DRAFT For Discussion
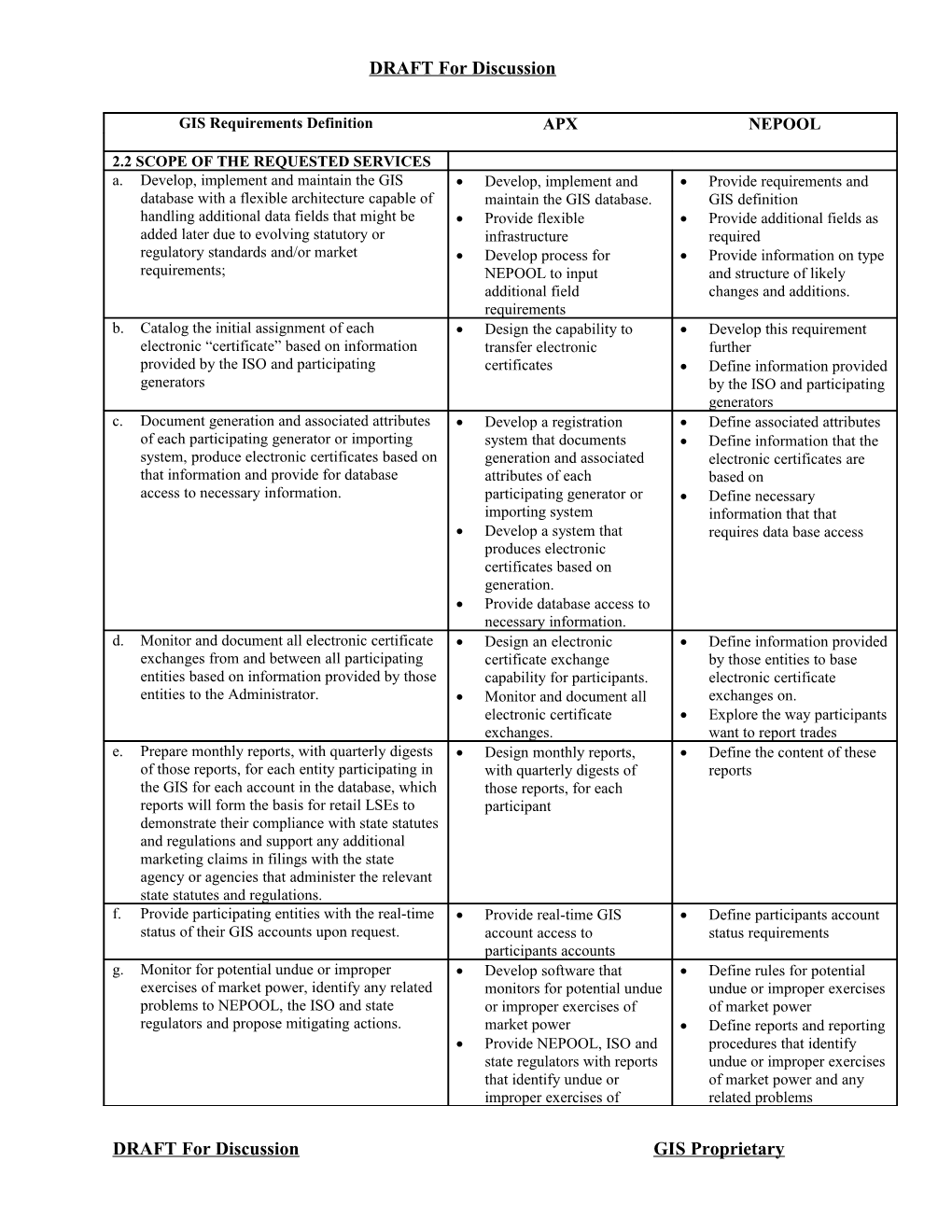
GIS Requirements Definition APX NEPOOL
2.2 SCOPE OF THE REQUESTED SERVICES a. Develop, implement and maintain the GIS Develop, implement and Provide requirements and database with a flexible architecture capable of maintain the GIS database. GIS definition handling additional data fields that might be Provide flexible Provide additional fields as added later due to evolving statutory or infrastructure required regulatory standards and/or market Develop process for Provide information on type requirements; NEPOOL to input and structure of likely additional field changes and additions. requirements b. Catalog the initial assignment of each Design the capability to Develop this requirement electronic “certificate” based on information transfer electronic further provided by the ISO and participating certificates Define information provided generators by the ISO and participating generators c. Document generation and associated attributes Develop a registration Define associated attributes of each participating generator or importing system that documents Define information that the system, produce electronic certificates based on generation and associated electronic certificates are that information and provide for database attributes of each based on access to necessary information. participating generator or Define necessary importing system information that that Develop a system that requires data base access produces electronic certificates based on generation. Provide database access to necessary information. d. Monitor and document all electronic certificate Design an electronic Define information provided exchanges from and between all participating certificate exchange by those entities to base entities based on information provided by those capability for participants. electronic certificate entities to the Administrator. Monitor and document all exchanges on. electronic certificate Explore the way participants exchanges. want to report trades e. Prepare monthly reports, with quarterly digests Design monthly reports, Define the content of these of those reports, for each entity participating in with quarterly digests of reports the GIS for each account in the database, which those reports, for each reports will form the basis for retail LSEs to participant demonstrate their compliance with state statutes and regulations and support any additional marketing claims in filings with the state agency or agencies that administer the relevant state statutes and regulations. f. Provide participating entities with the real-time Provide real-time GIS Define participants account status of their GIS accounts upon request. account access to status requirements participants accounts g. Monitor for potential undue or improper Develop software that Define rules for potential exercises of market power, identify any related monitors for potential undue undue or improper exercises problems to NEPOOL, the ISO and state or improper exercises of of market power regulators and propose mitigating actions. market power Define reports and reporting Provide NEPOOL, ISO and procedures that identify state regulators with reports undue or improper exercises that identify undue or of market power and any improper exercises of related problems
DRAFT For Discussion GIS Proprietary DRAFT For Discussion
