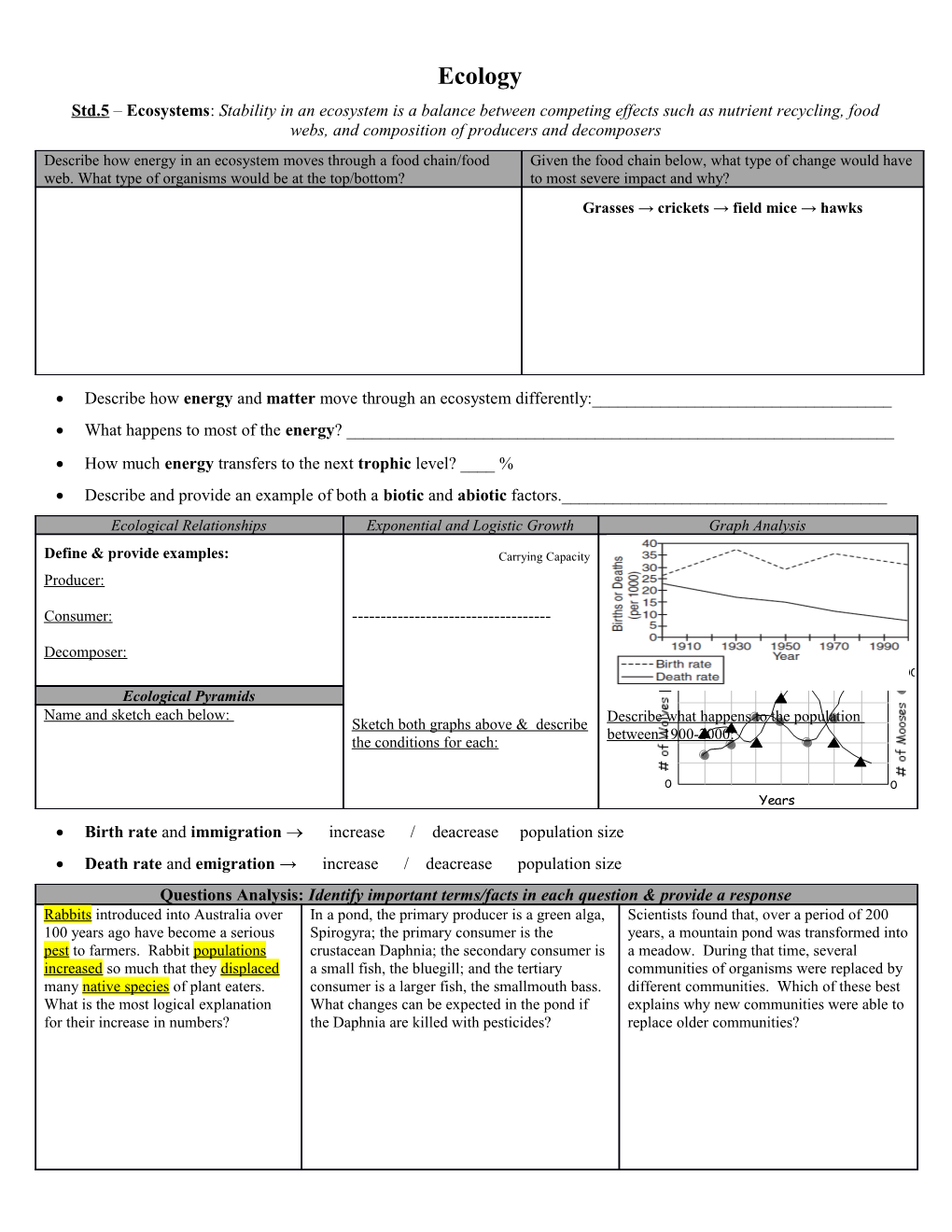
Ecology Std.5 – Ecosystems: Stability in an ecosystem is a balance between competing effects such as nutrient recycling, food webs, and composition of producers and decomposers Describe how energy in an ecosystem moves through a food chain/food Given the food chain below, what type of change would have web. What type of organisms would be at the top/bottom? to most severe impact and why? Grasses → crickets → field mice → hawks
Describe how energy and matter move through an ecosystem differently:______ What happens to most of the energy? ______ How much energy transfers to the next trophic level? ____ % Describe and provide an example of both a biotic and abiotic factors.______Ecological Relationships Exponential and Logistic Growth Graph Analysis
Define & provide examples: Carrying Capacity Producer:
Consumer: ------
Decomposer: 60 2400 Ecological Pyramids Name and sketch each below: Describe what happens to the population Sketch both graphs above & describe between 1900-2000: the conditions for each:
0 0 Years Birth rate and immigration increase / deacrease population size Death rate and emigration → increase / deacrease population size Questions Analysis: Identify important terms/facts in each question & provide a response Rabbits introduced into Australia over In a pond, the primary producer is a green alga, Scientists found that, over a period of 200 100 years ago have become a serious Spirogyra; the primary consumer is the years, a mountain pond was transformed into pest to farmers. Rabbit populations crustacean Daphnia; the secondary consumer is a meadow. During that time, several increased so much that they displaced a small fish, the bluegill; and the tertiary communities of organisms were replaced by many native species of plant eaters. consumer is a larger fish, the smallmouth bass. different communities. Which of these best What is the most logical explanation What changes can be expected in the pond if explains why new communities were able to for their increase in numbers? the Daphnia are killed with pesticides? replace older communities? Ecology Study Guide I. Ecology Ecology → interactions among organisms and environment. II. Energy Flow Photosynthesis: main source of energy Autotrophs – producers → plants and algae Heterotrophs – consumers (primary, secondary, etc.) III. Feeding Relationships and Energy Energy flows : 1 - way direction o Producers → 1st → 2nd →3rd level consumers Food webs - each step/link in a food chain = trophic level IV. Ecological Pyramids 3 Types = energy pyramid , biomass pyramid, and pyramid of numbers o Energy Pyramid – amounts of energy at each level o Biomass – mass of organic (living) matter o Numbers – relative numbers of individuals Energy Transfer o Only about 10% of the energy transfers → trophic levels o Energy used for respiration, movement, etc. o Some energy lost as heat V. Nutrient Cycles Nutrients = life sustaining chemical substances Water cycle, carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, & phosphorus cycle
Oxygen (O2), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), and Water (H2O) all cycle through process of photosynthesis & cellular respiration All cycles pass through both living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) components of an ecosystem.
------I. Populations
3 Characteristics :
Geographic Distribution – area inhabited by a population
Density – number of individuals per unit area (how many)
Growth Rate – fluctuations in population size
II. Population Size
3 factors affect population size: number of births, number of deaths, and number of individuals that enter or leave a population
III. Types of Growth
o Exponential Growth →“J-curve” o Individuals reproduce at a constant rate
o Unlimited resources = little competition
Logistic Growth → “S” Curve
o Increased completion, fewer resources; growth slows
Carrying Capacity = ecosystem cannot support further growth
IV. Limits to Growth
Limiting factor- causes population growth to decrease
o Density-dependent limiting factors =
. competition, predation, parasitism, and disease
o Density independent limiting factors =
. weather, natural disasters, human activity
V. Biodiversity
Variety of life in an in the biosphere = ↑ natural resource
Invasive Species: non-native species introduced in foreign environment – disrupts/ competes in local ecosystem.