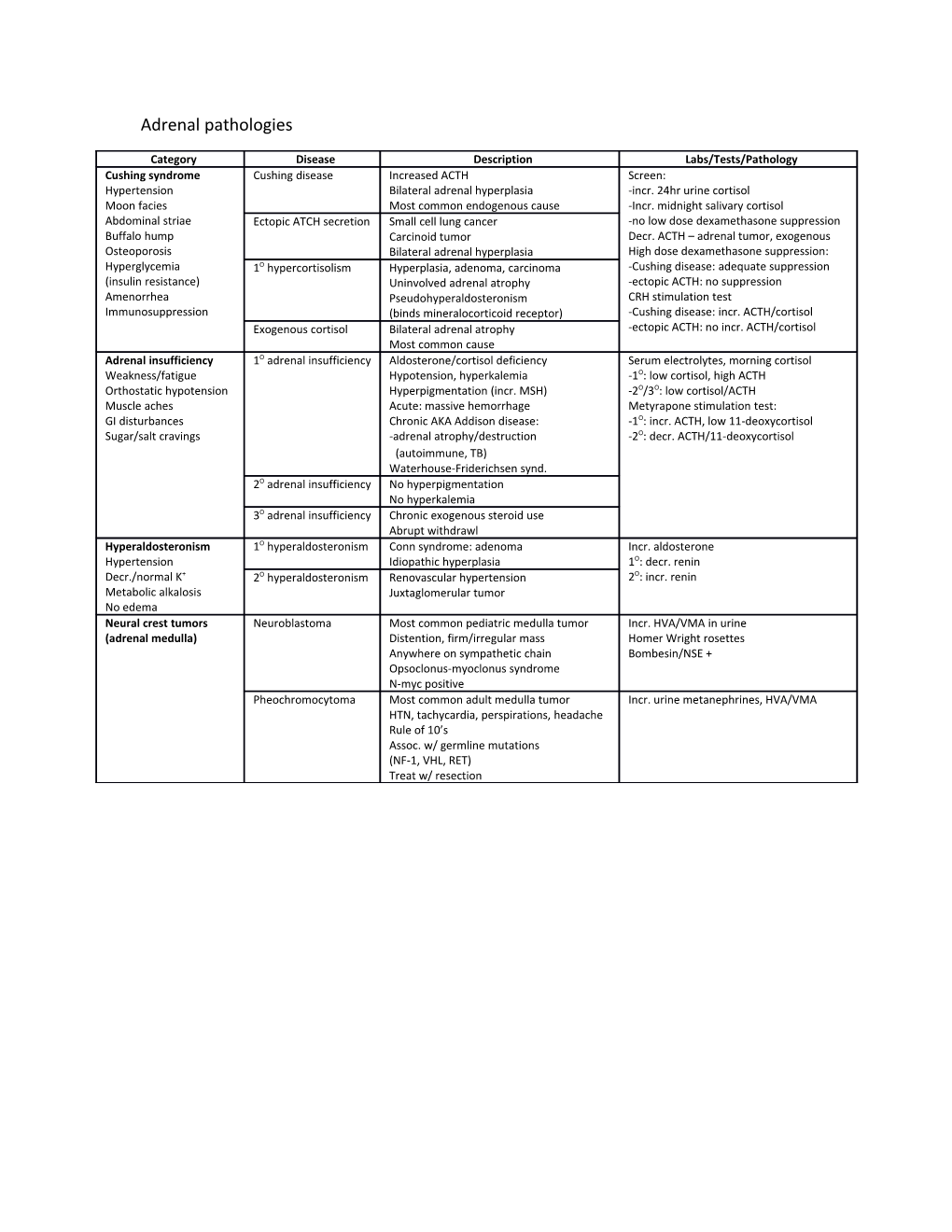
Adrenal pathologies
Category Disease Description Labs/Tests/Pathology Cushing syndrome Cushing disease Increased ACTH Screen: Hypertension Bilateral adrenal hyperplasia -incr. 24hr urine cortisol Moon facies Most common endogenous cause -Incr. midnight salivary cortisol Abdominal striae Ectopic ATCH secretion Small cell lung cancer -no low dose dexamethasone suppression Buffalo hump Carcinoid tumor Decr. ACTH – adrenal tumor, exogenous Osteoporosis Bilateral adrenal hyperplasia High dose dexamethasone suppression: Hyperglycemia 1O hypercortisolism Hyperplasia, adenoma, carcinoma -Cushing disease: adequate suppression (insulin resistance) Uninvolved adrenal atrophy -ectopic ACTH: no suppression Amenorrhea Pseudohyperaldosteronism CRH stimulation test Immunosuppression (binds mineralocorticoid receptor) -Cushing disease: incr. ACTH/cortisol Exogenous cortisol Bilateral adrenal atrophy -ectopic ACTH: no incr. ACTH/cortisol Most common cause Adrenal insufficiency 1O adrenal insufficiency Aldosterone/cortisol deficiency Serum electrolytes, morning cortisol Weakness/fatigue Hypotension, hyperkalemia -1O: low cortisol, high ACTH Orthostatic hypotension Hyperpigmentation (incr. MSH) -2O/3O: low cortisol/ACTH Muscle aches Acute: massive hemorrhage Metyrapone stimulation test: GI disturbances Chronic AKA Addison disease: -1O: incr. ACTH, low 11-deoxycortisol Sugar/salt cravings -adrenal atrophy/destruction -2O: decr. ACTH/11-deoxycortisol (autoimmune, TB) Waterhouse-Friderichsen synd. 2O adrenal insufficiency No hyperpigmentation No hyperkalemia 3O adrenal insufficiency Chronic exogenous steroid use Abrupt withdrawl Hyperaldosteronism 1O hyperaldosteronism Conn syndrome: adenoma Incr. aldosterone Hypertension Idiopathic hyperplasia 1O: decr. renin Decr./normal K+ 2O hyperaldosteronism Renovascular hypertension 2O: incr. renin Metabolic alkalosis Juxtaglomerular tumor No edema Neural crest tumors Neuroblastoma Most common pediatric medulla tumor Incr. HVA/VMA in urine (adrenal medulla) Distention, firm/irregular mass Homer Wright rosettes Anywhere on sympathetic chain Bombesin/NSE + Opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome N-myc positive Pheochromocytoma Most common adult medulla tumor Incr. urine metanephrines, HVA/VMA HTN, tachycardia, perspirations, headache Rule of 10’s Assoc. w/ germline mutations (NF-1, VHL, RET) Treat w/ resection Thyroid pathologies
