ADVANTAGE AND DISADVANTAGES
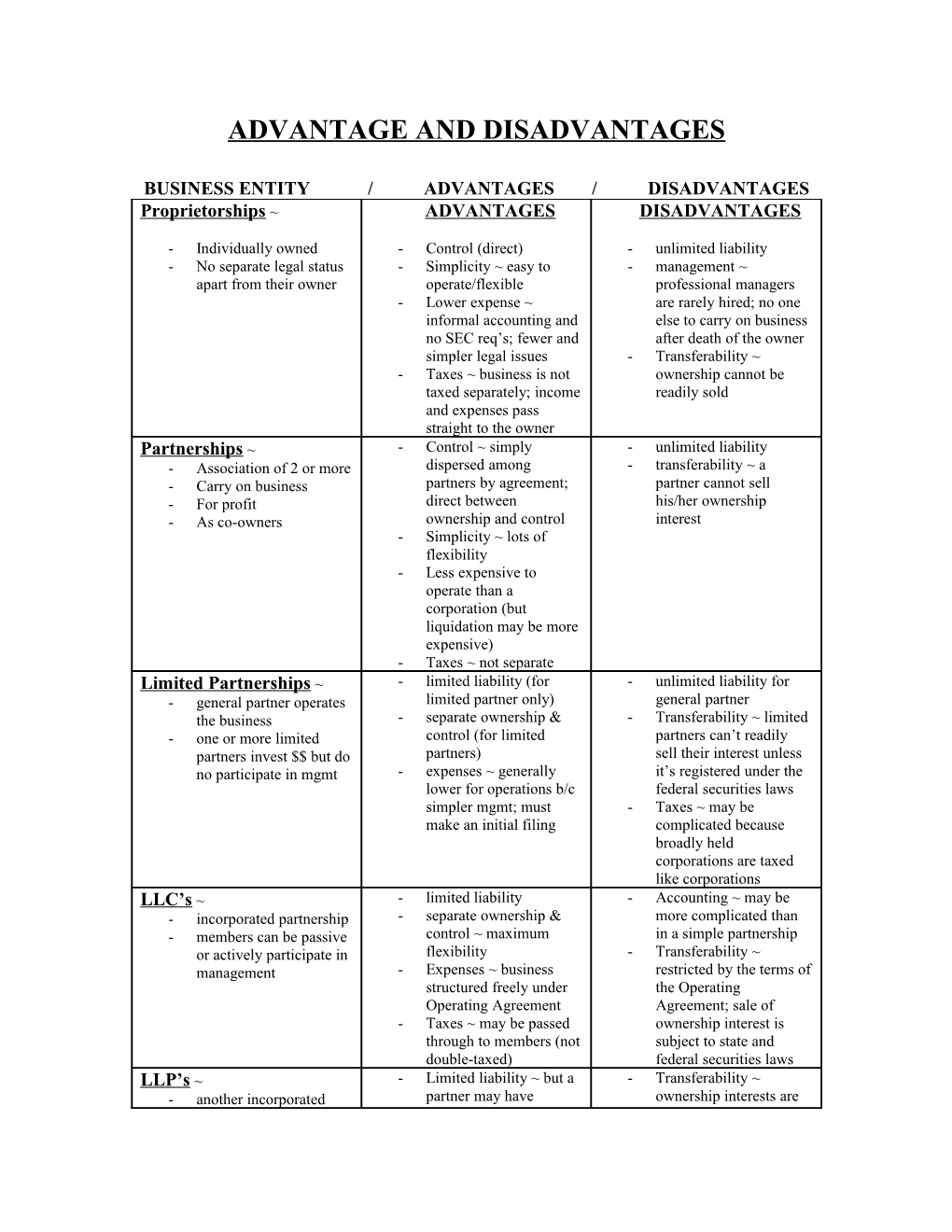
BUSINESS ENTITY / ADVANTAGES / DISADVANTAGES Proprietorships ~ ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES
- Individually owned - Control (direct) - unlimited liability - No separate legal status - Simplicity ~ easy to - management ~ apart from their owner operate/flexible professional managers - Lower expense ~ are rarely hired; no one informal accounting and else to carry on business no SEC req’s; fewer and after death of the owner simpler legal issues - Transferability ~ - Taxes ~ business is not ownership cannot be taxed separately; income readily sold and expenses pass straight to the owner Partnerships ~ - Control ~ simply - unlimited liability - Association of 2 or more dispersed among - transferability ~ a - Carry on business partners by agreement; partner cannot sell - For profit direct between his/her ownership - As co-owners ownership and control interest - Simplicity ~ lots of flexibility - Less expensive to operate than a corporation (but liquidation may be more expensive) - Taxes ~ not separate Limited Partnerships ~ - limited liability (for - unlimited liability for - general partner operates limited partner only) general partner the business - separate ownership & - Transferability ~ limited - one or more limited control (for limited partners can’t readily partners invest $$ but do partners) sell their interest unless no participate in mgmt - expenses ~ generally it’s registered under the lower for operations b/c federal securities laws simpler mgmt; must - Taxes ~ may be make an initial filing complicated because broadly held corporations are taxed like corporations LLC’s ~ - limited liability - Accounting ~ may be - incorporated partnership - separate ownership & more complicated than - members can be passive control ~ maximum in a simple partnership or actively participate in flexibility - Transferability ~ management - Expenses ~ business restricted by the terms of structured freely under the Operating Operating Agreement Agreement; sale of - Taxes ~ may be passed ownership interest is through to members (not subject to state and double-taxed) federal securities laws LLP’s ~ - Limited liability ~ but a - Transferability ~ - another incorporated partner may have ownership interests are partnership unlimited liability for his not easily transferred - popular with law firms own acts (think law firm) - Expenses - Taxes Corporations ~ - limited liability - double taxation ~ - Businesses that have - separate management & Corporation is taxed on separate legal status control ~ allows efficient profits and shareholders apart from their owners allocation of capital and are taxed on dividends professional mgmt of - management ~ may company operations manage for their own - Transferability ~ free, interests (not the interest provided there is a ready of the shareholdrers) market for the stock - Expenses ~ higher - Perpetual life ~ a SEC reporting and corporation continues in registration requirements existence until dissolved Complicated legal and accounting issues
CORPORATIONS FRAMEWORK Corporations Framework Non Corporate Business Enterprises -important b/c (a) may form agency or general partnership by default and (b) compare and contrasts other enterprises to corporation 1. Agency 2. Partnerships -general partnership -limited partnership -limited liability partnership 3. Advantages/Disadvantages of Types of Enterprises
Corporations
Theory of Corporation 1. Theory: separation of ownership and management
Formation of Corporation 1. Promoter’s Liability 2. Mechanics of Incorporation -Defective Incorporation 3. Capital Formation -how obtain -equity -debt
Management of Corporation 1. Election 2. Function 3. Director Compensation -also, Officer Compensation 5. Board Meetings 6. Board Committees 7. Officer’s and Power of Particular Office 8. Duty of Care (director and officer) -business judgment rule -exculpation from liability for breaching duty of care 9. Duty of Loyalty (director and officer) 10. D & O Insurance
