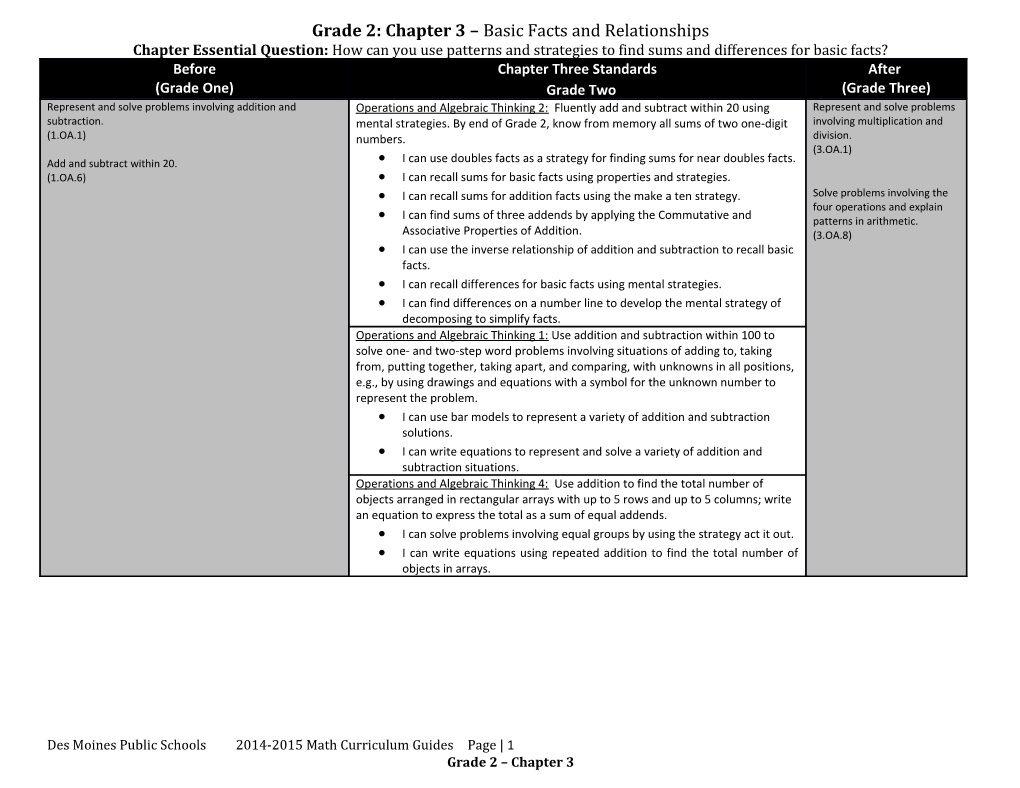
Grade 2: Chapter 3 – Basic Facts and Relationships Chapter Essential Question: How can you use patterns and strategies to find sums and differences for basic facts? Before Chapter Three Standards After (Grade One) Grade Two (Grade Three) Represent and solve problems involving addition and Operations and Algebraic Thinking 2: Fluently add and subtract within 20 using Represent and solve problems subtraction. mental strategies. By end of Grade 2, know from memory all sums of two one-digit involving multiplication and (1.OA.1) numbers. division. (3.OA.1) Add and subtract within 20. I can use doubles facts as a strategy for finding sums for near doubles facts. (1.OA.6) I can recall sums for basic facts using properties and strategies. I can recall sums for addition facts using the make a ten strategy. Solve problems involving the four operations and explain I can find sums of three addends by applying the Commutative and patterns in arithmetic. Associative Properties of Addition. (3.OA.8) I can use the inverse relationship of addition and subtraction to recall basic facts. I can recall differences for basic facts using mental strategies. I can find differences on a number line to develop the mental strategy of decomposing to simplify facts. Operations and Algebraic Thinking 1: Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. I can use bar models to represent a variety of addition and subtraction solutions. I can write equations to represent and solve a variety of addition and subtraction situations. Operations and Algebraic Thinking 4: Use addition to find the total number of objects arranged in rectangular arrays with up to 5 rows and up to 5 columns; write an equation to express the total as a sum of equal addends. I can solve problems involving equal groups by using the strategy act it out. I can write equations using repeated addition to find the total number of objects in arrays.
Des Moines Public Schools 2014-2015 Math Curriculum Guides Page | 1 Grade 2 – Chapter 3 Grade 2: Chapter 3 – Basic Facts and Relationships Chapter Essential Question: How can you use patterns and strategies to find sums and differences for basic facts? Each day the math block will begin with 15 minutes of Daily Math Review and Mental Math. The focus of DMR should be either prerequisite standard skills or previous chapter concepts that were not mastered. The focus of mental math should be based on the current Chapter’s skills and concepts. Adjust the amount of questions in DMR and MM to fit into the 15 minute time block.
