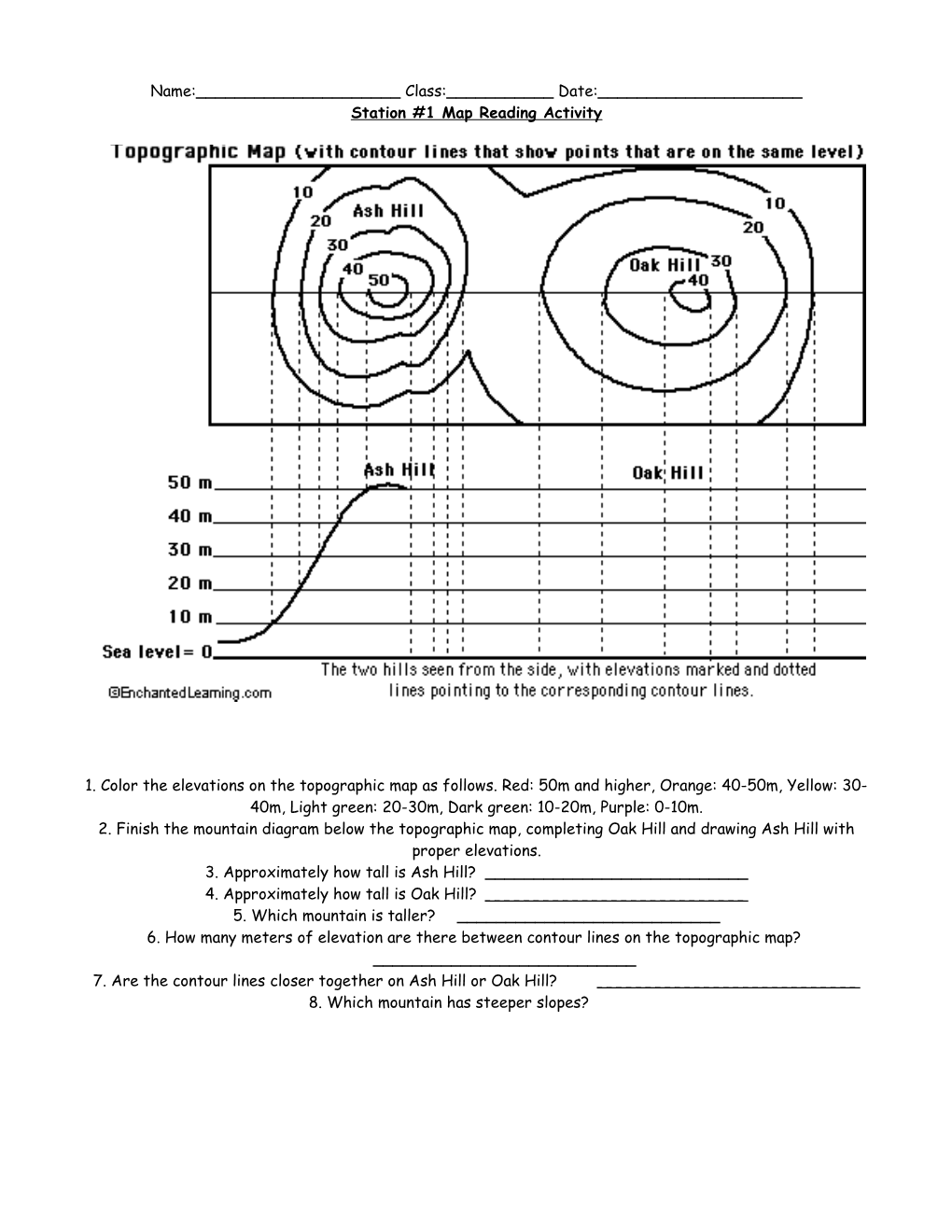
Name:______Class:______Date:______Station #1 Map Reading Activity
1. Color the elevations on the topographic map as follows. Red: 50m and higher, Orange: 40-50m, Yellow: 30- 40m, Light green: 20-30m, Dark green: 10-20m, Purple: 0-10m. 2. Finish the mountain diagram below the topographic map, completing Oak Hill and drawing Ash Hill with proper elevations. 3. Approximately how tall is Ash Hill? ______4. Approximately how tall is Oak Hill? ______5. Which mountain is taller? ______6. How many meters of elevation are there between contour lines on the topographic map? ______7. Are the contour lines closer together on Ash Hill or Oak Hill? ______8. Which mountain has steeper slopes? Station # 2 Contour Mapping
1. What is the contour interval of this map? ______2. Number all the contour lines. 3. What is the scale of miles of this map? ______4. By means of the scale, measure the distance from the top of hill B to the top of hill A. ______5. Which side of hill A has the steepest slope? ______6. How can you tell whether a landform has a steep or gentle slopes? ______7. In what direction from hill A is hill B? ______8. What is the elevation above sea level of hill A? 9. a) Which of the two hill is higher? ______b) How much higher? ______10. If you climbed to the top of hill B from C, how many feet would you climb? 11. In what direction is the Red River flowing? ______How do you know? ______12. Shade the area on the map which would be under water if the sea level rose 40 feet. 13. Calculate the gradient of the Red River from point D to the ocean. Station # 3: Drawing a Profile
