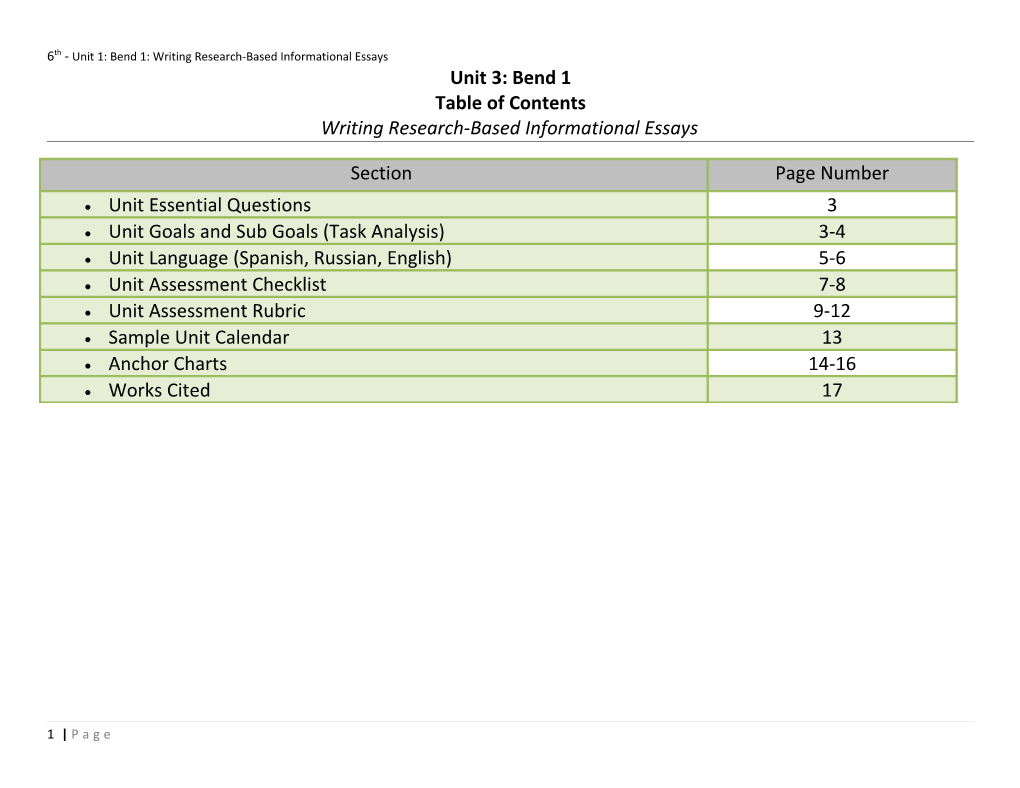
6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays Unit 3: Bend 1 Table of Contents Writing Research-Based Informational Essays
Section Page Number Unit Essential Questions 3 Unit Goals and Sub Goals (Task Analysis) 3-4 Unit Language (Spanish, Russian, English) 5-6 Unit Assessment Checklist 7-8 Unit Assessment Rubric 9-12 Sample Unit Calendar 13 Anchor Charts 14-16 Works Cited 17
1 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays Grade 6 Dates of Unit: Content: Unit 3, Bend 1 Unit Title: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays Stage 1 Identify Desired Results Standards: Writing (Alpha-numeric W.6.1 Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence. listing of W.6.2 Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection, standards organization, and analysis of relevant content. incorporated in W.6.4 Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and the unit) audience. (Grade-specific expectations for writing types are defined in standards 1-3 above.) W.6.5 With some guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach. W.6.7 Conduct short research projects to answer a question, drawing on several sources and refocusing the inquiry when appropriate. W.6.8 Gather relevant information from multiple print and digital sources; assess the credibility of each source; and quote or paraphrase the data and conclusions of others while avoiding plagiarism and providing basic bibliographic information for sources W.6.9 Draw evidence from literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. o b. Apply grade 6 Reading standards to literary nonfiction (e.g., "Trace and evaluate the argument and specific claims in a text, distinguishing claims that are supported by reasons and evidence from claims that are not"). W.6.10 Write routinely over extended time frames (time for research, reflection, and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences. Reading Literature RI.6.1 Cite textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as inferences drawn from the text. RI.6.2 Determine a central idea of a text and how it is conveyed through particular details; provide a summary of the text distinct from personal opinions or judgments. RI.6.3 Analyze in detail how a key individual, event, or idea is introduced, illustrated, and elaborated in a text (e.g., through examples or anecdotes). RI.6.5 Analyze how a particular sentence, paragraph, chapter, or section fits into the overall structure of a text and contributes to the development of the ideas. RI.6.6 Determine an author's point of view or purpose in a text and explain how it is conveyed in the text. RI.6.7 Integrate information presented in different media or formats (e.g., visually, quantitatively) as well as in words to develop a coherent understanding of a topic or issue. RI.6.9 Compare and contrast one author's presentation of events with that of another (e.g., a memoir written by and a biography on the same person). RI.6.10 By the end of the year, read and comprehend literary nonfiction in the grades 6-8 text complexity band proficiently, with 2 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays scaffolding as needed at the high end of the range. Speaking and Listening SL.6.1 Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 6 topics, texts, and issues, building on others' ideas and expressing their own clearly. SL.6.2 Interpret information presented in diverse media and formats (e.g., visually, quantitatively, orally) and explain how it contributes to a topic, text, or issue under study. SL.6.4 Present claims and findings, sequencing ideas logically and using pertinent descriptions, facts, and details to accentuate main ideas or themes; use appropriate eye contact, adequate volume, and clear pronunciation. SL.6.6 Adapt speech to a variety of contexts and tasks, demonstrating command of formal English when indicated or appropriate. Language L.6.1 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking L.6.2 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. L.6.3 Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening. L.6.6 Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate general academic and domain-specific words and phrases; gather vocabulary knowledge when considering a word or phrase important to comprehension or expression.
