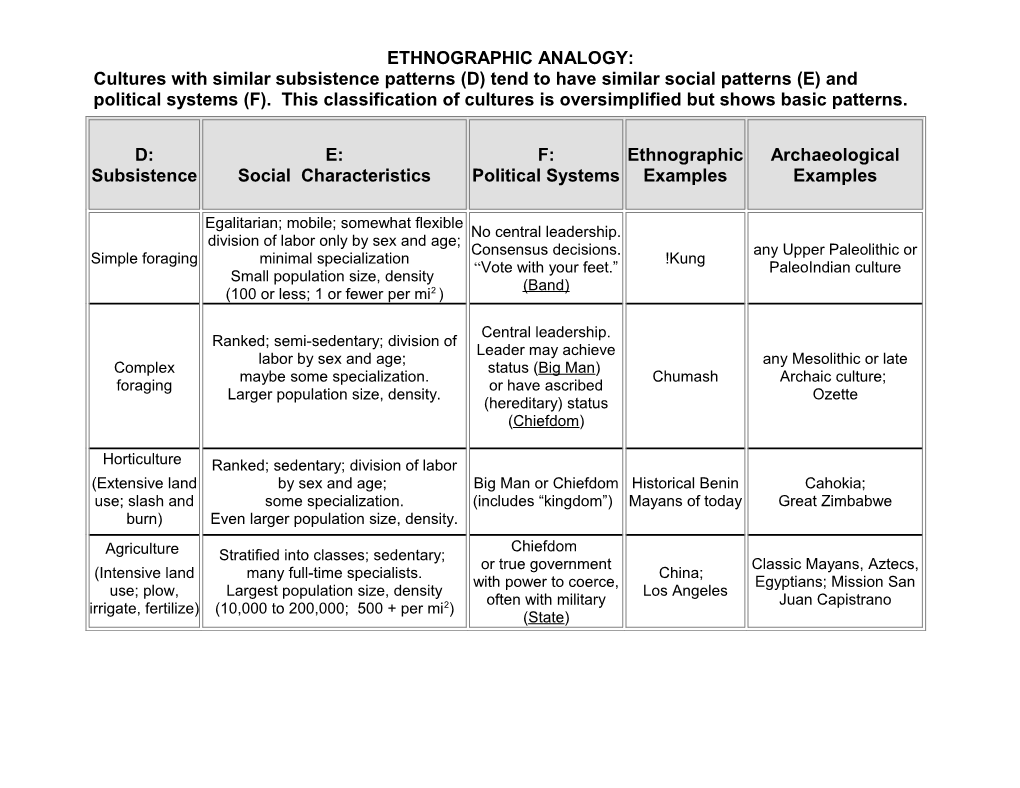
ETHNOGRAPHIC ANALOGY: Cultures with similar subsistence patterns (D) tend to have similar social patterns (E) and political systems (F). This classification of cultures is oversimplified but shows basic patterns.
D: E: F: Ethnographic Archaeological Subsistence Social Characteristics Political Systems Examples Examples
Egalitarian; mobile; somewhat flexible No central leadership. division of labor only by sex and age; Consensus decisions. any Upper Paleolithic or Simple foraging minimal specialization !Kung “Vote with your feet.” PaleoIndian culture Small population size, density ( Band ) (100 or less; 1 or fewer per mi2 )
Central leadership. Ranked; semi-sedentary; division of Leader may achieve labor by sex and age; any Mesolithic or late Complex status (Big Man) maybe some specialization. Chumash Archaic culture; foraging or have ascribed Larger population size, density. Ozette (hereditary) status (Chiefdom)
Horticulture Ranked; sedentary; division of labor (Extensive land by sex and age; Big Man or Chiefdom Historical Benin Cahokia; use; slash and some specialization. (includes “kingdom”) Mayans of today Great Zimbabwe burn) Even larger population size, density. Chiefdom Agriculture Stratified into classes; sedentary; or true government Classic Mayans, Aztecs, (Intensive land many full-time specialists. China; with power to coerce, Egyptians; Mission San use; plow, Largest population size, density Los Angeles often with military Juan Capistrano irrigate, fertilize) (10,000 to 200,000; 500 + per mi2) (State)