered and fractured to saprolitic-appearing residuum. MattiSedGloss050604; based weathered [Clast] can be completely disaggregated by hand with little difficulty, on Bull, 1991; Melton, 1965 emits punky sound as hammer head sinks into [clast]. unweathered Unweathered except for minor pitting of abrasion surface or incipient MattiSedGloss050604; based oxidation rinds; rings sharply to blow of hammer. on Bull, 1991; Melton, 1965 moderately Substantial weathering indicated by highly pitted surface or strongly MattiSedGloss050604; based weathered developed fractures; ferruginous material may coat sides of fracture on Bull, 1991; Melton, 1965 planes. Calcium-rich plagioclase and/or ferromagnesian minerals generally are strongly altered. [Clast] broken with difficulty by hand, emits dull sound when struck with hammer. slightly Slight weathering characterized by moderate surficial pitting, incipient MattiSedGloss050604; based weathered fracturing, and incipient to moderately developed oxidation rinds; emits on Bull, 1991; Melton, 1965 solid sound when stuck by hammer. Clast weathering Terms for specifying variations in weathering style of clasts on a SMR Vocabulary style terms surface. organization terms Weathering rinds Periphery of clasts is a "rather uniformly thick [zone] of chemical Birkeland, 1999; alteration". Rinds are usually on order of millimeters thick.. MattiSedGloss050604; SMRedits fractured Clasts are cracked and broken across and between constituent SMR based on weathering style particle, but not disaggregated.. MattiSedGloss050604; Webster, 2001 pitted weathing Clast surfaces marked by pits, indentations, depressions, or hollows. MattiSedGloss050604; style Webster, 2001; SMRedits Disaggregated Rock forming clasts separated into component particles.. MattiSedGloss050604; Webster, 2001; SMRedits Etched Corroded by dissolution of surface material. MattiSedGloss050604; Webster, 2001; SMRedits Outcrop Terminology to describe nature of weathered outcrop of a geologic SMR102603OWL weathering terms unit. This is a property of unit, not Earth material, because weathering DisplayName TextDescription Tracking is specific to the location of the unit on Earth. Resistant Consolidated condition of the rock is not modified perceptibly by no tracking record assigned weathering; is not easily broken, disaggregated, or pulverized. Mantled Upper surface of a map unit is mantled with disaggregated residual no tracking record assigned products derived from the rock types in the unit. Cavernous "Chemical and mechanical weathering on a cliff face, in which grains MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 weathering or flakes or rock are loosened so as to enlarge hollows and recesses..... The result is cavernous rock, which is -any rock that has many cavities, cells, or large interstices...resulting from cavernous weathering" Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. 102). Honeycomb Cavernous weathering that consists of innumerable small pits that MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 weathering resemble an enlarged honeycomb. "A type of chemical weathering in which innumerable pits are produced on a rock exposure. The pitted surface resembles an enlarged honeycomb....". Glossary of Geology (Jackson, 1997, p. 303).. Saprolitic An outcrop is modified by extreme weathering that thoroughly no tracking record assigned disaggregates the rock but preserves the coherent structure of the parent material; saprolitic material typically is rich in secondary clay minerals. Friable Consolidated condition of rock is modified enough by weathering that it MattiSetGlossary1.0 060103 crumbles naturally or is easily broken, disaggregated, or pulverized (based on Jackson, 1997, p. 252).
