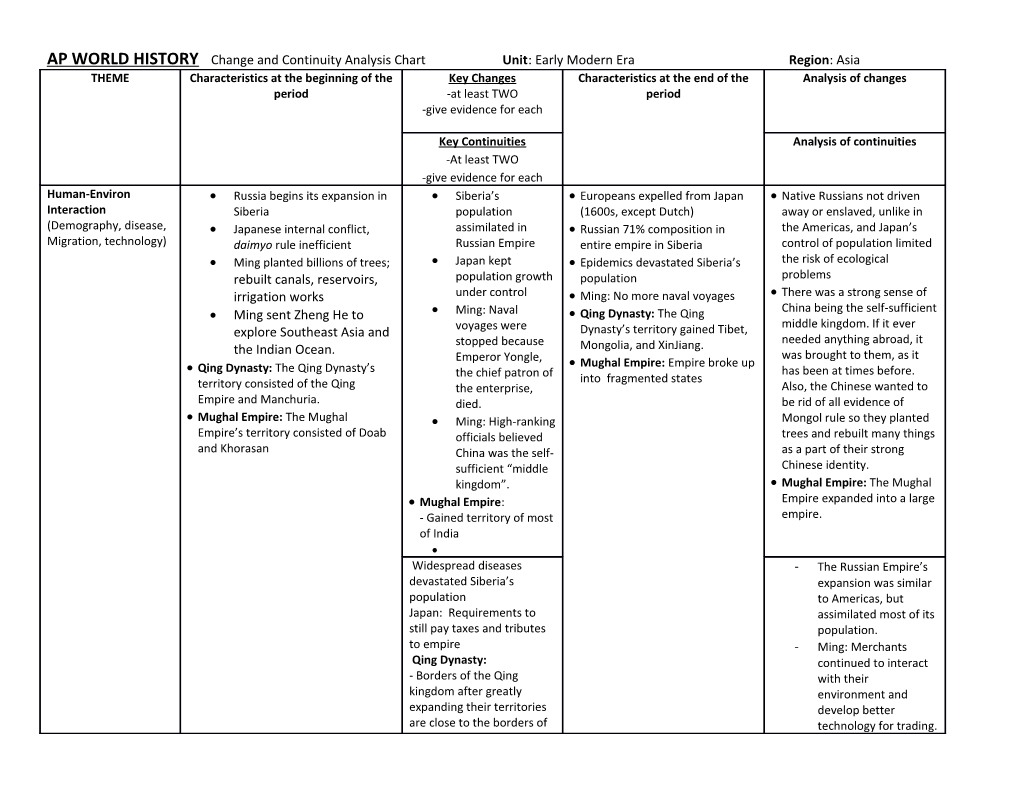
AP WORLD HISTORY Change and Continuity Analysis Chart Unit: Early Modern Era Region: Asia THEME Characteristics at the beginning of the Key Changes Characteristics at the end of the Analysis of changes period -at least TWO period -give evidence for each
Key Continuities Analysis of continuities -At least TWO -give evidence for each Human-Environ Russia begins its expansion in Siberia’s Europeans expelled from Japan Native Russians not driven Interaction Siberia population (1600s, except Dutch) away or enslaved, unlike in (Demography, disease, Japanese internal conflict, assimilated in Russian 71% composition in the Americas, and Japan’s Migration, technology) daimyo rule inefficient Russian Empire entire empire in Siberia control of population limited Ming planted billions of trees; Japan kept Epidemics devastated Siberia’s the risk of ecological rebuilt canals, reservoirs, population growth population problems irrigation works under control Ming: No more naval voyages There was a strong sense of China being the self-sufficient Ming sent Zheng He to Ming: Naval Qing Dynasty: The Qing middle kingdom. If it ever explore Southeast Asia and voyages were Dynasty’s territory gained Tibet, stopped because Mongolia, and XinJiang. needed anything abroad, it the Indian Ocean. was brought to them, as it Emperor Yongle, Mughal Empire: Empire broke up Qing Dynasty: The Qing Dynasty’s has been at times before. the chief patron of into fragmented states territory consisted of the Qing the enterprise, Also, the Chinese wanted to Empire and Manchuria. died. be rid of all evidence of Mughal Empire: The Mughal Ming: High-ranking Mongol rule so they planted Empire’s territory consisted of Doab officials believed trees and rebuilt many things and Khorasan China was the self- as a part of their strong sufficient “middle Chinese identity. kingdom”. Mughal Empire: The Mughal Mughal Empire: Empire expanded into a large - Gained territory of most empire. of India Widespread diseases - The Russian Empire’s devastated Siberia’s expansion was similar population to Americas, but Japan: Requirements to assimilated most of its still pay taxes and tributes population. to empire - Ming: Merchants Qing Dynasty: continued to interact - Borders of the Qing with their kingdom after greatly environment and expanding their territories develop better are close to the borders of technology for trading. contemporary China - Qing Dynasty: The - Although the nomadic Qing Dynasty regions of China are striving expanded into a large for independence, they are empire where the still a part of China as they same regions are still were during the Qing under China’s control. Dynasty.
