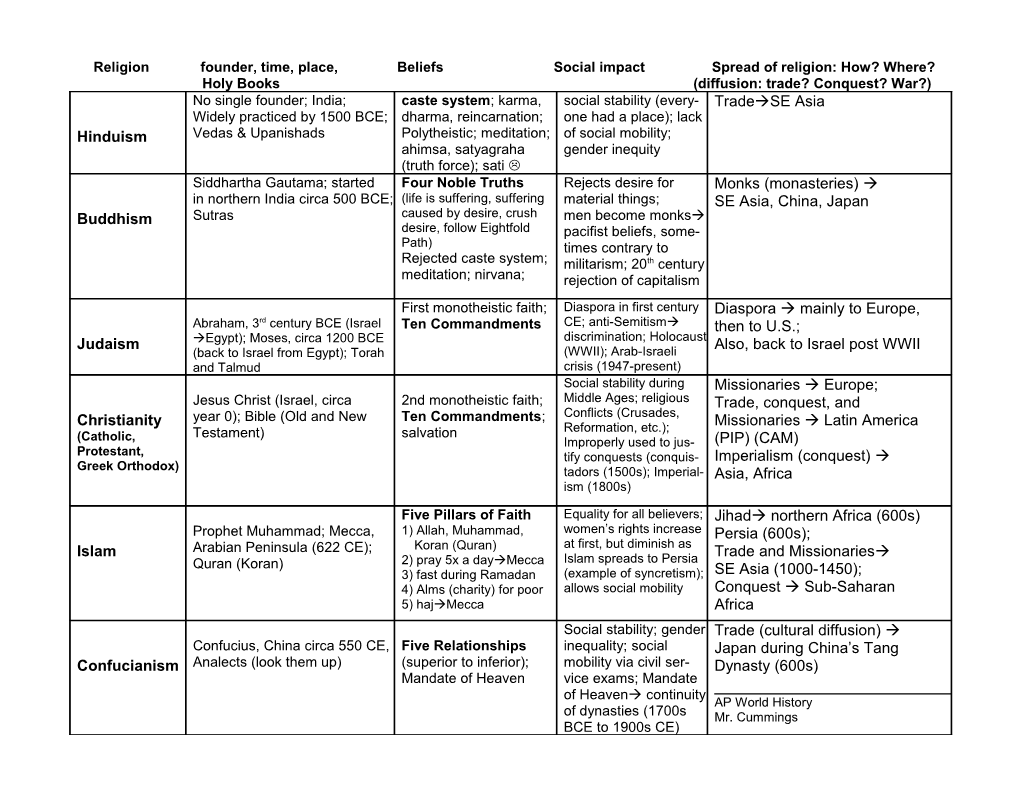
Religion founder, time, place, Beliefs Social impact Spread of religion: How? Where? Holy Books (diffusion: trade? Conquest? War?) No single founder; India; caste system; karma, social stability (every- TradeSE Asia Widely practiced by 1500 BCE; dharma, reincarnation; one had a place); lack Hinduism Vedas & Upanishads Polytheistic; meditation; of social mobility; ahimsa, satyagraha gender inequity (truth force); sati Siddhartha Gautama; started Four Noble Truths Rejects desire for Monks (monasteries) in northern India circa 500 BCE; (life is suffering, suffering material things; SE Asia, China, Japan Buddhism Sutras caused by desire, crush men become monks desire, follow Eightfold pacifist beliefs, some- Path) times contrary to Rejected caste system; militarism; 20th century meditation; nirvana; rejection of capitalism First monotheistic faith; Diaspora in first century Diaspora mainly to Europe, Abraham, 3rd century BCE (Israel Ten Commandments CE; anti-Semitism then to U.S.; Judaism Egypt); Moses, circa 1200 BCE discrimination; Holocaust Also, back to Israel post WWII (back to Israel from Egypt); Torah (WWII); Arab-Israeli and Talmud crisis (1947-present) Social stability during Missionaries Europe; Jesus Christ (Israel, circa 2nd monotheistic faith; Middle Ages; religious Trade, conquest, and Christianity year 0); Bible (Old and New Ten Commandments; Conflicts (Crusades, Missionaries Latin America Testament) salvation Reformation, etc.); (Catholic, Improperly used to jus- (PIP) (CAM) Protestant, tify conquests (conquis- Imperialism (conquest) Greek Orthodox) tadors (1500s); Imperial- Asia, Africa ism (1800s) Five Pillars of Faith Equality for all believers; Jihad northern Africa (600s) Prophet Muhammad; Mecca, 1) Allah, Muhammad, women’s rights increase Persia (600s); Islam Arabian Peninsula (622 CE); Koran (Quran) at first, but diminish as Trade and Missionaries Quran (Koran) 2) pray 5x a dayMecca Islam spreads to Persia 3) fast during Ramadan (example of syncretism); SE Asia (1000-1450); 4) Alms (charity) for poor allows social mobility Conquest Sub-Saharan 5) hajMecca Africa Social stability; gender Trade (cultural diffusion) Confucius, China circa 550 CE, Five Relationships inequality; social Japan during China’s Tang Confucianism Analects (look them up) (superior to inferior); mobility via civil ser- Dynasty (600s) Mandate of Heaven vice exams; Mandate of Heaven continuity AP World History of dynasties (1700s Mr. Cummings BCE to 1900s CE) AP WORLD HISTORY NAME ______
Religion founder, time, place, Beliefs Social impact Spread of religion: How? Where? Holy Books (diffusion: trade? Conquest? War?)
Hinduism
Buddhism
Judaism
Christianity (Catholic, Protestant, Greek Orthodox)
Islam
Confucianism