Field metamorphic grade classification DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Not Rock or sediment not metamorphosed. SMR 081303 metamorphosed Metamorphosed Rock is metamorphosed, may have any value for metamorphic grade. SMR 081303 grade not specified very low Rock very slightly metamorphosed, protolith structure ubiquitous; mineral SMR050804; metamorphic grade assemblage of zeolite facies, subgreenschist facies, or low temperature Smulikowski et al, part of blueschist facies. Mineral assemblages according to Fry (1984) 2003; Fry, 1984 Table 10-1: ultramafic-serpentine (quartz, magnesite); mafic-clay, chlorite, relict igneous minerals; calc-aluminous basic-zeolite, pumpellite, epidote, albite; pelite, semi-pelite -- clays, chlorite, sericite, quartz. very high Protolith structures almost always obliterated. Includes rocks SMR050804; metamorphic grade metamorphosed in granulite (or sanidinite), and high-temperature eclogite Smulikowski et al, facies. Mineral assemblages according to Fry (1984) Table 10-1: ultramafic- 2003; Fry, 1984; olivine, enstatite; mafic-hypersthene, diopside (hornblende); calc-aluminous SLTT, 2004 basic-plagioclase; pelite, semi-pelite -- hypersthene + Al-minerals (K- feldspar, quartz), or sapphirine. Medium Protolith structure typically obliterated. Includes rocks metamorphosed in SMR050804; metamorphic grade high-temperature epidote-amphibolite, low-temperature amphibolite, and Smulikowski et al, low temperature eclogite facies. Mineral assemblages according to Fry 2003; Fry, 1984 (1984) Table 10-1: ultramafic-olivine, talc (magnesite, anthophyllite); mafic- hornblende, (diopside, garnet); calc-aluminous basic-plagioclase; pelite, semi-pelite -- white mica, biotite, quartz (garnet, Al-minerals). DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Low metamorphic Metamorphic effects clearly visible, protolith structures typically still SMR050804; grade observable, includes rocks metamorphosed in greenschist, high- Smulikowski et al, temperature blueschist, very low temperature eclogite facies. Mineral 2003; Fry, 1984 assemblages according to Fry (1984) Table 10-1: ultramafic-serpentine (talc, magnesite); mafic-chlorite, actinolite (garnet); calc-aluminous basic- albite, epidote; pelite, semi-pelite -- white mica, chlorite, quartz, biotite (garnet, Al-minerals).. High metamorphic Protolith structures almost always obliterated, evidence of partial melting SMR050804; grade common. Includes rocks metamorphosed in high-temperature amphibolite, Smulikowski et al, pyroxene hornfels, and medium to high-temperature eclogite facies. Mineral 2003; Fry, 1984 assemblages according to Fry (1984) Table 10-1: ultramafic-olivine, anthophyllite, cummingtonite, enstatite; mafic-hornblende, (diopside, garnet); calc-aluminous basic-plagioclase; pelite, semi-pelite -- K-feldspar, biotite, quartz, Al-minerals (garnet), migmatite.
Particle geometry terms. Several vocabularies here for grain size, sorting, roundness, sphericity… DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Particle geometry Collection of vocabularies for describing particle shape and size.. SMRNGMDBImplement description ation123003 vocabulary Particle size terms Complicated because terminology attempts to represent a grain size OverhaulClassificationC distribution as well as the 'mean' grain size. oncepts071300 Grain Discernibility Terms to specify degree to which individiual constituent particles are SMR060104 Terms discernible in a compound material.. Aphanitic Greater than 90% of rock consists of material that is too fine grained SMRPhaneriticAphanitic to discern individual grains with a hand lense. Operationally, the rock is too fine-grained to interpret the genesis or lithology. SLTTm2004 endorsed the The IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks (SCMR) proposal to put the quantititative boundary of 'discernibility' at <0.1 mm (Schmid and others, 2002, Table 5). Such detailed grain size distinctions are impossible in the field, and very difficult under any conditions. Glassy Grains not discernible (<1 % of rock is discernible grains), rock is SMR060104 glassy--no fragmental texture.. Phaneritic Greater than 10% of rock consists of grains large enough to discern SMRPhaneriticAphanitic with hand lense. Operationally, enough of the rock is discernible to interpret the genesis or lithology. Phaneritic and Discernible grains are scattered in a groundmass of undiscernible SMR060104 aphanitic grains. >20% undiscernible grains.. Grain discernibility NGMDB lithology not specified vocabulary Simple grain size Grain size terminology for specifying the modal grain size in a MattiSLTTSed050604;H terms for unimodal, moderately to very well sorted (see Particle size