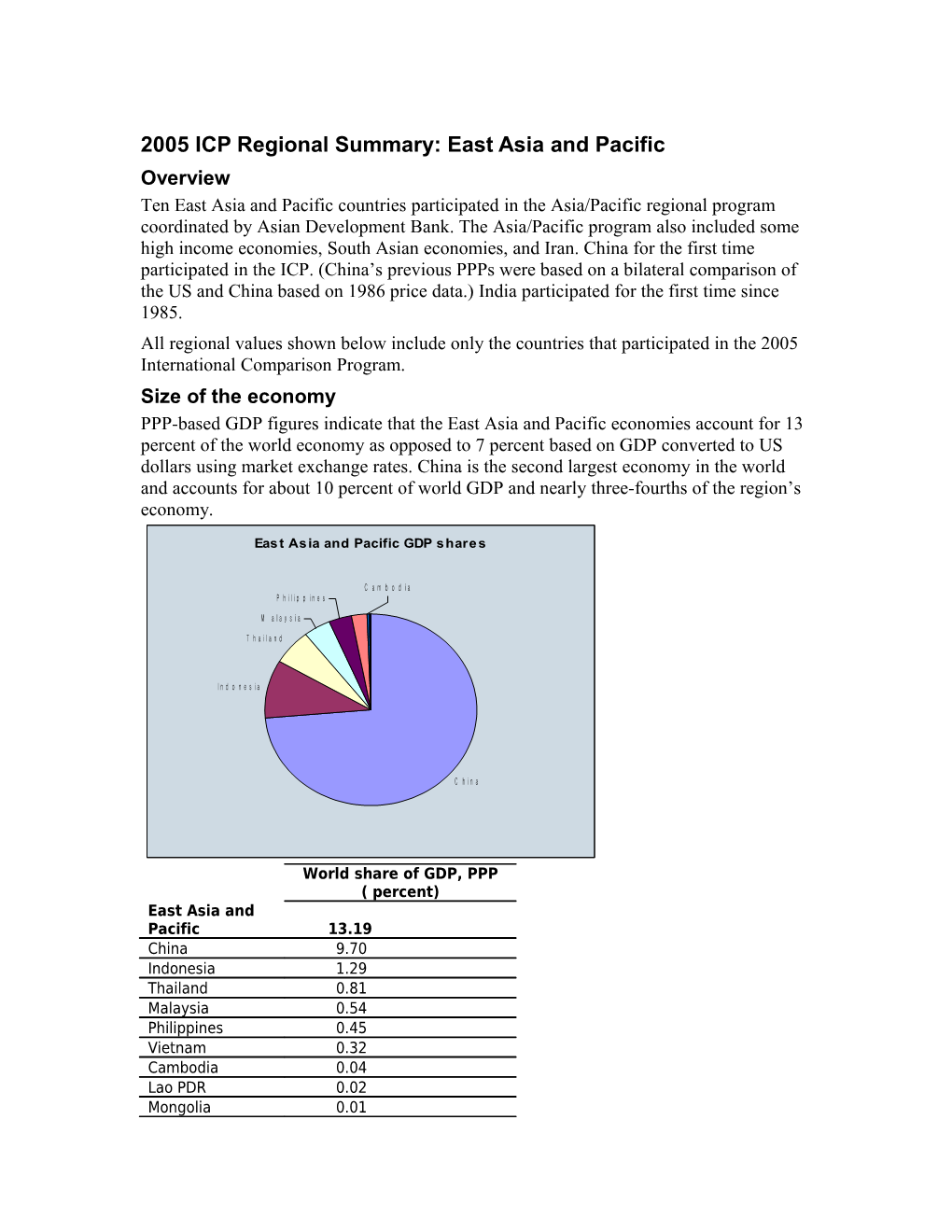
2005 ICP Regional Summary: East Asia and Pacific Overview Ten East Asia and Pacific countries participated in the Asia/Pacific regional program coordinated by Asian Development Bank. The Asia/Pacific program also included some high income economies, South Asian economies, and Iran. China for the first time participated in the ICP. (China’s previous PPPs were based on a bilateral comparison of the US and China based on 1986 price data.) India participated for the first time since 1985. All regional values shown below include only the countries that participated in the 2005 International Comparison Program. Size of the economy PPP-based GDP figures indicate that the East Asia and Pacific economies account for 13 percent of the world economy as opposed to 7 percent based on GDP converted to US dollars using market exchange rates. China is the second largest economy in the world and accounts for about 10 percent of world GDP and nearly three-fourths of the region’s economy.
