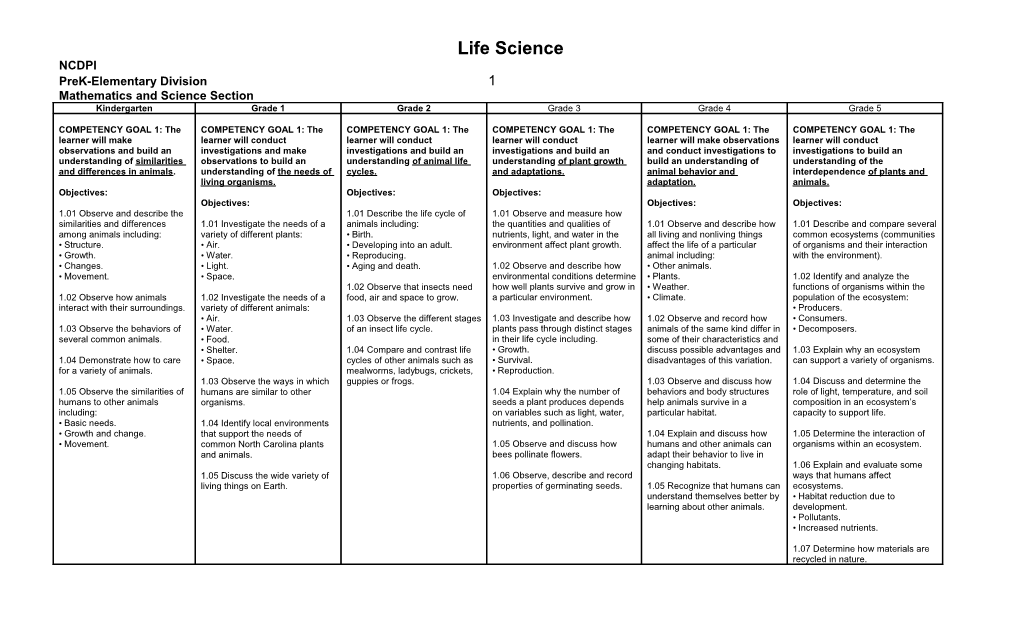
Life Science NCDPI PreK-Elementary Division 1 Mathematics and Science Section Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will make learner will conduct learner will conduct learner will conduct learner will make observations learner will conduct observations and build an investigations and make investigations and build an investigations and build an and conduct investigations to investigations to build an understanding of similarities observations to build an understanding of animal life understanding of plant growth build an understanding of understanding of the and differences in animals. understanding of the needs of cycles. and adaptations. animal behavior and interdependence of plants and living organisms. adaptation. animals. Objectives: Objectives: Objectives: Objectives: Objectives: Objectives: 1.01 Observe and describe the 1.01 Describe the life cycle of 1.01 Observe and measure how similarities and differences 1.01 Investigate the needs of a animals including: the quantities and qualities of 1.01 Observe and describe how 1.01 Describe and compare several among animals including: variety of different plants: • Birth. nutrients, light, and water in the all living and nonliving things common ecosystems (communities • Structure. • Air. • Developing into an adult. environment affect plant growth. affect the life of a particular of organisms and their interaction • Growth. • Water. • Reproducing. animal including: with the environment). • Changes. • Light. • Aging and death. 1.02 Observe and describe how • Other animals. • Movement. • Space. environmental conditions determine • Plants. 1.02 Identify and analyze the 1.02 Observe that insects need how well plants survive and grow in • Weather. functions of organisms within the 1.02 Observe how animals 1.02 Investigate the needs of a food, air and space to grow. a particular environment. • Climate. population of the ecosystem: interact with their surroundings. variety of different animals: • Producers. • Air. 1.03 Observe the different stages 1.03 Investigate and describe how 1.02 Observe and record how • Consumers. 1.03 Observe the behaviors of • Water. of an insect life cycle. plants pass through distinct stages animals of the same kind differ in • Decomposers. several common animals. • Food. in their life cycle including. some of their characteristics and • Shelter. 1.04 Compare and contrast life • Growth. discuss possible advantages and 1.03 Explain why an ecosystem 1.04 Demonstrate how to care • Space. cycles of other animals such as • Survival. disadvantages of this variation. can support a variety of organisms. for a variety of animals. mealworms, ladybugs, crickets, • Reproduction. 1.03 Observe the ways in which guppies or frogs. 1.03 Observe and discuss how 1.04 Discuss and determine the 1.05 Observe the similarities of humans are similar to other 1.04 Explain why the number of behaviors and body structures role of light, temperature, and soil humans to other animals organisms. seeds a plant produces depends help animals survive in a composition in an ecosystem’s including: on variables such as light, water, particular habitat. capacity to support life. • Basic needs. 1.04 Identify local environments nutrients, and pollination. • Growth and change. that support the needs of 1.04 Explain and discuss how 1.05 Determine the interaction of • Movement. common North Carolina plants 1.05 Observe and discuss how humans and other animals can organisms within an ecosystem. and animals. bees pollinate flowers. adapt their behavior to live in changing habitats. 1.06 Explain and evaluate some 1.05 Discuss the wide variety of 1.06 Observe, describe and record ways that humans affect living things on Earth. properties of germinating seeds. 1.05 Recognize that humans can ecosystems. understand themselves better by • Habitat reduction due to learning about other animals. development. • Pollutants. • Increased nutrients.
1.07 Determine how materials are recycled in nature. Life Science NCDPI PreK-Elementary Division 2 Mathematics and Science Section
Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
COMPETENCY GOAL 4: The COMPETENCY GOAL 4: The COMPETENCY GOAL 4: The learner will use appropriate learner will conduct learner will conduct tools and measurements to investigations and use investigations and use increase their ability to appropriate technology to appropriate technology to describe their world. build an understanding of the build an understanding of how form and function of the food provides energy and Objectives: skeletal and muscle systems materials for growth and repair of the human body. of the body. 4.01 Describe how tools can be used to make comparisons. Objectives: Objective
4.02 Observe and describe how 4.01 Identify the skeleton as a 4.01 Explain why organisms various tools and units of system of the human body. require energy to live and grow. measure are useful: 4.02 Describe several functions 4.02 Show how calories can be • Scissors. of bones: used to compare the chemical • Pencils. • Support. energy of different foods. • Crayons. • Protection. • Paper clips. • Locomotion. 4.03 Discuss how foods provide • Hammers. both energy and nutrients for 4.03 Describe the functions of living organisms. 4.03 Use nonstandard units of different types of joints: measure to describe and • Hinge. 4.04 Identify starches and sugars compare objects. • Ball and socket. as carbohydrates. • Gliding. 4.04 Demonstrate the use of 4.05 Determine that foods are standard units of measure and 4.04 Describe how different kinds made up of a variety of compare with nonstandard units of joints allow movement and components: of measure. compare this to the movement of Minerals (Teacher demonstration) mechanical devices. Vitamins Carbohydrates 4.05 Demonstrate that standard 4.05 Observe and describe how Proteins units of measure produce more muscles cause the body to Fats consistent results than move. nonstandard units, allowing information to be shared. (Teacher demonstration)