ALFARABI Private Dental College
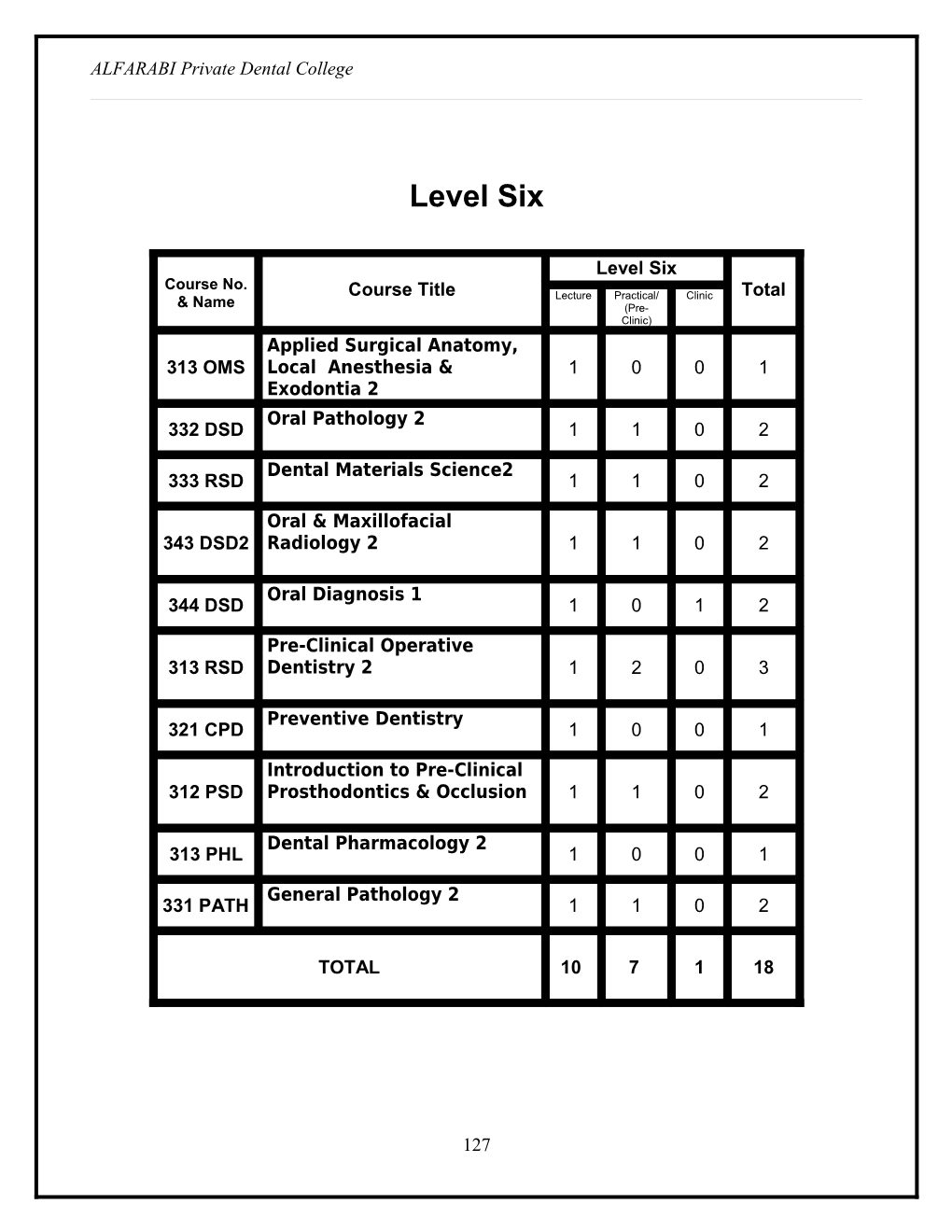
Level Six
Level Six Course No. Course Title Lecture Practical/ Clinic Total & Name (Pre- Clinic) Applied Surgical Anatomy, 313 OMS Local Anesthesia & 1 0 0 1 Exodontia 2 Oral Pathology 2 332 DSD 1 1 0 2
Dental Materials Science2 333 RSD 1 1 0 2
Oral & Maxillofacial 343 DSD2 Radiology 2 1 1 0 2
Oral Diagnosis 1 344 DSD 1 0 1 2
Pre-Clinical Operative 313 RSD Dentistry 2 1 2 0 3
Preventive Dentistry 321 CPD 1 0 0 1
Introduction to Pre-Clinical 312 PSD Prosthodontics & Occlusion 1 1 0 2
Dental Pharmacology 2 313 PHL 1 0 0 1
General Pathology 2 331 PATH 1 1 0 2
TOTAL 10 7 1 18
127 ALFARABI Private Dental College
Level Six Contact Hours Course Course Title Theory Practical Credits No. 313 OMS Applied Surgical Anatomy, Local 1 0 1 Anesthesia and Exodontia 2
Course Description
Introduction:
This course is a series of weekly lectures extending over the semester and formed of the following:
Exodontia [teeth extraction]: which covers sterilization, control of infection, the different methods for extraction [intra-alveolar and trans-alveolar], the used instruments [forceps and elevators], suture types and materials.