Category Disease Description Labs/Tests/Pathology Hypothyroidism Hashimoto Anti-TPO (microsomal) Hurthle cells Cold intolerance Anti-thyroglobulin Lymphoid aggregation Hypercholesterolemia Incr. risk of NHL Germinal centers Decr. reflexes Early hyperthyroid (follicle rupture) Hypothyroid myopathy Enlarged nontender thyroid Myxedema Cretinism Fetal hypothyroidism Bradycardia -maternal, agenesis, dysgenesis -dyshormonogenetic goiter Protruding umbilicus, large tongue Subacute granulomatous Self limited, follows flu-like illness Granulomatous inflammation (De Quervain) Jaw pain, very tender thyroid Incr. ESR Riedel thyroiditis Fibrous tissue replacement Inflammatory infiltrate
(extends to local structure) IgG4 related Fixed, hard, painless goiter Iodine deficiency Most common cause in world Low/normal thyroid hormone Hyperthyroidism Graves Most common cause Tall crowded follicular cells Heat intolerance Thyroid stimulating IgG Scalloped colloid Hypocholesterolemia (binds TSH receptors) Incr. reflexes Pretibial myxedema Thyrotoxic myopathy Exophthalmos Pretibial myxedema (incr. GAGs in retroorbital space) Periorbital edema Toxic multinodular Hyperfunctioning focal patches Arrhythmias (independent of TSH) Rarely malignant Thyroid storm Acute stressor worsens condition Incr. LFTs Delirium, fever, diarrhea, coma Treat w/ propranolol, PTU, prednisone, potassium iodide Jod Basedow Partially autonomous thyroid Deficient, treated w/ iodine Leads to thyrotoxicosis Cancer Follicular adenoma Benign solitary growth Absence of invasion Treat w/ thyroidectomy Usually nonfunctional (capsular or vascular) Hoarsness Follicular carcinoma Good prognosis Invades capsule, vasculature (recurrent laryngeal nerve damage) Hematogenous spread Uniform follicles Hypocalcemia Assoc. w/ RAS mutations (PT gland removal) Papillary carcinoma Excellent prognosis Empty nuclei w/ central clearing Incr. risk w/ RET, BRAF mutations Psmammoma bodies Nuclear grooves Medullary carcinoma Parafollicular cancer Amyloid stroma Produce calcitonin Assoc. w/ RET mutations Anaplastic carcinoma Older patients Invades local structures Very poor prognosis Parathyroid pathologies
Category Disease Description Labs/Tests/Pathology Hypoparathyroidism HypoPTH Surgical excision Hypocalcemia Autoimmune disease Hyperphosphatemia DiGeorge syndrome Chvostek: facial contraction (tapping facial nerve) Trousseau: carpal spasm (occlude brachial artery)
PseudohypoPTH Defective GS inherited from mother HyperPTH (Albright hereditary osteodystrophy) Kidney unresponsive to PTH Hypocalcemia Shortened 4th/5th digits Short stature
PseudopseudohypoPTH Defective GS inherited from father Normal labs Physical findings of pseudohypoPTH Normal PTH response Hyperparathyroidism 1O hyperPTH Parathyroid adenoma/hyperplasia Hypercalcemia Incr. PTH Weakness, depression Hypercalciuria Incr. ALP Kidney stones Hypophosphatemia Constipation, peptic ulcers Pancreatitis Osteitis fibrosa cystica: bone pain 2O hyperPTH Chronic renal disease Hypocalcemia (hypovitamin D) Hyperphosphatemia Other less common causes (renal failure only) 3O hyperPTH Refractory hyperPTH from renal disease Greatly incr. PTH Hypercalcemia Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia Defective Ca2+ sensing receptor Mild hypercalcemia (higher Ca2+ needed to suppress PTH) Hypocalciuria Excessive renal Ca2+ reuptake Normal/incr. PTH Pituitary Pathologies
