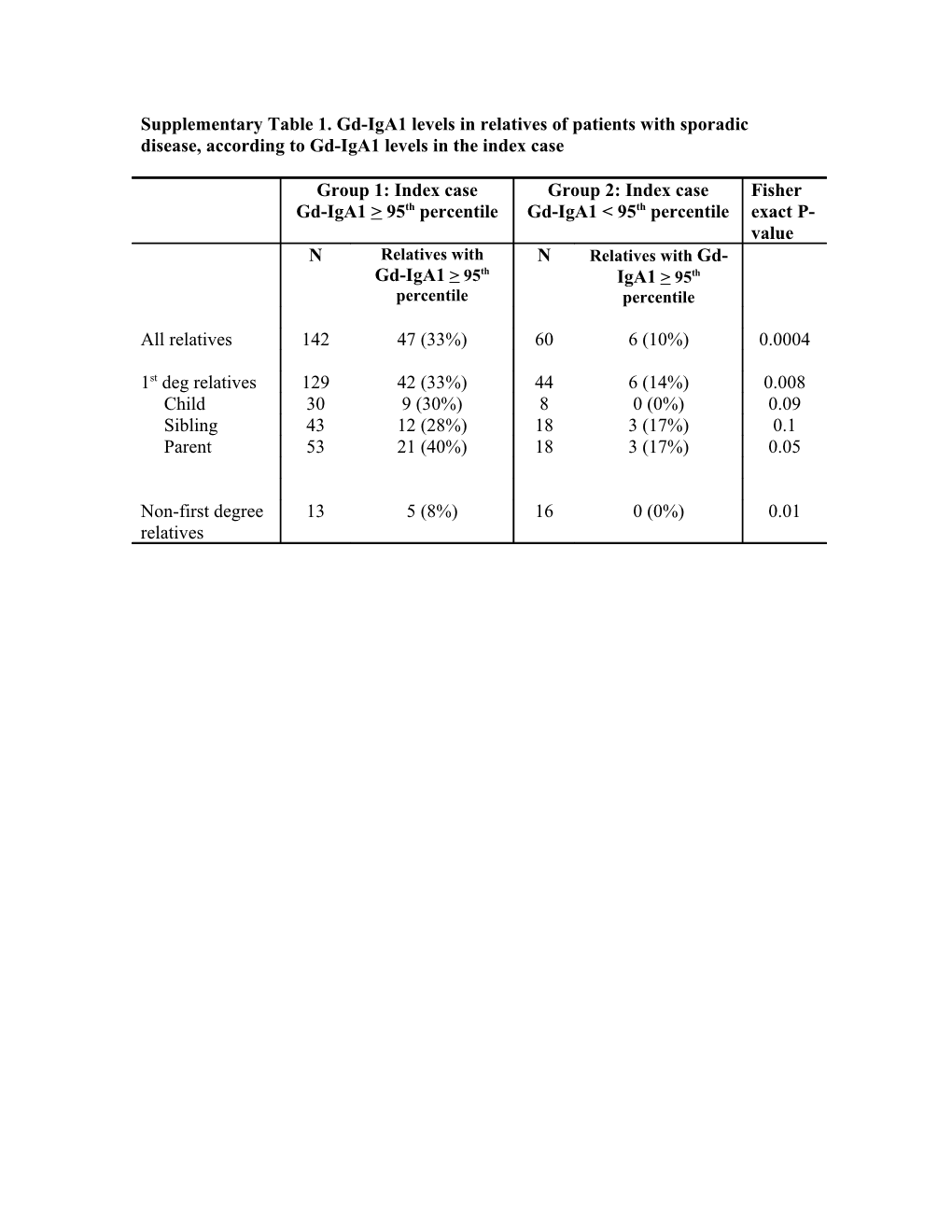
Supplementary Table 1. Gd-IgA1 levels in relatives of patients with sporadic disease, according to Gd-IgA1 levels in the index case
Group 1: Index case Group 2: Index case Fisher Gd-IgA1 > 95th percentile Gd-IgA1 < 95th percentile exact P- value N Relatives with N Relatives with Gd- Gd-IgA1 > 95th IgA1 > 95th percentile percentile
All relatives 142 47 (33%) 60 6 (10%) 0.0004
1st deg relatives 129 42 (33%) 44 6 (14%) 0.008 Child 30 9 (30%) 8 0 (0%) 0.09 Sibling 43 12 (28%) 18 3 (17%) 0.1 Parent 53 21 (40%) 18 3 (17%) 0.05
Non-first degree 13 5 (8%) 16 0 (0%) 0.01 relatives Supplementary Table 2. Heritabilities of measured traits in patient cohort
Trait h2 P-value Significant covariates
Height 0.72 3 x10-10 Sex
Urine protein / 0.7 0.001 Age, creatinine ratio IgAN affection status, Systolic BP, Diastolic BP, GFR
Body Mass Index 0.58 1 x 10-9 Systolic BP
Gd-IgA1 levels 0.54 0.0001 IgAN affection status, IgA levels
Glomerular Filtration 0.53 5 x10-6 Age, Rate IgAN affection status, Diastolic BP Urine P/C
Serum IgA levels 0.41 0.00003 IgAN affection status BMI Age
Diastolic blood pressure 0.25 0.02 Sex
Systolic blood pressure 0.22 0.03 Age, sex, GFR, Affection, Urine P/C
GFR=glomerular filtration rate BP= blood pressure P/C =protein to creatinine ratio Supplementary Table 3. Results of segregation analysis1 of Gd-IgA1 in study cohort
Model q h2 Transmission -2LnL param CHISQ Df p AIC probabilities (τ) Free free free Free 921 9 0 - - 939 ENV free 0 τAA=τAa=τaa 938 6 17 3 0.0008 950 SPO 1 0 N/A 26729 2 25808 7 0 26733 DOM free 0 MEND 932 4 11 5 0.05 940 DOM+poly free free MEND 921 5 0 4 0.99 931 REC free 0 MEND 934 4 13 5 0.02 942 REC+poly free free MEND 923 5 2 4 0.73 933 ADD free 0 MEND 934 4 13 5 0.02 942 poly 1 free N/A 26634 3 25713 6 0 26640 ENV+poly free free τAA=τAa=τaa 922 2 1 7 0.99 926