Also, it covers indications and contra-indications for teeth extraction, post-operative instructions and follow-up. Lastly, complications which may occur during or after extraction and surgery, how to reduce and manage.
Course Objectives:
The student should be able to:
1. Assess patients for suitability to all minor surgical procedures by taking systematic history, detailed medical history, thorough physical examination and proper use of investigation tools.. 2. Describe the methods and techniques employed to institute infection control- measures, sterilization, asepsis and disinfection.. 3. Describe the indications and contraindications of teeth extraction, and the different techniques and methods used to perform teeth removal.. 4. Describe the intra-alveolar technique and the principles of forceps and elevators use.. 5. Describe the indications for trans-alveolar technique, different designs of surgical flap, the methods employed for bone removal, and the different types of suture material.. 6. Give post-operative instructions and medications when necessary.
Course Contents:
Introduction to Oral Surgery
Patient Evaluation.
128 ALFARABI Private Dental College
Indications and contra-indications for teeth extraction.
Instruments and Armamentarium: Forceps, Parts and types, Elevators, Parts and types.
Intra-alveolar technique: Principles of forceps extraction. Position of the patient and the dentist. The use of the left hand. The use of forceps to move teeth in the upper and lower jaws.
Intra-alveolar technique: Principle of elevators use. Wedge, Lever and Fulcrum and Wheel and Axle.
Trans-alveolar Technique: Indications, design, classification and requirement of muco-periosteal flaps.
Trans-alveolar Technique: Principle of bone removal: burs, chisels, Rongeur. Tooth division, sutures: Types and techniques.
Postoperative instructions and therapeutics: Pack pressure and instructions concerning mouth wash, the use of cold and hot applications. Prescribing analgesics, antibiotics and anti- inflammatory drugs.
Complications of Exodontia: Fracture crown, roots, alveolar process and mandible, Displacement of teeth or roots into the antrum, inferior alveolar canal, the ptyregomandibular space and the infratemporal fossa, Dislocation of the TMJ, Infection, dry socket, Haemorrhage, Nerve affection.
Demonstration of Simple extraction using the video and hands on workshop , using real surgical extraction instruments and articulating model.
Teaching Methodology:
Lectures Assignments
Assessment Tools:
Total Marks = 100 Marks; distributed as follows:
• Student work and attitude 10 Marks • Mid-Term written Exam 30 Marks • Final written Exam 60 Marks
Recommended Books, References & Teaching Materials Required text books: 1. Handbook of Local Anesthesia by Stanley F. Malamed
129 ALFARABI Private Dental College
2. Tooth Extraction: A Practical Guide By Paul Robinson Reference textbook: 1. Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery By Peterson, Ellis, Hupp, Tucker. 4 editions (2003).
Level Six Contact Hours Course No. Course Title Theory Practical Credits 332 DSD Oral Pathology 2 1 1 2
Course Description
Introduction:
This course is offered as a continuation of 331 DSD, which is taught during the first half of the second year. The course is offered as lectures, practical [microscopic] sessions and clinicopathologic conferences [CPC] arranged in such a way that the practical and the CPC sessions are correlated with the subject matter [topics] covered in the didactic lectures.
Course Objectives:
Oral pathology is the specialty of dentistry and pathology which deals with the nature, identification, causes, processes, effect and management of diseases affecting oral and maxillofacial regions.