Disease Description Treatments Pituitary adenoma Benign, may be functional Dopamine agonists Prolactinoma most common (prolactinoma only) Mass effect Transsphenoidal resection (bitemporal hemianopia, headache) Nelson syndrome ACTH secreting adenoma Irradiation Enlargement post-adrenalectomy Resection Hyperpigmentation Bitemporal hemianopia, headache Acromegaly Excess GH production in adults Resection Large tongue, hands, feet Octreotide Coarse facial features, deep voice (somatostatin agonist) Diaphoresis, insulin resistance Pegvisomant Incr. risk of colorectal cancer (GH antagonist) High GH after glucose tolerance test Incr. serum IGF-1 Pituitary mass on imaging Gigantism Excess GH production in children HF is most common cause of death Laron syndrome Defective GH receptors Incr. GH, decr. IGF-1 Short height, small head circumference Saddle nose, large forehead Small genitalia Central Decreased ADH production Desmopressin Diabetes Insipidus (tumor, trauma, surgery, autoimmune) Hydration Decr. urine, incr. serum osmolality Water deprivation test (ADH analog incr. urine osmolality) Nephrogenic Decreased response to ADH HCTZ
Diabetes Insipidus (genetic, lithium, demeclocycline) (feedback incr. H2O reuptake) Normal/incr. ADH Indomethacin Decr. urine, incr. serum osmolality Amiloride Water deprivation test Hydration (minimal urine osmolality change) Syndrome of Ectopic ADH, CNS trauma, drugs Fluid restriction Inappropriate ADH Excessive water retention Salt tablets Euvolemic hyponatremia Diuretics (incr. ANP/BNP normalizes volume) ADH antagonists (continued urine excretion) Demecloclycine Osmolality: urine > serum Hypertonic saline Cerebral edema, seizures (causes osmotic demyelination) Hypopituitarism Neoplasm: nonsecreting adenoma, craniopharyngioma (Treat w/ HRT) Sheehan: intrapartum pituitary growth, postpartum bleeding, ischemic infarct Empty sella: atrophy/compression, idiopathic, common in obese women Apoplexy: sudden hemorrhage (existing adenoma), severe headache CNS trauma Radiation Pancreatic Pathologies
Disease Description More Description Type 1 Diabetes Polydipsia/polyuria/polyphagia Autoimmune B-cell attack Nonenzymatic glycosylation (anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase) Small: retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy, HTN Requires insulin replacement Large: atherosclerosis, CAD, PVD, gangrene, CVA Weak genetic linkage (MI most common cause of death) Leukocytic islet infiltrate