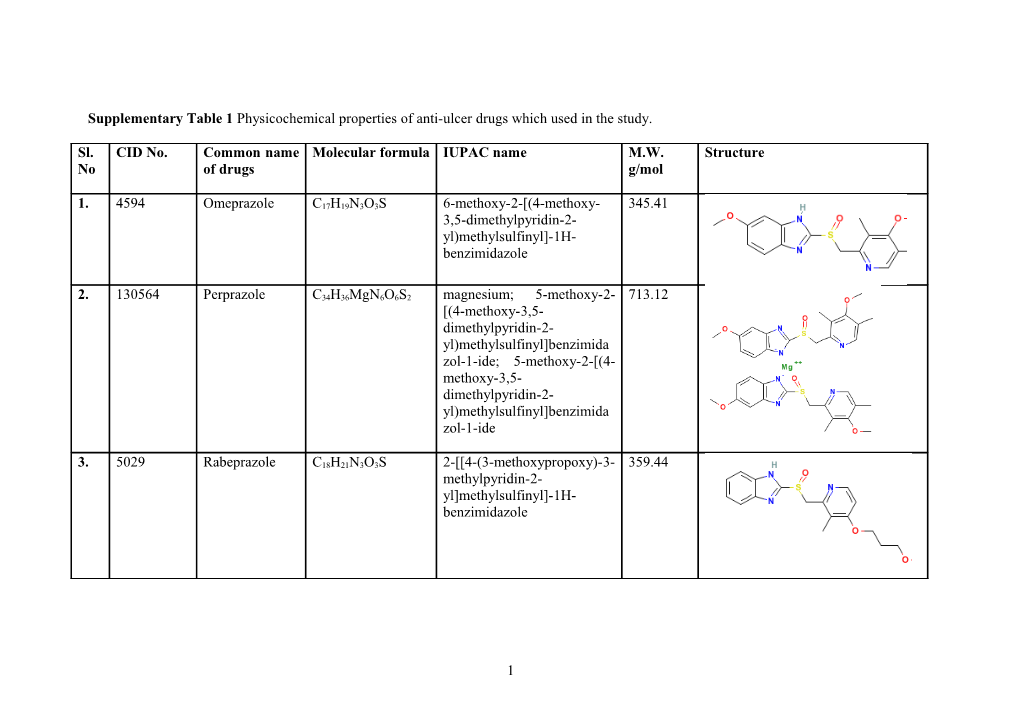
Supplementary Table 1 Physicochemical properties of anti-ulcer drugs which used in the study.
Sl. CID No. Common name Molecular formula IUPAC name M.W. Structure No of drugs g/mol
1. 4594 Omeprazole C17H19N3O3S 6-methoxy-2-[(4-methoxy- 345.41 3,5-dimethylpyridin-2- yl)methylsulfinyl]-1H- benzimidazole
2. 130564 Perprazole C34H36MgN6O6S2 magnesium; 5-methoxy-2- 713.12 [(4-methoxy-3,5- dimethylpyridin-2- yl)methylsulfinyl]benzimida zol-1-ide; 5-methoxy-2-[(4- methoxy-3,5- dimethylpyridin-2- yl)methylsulfinyl]benzimida zol-1-ide
3. 5029 Rabeprazole C18H21N3O3S 2-[[4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3- 359.44 methylpyridin-2- yl]methylsulfinyl]-1H- benzimidazole
1 4. 10959536 Losec C17H18N3NaO3S sodium 5-methoxy-2-[(4- 367.39 methoxy-3,5- dimethylpyridin-2- yl)methylsulfinyl]benzimida zol-1-ide
5. 23681230 Omepral C17H20N3NaO4S sodium 5-methoxy-2-[(4- 385.41 methoxy-3,5- dimethylpyridin-2- yl)methylsulfinyl]benzimida zol-1-ide hydrate
Supplementary Table 2 The amino acid residues and hydrogen bond formed between drugs and H+, K+ -ATPase S. No. Protein name Amino acids in H+, K+ ATPase Drugs Interaction of H+, K+ Distance of hydrogen ATPase and drugs bonds (Ǻ) 1. H+, K+ ATPase Asp740, Ala739, Asn290, Asn371, Omeprazole UNK1:H--Asp758:OD1 1.905 Lys370, Leu736, Asp758 2. H+, K+ ATPase Asp387, Asp728, Thr389, Ser750, Rabeprazole NDa NDa Ile747 a Not detected. Table 3 ATP4A gene regulatory network in H. sapiens
2 Name of Score Potential functions of proteins and enzymes Proteins ATP4B 0.945 ATPase, H+/K+ exchanging, beta polypeptide (291 aa) PPA1 0.899 Pyrophosphatase (inorganic) 1 (289 aa) LHPP 0.899 Phospholysine phosphohistidine inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase (270 aa) PPA2 0.899 Pyrophosphatase (inorganic) 2 (334 aa) FXYD5 0.855 FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 5 which involved in down-regulation of E-cadherin which results in reduced cell adhesion and promotes metastasis (178 aa) APLP1 0.779 Amyloid beta (A4) precursor-like protein 1 that may play a role in postsynaptic function. The C- terminal gamma-secretase processed fragment, ALID1, activates transcription activation through APBB1 (Fe65) binding. Couples to JIP signal transduction through C-terminal binding. That may interact with cellular G-protein signaling pathways. It can regulate neurite outgrowth through binding to components of the extracellular matrix such as heparin and collagen I (651 aa) COX7A1 0.730 Cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIIa polypeptide 1 (muscle) which is one of the nuclear-coded polypeptide chains of cytochrome c oxidase, the terminal oxidase in mitochondrial electron transport (79 aa) CTCF 0.702 CCCTC-binding factor (zinc finger protein); Chromatin binding factor that binds to DNA sequence specific sites. Involved in transcriptional regulation by binding to chromatin insulators and preventing interaction between promoter and nearby enhancers and silencers. Acts as transcriptional repressor binding to promoters of vertebrate c-myc gene and BAG1 gene. It also binds to PLK and PIM1 promoters which act as a transcriptional activator of APP. It regulates APOA1/C3/A4/A5 gene cluster and controls MHC class II gene expression. Plays an essential role in oocyte and preimplantation
