October – December 2016
ISMP QuarterlyActionAgenda One of the most important ways to prevent medication errors is to learn about problems that have occurred in other organizations and to use that information to prevent similar problems at your practice site. To promote such a process, the following selected items from the October–December 2016 issues of the ISMP Medication Safety Alert! have been prepared for an interdisciplinary committee to stimulate discussion and action to reduce the risk of medication errors. Each item includes a brief description of the medication safety problem, a few recommendations to reduce the risk of errors, and the issue number to locate additional information. Look for our high-alert medication icon under the issue number if the agenda item involves one or more medications on the ISMP List of High-Alert Medications (www.ismp.org/sc?id=479). The Action Agenda is also available for download in a Microsoft Word format (www.ismp.org/newsletters/acutecare/articles/ActionAgenda1701.doc) that allows expansion of the columns in the table designated for organizational documentation of an assessment, actions required, and assignments for each agenda item. Continuing education credit is available for nurses at: www.ismp.org/sc?id=480.
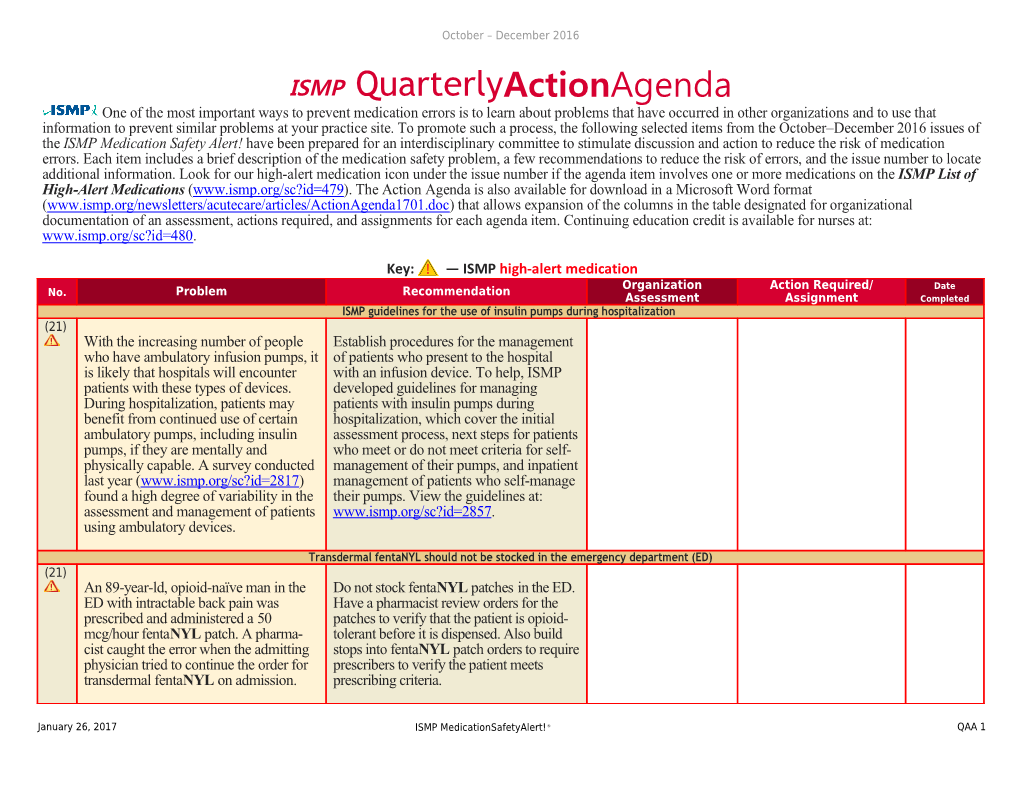
Key: — ISMP high-alert medication Organization Action Required/ Date No. Problem Recommendation Assessment Assignment Completed ISMP guidelines for the use of insulin pumps during hospitalization (21) With the increasing number of people Establish procedures for the management who have ambulatory infusion pumps, it of patients who present to the hospital is likely that hospitals will encounter with an infusion device. To help, ISMP patients with these types of devices. developed guidelines for managing During hospitalization, patients may patients with insulin pumps during benefit from continued use of certain hospitalization, which cover the initial ambulatory pumps, including insulin assessment process, next steps for patients pumps, if they are mentally and who meet or do not meet criteria for self- physically capable. A survey conducted management of their pumps, and inpatient last year (www.ismp.org/sc?id=2817) management of patients who self-manage found a high degree of variability in the their pumps. View the guidelines at: assessment and management of patients www.ismp.org/sc?id=2857. using ambulatory devices.