Essential Questions: (These How do writers compile information from various sources to determine meaningful topics? goals should be ¿Cómo escritores compilan información de diversas fuentes para determinar los temas aligned to Essential Questions.) significativos? Goals: Students will be able to take notes on a Students will be able to gather and Students will be able to write a first draft (These should be single source and determine key points. synthesize information from a variety that includes specific evidence using their aligned to the Goals above) of sources. notes. Learning I can compile my responses to different I can read and take notes on a variety I can choose a plan and convert my outline information by first studying the topic of materials from different sources on into paragraphs. (Session 4) Targets and then taking notes. (Session 1) one topic. (Session 2) (aligned to Puedo elegir un plan y convertir mi goals) Puedo compilar mis respuestas a Puedo leer y tomar apuntes sobre una esquema en párrafos. (Sesión 4) información diferente estudiando variedad de materiales de diferentes primero el tema y luego tomando fuentes acerca de un tema. (Sesión 2) apuntes. (Sesión 1) I can organize my notes into I can analyze different sources and I can cite specific evidence in my first draft subsections. (Session 1) determine 2-3 important ideas to say writing using both different articles and my about an overall topic. (Session 2) notes. (Session 4)
3 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays Puedo organizar mis notas en subsecciones. (Sesión 1) Puedo analizar diferentes fuentes y Puedo citar evidencia específica en mi determinar 2 o 3 ideas importantes primer borrador usando artículos que se enfocan en un tema general. diferentes y mis notas. (Sesión 4) (Sesión 2) I can analyze my notes from a single I can evaluate new sources by source of information and write a key considering their connection to my point. (Session 1) knowledge on the topic. (Session 3)
Puedo analizar mis notas de un solo Puedo evaluar nuevas fuentes fuente de información y escribir un considerando su relación con mis punto clave. (Sesión 1) conocimientos sobre el tema. (Sesión 3)
4 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays Stage 2 Determine Assessment Evidence ENGLISH Academic Language (What language will students need to sound like experts?) Academic Language Function(s): Academic Language Stems: Summarizing Easy for Beginners The article is about ______. Academic Vocabulary: The main idea is ______. source determine Medium for Intermediate key points This makes me think ______. compile The important thing about this is that ______. organize The main reason/purpose/point of this article ______. sub sections The key point is ______. analyze In the article, the author describes the issue of ______. gather synthesize variety Difficult for Advanced and Fluent materials The extraordinary thing about this is ______. topic The message I learn from this (story/topic/person) is evaluate ______. specific evidence The author/passage describes the issue of ______. cite convert outline
Assessment Goals Rubric Tools: Assessment Checklist
Stage 2 Determine Assessment Evidence
5 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays SPANISH Academic Language (What language will students need to sound like experts?) Academic Language Function(s): Academic Language Stems (to talk about their writing): Fácil para los principiantes Resumir El artículo se trata de ______. La idea principal es ______. Academic Vocabulary: Fuente Medio para el Intermedio Determiner puntos claves Esto me hace pensar ______. compilar Lo importante de esto es que ______. organizer El motivo/objetivo/punto principal de este artículo es subsecciones analizar ______. recopilar El punto clave es ______. Sintetizar En el artículo, el autor describe el problema de Variedad Materiales ______. Tema Evaluar Difícil para Avanzado y Fluido evidencia específica citar Lo extraordinario de esto es ______. convertir El mensaje que aprendí de este (cuento/tema/esta esquema persona) es ______. El autor/pasaje describe el problema de ______.
