ECG SUMMARY
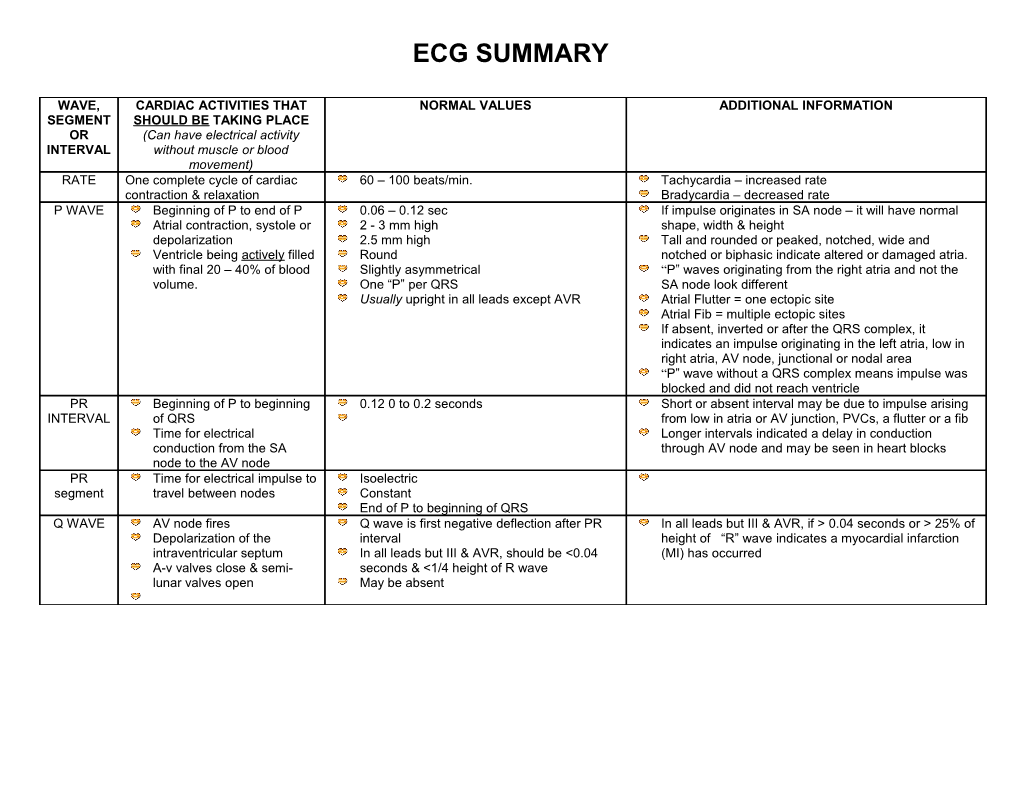
WAVE, CARDIAC ACTIVITIES THAT NORMAL VALUES ADDITIONAL INFORMATION SEGMENT SHOULD BE TAKING PLACE OR (Can have electrical activity INTERVAL without muscle or blood movement) RATE One complete cycle of cardiac 60 – 100 beats/min. Tachycardia – increased rate contraction & relaxation Bradycardia – decreased rate P WAVE Beginning of P to end of P 0.06 – 0.12 sec If impulse originates in SA node – it will have normal Atrial contraction, systole or 2 - 3 mm high shape, width & height depolarization 2.5 mm high Tall and rounded or peaked, notched, wide and Ventricle being actively filled Round notched or biphasic indicate altered or damaged atria. with final 20 – 40% of blood Slightly asymmetrical “P” waves originating from the right atria and not the volume. One “P” per QRS SA node look different Usually upright in all leads except AVR Atrial Flutter = one ectopic site Atrial Fib = multiple ectopic sites If absent, inverted or after the QRS complex, it indicates an impulse originating in the left atria, low in right atria, AV node, junctional or nodal area “P” wave without a QRS complex means impulse was blocked and did not reach ventricle PR Beginning of P to beginning 0.12 0 to 0.2 seconds Short or absent interval may be due to impulse arising INTERVAL of QRS from low in atria or AV junction, PVCs, a flutter or a fib Time for electrical Longer intervals indicated a delay in conduction conduction from the SA through AV node and may be seen in heart blocks node to the AV node PR Time for electrical impulse to Isoelectric segment travel between nodes Constant End of P to beginning of QRS Q WAVE AV node fires Q wave is first negative deflection after PR In all leads but III & AVR, if > 0.04 seconds or > 25% of Depolarization of the interval height of “R” wave indicates a myocardial infarction intraventricular septum In all leads but III & AVR, should be <0.04 (MI) has occurred A-v valves close & semi- seconds & <1/4 height of R wave lunar valves open May be absent WAVE, SEG. OR CARDIAC ACTIVITIES THAT SHOULD BE NORMAL VALUES ADDITIONAL INFORMATION INTERVAL TAKING PLACE QRS COMPLEX Ventricles completely depolarize Usually 0.06 – 0.12 seconds >0.12 seconds indicates ectopic foci or Lubb - First (S1) heart sound 5 – 30 mm high intraventricular conduction defect Begins at first positive or negative Large QRS may be seen with PVCs, deflection after PR interval ventricular tachycardia, bundle branch block, Ends where last wave of complex pacemakers, premature atrial contractions transitions into ST segment (J point) with aberrant conduction, agonal or Upright in Lead I, II & III, AVL, AVF, idioventricular rhythm V4 & V6 There are usually two negative deflections (Q Usually inverted AVR and V1 to V3 & S) but one can be missing May be biphasic in Leads III, V2 to V4 Q-T INTERVAL Measure in lead with largest amplitude T Shortens as heart rate increases Prolonged in hypokalemia and hypocalcemia wave With normal rate of 60 – 100 it Prolonged QT interval indicates a prolonged Beginning of QRS to end of T wave should be ½ the distance between refractory period (vulnerable period) and puts Time it takes for ventricular two R waves (R to R) the ventricles at risk for life threatening depolarization and repolarization to occur Approximately 0.36 – 0.44 seconds dysrhythmias such as TdP. S-T INTERVAL End of S to end of T wave
R-R INTERVAL Time between ventricular contractions R is first positive deflection following Count small boxes between R-R and divide Useful for calculating the heart rate either the Q wave or PR interval by 1500 Helps determine rhythm regularity S wave is first negative deflection Count large boxes between R-R and divide following R wave by 300 Count dark lines between R-R (300, 150 100, 75, 60, 50) ST SEGMENT Time after depolarization and before Follows QRS complex Greater than 1 mm above or below baseline repolarization of the ventricles Should be within 1 mm of the indicates myocardial ischemia or injury baseline (isoelectric line at PR segment) T WAVE Ventricular repolarization Between 2.5 & 5 mm high in limb Inverted and peaked indicates myocardial “Dub” or second (S2) heart sound leads ischemia Closure of semi-lunar valves and May be as tall as 10 mm in the Tall & peaked indicated hyperkalemia opening of a-v valves precordial leads Flattened in hypokalemia Usually goes in same direction as QRS complex Slightly asymmetrical towards the right Larger than “P” wave U WAVE May be papillary muscle repolarization May be present in hypokalemia
Time between Heart is polarized or at rest “T” and “P” wave No electrical activity Isoelectric line or baseline where are things are compared