Transdermal fentaNYL should not be stocked in the emergency department (ED) (21) An 89-year-ld, opioid-naïve man in the Do not stock fentaNYL patches in the ED. ED with intractable back pain was Have a pharmacist review orders for the prescribed and administered a 50 patches to verify that the patient is opioid- mcg/hour fentaNYL patch. A pharma- tolerant before it is dispensed. Also build cist caught the error when the admitting stops into fentaNYL patch orders to require physician tried to continue the order for prescribers to verify the patient meets transdermal fentaNYL on admission. prescribing criteria.
January 26, 2017 ISMP MedicationSafetyAlert! QAA 1 October – December 2016
ISMP QuarterlyActionAgenda Organization Action Required/ Date No. Problem Recommendation Assessment Assignment Completed
Lipid rescue for bupivacaine toxicity (23) A pregnant patient experienced stupor, Ensure appropriate rescue agents and seizures, hypotension, and tachycardia directions for their use are available in after she received fentaNYL and clinical areas. Develop standardized bupivacaine IV instead of penicillin G. protocols that permit emergency Prompt recognition of the error led to administration of a lipid rescue agent to treatment with fat emulsion. The patient treat bupivacaine toxicity to prevent any recovered and delivered a healthy delays in administration. infant.
Harm or death from phenytoin injection errors (23) The National Health Service Weigh each patient in metric units on Improvement in the UK issued an alert admission or during an emergency about errors with injectable phenytoin. department encounter. Avoid the use of a Contributing factors included: no weight stated, estimated, or historical weight. or wrong estimated weight, failure to take Review the patient’s medication history into account existing phenytoin levels before prescribing or dispensing loading when prescribing loading doses, wrong doses of phenytoin to make sure the patient infusion rates or diluent, loading dose was not taking it previously. Pharmacy continued as a maintenance dose, and should prepare and dispense all IV lack of monitoring. piggyback doses.
LANTUS (insulin glargine) overdose tied to confusing vial label (23) A patient received 900 units of Lantus Educate staff regarding safe insulin subcutaneously due in part to a dosing ranges and injection technique. confusing label on the Sanofi vial. If However, the best way to avoid a similar turned a certain way, the label lists “10 error is for the pharmacy to prepare, label, mL” directly below “100 units.” The and dispense patient-specific basal insulin nurse thought she had to administer 9 doses. We have notified Sanofi and the mL of insulin to deliver a 90 unit dose. US Food and Drug Administration about The hospital normally used Lantus pens, the labeling issue that contributed to a but the maximum dose that can be misunderstanding of the concentration. administered with the pen is 80 units, so the pharmacy dispensed a 10 mL vial. Other contributing factors included unfamiliarity with safe dosing ranges
January 26, 2017 ISMP MedicationSafetyAlert! QAA 2 October – December 2016
ISMP QuarterlyActionAgenda Organization Action Required/ Date No. Problem Recommendation Assessment Assignment Completed and the maximum volume for subcutaneous injections. Accidental intravenous (IV) infusion of a heparinized irrigation solution (24) A bag of lactated ringer’s with added Have pharmacy prepare or provide heparin intended for wound irrigation commonly used irrigation mixtures to the was mistakenly administered IV during operating room (OR) in pour bottles or a surgical procedure. The bag was not bags of a different size (e.g., 2 L) with a labeled as containing heparin. IV “FOR IRRIGATION ONLY” label. administration of bladder/wound Label all irrigation solutions immediately irrigations often involves confusion when an additive is mixed into the between unlabeled solutions, mix-ups solution. Consider mixing the heparin in between irrigation and parenteral sodium chloride 0.9% pour bottles. solution bags, or mix-ups between Separate fluid replacement and irrigation irrigation and venous access lines. solutions.
Don’t bring medications/solutions to the bedside or procedural area before they are ordered or needed (20) Bringing a controlled substance or any Any controlled substance or medication/solution into the patient’s medication/solution needed for a room, bedside, or procedural area before procedure should be obtained it is ordered or needed introduces the immediately before use. If obtained by an risk that it might be mistaken as a individual not administering it, a time-out different drug/solution that is packaged process should include verification of the similarly. One fatal event involved a drug/solution as it is handed to the nurse who mistakenly administered practitioner who will be administering it. fentaNYL and bupivacaine IV instead Barcode scanning is also recommended of penicillin. prior to drug administration.