3 embryo development (727 aa) C20orf114 0.683 Long palate, lung and nasal epithelium carcinoma-associated protein 1 Precursor (Von Ebner minor salivary gland protein)(VEMSGP). It may play a role in innate immunity in mouth, nose and lungs (484 aa) ALDOC 0.669 Aldolase C, fructose-bisphosphate (364 aa) COX6B1 0.665 Cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIb polypeptide 1 (ubiquitous) that connects the two COX monomers into the physiological dimeric form (86 aa) GKN2 0.645 Gastrokine 2 (184 aa) MRPL23 0.639 Mitochondrial ribosomal protein L23 (153 aa) CTCFL 0.639 CCCTC-binding factor (zinc finger protein)-like, Testis-specific DNA binding protein responsible for insulator function, nuclear architecture and transcriptional control, which probably acts by recruiting epigenetic chromatin modifiers. It plays a key role in gene imprinting in male germline, by participating in the establishment of differential methylation at the IGF2/H19 imprinted control region (ICR). It directly binds the unmethylated H19 ICR and recruits the PRMT7 methyltransferase, leading to methylate histone H4 'Arg-3' to form H4R3sme2. This probably leads to recruit de novo DNA methylation (663 aa) NDRG2 0.619 NDRG family member 2 that may be involved in dendritic cell and neuron differentiation. May have anti-tumor activity (371 aa) GLUD1 0.619 Glutamate dehydrogenase 1 that may be involved in learning and memory reactions by increasing the turnover of the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate (558 aa) ITLN2 0.617 Intelectin 2 as it may play a role in the defense system against pathogens (325 aa) DNAH8 0.569 Dynein, axonemal, heavy chain 8 which force generating protein of respiratory cilia. It produces force towards the minus ends of microtubules. Dynein has ATPase activity; the force-producing power stroke
4 is thought to occur on release of ADP. Involved in sperm motility; implicated in sperm flagellar assembly (4490 aa) CHD8 0.553 Chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 8 which acts as a chromatin remodeling factor and regulates transcription. It acts as a transcription repressor by remodeling chromatin structure and recruiting histone H1 to target genes. It suppresses p53/TP53-mediated apoptosis by recruiting histone H1 and preventing p53/TP53 transactivation activity. It acts as a negative regulator of Wnt signaling pathway by regulating beta-catenin (CTNNB1) activity. Negatively regulates CTNNB1- targeted gene expression by being recruited specifically to the promoter regions of several CTNNB1 responsiveness (2302 aa) WSB1 0.553 WD repeat and SOCS box-containing 1 the probable substrate-recognition component of a SCF-like ECS (Elongin-Cullin-SOCS-box protein) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins. It recognizes the type II iodothyronine deiodinase/DIO2 (421 aa)
5 Supplementary Fig. S1 The stereochemical arrangement of amino acids residue of modeled 3-D model of H+, K+ ATPase in favored region of Ramachandran plot. The red region indicates the most favored allowed region.
6 Omeprazole
Supplementary Fig. 2 Interaction of high affinity potent Omeprazole with H+, K+ ATPase shows in Asp758 with Omeprazole.
7 Fig. 4 (a) Interaction of high affinity potent Rabeprazole drug with amino acids in 3-D of H+, K+ ATPase. (b) Amino acid shows in stick and ball with Rabeprazole. Rabeprazole Rabeprazole
Supplementary Fig. 3 Interaction of high affinity potent Rabeprazole drug with 3-D model of H+, K+ ATPase. Amino acid shows in stick and ball with Rabeprazole.
8