Clinical Therapeutics IV: Test II
ACLS Drugs
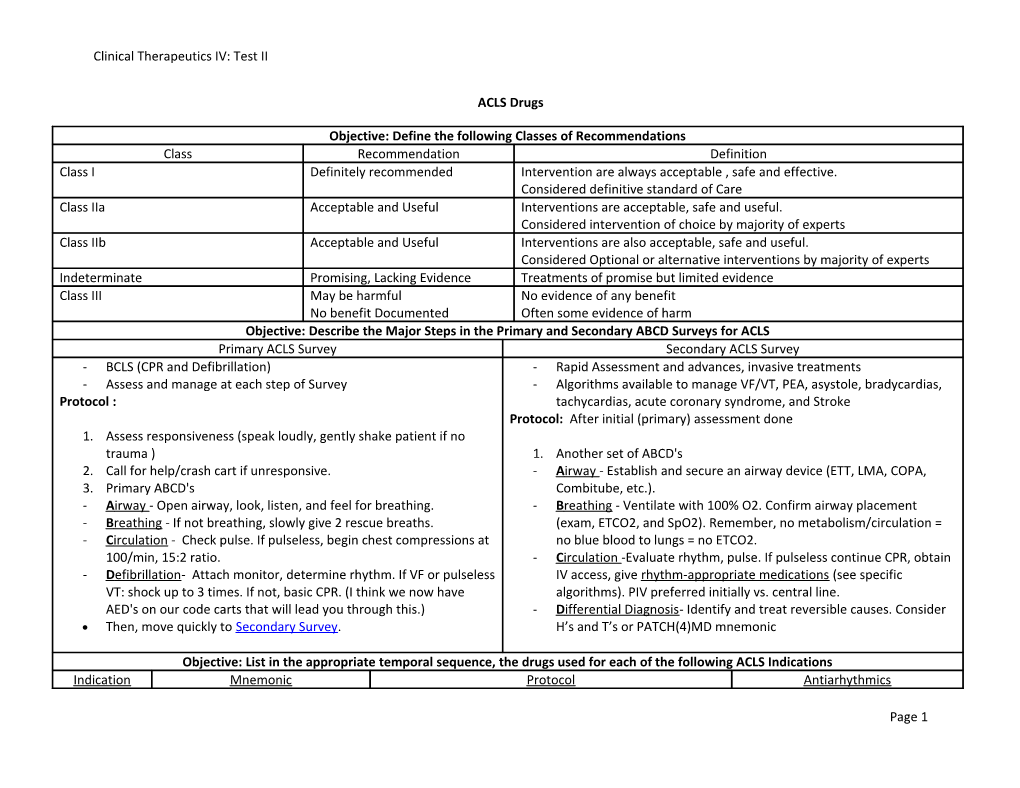
Objective: Define the following Classes of Recommendations Class Recommendation Definition Class I Definitely recommended Intervention are always acceptable , safe and effective. Considered definitive standard of Care Class IIa Acceptable and Useful Interventions are acceptable, safe and useful. Considered intervention of choice by majority of experts Class IIb Acceptable and Useful Interventions are also acceptable, safe and useful. Considered Optional or alternative interventions by majority of experts Indeterminate Promising, Lacking Evidence Treatments of promise but limited evidence Class III May be harmful No evidence of any benefit No benefit Documented Often some evidence of harm Objective: Describe the Major Steps in the Primary and Secondary ABCD Surveys for ACLS Primary ACLS Survey Secondary ACLS Survey - BCLS (CPR and Defibrillation) - Rapid Assessment and advances, invasive treatments - Assess and manage at each step of Survey - Algorithms available to manage VF/VT, PEA, asystole, bradycardias, Protocol : tachycardias, acute coronary syndrome, and Stroke Protocol: After initial (primary) assessment done 1. Assess responsiveness (speak loudly, gently shake patient if no trauma ) 1. Another set of ABCD's 2. Call for help/crash cart if unresponsive. - A irway - Establish and secure an airway device (ETT, LMA, COPA, 3. Primary ABCD's Combitube, etc.). - A irway - Open airway, look, listen, and feel for breathing. - B reathing - Ventilate with 100% O2. Confirm airway placement - B reathing - If not breathing, slowly give 2 rescue breaths. (exam, ETCO2, and SpO2). Remember, no metabolism/circulation = - C irculation - Check pulse. If pulseless, begin chest compressions at no blue blood to lungs = no ETCO2. 100/min, 15:2 ratio. - C irculation -Evaluate rhythm, pulse. If pulseless continue CPR, obtain - D efibrillation- Attach monitor, determine rhythm. If VF or pulseless IV access, give rhythm-appropriate medications (see specific VT: shock up to 3 times. If not, basic CPR. (I think we now have algorithms). PIV preferred initially vs. central line. AED's on our code carts that will lead you through this.) - D ifferential Diagnosis- Identify and treat reversible causes. Consider Then, move quickly to Secondary Survey. H’s and T’s or PATCH(4)MD mnemonic
Objective: List in the appropriate temporal sequence, the drugs used for each of the following ACLS Indications Indication Mnemonic Protocol Antiarhythmics
Page 1 Clinical Therapeutics IV: Test II
VF/Pulseless V “SCREAM” 1. Primary ABCD & Secondary ABCD 1. Amiodarone Tach Shock 2. IV infusion of NS (0.9%) KVO = 10ml/hr 2. Lidocaine CPR 3. Epinephrine Img IV/IO q3-5 times OR - 100mg IV push Rhythm check & Shock if indicated Vasopressin 40 untis IV/IO – 1 dose only (may replace - May repeat q3-5m Epi (or vasopressin) 1st or 2nd dose of epi) - Max individual dose is 1.5 mg/kg AM (Antiarrhythmics) 4. Shock/CPR - Max Total dose is 3mg/kg 5. Antiarrhtmics IV/IO 3. Magnesium Sulfate 6. Shock/CPR - For Torsades/suspected 