Lesson plan 1 – Explain it
This lesson explores ways of describing quadratic functions using graphs, symbols and words. t s e n
i Generalise ideas (GI) e c n m Use generalisations (WS) e e t t Use symbols, graphs, and e a Use words and symbols to describe patterns and generalisations (WS) t diagrams to help find and p S
m Use appropriate vocabulary to explain ideas (V) e communicate patterns and o c C n Compare and contrast ideas (CC)
e relationships. y s e
s Critically reflect (CR) E K Participate actively in a collaborative team or community (CT)
m Number and Algebra Level 5 Number and Algebra Level 6 Mathematics Level 7 u
l Form and solve simple Form and use quadratic
u Form and solve quadratic equations.
c quadratic equations. equations. i
r Relate tables, graphs, and Relate graphs, tables, and equations to quadratic, and Display the graphs of linear and r
u equations to simple quadratic relationships found in number and spatial patterns. non-linear functions and C
s relationships found in number connect the structure of the e
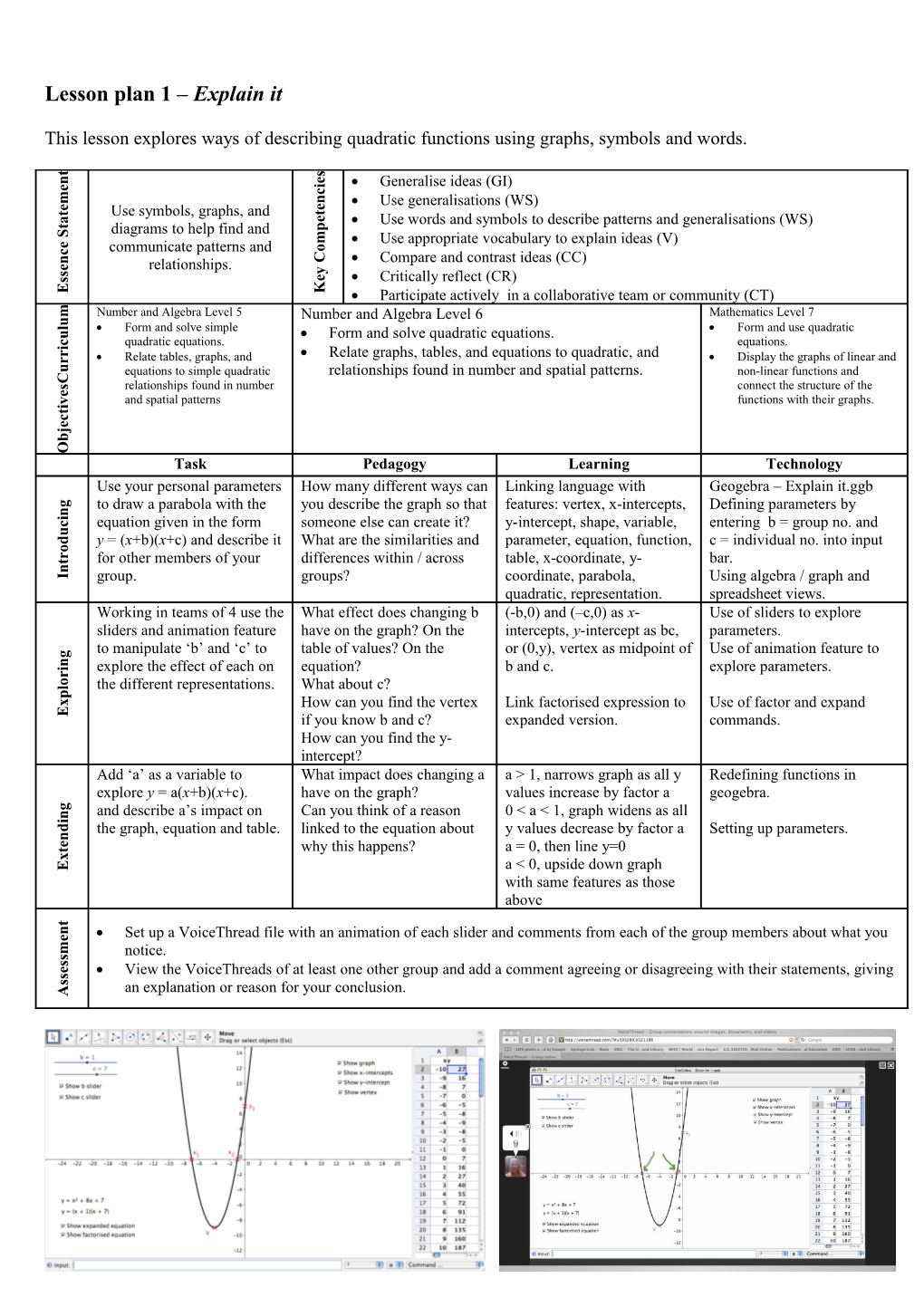
v and spatial patterns functions with their graphs. i t c e j b O Task Pedagogy Learning Technology Use your personal parameters How many different ways can Linking language with Geogebra – Explain it.ggb
g to draw a parabola with the you describe the graph so that features: vertex, x-intercepts, Defining parameters by n i
c equation given in the form someone else can create it? y-intercept, shape, variable, entering b = group no. and u
d y = (x+b)(x+c) and describe it What are the similarities and parameter, equation, function, c = individual no. into input o r
t for other members of your differences within / across table, x-coordinate, y- bar. n
I group. groups? coordinate, parabola, Using algebra / graph and quadratic, representation. spreadsheet views. Working in teams of 4 use the What effect does changing b (-b,0) and (–c,0) as x- Use of sliders to explore sliders and animation feature have on the graph? On the intercepts, y-intercept as bc, parameters. to manipulate ‘b’ and ‘c’ to table of values? On the or (0,y), vertex as midpoint of Use of animation feature to g n
i explore the effect of each on equation? b and c. explore parameters. r o
l the different representations. What about c? p
x How can you find the vertex Link factorised expression to Use of factor and expand E if you know b and c? expanded version. commands. How can you find the y- intercept? Add ‘a’ as a variable to What impact does changing a a > 1, narrows graph as all y Redefining functions in explore y = a(x+b)(x+c). have on the graph? values increase by factor a geogebra.