sorting allsworth&Knox, 1999, particulate terminology) bulk sample of grains (rock, sediment, disaggregated based on Wentworth, aggregates rock); basis for determination and confidence level are specified 1922; SMR050604 independently of this term. NADMSC SLTT and BGS both base terminology on size scale proposed by Wentworth, 1922; this usage DisplayName TextDescription Tracking is followed here.. medium grained Modal grain size in described particulate aggregate is between 0.25 MattiSLTTSed050604; and 2 mm; grains are mostly discernible with the unaided eye, Hallsworth&Knox, 1999; mineralogy of many grains can be determined.. Wentworth, 1922 fine grained Modal grain size in described particulate aggregate is between 0.032 MattiSLTTSed050604; and 0.25 mm. Grains require some magnification to be discerned; Hallsworth&Knox, 1999; only general mineralogy can be determined without microscopic Wentworth, 1922 inspection or other laboratory analysis.. very fine grained Modal grain size in described particulate aggregate is less than MattiSLTTSed050604; 0.032 mm; basically rock is too fine grained to discern particles Hallsworth&Knox, 1999; without significant magnification.. Wentworth, 1922 coarse grained Modal grain size in described particulate aggregate is between 2 and MattiSLTTSed050604; 16 mm. Individual mineral grains are easily discernible and can be Hallsworth&Knox, 1999; identified or at least characterized.. Wentworth, 1922 cryptocrystalline Too fine-grained for granular nature to be visible without aid of no tracking record microscope. assigned grain size not Use in descriptions in which the grain size is not specified. In a no tracking record specified normative description, this indicates that grainsize is not a assigned determining factor in rock classfication.. very coarse grained Modal grain size in described particulate aggregate is greater than MattiSLTTSed050604; 16 mm.. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999; Wentworth, 1922 Bimodal grain size Two grain size fractions are prominent in a rock. The terminology is SMR Vocabulary distribution terms the conjunction ('and') of the modal finer grained and modal coarser- organization terms grained fractions.. Aphanitic and Grain size distribution in which some constituents are discernible, SMR phaneritic bimodal and others are not. Example would be a porphyritic rock with an grain size aphanitic groundmass, or a cataclasite with identifiable fragments in an aphanitic matrix.. very fine and Two grain size fractions are prominent in a particulate aggregate, SMR coarse grained one very fine-grained and undiscernible, one with coarse-grained bimodal mode.. very fine and very Two grain size fractions are prominent in a particulate aggregate, SMR coarse grained one very fine-grained and undiscernible, one with very coarse- bimodal grained mode.. very fine and fine Two grain size fractions are prominent in a particulate aggregate, SMR grained bimodal one very fine-grained and undiscernible, one with fine-grained mode.. very fine and Two grain size fractions are prominent in a particulate aggregate, SMR medium grained one very fine-grained and undiscernible, one with medium-grained bimodal mode.. medium and coarse Two grain size fractions are prominent in a particulate aggregate, SMR grained bimodal one medium-grained mode, one with coarse-grained mode.. fine and coarse Two grain size fractions are prominent in a particulate aggregate, SMR grained bimodal one fine-grained mode, one with coarse-grained mode.. coarse and very Two grain size fractions are prominent in a particulate aggregate, SMR coarse grained one coarse-grained mode, one with very coarse-grained mode.. bimodal DisplayName TextDescription Tracking medium and very Two grain size fractions are prominent in a particulate aggregate, SMR coarse grained one medium-grained mode, one with very coarse-grained mode.. bimodal fine and very Two grain size fractions are prominent in a particulate aggregate, SMR coarse grained one fine-grained mode, one with very coarse-grained mode.. bimodal fine and medium Two grain size fractions are prominent in a particulate aggregate, SMR grained bimodal one fine-grained mode, one with medium-grained mode.. grain size