1We performed segregation analysis using the Pedigree Analysis Package (jPAP, ref 14 in text) to calculate the likelihood of finding the observed phenotype distribution under various models, including a general unrestricted model, Mendelian major-gene models, an environmental model, a polygenic model, and mixtures of various polygenic models with either a major-gene model or an environmental model. The parameters in the general models include 1- the disease allele frequency (q) of the high allele (a). 2- the arbitrary transmission probabilities (τAA, τAa, and τaa) for an individual of a given genotype transmitting allele A to the offspring. These transmission probabilities were fixed in the Mendelian models (MEND, τAA=1.0, τAa=.5, and τaa=0) and the environmental models (ENV, τAA=τAa=τaa). 3- the arbitrary genotypic means (μAA, μAa, and μaa), assuming a common variance for all the genotypes, and a residual genetic heritability (h2). In Mendelian transmissions, recessive inheritance is modeled by setting μAA=μAa and dominant inheritance is modeled by setting μAa=μaa. For the pure Mendelian- models and the environmental models, h2 was set to zero. . For the mixed models, h2 is estimated.
The significance of each model was estimated by computing the difference in natural log likelihoods (−2lnL) between the general (free) model and the model of interest. This difference approximates a χ2 statistic, with degrees of freedom (Df) equal to the difference in the number of parameters (param) used in the two models. The best fitting model(s) provide a likelihood that is not significantly different than that of the general model. The most parsimonious model is identified using Akaike's Information Criteria (AIC) , which is defined as AIC =-2LnL + 2param (Akaike H., IEEE Trans Automatic control AC 1974, 19:719-23). Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of total IgA levels among patients and relatives with familial (A) and sporadic IgAN (B). The dashed vertical lines indicate the 95th percentile cutoffs for controls. IgA values above the 95th percentile are shown in red. Supplemental Figure 2. Histogram showing the distribution of Gd-IgA1 in sporadic
IgAN patients (N=84), their relatives (N=202), and unrelated controls (N=141). The left panels show the raw values and the right panels the log10 transformed values. Gd-IgA1 values above the 95th percentile values for controls are shown in red.