market power and any Develop enforcement plan related problems when ISO-NE suspects Support NEPOOL, ISO and market abuses. state regulators strategy sessions in proposing mitigating actions. h. Cooperate with state agencies in the Cooperate with state Develop this requirement verification of retail LSE filings with those agencies. further. state regulators subject to the NEPOOL Information Policy. i. Work with NEPOOL and the ISO to formulate Support Working Groups Assign Working Group to operating rules and procedures for the GIS. with NEPOOL and the ISO perform this task to formulate operating rules Develop the plan for and procedures for the GIS. performing this requirement. j. Implement the appropriate policy with respect Design participant account Develop this requirement to confidential information. information confidentiality. further. 2.3 DESCRIPTION OF GENERATION INFORMATION SYSTEM DATABASE AND CERTIFICATE SYSTEM 2.3.1 Overview Develop, implement and The GIS, using information provided by the ISO maintain the GIS. and participating generators, will create a one-for- one match between energy produced and energy consumed in New England, as well as accommodates imports and exports. The ISO currently administers a wholesale electricity market that is settled each hour as to supply and load obligations. The GIS will contain hourly generation information for each individual New England generation unit that is subject to NEPOOL central dispatch or otherwise participates in the GIS, and it will create generator-specific and importing system- specific electronic “certificates” that identify the relevant generation attributes necessary for retail LSEs to demonstrate satisfaction of state generation information requirements. (4) Retail LSEs will be required to obtain certificates equal to the load they serve. The certificates will contain the information needed to allow retail LSEs to demonstrate their compliance with state requirements and to allow state agencies to verify that compliance. 4 Certificates associated with imports will either be “generator specific” or “system average” depending on the controlling regulatory standards in effect from time to time. 2.3.2 Sources of Generation Information for GIS The ISO currently provides monthly settlement Integrate the GIS with the Provide integration data for statements to all NEPOOL Participants that take MSS revenue quality meter the revenue quality meter part in the wholesale electricity markets readings. readings in the MSS. administered by the ISO, through the ISO’s market Design the GIS to support Provide rule design for the settlement system (“MSS”). Those monthly the import/export rules GIS to administer the MSS statements are based on hourly load and supply developed by NEPOOL. produced hourly scheduled assignments for all market participants as produced Ensure that the small energy flows of imports and by the ISO’s markets software. The initial wholesale generators that exports. generation credits produced by the real-time request inclusion in the Provide the procedures and