The course is designed to enable the students to diagnose different diseases using clinical, radiographic, microscopic features as well as biochemical and other analytical methods.
The didactic part is offered with the primary emphasis on diagnosis and differential diagnosis of diseases involving the mouth and the paraoral region.
Add extra credit hour for active learning and sharing in public health programs.
During the semester unscheduled quizzes and student assessment tests will be conducted in order to assess student progress.
The final examination will comprise of written and practical examinations.
Course Contents:
Manifestation of Disease in the Oral Cavity Diagnosis of the most common disease and condition in the oral cavity
130 ALFARABI Private Dental College
Management or treatment of oral disease in the clinic Keratoses and related disorders of oral mucosa
Oral epithelial tumours
Melanocytic naevi and malignant melanoma
Infections of the oral mucosa
Oral ulceration and vesiculobullous diseases
Teaching Methodology:
Classroom Lectures (power point, talking, blackboard) Pre-practical class projection of photomicrographs Laboratory (practical) microscopy / teachers supervision and explanation
Assessment Tools:
Total Marks = 100 Marks; distributed as follows: • Assignment/Homework 20 Marks • Lab. Exam 20 Marks • Mid-Term Exam 20 Marks • Final Exam 40 Marks
Recommended Books, References & Teaching Materials
Required Textbook and Atlas: 1. Oral Pathology Clinical - Pathologic Correlations Regezi, Sciubba & Jordan Latest Edition Sanders Pub.
2. Color Atlas of Oral Diseases, Clinical and Pathologic Correlations Cawson, Binnie, Barret & Wright Latest Edition. Saunders Pub.
Reference Textbook: 1. Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology Neville, Damm., Allen & Bougnot
131 ALFARABI Private Dental College
Latest Edition Saunders
Level Six Course No. Contact Hours Course Title Theory Practical Credits 333 RSD Dental Materials Science 2 1 1 2
Course Description Introduction:
This course continues where RSD 332 left off and logically progresses from direct restorations through indirect restorations. It provides basic information about direct and indirect restorative materials, bonding agents, and the new field of “Adhesive Dentistry.” It provides information about impression materials and gypsum materials. It provides step-by-step information about the casting procedure and the required dental materials. It augments the casting procedure with ceramo-metallic and ceramic materials. The indirect restorations section is completed with a presentation of temporary and permanent dental cements, including the most recent developments with resin cements. The course is completed with information about basic prosthodontic, endodontic, periodontic, and orthodontic materials and with a presentation on dental implant materials, designs, and special considerations.
Course Objectives:
Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Use basic knowledge learned in RSD 131 to describe fundamental strengths and weaknesses of each material, Characterize each material as to its proper selection and intended use, Describe each material’s correct manipulation and the technical considerations for doing so, and List laboratory and/or clinical advantages and disadvantages for each material.
2. Briefly describe any plans for developing and improving the course that are being implemented. (E.g. increased use of IT or web based reference material, changes in content as a
132 ALFARABI Private Dental College
result of new research in the field) - Increased use of Audiovisual aids like models, video, power point presentation, and pictures - Add a credit hour for lab in addition to theory class. - Use Book site & student resources: some useful video, websites, post test questions, quick answer questions
Course Contents:
• Introduction to restorative dental materials : Dental Disease, Replacement of Lost or Missing Teeth, Prevention of Disease and Trauma. • Impression Materials: Alginate Hydrocolloid Impression Material, Alginate Substitute Impression Material, Quick Review. • Impression Materials: Agar Hydrocolloid Impression Material, Elastomeric Impression Materials, Addition Silicone Impression Materials, Polyether Impression Materials. • Impression Materials: Condensation Silicone Impression Materials, Polysulfide Impression Materials, Disinfection of Elastomeric Impressions, Rigid Impression Materials. • Model and Die Materials: Desirable Qualities and Types of Products, Gypsum Products, Expoxy Products. • Waxes: Important Properties of Waxes,Pattern Waxes, Processing Waxes. • Casting Alloys, Wrought Alloys and Solders: Fundamental Concepts about Metals and Alloys, Dental Casting Alloys, Ceramic-bonding Casting Alloys. • Casting Alloys, Wrought Alloys and Solders: Sintered Alloy Composites, Wrought Alloys, Solders, Biocompatibility of Alloys and Solders. • Casting of Dental Alloys : Waxing and Spruing, Investing and Burnout, Casting and Pickling, Finishing and Polishing. • Polymers in Prosthodontics: Polymerization, Complete Dentures, Denture Soft Liners, Acrylic Polymers Combined with Alloys, Polymer Denture Teeth, Other Uses of Polymers in Prosthodontics • Dental Ceramics: Composition and Properties of Dental Ceramics, Ceramic-Alloy Restorations, All-ceramic Restorations. • Dental Implants: Important Principles, Clinical Issues, Implant Materials.
