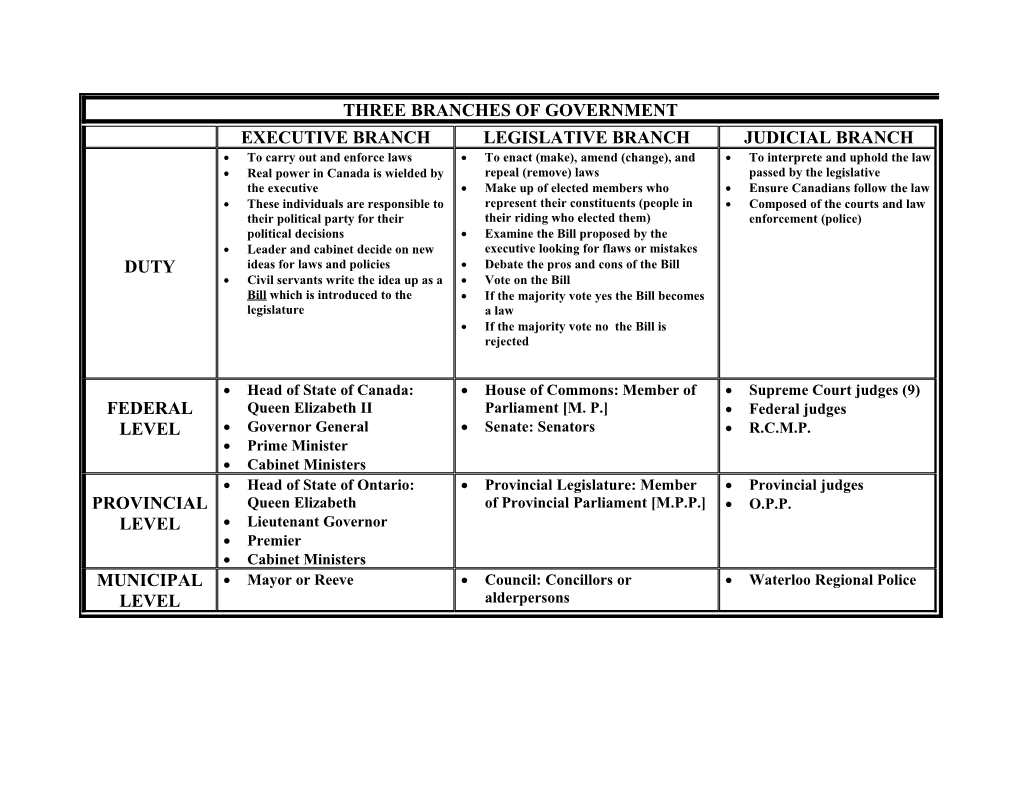
THREE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT EXECUTIVE BRANCH LEGISLATIVE BRANCH JUDICIAL BRANCH To carry out and enforce laws To enact (make), amend (change), and To interprete and uphold the law Real power in Canada is wielded by repeal (remove) laws passed by the legislative the executive Make up of elected members who Ensure Canadians follow the law These individuals are responsible to represent their constituents (people in Composed of the courts and law their political party for their their riding who elected them) enforcement (police) political decisions Examine the Bill proposed by the Leader and cabinet decide on new executive looking for flaws or mistakes DUTY ideas for laws and policies Debate the pros and cons of the Bill Civil servants write the idea up as a Vote on the Bill Bill which is introduced to the If the majority vote yes the Bill becomes legislature a law If the majority vote no the Bill is rejected
Head of State of Canada: House of Commons: Member of Supreme Court judges (9) FEDERAL Queen Elizabeth II Parliament [M. P.] Federal judges LEVEL Governor General Senate: Senators R.C.M.P. Prime Minister Cabinet Ministers Head of State of Ontario: Provincial Legislature: Member Provincial judges PROVINCIAL Queen Elizabeth of Provincial Parliament [M.P.P.] O.P.P. LEVEL Lieutenant Governor Premier Cabinet Ministers MUNICIPAL Mayor or Reeve Council: Concillors or Waterloo Regional Police LEVEL alderpersons