DRAFT For Discussion GIS Proprietary DRAFT For Discussion dispatch of generation based on telemetered data are MSS database are supported design that allows the small modified by revenue quality meter readings that are in the GIS. wholesale generators that submitted within 48 hours of the close of each day’s are not telemetered to be market. The MSS also produces hourly scheduled included in the overall MSS energy flows of imports and exports over the database. external ties to and from the NEPOOL control area. Those tie-lines connect to New Brunswick (1), Quebec (2), and New York (8). Small wholesale generators that are not telemetered as part of the real-time wholesale market but that request inclusion in the MSS database are included in the overall MSS database based on revenue-quality meter readings. Those readings are submitted within 48 hours of the close of each day’s market. The basic MSS database maintained for financial Integrate the GIS with the Provide the data interface settlement purposes will provide the initial set of MSS. information for the MSS. inputs for hourly generation credits by resource for Design the MSS Provide details of the basic the GIS database. The MSS will need to be modifications or the plan for MSS database. modified to include some additional information on the GIS to support the Define the MSS individual generation units, and the cost of that information. modifications. upgrade should be included in the capital costs of Design the GIS to accept the Provide characteristics that the GIS that are described below. In addition, labor characteristics that are not are not kept in the MSS that characteristics and possibly some other kept in the MSS and that are may be provided directly to characteristics that are not kept in the MSS may be provided directly to the the Administrator. provided directly to the Administrator by the Administrator. Provide POC for the MSS generators participating in the GIS. related inquiries. 2.3.3 Sources of Retail Load, Export and Wholesale Station Service Withdrawal Information for GIS Information for GIS ISO monthly settlement Develop the GIS to Define what ISO statements also include information on energy ascertain hourly retail load information type and at what withdrawals in the form of exports of energy to responsibility by retail LSE, frequency it will be neighboring control areas and supply of wholesale based on the combination of available for LSE’s station service power to some generating facilities ISO information available Define the information type when they are not generating. ISO monthly and information provided by and at what frequency it will settlement information for energy responsibility, that LSE. be provided by that LSE however, is not necessarily reflective of the associated participant’s retail LSE responsibility. For example, a monthly settlement statement may reflect the wholesale bilateral supply of wholesale energy by a wholesale supplier with no Adjusted Net Interchange reflected in the statement of the retail LSE. The ISO does have information as to the owner of each load asset, which is not necessarily the retail LSE for that load asset. It will be necessary for the Administrator to ascertain hourly retail load responsibility by retail LSE, based on the combination of ISO information available and information provided by that LSE. 5 5 Where either a retail load has switched to a different retail LSE or a retail LSE has contracted with a third party for the management of its generation disclosure obligations, such transfer or contract must be confirmed by the transferee or third party.