7. Others such as Sodium Bicarbonate, Dextrose hypomagnesaemia 8. Shock/CPR - 1-2g (2-4ml) diluted in 10 ml D5W or NS over 2 min PEA “PEA” for PEA 1. Primary ABCD & Secondary ABCD Patch(4)MD Problem search 2. Differential Dx- review & Treat most freaquent Pulmonary Embolism Epinephrine causes (Hs’s&T’s)/(PATCH(4)MD) Acidosis Atropine 3. Epinephrine 1mg IV/IO q3-5 mins OR Tension Pneumothorax Vassopressin 40 units IV/IO one dose as above Caradiac Tamponade 4. Atropine 1 mg IV if PEA <60bpm q3-5mins to total Hyper/hypokalemia, hypovolemia, dose of 0.04mg/kg or 3mg dose total hypoxia 5. Recheck rhythm and process as appropriate MI 6. After atropine consider high dose epi, sodium Drugs bicarbonate, Dextrose w/insulin for hyperkalemia, Shivering (hypothermia) naloxone, IV fluid, TCP, dopamine drip for hypotns Asystole “PEA” mnemonic 1. Primary Survey and Secondary Survey 2. TCP asap if available in monitored asystolic arrest 3. Epinephrine 1mg IVP 13-5 minute or Vassopressin 40 units IVP – 1 dose only 4. Atropine 1mg IVP 13-5 minutes up to a total dose of 0.04mg/kig or 3mg dose total 5. Differential Diagnosis 6. After Atropine consider high dose epi IV, continued TCP, sodium bicarbonate IV, continued defib, naloxone Indication Mnemonic Protocol Details Bradycardia “PEAD” 1. Primary Survey and Secondary Survey 1. Atropine= .5-1mg IV push q3-
Page 2 Clinical Therapeutics IV: Test II
Pacing 2. Are there signs and symptoms due to bradycardia? 5 min up to total dose of 0.04 HR<60 + sx Atropine YES= TCP, Atropine, Epinephrine infusion, mg/kg 3mg total Epinephrine Dopamine 2. Epinephrine Infusion= 1mg of Dopamine *2nd degree heartblock type II OR 3rd degree AV epi to 250 ml IV fluid such **H’s and T’s** block Transvenous pacemaker that final concentration is NO= 2nd degree heartblock type II or 3rd degree AV 4mcg/ml Note- atropine can be given while block transvenous pacemaker, if sx develop use 3. Dopamine= 400mg/250ml or setting up pacing. After failure of TCP until transvounse pacer is placed 800mg/250ml infusion bag atropine, either epinephrine OR *NO AV BLOCK Observe (1.6mg/ml or 3.2mg/ml); dopamine drip can be initated 3. If pulseless arrest develops go to PEA algorithms Dose = 2-10mcg/kg/min and (usually moderate dose of 5- consider Hs and Ts 10) SVT Ask 3 Questions Stable Unstable 1. Adenosine can be given three 1. Stable 1. Vagal Stimulation 1. Synchronized doses of 6,12,12 for a 2. Narrow 2. Adenosine 6mg IV push Cardioverson maximum total of 30mg/ml 3. Regular RAPIDLY If yet to 1-2-3 then think SVT then 3. Observe EKG for VAC evidence of Vagal maneuvers cardioversion Adenosine 4. If no cardioversion Cardizem Adenosine 12mg IV push rapidly and repeat it no cardioversion on EKG 5. Antiarrhythmic (diltizaem) depending on type of tachy Hyperkalemia “C BIG K” 1. Ca Chloride 10% solution (500-100mg) IV bolus 2. Na Bicarbonate 44-88mEq IV bolus, repeat q10min 3. Insulin 10 units IV for every 25 mg of dextrose 4. Glucose (Dextrose) 50% solution IV bolus 5. Kayexalate 15-60g PO or PR