g and describe a’s impact on Can you think of a reason 0 < a < 1, graph widens as all n i
d the graph, equation and table. linked to the equation about y values decrease by factor a Setting up parameters. n e
t why this happens? a = 0, then line y=0 x
E a < 0, upside down graph with same features as those above t
n Set up a VoiceThread file with an animation of each slider and comments from each of the group members about what you e
m notice. s s
e View the VoiceThreads of at least one other group and add a comment agreeing or disagreeing with their statements, giving s s an explanation or reason for your conclusion. A Lesson plan 2 – Key Ideas of it
This lesson explores converting within and between different representations of quadratic functions.
Use symbols, graphs, and diagrams to help find and t s
e Generalise ideas (GI) n communicate patterns and i e c Use generalisations (WS) n m relationships. e e t t
Learn to structure and to e Choose and use appropriate representation (Re) a t p
S organise, to carry out Interpret information and results in context (In)
m e o c procedures flexibly and Compare and contrast ideas (CC) C n
e
accurately, to process and y s Critically reflect (CR) e s
E communicate information, K Participate actively in a collaborative team or community (CT) and to enjoy intellectual challenge.
m Number and Algebra Level 5 Number and Algebra Level 6 Mathematics Level 7 u
l Form and solve simple Form and use quadratic
u Form and solve quadratic equations.
c quadratic equations. equations. i
r Relate tables, graphs, and Relate graphs, tables, and equations to quadratic, and Display the graphs of linear and r
u equations to simple relationships found in number and spatial patterns. non-linear functions and C
s quadratic relationships connect the structure of the e
v found in number and functions with their graphs. i t spatial patterns c e j b O Task Pedagogy Learning Technology
g Formulate a class Identify common Correct use of terminology to Show VoiceThreads of n i summary of the key ideas misconceptions and have label features. different groups, identify c u
d from Lesson 1 via group other students’ address these, Clear explanation of effect of common themes / o
r VoiceThreads. refer back to geogebra as b and c. misconceptions. t n
I appropriate. Work in teams of 4 to What effect does each Conversions within Use of text tool explore functions in parameter have on the graph? representations competed square form On the table of values? On Expanding / factorising Expand y = a(x + b)2 + c. the equation? Factor
g completing the square n
i Form and test conjectures How can you find the vertex, r o l about the effect of each y-intercept, x-intercepts from Conversions between Animation p
x parameter. each representation? representations E Explore how the Can you predict different technology vs pen and representations before paper methods converts pressing enter? between representations. Set up a geogebra What impact does changing a, Completing the square to find Setting up a geogebra sheet to worksheet to explore b and c have on the graph? quadratic formula. explore a function. g
n 2 i y = ax + bx + c. Can you think of a reason Effect of a on shape, b and c Trace function to determine d
n linked to the equation about on location of graph. effect of b. e t
x why this happens? Understand these a b and c E are not the same as those above. t n e
m Add to your VoiceThread file, showing ways of finding the missing representation if given the other two, e.g. the graph if s s
e given the equation or table of values etc. s s A Lesson Plan 3 – Connect it
This lesson links different representations to class of area problems.