DRAFT For Discussion GIS Proprietary DRAFT For Discussion
2.3.4 GIS Database While it may be technically feasible to expand the Build a GIS Database Provide additional fields as ISO-administered MSS and other databases to Design the GIS database to available include the additional fields necessary for a GIS be expandable to include Define the NEPOOL database, at this time this RFP seeks responses to new fields products. develop and administer a separate, stand-alone GIS Provide feedback on database. On a practical level, both databases could registration and data screens utilize the same platform if the legal and operational developed to meet NEPOOL issues related to a shared platform can be resolved. requirements. However, having separate databases will provide advantages in terms of access, data manipulation, maintenance, and, most importantly, modifications. It is highly likely that the GIS database will need frequent modifications in the first few years to accommodate the introduction of new or revised state requirements and changes in the underlying GIS rules. In addition to the hourly data, which will be listed on the certificates, provided from the MSS database, the GIS database will need to include fields for other data, on a product-by-product basis. At this time, some of those fields are known, but the GIS database should include the ability to be expanded to include many additional fields. The current list includes, but is not limited to, the following: Fuel Source Hydro size Less than 100MW Greater than 100MW Hydro type Solid waste Biomass sustainable low emission, advanced other Qualifying cogeneration (ME) Vintage (year commercially operational or as otherwise required by state regulations) Union labor (MA) Emissions factors for SOx, NOx, and CO2 which may vary over time or by fuel Eligibility for state RPS (MA, ME, CT) 6 6 Eligibility will be determined by the applicable regulatory agency. Identification of specific unit Location Time and date of generation The Administrator will develop and maintain the Develop and maintain the Define the content of the database, as well as catalog the initial assignment of database reports on net retail LSEs’ certificates and any trading of certificates, and Catalog the initial attribute accounting to provide reports on net retail LSEs’ attribute assignment of certificates facilitate verification by the accounting to facilitate verification by the Catalog any trading of appropriate state agency. appropriate state agency. Entry and updating of certificates generator-specific attributes may be performed by Provide LSE Reports the generator owner or its designated agent, subject
DRAFT For Discussion GIS Proprietary DRAFT For Discussion to confirmation by the Administrator. Facilitate entry and updating of generator-specific attributes 2.3.5 Production of Certificates The Administrator will produce electronic Develop electronic Define the data certificates based on the hourly generation certificates that meet the requirements for the information from the settlements database and/or NEPOOL rules and data electronic certificates. from information provided by generators. The requirements. certificates will be numbered and may or may not include additional information from the other fields in the GIS database. Each certificate will provide sufficient information (or access to information in the GIS database) so that a retail LSE will be able to determine, in combination with other certificates, its ability to comply with individual state statutes and regulations. 7 7 It is not intended that the GIS will impact the allocation of generation attributes under bilateral agreements. The owner for each generator whose output is Design the GIS to provide Provide the NEPOOL rules settled through the NEPOOL wholesale energy generators with the for certificate creation, market will receive from the Administrator a capability to review and dispute, and resolution. monthly statement of the certificates created by its request modifications to monthly generation. As with financial settlements, their MSS generation data certificate settlements for each month will be before certificates are provided by the Administrator prior to the 15 the of created. the following month, with an opportunity for the Provide generators with a generation owner to review and request method to dispute the modifications, if appropriate, for a time thereafter number of certificates consistent with after-the-fact adjustments in the awarded after award. MSS. In addition, the GIS will need to reflect end-of-the- Incorporate GIS rules to Provide GIS rules that allow month adjustments to meter reads and load asset incorporate end-of-the- the time to incorporate end- values effected by the ISO. month adjustments to meter of-the- month adjustments reads and load asset values. to meter reads and load asset values. 2.3.6 Transfer of Certificates Certificates may be transferred through a variety of Develop certificate transfer Define the NEPOOL rules mechanisms, and the Administrator should mechanisms defined by the for certificate transfer. encourage flexible approaches for the exchange of NEPOOL rules. Define trading period. certificates. Entities should be able to self-supply, Design the GIS database to Define the central bulletin arrange bilateral exchanges in advance of actual be flexible enough to permit board or auction generation, purchase certificates through new types of transfers. requirements. a central bulletin board or auction, and exchange certificates through private arrangements over a later period of time. In addition, the GIS database must be flexible enough to permit new types of transfers as they arise. Regardless of the exchange process used, any entity transferring certificates will be required to notify the Administrator of the transfer prior to the close of the trading period. 2.3.7 Retirement of Certificates Issuance and trading of certificates between and Design the GIS to provide a Define the LSE’s four among entities participating in the GIS will occur three-month + lag period for quarterly reports. over a three-month period. After each calendar issuance and tracking of Define the “Lag Period”.