Culture Japanese daimyos allowed for Expulsion of Much of Siberia’s native - The expansion of the (Religions, philosophies, Christianity from foreign Christian population ‘russified’ Russian Empire spread Science, technology, traders missionaries from Except for the Dutch merchants, its culture, where art, Began spread of culture with Japan nearly all Christian missionaries Japan closed itself off architecture) expansion of the Russian Russian expansion were forced to leave Japan to foreign influence Empire spread culture Ming: Chinese society turned - Ming: There was a Ming: revival of Confucianism Ming: Reverted inward strong sense of China Ming: Attempted to remove back to traditional Qing Dynasty: Unification with being the self- any traces of Mongol rule Chinese ways nomadic states, spread of sufficient middle Qing Dynasty: The Manchurian rulers because of the Chinese culture kingdom. If it ever immersed themselves in Chinese Mongol rule Mughal Empire: Spread of needed anything culture and Confucianism Ming: Persian art, language, religion, abroad, it was brought to them, as it has been Mughal Empire: Mostly non-Muslim Confucianism, civil and architecture at times before. Also, populations, claim descended from service exam the Chinese wanted to Mongols Qing Dynasty: - Many nomadic people be rid of all evidence adopted the Chinese of Mongol rule so they culture and style of the planted trees and Manchurian rulers. rebuilt many things as a part of their strong Mughal Empire: Chinese identity. - Akbar integrated Hindus Qing Dynasty: Nomadic people and Muslims together under China’s control tried to - Emperor Aurangzeb blend in more with their new imposed Islam supremacy society by adopting Chinese culture. Mughal Empire: Religion played a huge role in the Mughal Empire and often affected society. - Dutch traders only Religion imposed on people allowed in Japan resulted in acceptance only in Widespread conversion Russia to Christianity in Russia Qing Dynasty: Many - Because Qing officials traditional cultures and were lax about foreign philosophies are kept intact cultures, many nomadic throughout Chinese history. cultures in China are still Mughal Empire: The rule of intact today. the Mughal Empire brought a - Confucianism is still huge amount of Persian culture widely practiced today to India that still exists today. Mughal Empire: - Brought Persian art/architecture to India such as the Taj Mahal - Language Urdu created out of mix of Arabic and Hindi Politics Previous daimyo feudal lords Russia: Catherine Tokugawa shogunate Religious tolerance (State-building, in Japan, at constant the Great, established (1603) within empires led to conflict, Political competition with each other religious tolerance Catherine the Great’s rule larger-scale structures, Empires, Tokugawa Shogunate for Muslims (1762-1796) acceptance and less Revolts and revolution) Russian tsardom and Japan: Expansion Russian empire comprised chance of revolt expansion of economies of nearly all of the Siberia Ming: Pirates raided Ming: strong central Ming political and some of Eastern port cities and the government leaders became Europe weather wouldn’t Ming: Zheng He’s expeditions increasingly Ming: peasants revolted cooperate. The Ming traveled to distant places to powerless by the 17th century emperor invited Qing submit them to the tribute Mughal Empire: Ming: Qing warriors from warriors to help crush system -Military leader Akbar Manchuria ousted a peasant revolt but was overthrown Qing dynasty: Started by foreign reformed government emperor instead. nomadic Manchurian rulers and doubled the size of Qing Dynasty: After the end of Qing Dynasty: Mughal Empire: Created by a the dynasty the Qing Dynasty, the Republic of Islamized Turkic group (1526) -Brutal conquests result in a China became the new Mughal Empire: period of political unity in government. Although the methods India Mughal Empire: After the end of to conquering states the empire, India fractured into had extreme military multiple independent states and actions, it worked in the British took over uniting the kingdoms together under the Mughal Empire.