range Terms for specifying range of grain sizes present in a bulk particulate SMR terms aggregate; connotes minimum and maximum grain size at 5% and 95% on cumulative frequency plot of grain size distribution.. very fine to fine Size range. no tracking record grained assigned very fine to medium no tracking record grained assigned fine to very coarse no tracking record grained assigned fine to medium no tracking record grained assigned medium to very no tracking record coarse grained assigned fine to coarse no tracking record grained assigned coarse to very no tracking record coarse grained assigned very fine to very Grain size distribution in which particles ranging in size from. no tracking record coarse grained Comment: assigned medium to coarse no tracking record grained assigned very fine to coarse no tracking record grained assigned Sedimentary clast Terms used to specify the size of clasts in a sedimentary rock. More Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, size terms detailed grain size specification than terms for particulate based on Wentworth, aggregates, size class boundaries between coarse and very coarse- 1922; SMR grained has no equivalent boundary in this scheme; other aggregate size terms have corresponding equivalence in this system. These terms denote that all described particles are within the specified size range (within error bounds). Dimensions specified are for longest diameter of particle.. Sand size Particles have longest diameter between 0.032 mm and 2 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR medium sand Particles have longest diameter between 0.25 mm and 0.5 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR very coarse sand Particles have longest diameter between 1 mm and 2 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR DisplayName TextDescription Tracking fine sand Particles have longest diameter between 0.125 mm and 0.25 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR very fine sand Particles have longest diameter between 0.032 mm and 0.125 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR coarse sand Particles have longest diameter between 0.5 mm and 1 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR Gravel size Particles have longest diameter greater than 2.0 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR Pebble size Particles have longest diameter between 4 mm and 64 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR Cobble size Particles have longest diameter between 64 mm and 256 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR small cobble Particles have longest diameter between 64 mm and 128 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR large cobble Particles have longest diameter between 128 mm and 256 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR Boulder size Particles have longest diameter greater than 256 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR small boulder Particles have longest diameter between 256 mm and 512 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR medium boulder Particles have longest diameter between 0.5 m and 2 m. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR large boulder Particles have longest diameter greater than 2 m. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR Granule size Particles have longest diameter between 2 mm and 4 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR Mud size Particle size less than 0.032 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR Silt size Particle size = 0.004 mm and less than 0.032 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR Clay size Particle size less than 0.004 mm. Hallsworth&Knox, 1999, based on Wentworth, 1922; SMR DisplayName TextDescription Tracking Heterogranular Terminology for specifying grain size in poorly to very poorly sorted SMR grain size (see particle sorting terms) bulk sample of grains, or for polymodal distribution terms size distributions not well represented by other terms. This vocabulary does not include terms that are equivalent to terms in the simple grain size terms vocabulary.. sand with gravel Particle size distribution in which gravel-size particles are present, MattiSLTTSed100103; and mud but form less than 