DRAFT For Discussion GIS Proprietary DRAFT For Discussion quarter and at the end of a short additional period trading of certificates (the “Lag Period”) to be defined, the retail LSE between and among entities accounts maintained by the Administrator will be participating. closed and a report sent to each account holder. Provide the capability to Compliance with state requirements will be close accounts. determined by regulatory authorities on an annual Provide the LSE’s four basis based on the four quarterly reports produced in quarterly reports. each year. In order to ensure a one-to-one match of generation Provide a preliminary Develop the NEPOOL rules and load for accounting purposes, at the end of each determination of those for “Unsettled Certificates.” quarterly period but prior to the end of the Lag certificates explicitly Define the content of the Period, the Administrator will make a preliminary associated with a retail LSE final report of the aggregate determination of those certificates explicitly load, Direct Tags characteristics of remaining associated with a retail LSE load, Direct Tags Transaction or export Unsettled Certificates for Transaction (as defined below) or export transaction. that quarter the “Residual transaction. All remaining certificates will be Provide a preliminary report Mix”. deemed “Unsettled Certificates.” The Administrator of the aggregate will issue a preliminary report of the aggregate characteristics of those characteristics of those Unsettled Certificates, as Unsettled Certificates, as well as a detailed listing of those Unsettled well as a detailed listing of Certificates authorized for release by their current those Unsettled Certificates title-holders, to all entities participating in the GIS authorized for release by at the end of each calendar quarter to facilitate their current title-holders. further trading of those Unsettled Certificates during Provide a final report of the the Lag Period if needed or desired. At the end of aggregate characteristics of the Lag Period, all trading of certificates for that remaining Unsettled quarter will cease and the Administrator will issue a Certificates for that quarter final report to regulators and entities participating in the “Residual Mix”. the GIS of the aggregate characteristics of remaining Unsettled Certificates for that quarter (the “Residual Mix”).8 8 For purposes of compliance with certain regulations, it is anticipated that some regulators may reference the aggregate characteristics of the Residual Mix with respect to Retail LSEs whose total certificates as designated in the final report fall short of their total retail load. It is anticipated that certain renewable (or other) Design the GIS to avoid the Develop the NEPOOL rules generators may continue a current practice of selling possibility of double for “Unsettled Certificates”, the rights to attributes represented by certificates, or counting certificates. “Direct Tags Transactions”, the certificates themselves, directly to retail end- and the “Residual Mix”. users independent of transactions between those retail end-users and their retail LSEs (“Direct Tags Transactions”). To avoid the possibility of double counting certificates, the Administrator will provide a mechanism for generators to inform the Administrator of certificates transacted under verifiable Direct Tags Transactions. At the end of each quarter, the Administrator will exclude any such certificates from determination of any retail LSE’s account balance, and from the determination of Unsettled Certificates and the Residual Mix. The Administrator must monitor for potential Design the GIS to monitor Develop the NEPOOL rules exercises of undue market power by generators, for potential exercises of for defining exercises of LSEs and other entities participating in the GIS, undue market power. undue market power.
