Identifying Unknown Bacteria – Class Set
Bacteria and other microbes are considerably difficult to identify. Bacteria are extremely small and show only a few variations in appearance. Testing for chemical characteristics is often needed to distinguish between bacteria that are similar in appearance. The table below gives characteristics for a variety of bacteria that often need to be identified in medical laboratories.
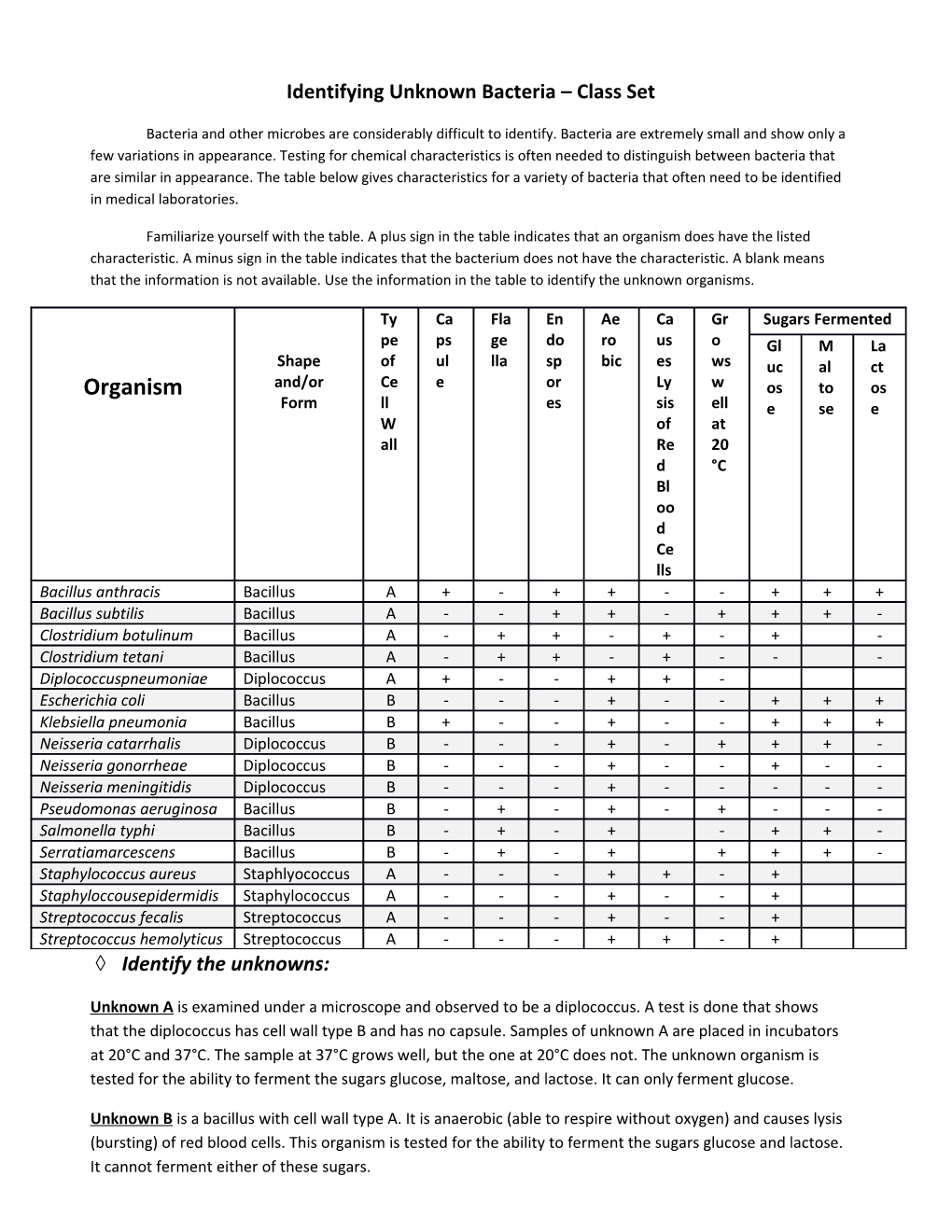
Familiarize yourself with the table. A plus sign in the table indicates that an organism does have the listed characteristic. A minus sign in the table indicates that the bacterium does not have the characteristic. A blank means that the information is not available. Use the information in the table to identify the unknown organisms.
Ty Ca Fla En Ae Ca Gr Sugars Fermented pe ps ge do ro us o Gl M La Shape of ul lla sp bic es ws uc al ct Organism and/or Ce e or Ly w os to os Form ll es sis ell e se e W of at all Re 20 d °C Bl oo d Ce lls Bacillus anthracis Bacillus A + - + + - - + + + Bacillus subtilis Bacillus A - - + + - + + + - Clostridium botulinum Bacillus A - + + - + - + - Clostridium tetani Bacillus A - + + - + - - - Diplococcuspneumoniae Diplococcus A + - - + + - Escherichia coli Bacillus B - - - + - - + + + Klebsiella pneumonia Bacillus B + - - + - - + + + Neisseria catarrhalis Diplococcus B - - - + - + + + - Neisseria gonorrheae Diplococcus B - - - + - - + - - Neisseria meningitidis Diplococcus B - - - + - - - - - Pseudomonas aeruginosa Bacillus B - + - + - + - - - Salmonella typhi Bacillus B - + - + - + + - Serratiamarcescens Bacillus B - + - + + + + - Staphylococcus aureus Staphlyococcus A - - - + + - + Staphyloccousepidermidis Staphylococcus A - - - + - - + Streptococcus fecalis Streptococcus A - - - + - - + Streptococcus hemolyticus Streptococcus A - - - + + - + Identify the unknowns:
Unknown A is examined under a microscope and observed to be a diplococcus. A test is done that shows that the diplococcus has cell wall type B and has no capsule. Samples of unknown A are placed in incubators at 20°C and 37°C. The sample at 37°C grows well, but the one at 20°C does not. The unknown organism is tested for the ability to ferment the sugars glucose, maltose, and lactose. It can only ferment glucose.
Unknown B is a bacillus with cell wall type A. It is anaerobic (able to respire without oxygen) and causes lysis (bursting) of red blood cells. This organism is tested for the ability to ferment the sugars glucose and lactose. It cannot ferment either of these sugars. Unknown C is a bacillus that produces endospores during harsh times. This organism was tested for its ability to ferment glucose, maltose and lactose. It can ferment all three sugars.
Unknown D has cell wall type A and does not produce endospores. It does not grow well at 20°C but does cause lysis of red blood cells. When viewed with a microscope this organism appears to be diplococcus.
Unknown E uses a flagellum for propulsion and cell wall type B. It does not grow well at 20°C and cannot ferment lactose.
Unknown F is a bacillus with cell wall type A. It is anaerobic and causes lysis of red blood cells. This organism is tested for the ability to ferment the sugars glucose and lactose. It can ferment only one of these sugars.
Unknown G is observed to be diplococcus using a compound light microscope. A test reveals the absence of a capsule and presence of cell wall type B. Sample G does not grow well at 20°C. The organism was tested for its ability to ferment glucose, maltose and lactose. It cannot ferment any of these sugars.
Unknown H is shown to have cell wall type A. It is aerobic and known to cause lysis of red blood cells. It does not produce endospores. When tested, it can ferment glucose and has a streptococcus shape.
Create a dichotomous key for the 8 unknowns using the information in the table.
1 A Type A Cell Wall present. Go to 2.
B Type B Cell Wall present. Go to 3.
2 A
B
3 A
B
4 A
B
5 A
B
6 A
B
7 A
B
8 A
B
9 A
B