Objective: List the Major indications, precautions, Dosages and administration techniques for the following Drugs Drug Indications Precautions Dosing Administration
Page 3 Clinical Therapeutics IV: Test II
Adenosine 1st line for most narrow- Do NOT use in poisoning or drug- - First dose 6mg IV push Rapidly Technique: complex SVT induced tachycardia - Can give 2 more doses of 12mg 1. Reverse trendelenburg for a total of 30 mg MAX position ADRs- flushing, chest pain, brief 2. IV rapid Push over 1-3 seconds asystole or bradycardia in IV port closest to trunk (antecubital) follow w NS Flush 3. Elevate Extremity after admin Atropine 1. Asystole (PEA) Caution in presence of myocardial - PEA /Asystole=1mg IV push q3- Intravenous 2. PEA with HR<60 (PEA) ischemia and hypoxia because 5 mins Intraosseous 3. Symptomatic increases myocardial oxygen - Bradycardia= can be lower 0.5 Bradycardia (First line demand to 1mg IV push q3-5min while waiting for TCP) - Max dose 0.04mg/kg or 3mg Don’t use in 2nd degree type II and total 3rd degree Heart block bradycardias - Intratracheal = 2-3 mg diluted in 10ml NS Dopamine Infusion Used after - Prepare a 400mg/250ml or Practice Question: atropine for symptomatic 800mg/250ml infusion bag -70kg pt x 2mcg/kg/min bradycardia or in (1.6mg/ml or 3.2mg/ml) =140mcg/min hypotension with signs - Dose 2-10 mcg/kg/min -140mcg/min x60min=8400 mcg/hr and symptoms of shock -8.4mg/xml=1.6mg/ml -X= 5.25ml/hr = 6ml/hr Epinephrine 1. Vfib/Vtach= 1st line Increased BP and HR may cause - 1mg IV/IO q3-5mins during - Each dose should be followed after failure of defib myocardial ischemia, angina and resuscitation with 20ml NS 2. PEA= 1st line after increased myocardial oxygen - 1mg/ml -30ml vials also problem search (PEA) demand available for higher doses/infs 3.Asystole = 1st line for - Infusion (sx badycardia) after problem search prepare infusion by adding 1mg 4.Symptomatic Brady= of epi to 250ml of IV fluid (final Infusion After TCP concentration 4mcg/ml) pacing and Atropine - Dose Infusion: 2-10mcg/min or 120-600mcg/hour Drug Indications Precautions Dosing Administration Lidocaine 1. Antiarrhythmic for Caution in Heat block, WPW, CHF, - 1-1.5mg/kg = 100mgIVpush
Page 4 Clinical Therapeutics IV: Test II
VFib/Vtach hypovolemia, severe resp - May repeat 0.5-1.5mg/kg q3-5 depression and shock, psychosis mins - Max Individual = 1.5mg/kg - Max Total Dose= 3mg/kg exclusive of a lidocaine drip - Endotrach = 2-4mg/kg diluted with NS to a total volume 10ml Magnesium 1. Torsades - May Cause hypotension with - 50% vials - Give IV push over 2 minutes 2. Hypomagnesaemia rapid administration - Dose is 1-2 g (2-4ml) diluted in - Profound Flushing 10 ml D5W or NS - Caution in renal Failure Vasopressin 1. VFib/VTach = may Long ½ Life - 40 units IVP replace 1st or 2nd dose High doses = Vasoconstriction - 1 Dose only of epi in protocol 2. PEA (same as above) 3. Asystole(same above) Objective: List the Indications for the following Drugs used in ACLS Amiodarone Antiarrhythmic fo VFib/Vtach Dextrose With Insulin for Hyperkalemia Naloxone Opiate Antidote CCBs Beta Blockers Digoxin Calcium Chloride Hyperkalemia
Page 5