DRAFT For Discussion GIS Proprietary DRAFT For Discussion notify NEPOOL, the ISO and state regulators of Provide reports that Develop the NEPOOL rules potential problems and propose mechanisms for NEPOOL, the ISO and state for market power penalties. preventing and mitigating such exercises, to the regulators could use to Develop reports that extent such problems arise. identify and document monitor participant activity market power violators. for potential exercises of undue market power. 2.3.8 Retail LSE Obligations Each retail LSE will have a certificates account with Provide LSE’s with Provide access to LSE retail the Administrator. Each account will have a certificate accounts. energy sales. certificates obligation equal to all of its retail energy Integrate the LSE retail Define retail line loss sales in each calendar quarter, including retail line energy sales data into the NEPOOL rules. losses consistent with local distribution company GIS. allocation of line losses (“Certificates Obligation”). Accommodate retail line loss. The Certificates Obligation may be disaggregated Provide disaggregation of Define retail LSE products. into accounts for each product offered by the retail LSE’s Certificates Define retail LSE’s LSE, at the retail LSE’s discretion. Obligation into LSE product discretion for disaggregation offerings. of their products. (Real time vs. working group) To the extent required to demonstrate compliance Provide LSE’s with the Develop NEPOOL rules for with state or other statutes or regulations, retail capacity to view their compliance. LSEs must obtain, through bilateral transactions or Certificates Obligation and otherwise, certificates equal to all or part of its with the ability to acquire Certificates Obligation in each quarter. certificates using the GIS. The final balance of certificates in each of a retail Provide the reporting Define the report for the LSE’s accounts, as well as any shortfall in capability to deliver to the LSE’s Certificate certificates relative to its Certificates Obligation, LSE and regulators the LSE Obligation. will be reported to each retail LSE and to regulators final balance of certificates if applicable. and shortfall. 2.3.9 Verification of Retail LSE Claims The GIS will maintain one or more accounts based Design the capability to Define LSE products and on the request of each participating entity that follow and document all their requirement for serves retail load. For retail LSEs selling multiple certificate exchanges. separate accounts. products, there will be an account for each product. Design accounts to specify Define capability to follow The Administrator will need the capability to follow the corresponding megawatt and document all certificate and document all certificate exchanges from and hours assigned to each exchanges. between all relevant accounts. Each account will wholesale, retail and Define where the also specify the corresponding megawatt hours product account. information will be acquired assigned to each wholesale, retail and product to specify the corresponding account. MWh’s assigned to each wholesale, retail and product account. On a quarterly basis, the Administrator will provide Provide the Quarterly Retail Define the Quarterly Retail a report to each participating entity for each account LSE Regulatory Filing LSE Regulatory Filing in the database. Those quarterly reports will form Report. Report. the basis for the retail LSEs to make filings with the Allow state regulators read- state agency or agencies that administer the relevant only access to view state statutes and regulations. Auditing of claims Quarterly Retail LSE will be the responsibility of the state regulators. Regulatory Filing Reports. 2.3.10 Exports and Imports Exports of power from the NEPOOL control area Design the GIS to support Provide further definition of will be treated like other energy withdrawals within the export/import applicable regulatory the NEPOOL control area. The exporting entity may requirements. policies concerning exports. export certificates equivalent to the MWhs of power Define all energy
DRAFT For Discussion GIS Proprietary DRAFT For Discussion exported or may export power without associated withdrawals within the certificates. Moreover, certificates may be exported NEPOOL control area. without associated power to the extent consistent Assign Working Group with applicable regulatory policies. Export/Import definition. Cooperate with adjoining control areas to reduce seams. Imports of power from outside the NEPOOL control Account for the total Develop a method for area may produce certificates. Ultimately, the total imported MWhs in the recognizing all imports. imported MWhs will need to be accounted for. NEPOOL control area. Coordinate with Northeast Ideally, a method would be developed for Design the GIS to be regulators to address recognizing the specific attributes of some, if not flexible in relation to regulatory treatments are all, imports to the extent allowed or required by the imports/exports. adopted with respect to applicable statutes and regulations. There will need Ensure that import/export imports. to be coordination among regional control areas in MWhs are not counted order to ensure that attributes are not counted twice twice. (once in each control area). Some preliminary discussions among Northeast regulators suggest that coordination efforts are reasonable and worth pursuing, and those regulators are continuing those discussions. The GIS will need to be flexible enough to permit the Administrator to address whatever regulatory treatments are adopted with respect to imports.