1. What is the gradient of the slope between point A and point B. Show all work including the formula.
2. Construct a profile of this map from point C to D. Station # 3: Drawing a Profile Station #4: Contour Mapping Rules
Directions: Read these rules and use them to fill in the blanks for the Conclusion Questions.
1. A contour line represents a single equal elevation: that is, all points on the same contour line have the same elevation.
2. Where one closed contour line surrounds another, the inner contour line represents the higher elevation.
3. The elevation represented by a contour line is always a simple multiple of the contour interval.
4. A contour line that closes within the limits of the map indicates a hill, ridge or plateau.
5. Commonly, every fifth contour line (index contour) is darker and its elevation is shown.
6. On the same map, closely spaced contour lines indicate a relatively steep slope, widely spaced contour lines indicate a relatively gentle slope, and uniformly spaced contour lines indicate a uniform slope.
7. Contour lines do not cross other contour lines. Exception: on a vertical cliff or a nearly vertical cliff, contour lines touch because they are on top of one another
8. Every contour line eventually closes against itself. However, the map area may not be large enough to show this closure. Therefore, the contours will end at the edge of the map.
9. Closed depressions are shown by hachured contour lines. The hachures point into the depression.
(Hachures = short dashes)
10. A hachured contour line, lying between two different contour lines, is the same elevation as the lower contour line.
11. Where two adjacent contours indicate opposite slopes (hachured contour next to plain contour), both are the SAME elevation.
12. Where a contour line crosses a stream or valley, the contour bends to form a “V” that points upstream or up the valley. Therefore the river flows opposite the direction of the “v”
13. A topographic map is aerial view of a location with contour lines that indicate areas of equal elevation above sea level (sea level = 0m) Station #4: Contour Mapping Rules
Conclusion Questions
1. The difference in value between two contour lines is called the ______.
2. The zero contour line is ______.
3. The line that is shaded darker than the other contour lines is the ______.
4. A topographic map shows ______.
5. The closer the contour lines, the ______the slope; the father
apart the contour lines, the ______the slope.
6. Contour lines form ______when they cross streams or valleys.
This ______points ______or ______.
7. Closed depressions are shown by ______.
8. Every contour line eventually ______.
9. Gradient is equal to ______. *First page of your ESRT*
10. A ______is a side view of a particular area.
11. The ______can be determined by estimating the distance between contour lines Station #5: Critical Thinking (you can do it!)
An island measures 10 kilometers from east to west and 8 kilometers from north to south. A single hill on the east side of the island has a maximum elevation of 57 Meters and is steepest to the north. In the box below, draw a simple contour map to represent this island, using a distance scale of 1 centimeter = 1 kilometer and a contour interval of 10 meters. Station #6 Classzone
Steps to use classzone
1. use internet browser to go to classzone.com 2. Choose subject: Science 3. Click on Earth Science textbook 4. Click on “Go to the Exploring Earth Web site” 5. Enter Keycode number ES0307 and click go 6. Follow the instructions on the screen. 7. Use the worksheet provided to record your answers.
Questions: 1. Write a detailed description of the topography that you encounter during this flyby. 2. Describe the pattern of the contour lines around features on the photo. 3. Which part of this land is the last to flood as the water rises? 4. What is the elevation of the points marked A, B, and C? 5. Describe the overall shape of the landscape. 6. What do closely spaced contour lines indicate about the shape of a feature? In other words, when the lines are close together, does the feature have gentle slopes or steep slopes? 7. What is the pattern of the contour lines around a simple hill? 8. Make a sketch of the pattern of the contour lines moving up the valley. Draw an arrow to indicate the direction in which water flows across the lines. 9. What landform feature does the model show, and what do the hachures on contour lines indicate? 10. Describe the structure inside the box on the map. 11. Identify the features marked at A and B. Where is the elevation highest on this map/ Where is it lowest? 12. Which of the landforms was easiest to recognize from its topographic map?