30% of aggregate, and sand:mud ratio is greater SMR than 1:1.. sand gravelly Particle size distribution in which gravel-size particles form between MattiSLTTSed100103; 5% and 30% of aggregate, and sand:mud ratio is greater than 9:1.. SMR sand gravelly Particle size distribution in which gravel-size particles form between MattiSLTTSed100103; muddy 5% and 30% of aggregate, and sand:mud ratio is between 1:1 and SMR 9:1. sand slightly Particle size distribution in which gravel-size particles are present, MattiSLTTSed100103; gravelly muddy but form less than 5% of aggregate, and sand:mud ratio is between SMR 1:1 and 9:1. sand slightly Particle size distribution in which gravel-size particles are present, MattiSLTTSed100103; gravelly but form less than 5% of aggregate, and sand:mud ratio is greater SMR than 9:1. fine grained with Particle size distribution in which gravel-size particles are present, MattiSLTTSed100103; gravel but form less than 30% of aggregate, and mud: sand ratio is greater SMR than 1:1.. mud slightly Mud:sand grain-size ratio greater than 9:1 and gravel size particles no tracking record gravelly are present, but form less than 5% of aggregate (from Folk, 1954, assigned Figure 1a). mud slightly Mud:sand grain-size ratio between 1:1 and 9:1 and gravel size no tracking record gravelly sandy particles are present, but form less than 5% of aggregate (from Folk, assigned 1954, Figure 1a). mud gravelly Mud:sand grain-size ratio greater than 1:1 and having between 5% no tracking record and 30% gravel-size particles (from Folk, 1954, Figure 1a). assigned mud and sand For grain size distributions in aggregates that contain no particles MattiSLTTSed100103; without gravel greater than 2 mm in diameter. Classified on triangular plot with SMR sand, silt, and clay size fractions as the three corners.. silt clayey sandy Sediment having between 50% and 10% sand-size particles and a MattiSLTTSed100103; silt:clay grain-size ratio between 2:1and 1:2, as determined by SMR quantitative modal grain-size estimate (from Folk, 1954, Figure 1b). Sand dominant Having less than a trace (0.01%) gravel-size particles and a MattiSLTTSed100103; sand:mud ratio greater than 9:1, as determined by semi-quantitative SMR modal grain-size estimate (from Folk, 1954, Figure 1a).. Clay sandy Sediment having between 50% and 10% sand-size particles and a MattiSLTTSed100103; clay:silt ratio between greater than 2:1 (from Folk, 1954, Figure 1b). SMR Clay size fraction dominant over sand size fraction. sand clayey Having between 90% and 50% sand-size particles and a clay:silt MattiSLTTSed100103; ratio greater than 2:1 (from Folk, 1954, Figure 1b). SMR clay dominant Grain size distribution without gravel, having less than 10 percent MattiSLTTSed100103; sand, in which the clay:silt ratio is greater than 2:1. SMR silt clayey Sediment having less than 10% sand-size material and a silt:clay MattiSLTTSed100103; ratio between 2:1 and 1:2, as determined by quantitative modal SMR DisplayName TextDescription Tracking grain-size determination (from Folk, 1954, Figure 1b). Silt sandy Sediment having between 50% and 10% sand-size particles and a MattiSLTTSed100103; silt:clay ration greater than 2:1 (from Folk, 1954, Figure 1b). SMR sand silty Having between 90% and 50% sand-size particles and a silt:clay MattiSLTTSed100103; ratio greater than 2:1 (from Folk, 1954, Figure 1b). SMR Silt dominant Grain size distribution without gravel, with < 10 percent sand, in no tracking record which silt:clay ration is greater than 2:1. assigned sand muddy Having less than a trace (0.01%) gravel-size particles and a MattiSLTTSed100103; sand:mud grain-size ratio between 1:1 and 9:1, as determined by SMR semi-quantitative modal grain-size estimate (from Folk, 1954, Figure 1a). sand clayey silty Having between 90% and 50% sand-size particles and a silt:clay MattiSLTTSed100103; grain-size ratio between 2:1and 1:2, as determined by quantitative SMR modal grain-size estimate (from Folk, 1954, Figure 1b). gravel with sand Particle size distribution in which gravel-size particles form more than no tracking record and mud 30% of aggregate.. assigned gravel sandy Having between 80% and 30% gravel-size particles and sand:mud MattiSetGlossary1.0 