Russian expansion to gain Resources of Japan and opportunity in controlling Russia gave it natural the need of its resources advantage in building an Japan: Wealth of empire empire caused it to expand China has had a long history Ming: Maintained central of being unified, and tried to government maintain this way no matter Qing Dynasty: what. - Overthrown by Qing Dynasty: The Qing rebellions and replaced Dynasty was deteriorating, by the Republic of China, and it only took a couple which is still the more rebellions to government of China completely overthrow it and today. replace it with a new - government. Mughal Empire: Mughal Empire: Small - Centralized governing kingdoms were united brought together small through the method of kingdoms centralized governing.
Economics Russia/Siberia most small- Russia controlled Russian expansion brought Natural and geographic (Agric, trade, scale, hunting-herding, people most of the fur Poles, Germans, advantages gave advantages in commerce, labors Small-scale Japanese trade Ukranians, Baltics developing a market-based systems, economy, feudal-based Japan’s natural Siberians “Russified”, economy industrialization, Ming: Growing economy; resources, and adopted Christianity - Ming: At first money capitalism, socialism) trade flourished silver mines gave it Japan gained power in the was too easily Ming: attempted to support an advantage silver trade, as well a counterfeited. After failing economy with silver- Ming: Repaired market-based economy they switched to silver based currency canals, reservoirs, Ming: silver exchange currency, the government couldn’t Qing Dynasty: The Silk Road of China and other public fueled economy, but control inflation. China was a prosperous trading route work because the resulted in inflation tried to self-sufficient, Mongols Ming: by 17th century, Mughal Empire: Wealthy economy cutting off maritime from conquering all the lands in India destroyed them. famines crippled economy Ming: Economy voyages and therefore Qing Dynasty: The economy of affecting their started to fail China took a huge downfall because the silver economy. Mughal Empire: After the death - Qing Dynasty: The exchanged of Aurangzeb, the empire went resulted in economy of the Qing into chaos and the economy Dynasty eventually inflation the suffered. government could suffered because not control. oceanic trade became Qing Dynasty: a more popular - Land-based commerce method of trading. could not compete with - Mughal Empire: The oceanic trade peasant revolts - Many nobles lost their stopped the Mughal lands and went into debt, Empire from retaining became beggars its power and Mughal Empire: economy. - Peasant revolts against heavy taxation
Russia: Market-based - Use of agricultural economies continued to innovations in Japan thrive kept it from having an Agricultural necessities ecological crisis were continued to be used - Global commerce was in Japan profitable, and Europe Ming: Private Chinese was just beginning to merchants and craftsmen sail out into Asia continued to settle and - Qing Dynasty: trade in Japan, Philippines, - Mughal Empire: Taiwan, Southeast Asia, but Connections with the without support of their powerful British East government India Company turned Mughal Empire: from trading and -Trading with the British exchanging to East India Company complete take over eventually led to the from them. company taking control of India
Social Japanese conflicts between daimyos Influx of Russian settlers - Mercantilism encouraged, - The amount of (Gender roles/ Much separation between people in Encouraged pastoralists to further advance the resources needed led relations, family, racial Russian empire and natives to abandon their ways economy to expansion and & ethnic constructions, Qing Dynasty: The Manchurian rulers Qing Dynasty: - Acceptance of Eastern assimilation into social and economic segregated themselves from the rest - The local nomads who Europeans and native Russian population classes) of the Chinese became officials would Siberians into much of the - Ming: Trade was Mughal Empire: Mughal Muslims had abuse their power by Russian culture becoming more global, more authority over the Indian demanding extra taxes or - Ming: sense of ethnic causing merchants to Hindus. labor. superiority flourish. -Nomadic regions were - Ming: Emerging wealthy - Qing Dynasty: strictly off limit from merchant class Although China was normal Chinese people to - Qing Dynasty: All of united with the Qing preserve the Mongol’s China’s citizens are equal; Dynasty ruling the “fighting spirit” there is no segregation of states together, there Mughal Empire: any type of Asian. was still some form of - Akbar created a new - Mughal Empire: Hindus segregation between policy where everyone and Muslims are equal the Chinese and their was equal no matter the since they are split into nomadic neighbors. religion they practiced - Mughal Empire: The - Aurangzeb antagonized different regions; there is equality between Hindus no one religion that has Hindus and Muslims power over the other. often varied depending on what the views of the current ruler were.
Russian Empire remained - Japan’s rejection of intact until 1991 (collapse foreign influence did of Soviet Union) not allow it to expand Japan retained much of its the same way Russia core traditional beliefs did through the Early Modern - Ming: China is pretty era homogenous and has Ming: Chinese superiority had a long history of unification.