Name ___Answer Key_____ Period ______Date ______
Healthy Environment What is your favorite room in your house? Why?
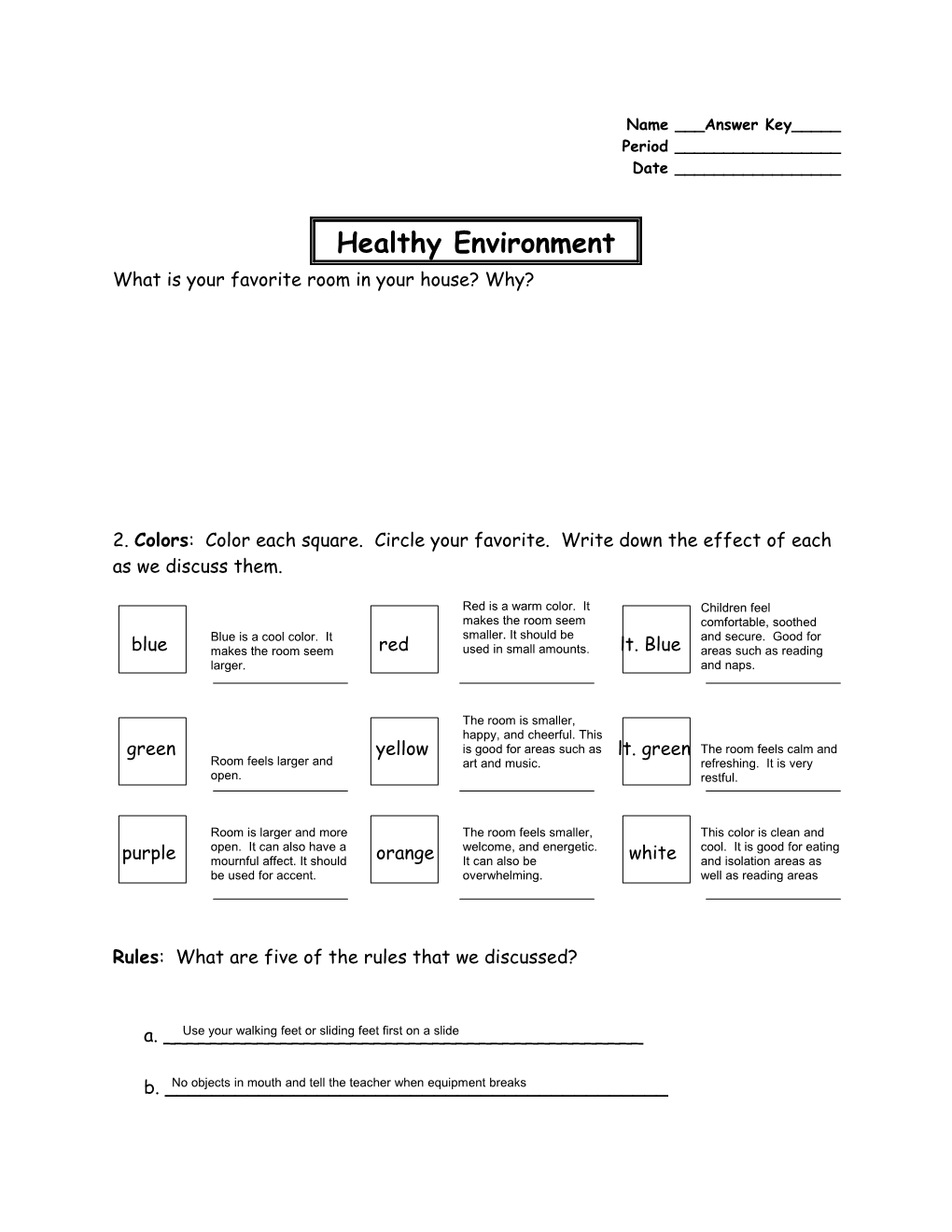
2. Colors: Color each square. Circle your favorite. Write down the effect of each as we discuss them.
Red is a warm color. It Children feel makes the room seem comfortable, soothed Blue is a cool color. It smaller. It should be and secure. Good for blue makes the room seem red used in small amounts. lt. Blue areas such as reading larger. and naps.
The room is smaller, happy, and cheerful. This green yellow is good for areas such as lt. green The room feels calm and Room feels larger and art and music. refreshing. It is very open. restful.
Room is larger and more The room feels smaller, This color is clean and open. It can also have a welcome, and energetic. cool. It is good for eating purple mournful affect. It should orange It can also be white and isolation areas as be used for accent. overwhelming. well as reading areas
Rules: What are five of the rules that we discussed?
a. ______Use your walking feet or sliding feet first on a slide
b. ______No objects in mouth and tell the teacher when equipment breaks c. ______Cover your mouth when you cough or sneeze
Use blocks for building, not for hitting d. ______
Wash hands before and after eating and using the toilet e. ______
Other Examples: Contact parents when an unknown person comes to pick up a child, going in the same direction for tricycles, children should not be left unattended, children shouldn’t have small objects in mouths, watch carefully with activities having to do with water, sit on the swings—not stand, cover your mouth when cough and sneeze, use blocks for building, not for hitting, wipe up spills right away, wash your hands before eating and after toileting, tell teacher when equipment breaks. See list in Book “Working With Children”, pg149)
Hazards: Write down the seven hazards that you find around the room.
1. Cords hanging off the edge of things
2. Plant sitting out on the table
3. A blank card without the emergency numbers
4. Toys on the floor
5. Dirty toys out
6. Dirt on the floor
7. Cleaning supplies out where the kids can reach
Others: pushpins out, cords from blinds hanging, marbles on floor, tools out, chairs stacked up on table. 5. Basic Activity Areas What activities are done in each area?
Active
Block building, dramatic play, and music
Wet Dry
Art area, woodworking, sensory, science Manipulative, eating
Quiet Sleeping, reading (literacy), private space
6. Purposes of Various areas: Block-building: Give children practice sorting, grouping, comparing, arranging, making decisions, cooperating, and role-playing. Best location: carpeted area. Art area: near a water source. Arranged so that groups or individuals can use it. Label shelves. Dramatic Play: a.k.a. home-living or housekeeping area. Looks like real home. Stove, fridge, table, chairs, sink and doll bed. Sensory: sensory table (water or sand table) should be near water source. Other items may also be placed in the area (shovels, etc.) Wood working: near art area for painting after building. Place it outside of traffic. Sleeping Area: Most preschool kids nap after lunch. If no separate area, then keep room arrangements flexible Small Manipulative: Dry, quiet place. Table blocks, puzzles, plastic building pieces, stringing beads, sewing cards, and color cubes are some items. Table, chairs are also useful. Library: located in the quietest part of the room. Often next to the manipulative area. Books and magazines. Music: Rhythm instruments, cassette players, and audio tapes are found here. Private Space: where kids can be alone. Should be small. 7. Other important facts to remember: Arrange areas around the edges. Store objects together that are used for the same activities, store objects together that are used for the same activities, place the art area near a water source, place quiet activities far away from active activities, place dry activities far from wet activities, provide open space for block-building and group activities, Provide a private space where children can be alone. 8. Immunizations for Preschool Children
Age Immunization
2 Months Oral Polio, DTP, and HbCV
Oral Polio, DTP, and HbCV 4 Months
DTP and HbCV 6 Months
Oral Polio; Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR); and HbCV 12-15 Months
DTP (booster) 15-18 Months
Oral Polio and DTP (booster) 4-6 Years
Note: HbCV= haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine. It provides protection against bacterial infections. DTP= Diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (whooping cough)