Teaching Methodology:
Lectures Take home assignments Practical
Assessment Tools:
Total Marks = 100 Marks; distributed as follows: • Assignment/Homework 20 Marks • Lab. Exam 20 Marks
133 ALFARABI Private Dental College
• Mid-Term Exam 20 Marks • Final Exam 40 Marks
Recommended Books, References & Teaching Materials
All reading assignments will be from the required textbooks:
1. Dental Materials and their Selection, Third Edition edited by William J.O’Briend, 2002. 2. Restorative Dental Materials, 11th edition edited by Robert G. Craig and John M. Powers, 2002.
Level Six Contact Hours Course Course Title Theory Pre-Clinical Credits No. 343 DSD2 Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology 2 1 1 2
Course Description
Introduction:
This course designed to give the students basic cognitive knowledge of the principals, concepts of radiography and interpretation of radiographs.
Course Objectives:
• Ability to understand the discovery of radiation. • Ability to recognize the specific properties of x-ray. • Ability to recognize the advanced modalities in radiology science. • Ability to recognize the harmful effect of x-ray. • Ability to recognize the methods of protection from radiation. • Ability to describe lesion from radiograph. • Ability to make differential diagnosis.
Course Contents:
• Introduction • Anatomical landmarks. • Extra oral technique.
134 ALFARABI Private Dental College
• Radiation Biology • Panoramic radiography. • Methods of Interpretation. • Inflammatory jaw lesions. • Digital radiography.
Teaching Methodology:
Lectures
Practical Sessions
Assessment Tools:
There will be two continuous assessments during the semester, covering material from reading in the textbook, lectures and practical sessions. Students are encouraged to discuss the answers of questions in the exams in groups as an aid for understanding and learning the material in their radiology course.
Total Marks = 100 Marks; distributed as follows: • Assignment/Homework 20 Marks • Lab. Exam 20 Marks • Mid-Term Exam 20 Marks • Final Exam 40 Marks
Recommended Books, References & Teaching Materials
1. Oral Radiology Principles and Interpretation. 5th Edition. By White and Pharoh (2004)
2. Dental Radiography, Principles and Techniques. 2nd Edition. By Joen Haring and Laura Jansen.
135 ALFARABI Private Dental College
Level Six Contact Hours Course Course Title Theory Clinical Credits No. 344 DSD Oral Diagnosis 1 1 1 2
Course Description
Introduction:
The course is designed to expose the dental student to basic knowledge and skills that are involved in the diagnostic process and treatment planning in dental practice. The training would enable the student to effectively communicate with the patients, interview them and carry out a general appraisal and a detailed and systematic examination of the extra-oral and intra-oral structures. The course is offered through lectures and clinical practice during the second semester.
Lectures will provide adequate information on the various steps involved in the interviewing process, clinical methods and on relevant aspects of the diagnostic tools employed and treatment planning. Clinical practice in the clinics will closely follow the lecture schedule. Students in pairs will practice on each other all the steps involved. During the semester unscheduled quizzes and two student assessment tests will be conducted in order to assess student progress. The final examination will comprise of written and practical examinations.
Course Objectives:
136 ALFARABI Private Dental College
By the end of the semester student should be able to:
1. Communicate with the patient effectively. 2. Take general and oral health history and ask appropriate questions based on the signs & symptoms. 3. Perform extra- oral and intra-oral examination thoroughly and systematically. 4. Order or do the diagnostic procedures as required. 5. Recognize any abnormality in oral and peri-oral tissues and describe them. 6. Recognize the need for medical or/and dental referral or consultation. 7. Develop a treatment plan for the patient.