Assessment Goals Rubric Tools: Assessment Checklist
6 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays Assessment Checklist – Unit 3 Bend 1
7 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays I I can I can ca I can choos compile n evaluate e a my org new plan respons ani I can sources and es to ze analyze I can by conve I can cite differen my my analyze thinking rt my specific t no notes I can read different about outlin evidenc informa tes from a and take sources how e into e in my tion by int single notes on and they tie paragr first first o source a variety determi into aphs. draft studyin su of of ne 2-3 what I (Sessi writing g the bs inform materials importa already on 4) using topic ect ation from nt ideas know both and ion and different to say about different then s. write a sources about an the articles taking (Se key on one overall whole and my notes. ssi point. topic. topic. topic. notes. (Session on (Sessio (Session (Session (Session (Session Student Name 1) 1) n 1) 2) 2) 3) 4) Notes
8 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays B = Beginning D = Developing P = Proficient M=Mastery
9 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays Lista de control – Unit 1 Bend 1
10 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays Puedo evaluar nuevas fuentes P considerando su relación con mis u conocimientos sobre el tema. e (Sesión 3) d o
c i t a r e v i d e n c i a
e s p e c í f i c a
e n
m i p r i m e r b o r r a d o r u s 11 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays
C = Comenzando D = Desarrollando P = Proficiente M = Maestría
12 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays
Unit of Study Informational Writing Checklist
STRUCTURE
OVERALL LEAD TRANSITIONS ENDING ORGANIZATION I I I made us deliberate c ed choices about h su how to order o b sections and s he about the e ad sequence of in information a g and ideas I can II an within convey wrote f d/ sections. I ideas I wrote a o or chose and an concl c cl structures inform introduc usion u ea such as ation tion in in s r compare-and- about which I I used transitions to which e in contrast, a interest help readers I d tr categories, subject ed understand how restat o and claim-and- in a readers, different bits of ed t d support to well- perhaps information and the o uc organize structu with a different parts of my impor p to information red quote or writing fit together. I tant i ry and ideas. text. significa used transitions to ideas c tr Some sections Someti nt fact. I help connect ideas, and . an are written as mes I let information, and offere sit arguments, incorp readers examples, and to imply d a io explanations, orated know relationships such as final ns stories, or argum the when material insigh to procedural ents, subtopic exemplifies, adds on t or se passages. explan s that I to, is similar to, implic pa ations, could explains, is a result of, ation ra stories, develop or contrasts, I used for te or later transitions such as for the se proced and how instance, such as, reade cti ural my text similarly, therefore, as r to o passag would a result, in contrast to, consi ns Student Name es. unfold. and on the other hand. der. .
13 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays
- = Not Yet √ = Starting To + = Yes!
Development
ELABORATION
I used trusted I included sources and I worked to make my information varied kinds of information understandable and interesting. To information from do this, I may have referred to such as facts, authorities on earlier parts of my text, summarized quotations, the topic and background information, raised example, and gave the questions, and considered possible Student Name definitions. sources credit. implications.
14 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays
- = Not Yet √ = Starting To + = Yes!