East Asia and Pacific GDP shares
C a m b o d i a P h i l i p p i n e s
M a l a y s i a
T h a i l a n d
I n d o n e s i a
C h i n a
World share of GDP, PPP ( percent) East Asia and Pacific 13.19 China 9.70 Indonesia 1.29 Thailand 0.81 Malaysia 0.54 Philippines 0.45 Vietnam 0.32 Cambodia 0.04 Lao PDR 0.02 Mongolia 0.01 Fiji 0.01
Living Standards The region’s GDP per capita is $4020 in PPP terms. Malaysia and Thailand exceed the average by a large amount but Lao and Cambodia lag with per capita GDP less than half the region’s average.
GDP per capita
14,000
12,000
10,000
8,000
6,000
4,000
2,000
- Malaysia Thailand Fiji China Indonesia Philippines Mongolia Vietnam Lao PDR Cambodia
GDP per capita, economy PPP ($) East Asia and Pacific 4,020
Malaysia 11,466
Thailand 6,869
Fiji 4,208
China 4,091
Indonesia 3,234
Philippines 2,932
Mongolia 2,644
Vietnam 2,142
Lao PDR 1,811
Cambodia 1,453 Actual Individual Consumption Actual individual consumption is measured by the total value of household final consumption expenditure, expenditures by non-profit institutions (such as NGOs and charities) serving households, and government expenditure on individual consumption goods and services (such as education or health). The East Asia and Pacific region lags all but South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa in individual consumption per capita.
Actual Individual Consumption per capita (World=100%)
400%
300%
200%
100%
0% East Asia Europe and High-income Latin Middle-East South Asia Sub- and Pacific Central Asia America and and North Saharan Caribbean Africa Africa
Actual Individual Consumption per capita (World =100%)
100.0% 90.0% 80.0% 70.0% 60.0% 50.0% 40.0% 30.0% 20.0% 10.0% 0.0% Malaysia Thailand Fiji Indonesia Philippines China Mongolia Vietnam Cambodia Lao PDR PPP-based measures of collective government consumption Collective government consumption expenditures consist of expenditures incurred by general and local governments for collective consumption services such as defense, justice, general administration, and the protection of the environment. Lower prices for such services in developing countries tend to reduce the dispersion of collective government consumption per capita across regions compared to that observed for per capita GDPs.
Collective Government Consumption per capita (World=100%)
400%
300%
200%
100%
0% East Asia Europe and High-income Latin Middle-East South Asia Sub- and Pacific Central Asia America and and North Saharan Caribbean Africa Africa
Collective Government Consumption per capita (World =100%)
180.0% 160.0% 140.0% 120.0% 100.0% 80.0% 60.0% 40.0% 20.0% 0.0% Malaysia China Thailand Fiji Lao PDR Mongolia Vietnam Philippines Indonesia Cambodia PPP-based measures of gross fixed capital formation Gross fixed capital formation measures countries’ investment expenditures, which are mostly comprised of purchases of equipment and construction services. The East Asia and Pacific region is on par with Europe and Central Asia and Latin America and Caribbean in investment per capita. It lags these regions by a substantial margin in GDP and consumption per capita.
GFCF per capita (World=100%)
400%
300%
200%
100%
0% East Asia Europe and High-income Latin Middle-East South Asia Sub- and Pacific Central Asia America and and North Saharan Caribbean Africa Africa
Gross Fixed Capital Formation per capita (World =100%)
140.0%
120.0%
100.0%
80.0%
60.0%
40.0%
20.0%
0.0% Malaysia Thailand China Fiji Mongolia Vietnam Indonesia Lao PDR Philippines Cambodia Price level indexes A price level index (PLI) is the ratio of a PPP to the market exchange rate of the numeraire currency. PLIs are used to compare price levels between countries. The PLI indicates the relative price of GDP (or its components) in a country, as if it were “purchased” after acquiring local currency at the prevailing exchange rate. PLIs are generally low in poorest countries. This reflects the common experience of travelers who find many (but not all) of the goods and services in the poorest countries relatively cheap compared to similar products in their home country.
Price levels generally increase with GDP per capita. In East Asia and the Pacific, Lao has the lowest prices. Fiji has the highest prices, followed by Malaysia.
GDP Price Level Indexes, World = 100
120%
Fiji 100%
80%
60%
Malaysia
40%
Lao, PDR
20%
0% GDP per capita