Course Contents:
Introduction / Diagnostic Method Infection Control Patient History Methods of Clinical Examination Physical Assessment Extra-oral Examination Intra-oral Examination Examination of Teeth Examination of Periodontium Examination of Occlusion and Edentulous Mouth Radiographic Examination Treatment Plan Supplementary Examination Clinical Signs of Disease
Teaching Methodology:
Lectures Clinical & Practical Sessions Practicing Clinical Examination with Fellow Students
Assessment Tools:
Total Marks = 100 Marks; distributed as follows: • Student’s Practical Work 30 Marks
137 ALFARABI Private Dental College
• Final Practical Work 20 Marks • Mid-Term Exam 15 Marks • Final Written Exam 35 Marks
To obtain a passing grade, the student must have a final cumulative score of 60%.
Recommended Books, References & Teaching Materials
Required textbooks Principles of Oral Diagnosis: Gary C. Coleman John F. Nelson 1st Ed (1993) Reference Book: Oral Diagnosis, Oral medicine & Treatment Planning: Steven L. Bricker, Robert P. Langlais, Craig S. Miller. 2nd Ed (1999)
Level Six Contact Hours Course Course Title Theory Practical Credits No. 313 RSD Pre-Clinical Operative Dentistry 2 1 2 3
Course Description
Introduction:
This course consists of two main components, the principles of cavity preparations for the currently available restoratives and their physical and manipulative characteristics and cavity restoration. They are provided by the RSD Department during the two semesters of the second year of the dental program. It is a 1+2+0, equivalent to 3 credit hours course.
Course Objectives: 1. The primary objectives of this course is to present the basic principles, techniques and rational of operative procedures and apply them. 2. Present a step-by-step procedure for each cavity preparation and cavity restoration. 3. Train the students in different operations (cavity preparation and restoration) by doing specific standardized exercises on Typodont Models mounted on mannequins. 4. Train the students in these operations in a situation similar to the clinical set-up. 5. Train students to recognize their own mistakes, and how to correct them.
Upon completion of the Lecture portion of this course, the student should be able to: 1) Determine the factors under consideration when deciding whether to restore posterior teeth with composite.
138 ALFARABI Private Dental College
2) Describe the main types of glass ionomer cements and the advantages and disadvantages of each of the materials. 3) Understand the appropriate application of bases and liners beneath dental restorations and the purpose of those procedures. 4) Describe the indications of complex amalgam restorations and selection of type of retention either pin retained or pinless retained amalgam. 5) Differentiate between indications of cast gold inlay and onlay and how to make each one. 6) Understanding the types of indirect esthetic restorations, indications of each.
Upon completion of the Laboratory portion of this course, the student should be able to:
1) Adequately prepare the posterior tooth for composite restoration . 2) Learn to apply bases and liners under dental restoration. 3) Describe, prepare, place, finish and polish restorations for:
a) Slot-preparations b) Class II composite c) Class I amalgam d) Class II amalgam e)cusp reduction and capping with amalgam
4)learn how to prepare the tooth for cast gold inlay and onlay and fabricating provisional restorations
Course Contents:
Glass Ionomer Cement (Material and Clinical Manipulation). Resin Modified Glass Ionomer and Compomers. Pulp Protection by the Use of Insulating Bases and Liners. Introduction to the Complex Amalgam Restoration . Pin-retained Complex Amalgam Cavity Preparation. Pinless-retained Complex Amalgam Preparation . Restorative Technique of Complex Amalgam Restoration. Tooth Preparation for Cast Gold Inlay and Onlay Restorations. Indirect Posterior Esthetic Restorations. Failure of Restoration. Biological Influence of Restorative Procedures and Materials.
Teaching Methodology:
Lectures
Pre-Clinical and Practical Sessions
Assessment Tools:
139 ALFARABI Private Dental College
Total Marks = 100 Marks; distributed as follows: • Assignment/Homework 20 Marks • Lab. Exam 20 Marks • Mid-Term Exam 20 Marks • Final Exam 40 Marks
Evaluation Methods:
All preparations and restorations listed on the progress sheet will be approved and graded by the designed instructor. All timed practical exercises will be completed during assigned laboratory periods.
Written examinations will be based on the LECTURE MATERIAL; HAND-OUTS, READING ASSIGNMENT, PRINT-OUT and information given during lab sessions.