Type 2 Diabetes Sorbitol accumulation: neuropathy, cataracts Incr. insulin resistance Diagnostic tests: Treat w/ drugs, insulin HbA1c (>6.5%), fasting (>126mg/dL), tolerance (>200mg/dL) Strong genetic linkage Islet amyloid deposit Diabetic Ketoacidosis Usually seen in T1DM Hyperglycemia Excess fat catabolism, ketogenesis Anion gap metabolic acidosis Delirium/psychosis, fruity breath Incr. ketone levels Kussmaul respirations (rapid/deep breathing) Hyperkalemia Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, dehydration (depleted intracellular K+) Mucormycosis, cerebral edema, arrhythmias, heart failure Treat w/ insulin, K+, fluids Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Hyperglycemia, dehydration, hyperosmolarity Hyperglycemia (can be >600mg/dL) Nonketotic Syndrome Focal neuro deficits, coma, death No acidosis/ketones Treat w/ fluids, insulin Glucagonoma a-cell tumor, incr. glucagon levels, hyperglycemia Necrolytic migratory erythema, DVT, weight loss, depression Treat w/ octreotide, surgery Insulinoma B-cell tumor, incr. insulin levels, hypoglycemia Whipple triad: hypoglycemia, symptoms of hypoglycemia, symptoms resolve w/ treatment Incr. C-peptide levels (differ from exogenous insulin injection) Treat w/ surgery Somatostatinoma δ-cell tumor, incr. somatostatin levels Decr. secretin, CCK, glucagon, insulin, gastrin Glucose intolerance, steatorrhea, gallstones Treat w/ octreotide, surgery
Other Endocrine Pathologies
Disease Description Carcinoid syndrome Neuroendocrine tumor, secretes serotonin Most common small intestine malignancy GI tract: liver metabolizes serotonin, symptoms not present Metastasis: serotonin not metabolized, symptoms present Diarrhea, flushing, wheezing Right side valve disease (tricuspid regurg., pulmonic stenosis) Incr. urinary 5-HIAA, rosettes on pathology Pellagra: niacin converted to serotonin 1 nd /3 rule: metastasize, 2 malignancy, and/or multiple Treat w/ octreotide, surgery Zollinger-Ellison syndrome Gastrin-secreting tumor in pancreas or duodenum Acid hypersecretion, causes duodenal/jejunal ulcers Abdominal pain, diarrhea Secretin test: gastrin levels remain high after giving secretin MEN-1 Mutation in MEN1 (menin), autosomal dominant Pituitary tumors: prolactin/GH Pancreatic tumors: gastrinoma, insulinoma, VIPoma, glucagonoma Parathyroid adenoma: hypercalcemia MEN-2A Mutation in RET (tyrosine kinase) Parathyroid hyperplasia: hypercalcemia Medullary thyroid carcinoma: parafollicular cell neoplasm (requires prophylactic thyroidectomy) Pheochromocytoma MEN-2B Mutation in RET (tyrosine kinase) Pheochromocytoma Medullary thyroid carcinoma: parafollicular cell neoplasm (requires prophylactic thyroidectomy) Mucosal neuromas: oral/intestinal ganglioneuromatosis Marfanoid habitus