15 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays Lista de Control de la Unidad de Escritura Informativa
ESTRUCTURA LA EN EL CONCLU ORGANIZACIÓN GENERAL PRINCIPIO TRANSICIÓNES -SIÓN E Us Hice decisiones l é deliberadas acerca e u de cómo ordenar g n las secciones y í su acerca de la bt secuencia de u ít información e n ul ideas dentro de o las secciones. Elegí t y/ estructuras tales e o como comparar y Puedo Escribí m tr contrastar, transm una a an categorías, y la itir introduc sic reclamación-y- ideas e ción en Escribí e io apoyo para inform la que una n ne organizar la ación interesé Usé transiciones para concl f s información y las acerca a los ayudar a los lectores a usión o in ideas. Algunas de un lectores, comprender cómo los en la c tr secciones se tema tal vez diferentes bits de que a o escriben como en un con una información y volvía d d argumentos, texto cita o un diferentes partes de mi a o uc explicaciones, bien hecho escritura encajan entre conta . to cuentos o pasajes estruct significa sí. Usé transiciones r las ri de procedimiento. urado. tivo. para ayudar a conectar ideas as A Dejé ideas, información y impor cl veces que los ejemplos, y dar a tantes ar he lectores entender las y as incorp saben relaciones, como ofrecí pa orado los cuando ejemplifica una ra argum subtem materiales, se suma a, visión se entos, as que es similar a, explica, es final o pa explica podía el resultado de, o implic ra ciones, desarrol contrastes, que utilizan acion r histori lar más las transiciones, como, es la as o adelant por ejemplo, tales para s pasajes e y como, de manera la se de cómo mi similar, por lo tanto, consid cc Nombre del/la proced texto se como resultado, en eració io imient desarrol contraste con, y en la n del ne Estudiante o. laría. otra mano. lector. s.
16 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays
- = No Todavía √ = Comenzando + = ¡Sí!
DESARROLLO
ELABORACIÓN
Incluí diversos Usé fuentes He trabajado para hacer mi escritura tipos de confiables e comprensible e interesante. Para información, información de ello, puede que haya contemplado como hechos, las autoridades partes anteriores de mi texto, citas, sobre el tema y información de fondo, preguntas Nombre del/la ejemplos y dio el crédito a planteadas, y consideré las Estudiante definiciones. esas fuentes. implicaciones posibles.
17 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays
- = No Todavía √ = Comenzando + = ¡Sí!
Stage 3 Plan Learning Experiences and Instruction SAMPLE UNIT CALENDAR
Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday I can compile my responses I can organize my notes I can analyze my notes I can read and take notes to different information by into subsections. (Session from a single source of on a variety of materials first studying the topic and 1) information and write a key from different sources on then taking notes. (Session point. (Session 1) one topic. (Session 2) 1)
I can analyze different I can evaluate new sources sources and determine 2-3 by thinking about how they important ideas to say tie into what I already about an overall topic. know about the whole (Session2) topic. (Session 3)
I can choose a plan and I can cite specific evidence convert my outline into in my first draft writing paragraphs. (Session 4) using both different articles and my notes. (Session 4)
18 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays
Anchor Chart:
Yendo desde un Punto Clave a un Plan para un Ensayo Informativo Lógico Si has dado cuenta de una manera que (el tema – eg. jóvenes sobrepasan obstáculos o cambian a las personas), ¿qué puede ser otra manera? Si has encontrado una causa o razón para (el tema – eg. el activismo adolescente), ¿qué puede ser
19 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays causa o razón? Si has encontrado un efecto que (el tema – eg. el activismo adolescente ha creado), ¿qué puede ser efecto? Si has encontrado una fuente de apoyo para (el tema – eg. adolescentes activistas), ¿qué puede ser fuente de apoyo? Si has encontrado un rasgo de (el tema – eg. adolescentes avtivistas), ¿qué puede ser
Works Cited:
20 | P a g e 6th - Unit 1: Bend 1: Writing Research-Based Informational Essays Calkins, Lucy, Maggie Beattie. Roberts, and Emily Strang-Campbell.Research-based Information Writing: Books, Websites, and Presentations. Portsmouth: Heinemann, 2014. Print.
21 | P a g e