Learn to create models t s
e Plan and carry out an investigation (PI) n and predict outcomes, to i e c Find, use, and justify a model (Mo) n m conjecture, to justify and e e t t
verify. e Choose and use appropriate representation (Re) a t p
S Generalising and Interpret information and results in context (In)
m e o c representing the patterns Compare and contrast ideas (CC) C n
e
and relationships found in y s Manage time effectively (MT) e s
E numbers, shapes, and K Show awareness of the needs of others (AN) measures.
m Number and Algebra Level 5 Number and Algebra Level 6 Mathematics Level 7 u
l Form and solve simple Form and use quadratic
u Form and solve quadratic equations.
c quadratic equations. equations. i
r Relate tables, graphs, and Relate graphs, tables, and equations to quadratic, and Display the graphs of linear and r
u equations to simple relationships found in number and spatial patterns. non-linear functions and C
s quadratic relationships connect the structure of the
e Find optimal solutions, using numerical approaches.
v found in number and functions with their graphs. i t spatial patterns c e j b O Task Pedagogy Learning Technology Area problem – what is Have students explore the Linking area problems to Use of sliders for lengths the maximum paddock problem without using quadratics. you can make with 50m of geogebra, then make Linking features of side Calculating lengths / areas g n
i fencing wire, if you only predictions about how the length and area to geogebra c
u have to fence three sides different representations in representations. Trace to spreadsheet d
o of the paddock. geogebra would show their Linking this area problem to r t
n findings. factorised quadratic. I Show VoiceThreads, identify any common themes / misconceptions. Work in teams of 4 to What do you notice about the Generalising finding the Use of trace tool generalise the above maximum in each case? vertex coordinates of Use of trace to spreadsheet problem to any length of Why does plotting the area y = x (l – 2x) as a way of Use of spreadsheet functions g n
i wire. result in a parabola? finding the maximum. to find x, y, first difference r o
l Link numerical Why does the vertex give the Numerical solutions of and second difference. p
x representation to finding maximum area? equations. E formula. What does the x-coordinate of Using second difference the vertex tell you? method to find formula for a numeric quadratic pattern. Set up a worksheet to What are the similarities and Multiplication of a variable Setting up a geogebra sheet to explore another version of differences between area / by itself leads to squared explore a maxima or minima this area (or multiplication problems? variable which links to problem. g n i multiplication) problem quadratics. d
n with different constraints. How can the second Identifying terms of quadratic e
t 2
x Link ax + bx + c to difference method be justified pattern as c, a + b + c, 4a + 2b E second difference method using algebra? + c, … => first difference is a of finding equation. + b, 3a + b, 5a + b and second difference is 2a.
s Add to your VoiceThread file, clearly explaning your solution or solutions to the paddock area problem. s e
s Upload an example with explanation of how to find the formula of a numeric quadratic pattern. s
A Upload a proof or explanation of the second difference method.
Lesson Plan 4 – Look at it another way
This lesson links different representations to modelling problems.
Create models to represent Plan and carry out an investigation (PI) t s e n both real-life and i Find, use, and justify a model (Mo) e c n m hypothetical situations. Interpret information and results in context (In) e e t t
Develop the ability to e a Compare and contrast ideas (CC) t p
S think creatively, critically,
m Manage time effectively (MT) e o
c strategically, and C n Critically reflect (CR)
e
logically. y s e
s Participate actively in a collaborative team or community (CT)
E Learn to create models K and predict outcomes.
m Number and Algebra Level 5 Number and Algebra Level 6 Mathematics Level 7 u
l Form and solve simple Form and use quadratic
u Form and solve quadratic equations.
c quadratic equations. equations. i
r Relate tables, graphs, and Relate graphs, tables, and equations to quadratic, and Display the graphs of linear and r
u equations to simple relationships found in number and spatial patterns. non-linear functions and C
s quadratic relationships connect the structure of the e
v found in number and functions with their graphs. i t spatial patterns c e j b O Task Pedagogy Learning Technology Use geogebra to explore Identify what the x and y Link context to word Scaling / enlarging images. the time lapse photo of represent in this context. problems to solving quadratic g n
i the motion of a bouncing What do the parameters equations. Setting up a mathematical c
u ball. represent? Link representation to method model in geogebra. d
o What questions could What effect would changing of solving equations. r t
n your model be used to the parameters have on the Learning about modelling real I answer? context? life events. What about scale? Work in teams of 4 to Summarise all you have Connecting features of Time lapse photos from explore one of the other learnt about quadratic different representations to internet (or create own). photos of your choice. representations in this meaning in context . Setting up a mathematical g n
i particular context. What do Link to other pen and paper model in geogebra. r o
l Write 5 questions for the vertex, intercepts etc solution methods. p
x other groups to solve. represent. Linking solving equations to E What are the advantages of what is happening in the modelling motion with a different representations. quadratic function? Design an data collection Summarise all you have Definition of variables Video clips exercise, e.g. video and learnt about quadratic Solutions of quadratics in g n i find a model to representations in this context. Use of geogebra to model. d
n mathematically describe particular context. Quadratic formula. e t
x the situation. Link to limitations and E justifications of a mathematical model.
t Add to your VoiceThread file, either a time lapse photo, or a video of a natural phenomenon that can be modelled with a n
e quadratic function, clearly explaining your findings and summarising the key ideas from this unit. m
s Add at least 5 questions for other groups to answer. s e s
s Herbert Simon (1981) said "solving a problem simply means representing it so as to make the solution transparent." (p. A 153) add your thoughts to this VoiceThread page about what he might have meant.