grain-size ratio greater than 9:1, as determined by semi-quantitative 060103 modal grain-size estimate (from Folk, 1954, Figure 1a). Muddy sandy Having between 80% and 30% gravel-size particles and a sand:mud MattiSetGlossary1.0 gravel grain-size ratio between 1:1 and 9:1, as determined by semi- 060103 quantitative modal grain-size estimate (from Folk, 1954, Figure 1a). Muddy gravel Particle size distribution having between 80% and 30% gravel-size MattiSetGlossary1.0 particles and having a mud:sand grain-size ratio greater than 1:1, as 060103 determined by semi-quantitative modal grain-size estimate (from Folk, 1954, Figure 1a). gravel dominant Particle size distribution with greater than 80% gravel-size particles no tracking record with sand or mud present (from Folk, 1954, Figure 1a). assigned Particle size sorting Terms for specifying the grain size distribution in an aggregation of SMR terms particles. sedimentary Terms to quantify the range of particle sizes in a sedimentary SMR, from particle sorting material. Also referred to as particle sorting. Following MattiSLTTSed050604 terms recommendation of NADMSC SLTT, use Inclusive Graphic Standard Deviation (IGSD) proposed by Folk (1968, 1974) as quantitative determinant for sorting terms.. extremely poorly IGSD value (Folk 1968, 1974) (phi units) is greater than 5.0. MattiSLTTSed050604 sorted moderately sorted IGSD value (Folk, 1968, 1974) (phi units) between 0.71 and 1.0. MattiSLTTSed050604 Sorting variable Sorting varies on scale of lithology description. mattiSedPickList3- 051603; SMR050304 moderately to well IGSD value varies between 0.35 and 0.71 on the scale of description SMR, from sorted (e.g. bed to bed variation). MattiSLTTSed050604 poorly to well IGSD value varies between 0.35 and 2.0 on the scale of description SMR, from sorted (e.g. bed to bed variation). MattiSLTTSed050604 poorly to IGSD value varies between 0.71 and 2.0 on the scale of description SMR, from moderately sorted (e.g. bed to bed variation). MattiSLTTSed050604 bimodal clast size Sedimentary rock in which clasts or particle sized are clustered in SMR DisplayName TextDescription Tracking distribution two distinct size ranges.. well sorted IGSD value (Folk, 1968, 1974) (phi units) between 0.35 and 0.5. MattiSLTTSed050604 Grain size distribution in which there is little variation in grain size.. poorly sorted IGSD value (Folk, 1968, 1974) (phi units) between 1.0 and 2.0. MattiSLTTSed050604 moderately well IGSD value (Folk, 1968, 1974) (phi units) between 0.5 and 0.71. MattiSLTTSed050604 sorted very poorly sorted IGSD value (Folk, 1968, 1974) (phi units) between 2.0 and 5.0. MattiSLTTSed050604 very well sorted IGSD value (Folk, 1968, 1974) (phi units) is less than 0.35. MattiSLTTSed050604 Metamorphic grain Terms for specifying grain size distribution in a metamorphic or OverhaulClassificationC sorting terms cataclastic rock.. oncepts071300 bimodal sorting Particles in a metamorphic or catalcastic rock are of two distinctly SMR metamorphic rock different sizes.. porphyroclastic Mineral grains in a cataclastic rock fall into a distinctly finer grain size SMR group and a coarser grain size group; coarser particles are fractured.. porphyroblastic Metamorphic mineral grains formed by metamorphic crystallization or SMR recrystallization are of two distinctly different sizes; larger grains are subhedral to euhedral. Blastogranular Grain sorting term for metamorphic rocks in which volumentrically based on Bates & significant amounts of large paleoblasts (relict grains) are enclosed in Jackson, 1997 a groundmass of smaller neoblasts. Heteroblastic Essential mineral constituents in a metamorphic rock are of widely based on Bates & varying grain size. Jackson, 1997 homeoblastic Metamorphic mineral grains are all of approximately the same size. OverhaulClassificationC oncepts071300 Particle sorting not Particle sorting in an aggregate of particles is not specified in a mattiSedPickList3- specified description; use in normative description to indicate that sorting may 051603 take on any value.. Igneous grain Terms for specifying particle sorting in igneous rocks. OverhaulClassificationC sorting terms oncepts071300 porphyritic Particle size distribution is bimodal or poly