GENVOYA (elvitegravir, cobicistat, emtricitabine, tenofovir alafenamide) and STRIBILD (elvitegravir, cobicistat, emtricitabine, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) (21) We continue to receive reports of mix- Examine how these drugs are displayed in ups between Genvoya and Stribild. Both computer systems, and take steps to share the same indication, are dosed once differentiate between the two by listing daily, and the tablets look nearly the ester form of tenofovir in all bolded identical. The products differ only in the uppercase letters (e.g., tenofovir ester derivative of tenofovir but are not DISOPROXIL FUMARATE vs. interchangeable. Product labeling and tenofovir ALAFENAMIDE) and by computer presentations of the generic including their brand names. names list the different forms of
January 26, 2017 ISMP MedicationSafetyAlert! QAA 3 October – December 2016
ISMP QuarterlyActionAgenda Organization Action Required/ Date No. Problem Recommendation Assessment Assignment Completed tenofovir as the last ingredient, making it easy to miss the difference.
Problems using the TANZEUM (albiglutide) pen (in QuarterWatch) (20) Tanzeum has a lengthy and complicated Refer patients using Tanzeum to the process for reconstitution that takes at manufacturer’s website where they can least 30 minutes and requires more than a access an instruction manual, as well as a dozen steps. During a 12-month period, brief informational video on proper the US Food and Drug Administration reconstitution technique (FDA) received 1,500 reports of patients (www.tanzeum.com/how-to-use.html). using the pen incorrectly.
Standardize 4 Safety: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP) standardized concentrations for intravenous (IV) medications (22) ASHP announced availability of the Use the new standardized IV first list of recommended concentrations concentrations to help reduce for adult IV continuous infusions compounding errors, to standardize smart (www.ismp.org/sc?id=2830) developed pump libraries, and reduce the risk of as part of an interprofessional effort to selecting the wrong concentration from reduce medication errors. computer drop-down lists.
Do not give ZURAMPIC (lesinurad) without a xanthine oxidase inhibitor (22) Zurampic carries a boxed warning about AstraZeneca plans to offer a combination the risk for acute renal failure when product with lesinurad and allopurinol in used without a xanthine oxidase the future. Until a combination product is inhibitor, such as allopurinol or available, develop a linked order set that febuxostat. In clinical trials, patients requires both drugs to be ordered, and taking this drug alone experienced renal place reminders in computer systems and failure at a rate of 9.3% compared to 1% on auxiliary labels. when taken with a xanthine oxidase inhibitor.
January 26, 2017 ISMP MedicationSafetyAlert! QAA 4 October – December 2016
ISMP QuarterlyActionAgenda Organization Action Required/ Date No. Problem Recommendation Assessment Assignment Completed
Potential issues with SOLIQUA 100/33 (insulin glargine, lixisenatide) and XULTOPHY 100/3.6 (insulin degludec, liraglutide) (25) Two new combination To indicate to users that these products insulin/glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) contain two different ingredients, agonists, Soliqua 100/33 and Xultophy computer system drop-down lists and 100/3.6, are dosed in insulin units, pharmacy communications should use which could lead practitioners to brand names if your system allows. If mistakenly think the products contain using generic names, make sure both only insulin and prescribe an additional ingredients are displayed and not GLP-1 agonist separately. Also, both truncated. Educate patients taking these products may be used at doses lower products to make sure they understand than currently approved for the single they contain both insulin and a GLP-1 GLP-1 component. Thus, converting agonist. between the combination products and the individual ingredients could be problematic.
Vecuronium and vancomycin vial mix-ups (23) Mylan’s vancomycin 1 g vial and If both of these manufacturer’s drugs are vecuronium 20 mg vial look nearly used in your facility, consider purchasing identical when the caps are removed. one of the products from an alternate Both of these vials are stored in the manufacturer to avoid potential mix-ups. pharmacy and used in the operating room.
Hydroxyurea and hydrOXYzine mix-up (25) During order entry, hydroxyurea (an Use dose range checking software to institutionally compounded liquid form detect doses for hydroxyurea that are of 100 mg/mL) was selected from a outside the normal range. It may also be drop-down list instead of hydrOXYzine helpful to differentiate hydroxyurea from for itching. The patient received hydrOXYzine by using the brand name hydroxyurea 25 mg every 6 hours for 2 HYDREA or DROXIA. We also days until medical staff questioned why encourage prescribers to include an the patient was receiving this drug. indication for all medication orders.
January 26, 2017 ISMP MedicationSafetyAlert! QAA 5 October – December 2016
ISMP QuarterlyActionAgenda Organization Action Required/ Date No. Problem Recommendation Assessment Assignment Completed
January 26, 2017 ISMP MedicationSafetyAlert! QAA 6