Recommended Books, References & Teaching Materials
1. Sturdevant’s Art and Science of Operative Dentistry, 4th edition 2002 2. Baum, Phillips and Lund.. Textbook of Operative Dentistry, 3rd edition 1995. 3. Pickard’s Manual of Operative Dentistry 7th edition 2000. 4. Schwartz et al. Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry- a contemporary approach, 2nd edition 2001. 5. Hand-outs (if needed)
140 ALFARABI Private Dental College
Level Six Contact Hours Course Course Title Theory Practical Credits No. 321 CPD Preventive Dentistry 1 0 1
Course Description
Introduction:
To provide dental students with an understanding of concepts, principles and methods of prevention of dental diseases with emphasis or primary preventive measures.
Course Objectives:
At the end of the course, the students should understand the following:
Basic concepts and principles of preventing dental diseases. Factors involved in the causation of dental caries and periodontal diseases. Different measures for primary prevention of the common dental diseases (dental caries and periodontal diseases).
Course Contents:
Introduction to Preventive Dentistry Concepts and Principles of Preventive Dentistry
141 ALFARABI Private Dental College
Development of Dental Plaque and its Role in Oral Disease Development Common dental diseases (Dental Caries and Periodontal Disease) Plaque Control Measures (Mechanical and Chemical) The Use of Fluoride Therapy Pit and Fissure Sealants Caries Susceptibility Tests Effect of Diet and Nutrition on Oral Health and Dental Caries Dental Public Health Programs
Teaching Methodology:
- Theoretical approach through lectures and discussion. - Practical through the demonstration of some primary preventive procedures.
Assessment Tools:
Total Marks = 100 Marks; distributed as follows: • Student work and attitude 10 Marks • Mid-Term written Exam 30 Marks • Final written Exam 60 Marks
Recommended Books, References & Teaching Materials
Required Reading : Primary Preventive Dentistry, 5th Edition By: Norman O. Harris, Franklin Garcia-Godoy
142 ALFARABI Private Dental College
Level Six Contact Hours Course Course Title Theory Practical Credits No. 312 PSD Introduction to Pre-Clinical 1 1 2 Prosthodontics & Occlusion
Course Description
Introduction:
This is the first course in Prosthodontics. It consists of didactic and practical components. It has two parts: (1) is introductory to prosthodontics in the form of lectures, and (2) the practical components covering some of the basic technical aspects in prosthodontics. The second part for Patient Simulation Clinic (PSC) is introductory to occlusion, and is designed to provide the students with a basic knowledge concerning the static and dynamic aspects of occlusion and the importance of occlusion for all facets of dentistry. The laboratory phase of this course is a coordinated effort in helping the basic technical skills in prosthodontics and occlusion.
Course Objectives:
1. The primary goal of this course is to familiarize the student with the biological and technical aspects of prosthodontic in general, dental anatomy and occlusion in particular. 2. The student should demonstrate abilities of understanding and using different prosthodontic terminologies. 3. The student should demonstrate the abilities and skills to do all the assigned laboratory procedures. 4. The student should be able to illustrate the basic knowledge and skills of how to examine and
143 ALFARABI Private Dental College
analyze occlusion.
Course Contents:
Introduction to Prosthodontics Oral Anatomy in Relation to Complete Dentures Construction Principles for Complete Denture Prosthodontics Stock Impression Trays, and Construction of Casts Mandibular Positions and Jaw Relations. Introduction to Articulators Arrangements of Anterior and Posterior Teeth Complete Denture Wax-up and Flasking Procedure Denture Repairs Components and Functions of a Removable Partial Dentures Surveying of partially Edentulous Casts Abutment Teeth Preparation Direct and Indirect Retainers Laboratory Procedures of making a Conventional Removable Partial Dentures Denture Base and Teeth for Removable Partial Dentures
Teaching Methodology:
Lectures Practical Sessions
Assessment Tools: Total Marks = 100 Marks; distributed as follows: • Assignment/Homework 20 Marks • Lab. Exam 20 Marks • Mid-Term Exam 20 Marks • Final Exam 40 Marks
Recommended Books, References & Teaching Materials
Textbook: Gross, M. D. Occlusion in Restorative Dentistry, Technique and Theory, Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, 1982.