modal, with euhedral SMR crystals set in a distinctly finer grained groundmass. equigranular Particles are all of approximately the same size. syn. Homogranular. SMR Heterogranular Grain sorting term for igneous rock in which particles have widely based on Bates & varying sizes. Jackson, 1997 Seriate Grain size term for igneous rock in which particles have a based on Bates & continuously varying range of sizes. Jackson, 1997 Crystal Vocabulary of terms for describing development of crystal faces SMR Vocabulary ShapeTerms bounding particles in a crystalline compond material.. organization terms Cement particle Terms for describing the geometry of crystals forming cement in a SMR Vocabulary geometry terms sedimentary rock. organization terms laminar cement Cement that forms concentric layers, commonly coating and mattiSedPickList3- concentric to mineral grains in the framework. . 051603; SMR050304 bladed cement Cement, typically calcite, consists of intergrown blade-shaped MattiSedPickList082903 crystals, commonly aligned.. fibrous cement Constituent forms cement crystallized with fibrous crystal habit, mattiSedPickList3- DisplayName TextDescription Tracking typically in radiating bundles.. 051603; SMR050304 Laminar geometry Mineral material forming cement in sedimentary rock forms thin, MattiSedPickList082903 deprecated plate-like grains that form layers. Duplicate term, deprecate. ; SMRdeprecate090404 cement grain Constituent forms cement, with cement geometry/fabric unknown.. SMRAdditions geometry unknown fibrous grain Mineral grains in cement have fibrous shape. MattiSedPickList082903 geometry Crystal shape Crystal shape obscured due to subgrain development and grain SLTT_SMR uncertain due to boundary migration during plastic deformation. deformation Crystal Shape Particle shape varies to the point that a single term can not capture SMR variable the variability. Crystal shape not Explicit indication that particle shape is not constrained by a SLTT_SMR specified description. Igneous crystal Shape of particle due to crystallization from melt, compared to ideal SMRNGMDBImplement shape terms crystal shape for mineral phase.. ation123003 euhedral Particles are completely bounded by crystal faces. SMR_WilliamsTurnerGil bert1954 anhedral Particles have no bounding crystal faces. SMR_WilliamsTurnerGil bert1954 subhedral Particles are partly bounded by crystal faces. SMR_WilliamsTurnerGil bert1954 Particle shape Particle shape is uncertain. SLTT_SMR uncertain Metamorphic Terms to describe shape of mineral phases formed by metamorphic SMRNGMDBImplement crystal shape terms crystallization. ation123003 idioblastic Particles are bounded by crystal faces. SMRBaseOnBatesJacks on1987 lepidoblastic Particles have flaky, scaly, plate-like habit. SMRBaseOnBatesJacks on1987 fibroblastic Particles have fibrous habit. SMRBaseOnBatesJacks on1987 nematoblastic Particles have slender prismatic crystal form. SMRBaseOnBatesJacks on1987 xenoblastic A mineral that has grown during metamorphism without deveopment SMRBaseOnBatesJacks of characteristic crystal faces. on1987 diffuse shape Particle boundaries too poorly defined to determine shape. MattiSedPickList082903 Crystal shape Particle shape is obscured by material that has been deposited by SLTT_SMR uncertain due to accretion to grain boundaries, typical in sedimentary rocks during overgrowths diagenesis. Particle roundness Vocabulary of terms for specifying average roundness of some SMRNGMDBImplement terms collection of particles. Roundness is a measure of the sharpness of ation123003 the edges between surfaces bounding a particle (see Jackson, 1997; Wadell, 1932). A grain shape term. Quantitatively defined as the average ratio of the radius of curvature grain corner (intersection of relatively straight edges) to the radius of the smallest circle that will circumscribe the grain for all corners in the silhouette of the DisplayName TextDescription Tracking maximum projection plane of the particle. (Pettijohn et al. 1973, p83). angular subangular Roundness variable on scale of description, ranging from angular to SLTT_SMR subrounded subrounded. Very angular Particles have sharp corners between faces, no evidence of mattiSedPickList3- abrasion. 