Theory of Corporate Governance 1. Node Interest
Ownership of Corporation 1. Function 2. Shareholder Meetings
Corporate Democracy 1. Board of Directors’ Control and Manipulation of Voting Machinery 2. Shareholder’s Rights to Access Books and Records 3. Proxy Solicitations (for (a) proper proposals and (b) removal of directors) 4. Shareholder’s Exercise of Voice
Limited Liability - Disregarding 1. Piercing the Corporate Veil
Limited Liability - Characteristics of 1. Reduces Owners Need/Cost to Monitor (a) Management and (b) other Shareholders 2. Proposed Special Exception Rule to Limited Liability for Tort Victims 3. Costs of Limited Liability to Society
Ultra Vires Doctrine 1. Rule
Corporate Responsibility 1. Charitable Contributions
Liquidation Restrictions on Stock (for Insiders) 1. 16(a) - (b) 2. Insider Trading D & O INSURANCE ISSUES
D&O INSURANCE ISSUES
I. EFFECT OF JOINT & SEVERAL LIABILITY & INCENTIVES TO SETTLE: A) Key Provisions ~ 1) Lead Plaintiff Provision: The suit must be brought by the person who has suffered the most damage (i.e. – the person with the most stock) a. The Effects: 1. Lawyers forced to develop relationships with these people 2. Securities C/A lawsuits further concentrated 3. Backfired: These P’s are just as (if not more so) aggressive in pursuing the lawsuits. 4. BUT: There is an argument that less frivolous, more substantive, lawsuits are being brought 2) Proportionate Liability Provisions: a. Understand: Historically, there was joint & several liability 1. The effect ~ As expected costs of losing at trial go up, so do incentives to settle “The Wratcheting Effect” – there are incentives to actively keep knocking off individual Δ’s by getting them each to settle . . . settle . . . settle . . . etc. b. BUT, with Proportionate Liability – D&O’s are only liable for their share of the harm 1. The Effect ~ REVERSES the “wratcheting effect” NOW plaintiffs don’t want to settle; they’d rather wait things out because the $$$ paid will be coming from the insurance policies 2. BUT . . . this doesn’t reduce exposure to suit, it just lowers D&O’s level of liability 3. One Problem ~ have to set the bar by allocating each Δ’s responsibility
II. HOW IS D&O INSURANCE REACTING TO TODAY’S WORLD? A) Class Action Securities Litigation – 1) Whenever stock prices drop significantly, P’s are likely to file a C/A lawsuit a. This has exploded recently due to: 1. Financial Restatements ~ companies are ready to settle because it’s difficult to defend these cases in front of a jury. 2. Institutional Investors ~ now serving as lead P’s, so settlement negotiations are driven by “true desire to maximize shareholder recovery” rather than just maximizing the fee for P’s attorneys 3. Plaintiff Leverage ~ because Δ’s don’t want to go to a jury trial . . . settlements going up Up UP. Ties in to threat of HUGE DAMAGES awards by juries 4. Entity Coverage ~ has inflationary effect on D&O settlements Everybody’s insured; will settle the potentially catastrophic lawsuit at any price within policy limits
2) Consequences of increasing settlement amounts a. limits of liability ~ increasing b. premiums ~ increasing c. specific provisions added to policy terms to try and realign interests of insureds and insurers d. insurer claim involvement B) Measures Taken to Attract Effective Directors – 1) Adopt governance best practices a. ensures consistently high quality of performance b. example – board evaluations, meetings, education, board structure, etc . . . 2) Compensation schemes a. deferred compensation schemes b. minimum stock ownership requirements c. The Idea ~ pay the directors in a way to induce the most qualified candidates to serve 3) Insurance coverage for inside & outside directors