IB Math SL – year 2 - What is a histogram?
The histogram is a ______showing a count of how the data points fall in various ranges. A histogram is used when the data to be represented is ______.
The groups of data are called ______or ______, because one can think of them as containers that hold the data and get "filled up." A frequency table, which shows ______a test score occurred, helps us draw a histogram.
Consider the exam scores of a group of students.
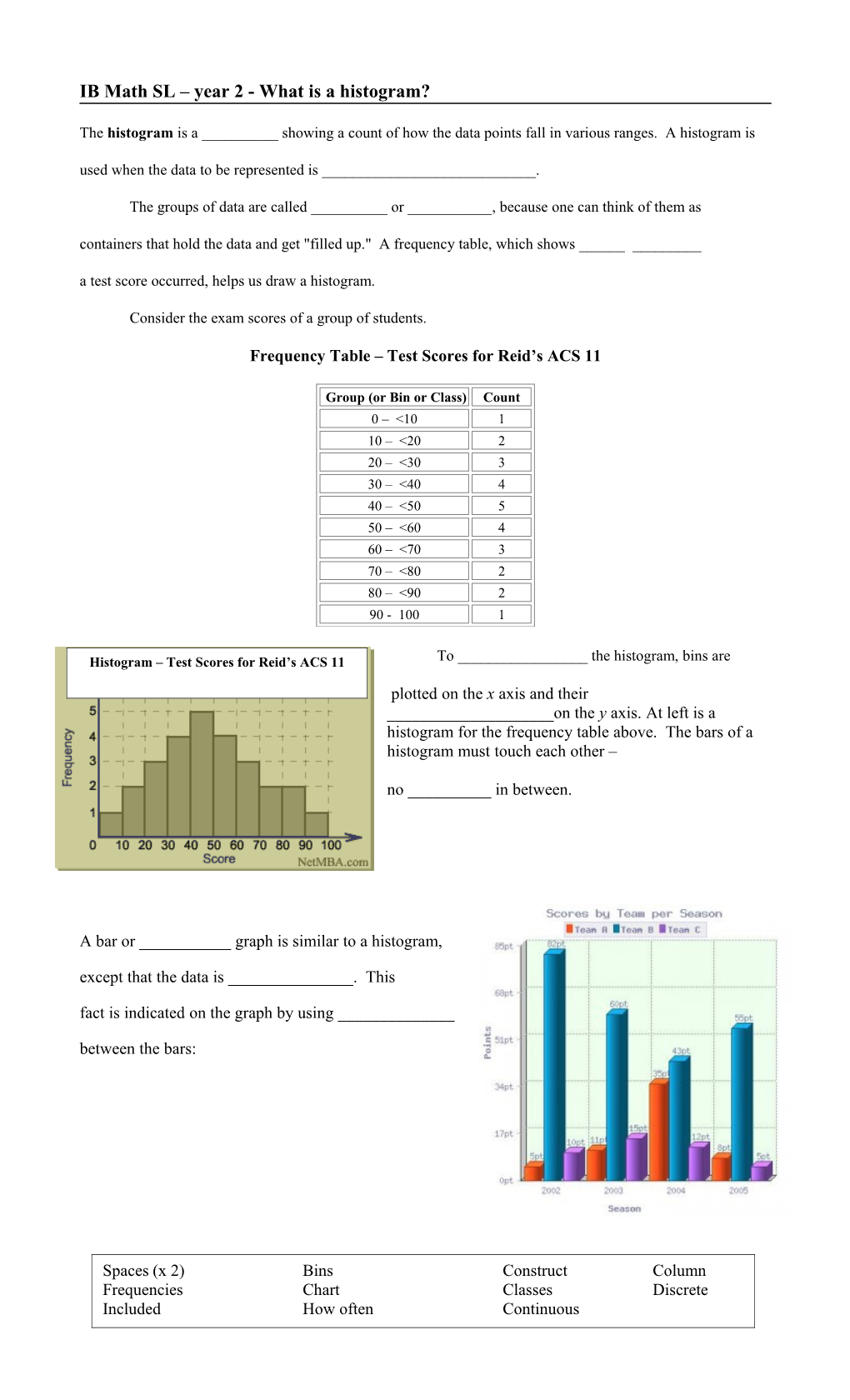
Frequency Table – Test Scores for Reid’s ACS 11
Group (or Bin or Class) Count 0 – <10 1 10 – <20 2 20 – <30 3 30 – <40 4 40 – <50 5 50 – <60 4 60 – <70 3 70 – <80 2 80 – <90 2 90 - 100 1
Histogram – Test Scores for Reid’s ACS 11 To ______the histogram, bins are plotted on the x axis and their ______on the y axis. At left is a histogram for the frequency table above. The bars of a histogram must touch each other –
no ______in between.
A bar or ______graph is similar to a histogram, except that the data is ______. This fact is indicated on the graph by using ______between the bars:
Spaces (x 2) Bins Construct Column Frequencies Chart Classes Discrete Included How often Continuous Create a histogram to create one for this data:
The following data represents the number of games each of CP Allen’s sports teams won this year: 7, 15, 24, 4, 4, 29, 36, 4, 7, 6, 18, 25, 32, 17, 5, 4, 28, 30, 35
Range and number of bins Tally and frequency chart
Number of teams (frequency)
Number of games won
Frequency Polygon - CP Allen Sports team performance
6 What about a frequency polygon? 5 s m
a 4
A frequency polygon is almost the same thing as a e t
f o histogram: you still do a tally chart, and create a graph. 3 r e However, instead of drawing bars, you place dots in the b m 2 u
middle of each bin and then connect the dots with a line: N 1
0 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 Number of games won
What is obvious from a histogram: What is not obvious on a histogram The distribution (spread) of the data The mean The range (lowest to highest) The median The class/bin where the mode falls (the If there were any outliers modal class) How many data points there were in total (not including outliers)