051603 Well rounded Particle surface has near circular curvature and no corners; original mattiSedPickList3- faces completely obliterated by smoothing of corners.. 051603 Angular Particles have sharp corners between faces; very little or no mattiSedPickList3- evidence of abrasion, numerous secondary corners are present. 051603;Bates&Jackson, 1987; SMR Subangular Roundness variable on scale of description, ranging from SLTT_SMR subrounded subrounded to subangular. subrounded Roundness variable on scale of description, ranging from rounded to SLTT_SMR rounded subrounded. Clast roundness Terms for describing roundness of clasts in sedimentary or SMR Vocabulary terms pyroclastic rocks, or fragments in breccia. organization terms Rounded Original corners have been smoothed to broadly arcuate surfaces, mattiSedPickList3- original faces almost completely removed by abrasion of corners.. 051603;Bates&Jackson, 1987; SMR angular subangular Roundness variable on scale of description, ranging from angular to SLTT_SMR subangular. Subrounded Particle shows considerable but incomplete abrasion, an original mattiSedPickList3- general form is still discernible, and many of its edges and corners 051603;Bates&Jackson, are noticiably smoothed; faces between edges are reduced in size 1987; SMR due to smoothing of corners.. Subangular Sharp angles between faces are somewhat smoothed but still mattiSedPickList3- apparent; shows definite effects of slight abrasion, retains original 051603;Bates&Jackson, form of source particle; faces between corners not significantly 1987; SMR modified by abrasion.. Subangular Roundness variable on scale of description, ranging from rounded to SLTT_SMR subrounded subangular.. rounded Particle form terms Vocabulary to terms for specifying average shape of some collection SMRNGMDBImplement of particles. Sphericity is a measure of the degree to which the shape ation123003 of a particle approximates a sphere (see Jackson, 1997; Wadell, 1932). A grain shape term based on the ratio of lengths of long, intermediate and short axes of grain shape.. particle form Particle form is obscured because of development of new grain SLTT_SMR uncertain due to boundaries by recrystallization, typically during metamorphic recrystallization overprinting. equant particle Compact in Sneed & Folk ( 1958); ratio of S/L is greater than 0.7.. mattiSedPickList3- form 051603 prolate Elongated group in Sneed&Folk, (1958); S/L is less than 0.7 and (L- mattiSedPickList3- I)/(L-S) is greater than 0.66. 051603; Pettijohn et al., 1973; SMR Strongly prolate Very elongated in Sneed&Folk, (1958); S/L is less than 0.3 and (L-I)/ no tracking record (L-S) is greater than 0.66. assigned DisplayName TextDescription Tracking slightly prolate Compact-elongated in Sneed&Folk, (1958); S/L is between 0.5 and no tracking record 0.7 and (L-I)/(L-S) is greater than 0.66. assigned prolate medium Just elongated in Sneed&Folk, (1958); S/L is between 0.3 and 0.5 SMR and (L-I)/(L-S) is greater than 0.66. oblate Platy group in Sneed&Folk, (1958); S/L is less than 0.7 and (L-I)/(L- mattiSedPickList3- S) is less than 0.33. 051603 oblate medium Just platy in Sneed&Folk, (1958); S/L is between 0.3 and 0.5 and (L- no tracking record I)/(L-S) is less than 0.33. assigned Grains slightly Compact-platy in Sneed&Folk, (1958); S/L is between 0.5 and 0.7 no tracking record flattened and (L-I)/(L-S) is less than 0.33. assigned grains strongly Very platy in Sneed&Folk, (1958); S/L is less than 0.3 and (L-I)/(L-S) no tracking record flattened is less than 0.33. assigned bladed particle Bladed group in Sneed&Folk, (1958); S/L is less than 0.7 and (L-I)/ mattiSedPickList3- shape (L-S) is between 0.33 and 0.66. 051603 very bladed S/L is less than 0.3 and (L-I)/(L-S) is between 0.33 and 0.66 no tracking record Sneed&Folk, (1958). assigned compact-bladed S/L is between 0.5 and 0.7 and (L-I)/(L-S) is between 0.33 and 0.66 no tracking record Sneed&Folk, (1958). assigned bladed medium S/L is between 0.3 and 0.5 and (L-I)/(L-S) is between 0.33 and 0.66 no tracking record Sneed&Folk, (1958). assigned Particle geometry For compound material description that do not specify grain size, SMRNGMDBImplement not specified grain sorting, or grain shape.. ation123003