Supplementary references : Owall, Kayser, and Carlsson. Prosthodontics, Principles and Management Strategies. Mosby-Wolf 144 ALFARABI Private Dental College
1996. Phoenix, Cagna, and DeFreest. Stewart’s Clinical Removable Partial Prosthodontics. Quintessence Publishing Co, 2003 (third edition). Shllingburg, Hobo, Whitsett, Jacobi, and Brackett. Fundamentals of Fixed Prosthodontics. Quintessence Publishing Co, 1997 (third edition). Handouts by different lecturers.
Level Six Contact Hours Course No. Course Title Theory Practical Credits 313 PHL Dental Pharmacology 2 1 0 1
Course Description
Introduction:
This course presents the basic principles of pharmacology including the pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, adverse, reactions, and contra-indications of selected drug groups. Emphasis will be placed on those drug groups especially relevant to dental practice including anti-infectives, antibiotics and anti- viral drugs. In addition, the most common classes of drugs the dental patient is taking in the management of common diseases and disorders will be covered, Anti-microbial and chemotherapeutic agents, Analgesics, Glucocorticoids, Drugs acting on hard and soft tissues of the mouth and Drugs acting on Gl and respiratory systems
Course Objectives:
• Ability to understand general principles in pharmacology • Ability to clearly understand how to use analgesic drugs
• Ability to clearly understand antivirus drugs
• Ability to clearly understand antifungal drugs
• Ability to emphasis on pharmacological actions and therapeutic applications of drugs used or
145 ALFARABI Private Dental College
implicated in dentistry.
Course Contents:
Antimicrobial drugs: General consideration Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory, Antipiretics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Antifungal drugs Antiviral drugs Anthelmintic drugs Drug acting on nervous system: Sedative–hypnotics, antiepliptics and antiparkinsonian drug Psychopharmacological agents and antihistaminics Cardiovascular drugs: Drugs for the management of hypotension and hypertension, Heart failure /arrhythmia Cardiovascular drugs: Anticoagulants, antiplatelet and hematinic Drug acting on kidney General Anaesthesia and skeletal muscle relaxant Local Anaesthesia Glucocorticoids
Teaching Methodology:
Lectures Assignments
Assessment Tools:
Total Marks = 100 Marks; distributed as follows: • Student work and attitude 10 Marks • Mid-Term written Exam 30 Marks • Final written Exam 60 Marks
Recommended Books, References & Teaching Materials
Textbooks:
Title : Pharmacology and Therapeutics for Dentistry Author: Neidle, Enid A., and Yagiela, John A. Publisher: Mosby
146 ALFARABI Private Dental College
Level Six Contact Hours Course Course Title Theory Practical Credits No. 331 PATH General Pathology 2 1 1 2
Course Description
Introduction:
This course will provide the student with the general concept of pathophysiology. That will be discussed with appropriate references to the general pathological process due to injury and diseases. Organ systems and diseases relevant practice are studied in details to establish a sound foundation for clinical practice. A significant part of coursework involves microscopic study of tissue specimens.
Course Objectives:
The aim of this program is to provide the postgraduate student with the advanced medical knowledge and skills essential for the mastery of practice of pathology and necessary to provide further training and practice in the field of pathology through providing:
1. Recent Scientific knowledge essential for the mastery of practice of pathology according to the international standards. 2. Skills necessary for proper processing and diagnosis of submitted tissue specimens including problem solving and decision-making skills. 3. Ethical principles related to handling tissue specimens of the patients.
147 ALFARABI Private Dental College
4. Active participation in community needs assessment and problems identification. 5. Maintenance of learning abilities necessary for continuous medical education. 6. Maintenance of research interest and abilities.
Course Contents:
Ischemia and infarction. Cellular adaptation General aspects of neoplasia Common specific tumours. Diseases of oral cavity and Salivary Glands Common diseases of bones. Diseases of red blood cells Diseases of white blood cells
Teaching Methodology:
Lectures Practical sessions
Assessment Tools:
Students will have mid-course exam up of written paper. At the end of the course students will have practical and written exam.
Total Marks = 100 Marks; distributed as follows: • Assignment/Homework 20 Marks • Lab. Exam 20 Marks • Mid-Term Exam 20 Marks • Final Exam 40 Marks
Recommended Books, References & Teaching Materials
1. Required Text(s) Essential Pathology for Dental Students 3rd Edition 2- Electronic Materials, Web Sites etc 3- Other learning material such as computer-based programs/CD, professional standards/regulations
148 ALFARABI Private Dental College
149