2.3.11 Potential Database Adjustments Related to State Policies An initial design assumption has been that the GIS Integrate the GIS to the database would include only the NEPOOL ISO’s MSS database. generation volumes reflected in the ISO’s MSS database. Thus, it has been assumed that (i) generating units that do not provide If required, provide a Define requirements for separately metered data to the NEPOOL manual capability for generating units that do not wholesale market system, including generating units that do not provide separately metered generation located behind retail customer provide separately metered data to the NEPOOL meters, would not be included in the GIS data to the NEPOOL wholesale market system. database wholesale market system. (ii) certain generating units that are not Support line loss reduction Define line loss connected to NEPOOL pool transmission requirements. requirements. facilities would have their outputs reduced in the GIS to the same extent that they are reduced in the MSS for line losses (iii) the output of each generating unit would be The APX GIS will have the Define individual states measured at its interconnection meter and capability for automated regulatory generation would thus be reduced for station service meter data entry and manual requirements. to the same extent that they are reduced in meter data entry. the MSS. Individual states could, however, Design the GIS to be implement their own procedures to allow flexible enough to reflect and recognize for regulatory purposes the additional data sources. incremental generation amounts and attributes associated with such limitations, and such qualifying generation amounts could, when reliably metered, then be included in the GIS database and certificate program. The GIS would need to be
DRAFT For Discussion GIS Proprietary DRAFT For Discussion
flexible enough to reflect such additional data sources. 2.3.12 Development of Emission Factors Emissions data necessary to issue certificates will Design participant Assign Working Group be supplied to the Administrator by individual Registration system to Emission factors definition. generators. Details with respect to sources of include emission factors. Define emission sources. emissions data, mechanisms for transferring data to Define the timing of the Administrator, and the timing of data submittals emissions data submittals. are to be discussed by the Committee and will be resolved in consultation with the Administrator. The GIS must accommodate co-firing multi-fuel Design the GIS to Define rules of to include units. The Administrator will need to develop a accommodate duel fuel duel fuel units. mechanism to allow new generation units (with no units. Define prospective history) and retrofitted generation units (with Design the GIS to be emissions factors. anticipated reduced emissions) to adopt prospective flexible enough to adopt emissions factors. prospective emissions factors.
2.3.13 Pumped Storage Pumped storage and generation presents a complex Design the GIS to meet the Assign Working Group the issue for the GIS. The pumps that put the water into requirements for pumped pumped storage definition. storage consume energy generated in some hours of storage. Define a method of the real-time wholesale energy market for use in accounting for pumped generating energy in subsequent hours. The real- storage. time generation that runs the pumps will have certificates issued at the end of the month equal to the megawatt hours of energy that the pumps use. When the stored water is released, additional generation (about 30 percent less than the energy that initially pumped the water) occurs that is sold into the wholesale market and ultimately to retail consumers. The retail LSE that purchases the electricity Design the GIS to meet the produced by the pumped storage facility has the requirements for pumped obligation to acquire certificates for the megawatt storage. hours of electricity sold to its retail customers. In order to balance the total amount of monthly certificates assigned to retail loads with the total monthly megawatt hours of generation, the losses associated with pumped storage (approximately 30 percent) need to be allocated. The proposed solution is to require all retail LSEs to Support the Working Group Assign Working Group to assume a pro-rata share of pumped storage losses. in proposing alternatives to propose alternatives to That means that each LSE will need to purchase reflect the benefits pumped reflect the benefits pumped additional certificates to account for its retail load storage provides to the storage provides to the pro-rata share of certificates needed to cover these region after initial region after initial losses, estimated at less than one-half of one percent implementation. implementation. of its retail sales. While initially the emission reduction benefits of peak clipping from pumped storage facilities and other load management programs will not be explicitly recognized in the certificate program, the Administrator will propose alternatives to reflect the benefits they provide to the region after initial implementation.
DRAFT For Discussion GIS Proprietary