Suggested Chapter Pacing All lessons are paced for one day, unless otherwise indicated. Teachers may adjust to meet students’ needs. La Review Prerequisite Skills Pre- Show What You Know Assessment un Math Mountains: TE 159I Assessment Identify Tier 2 and Tier 3 Groups for Small Group Instruction. chi Hop on the Line: TE 159I ng Vocabulary Activity Preview Chapter Centers the Vocabulary Builder School – Home Letter Day Before Develop vocabulary for describing Introduce chapter games, Ch Identify students who will need further vocabulary Read together and send Lesson 3.1 addition and subtraction. activities, and literature students apt support for Chapter Three. home. er TE 161H,162A-C will be using during center time. I Can Statement Essential Question Implementation Notes
Introduce Way to Go! Activity Introduce Doubles Fun on the Farm Lesson 3.1 I can use doubles facts as a strategy for How can you use doubles facts to find Operations and Algebraic Introduce Caterpillar Chase game Thinking 2 finding sums for near doubles facts. sums for near doubles facts? Make certain to present both ways of solving near-doubles (doubles + 1; doubles – 1). Introduce Ring Toss activity Lesson 3.2 I can recall sums for basic facts using Operations and Algebraic What are some ways to remember sums? Teachers may want to have students identify all of the problems that fall Thinking 2 properties and strategies. under the umbrella of a strategy and solve all at once. (e.g., “What problems are doubles or near doubles. Let’s star them and solve them.”) Lesson 3.3 I can recall sums for addition facts How is the make a ten strategy used to Finding a fact by deriving through 10 can be shown very nicely on a number Operations and Algebraic line in addition to the tree diagram shown in the book. Thinking 2 using the make a ten strategy. find sums? Lesson 3.4 I can find sums of three addends by Teacher should emphasize that making a 10, if possible, should be the first Operations and Algebraic applying the Commutative and How do you add three numbers? priority. Thinking 2 Associative Properties of Addition. Introduce Canine Collection activity Introduce Game Time! Lesson 3.5 I can use the inverse relationship of Introduce Caterpillar Chase Operations and Algebraic addition and subtraction to recall basic How are addition and subtraction related? Thinking 2 facts. Bar models and Part/Whole Boxes can both be used to show the relationship between addition and subtraction. Be aware that some problems are written in the sum = addend + addend and difference = minuend – subtrahend format.
Des Moines Public Schools 2014-2015 Math Curriculum Guides Page | 2 Grade 2 – Chapter 3 Grade 2: Chapter 3 – Basic Facts and Relationships Chapter Essential Question: How can you use patterns and strategies to find sums and differences for basic facts? Introduce A Heap of Sheep Introduce Benny, Bessie, and the Blueberries Lesson 3.6 I can recall differences for basic facts What are some ways to remember Introduce On the Ferris Wheel game Operations and Algebraic using mental strategies. differences? Thinking 2 Other than -1, -2, and -3; teachers may want to have students rewrite subtraction problems as missing addend addition problems. Mid-Chapter Checkpoint is optional. This work can be done via an open number line as well. Subtraction on a I can find differences on a number line Lesson 3.7 How does getting to 10 in subtraction help number line can be shown as: Operations and Algebraic to develop the mental strategy of when finding differences? Take Away (as it is shown in the book) Thinking 2 decomposing to simplify facts. o o Distance between the two numbers
I Can Essential Question Implementation Notes Statement I can use bar Introduce Quilting Bee activity models to Introduce Game Time! Lesson 3.8 represent a How are bar models used to show addition Operations and Algebraic Thinking 1 variety of addition and subtraction problems? Bar models and Part/Whole Boxes can both be used to show the relationship and subtraction between addition and subtraction. situations. I can write Be aware that students may use a different, but acceptable equation to solve equations to the problem. represent and How are number sentences used to show Lesson 3.9 solve a variety of Operations and Algebraic Thinking 1 addition and subtraction situations? addition and subtraction situations. I can solve Two-Color Counters problems Talk about strategies other than counting by ones to find the totals. Lesson 3.10 involving equal How can acting it out help when solving a Operations and Algebraic Thinking 4 groups by using problem about equal groups? the strategy act it out. I can write Two-Color Counters equations using Introduce Lucy Goosey activity Lesson 3.11 repeated addition How can you write an addition sentence Operations and Algebraic Thinking 4 to find the total for problems with equal groups? Teachers can build Commutativity by talking about counting columns as well. number of objects in arrays.
Resources and Centers for Chapter 3 Technology Hands-On Resources Centers Digital Lesson: Engage MathBoard Activity: Way to Go! Fastt Math Two-color counters Activity: Ring Toss Interactive White Board Lesson Math Journal Activity: K9 Collection Des Moines Public Schools 2014-2015 Math Curriculum Guides Page | 3 Grade 2 – Chapter 3 Grade 2: Chapter 3 – Basic Facts and Relationships Chapter Essential Question: How can you use patterns and strategies to find sums and differences for basic facts? e Student Edition Other Hands-On Resources may be needed for Small Group Instruction Activity: A Heap of Sheep Activities. Mega Math Activity: Quilting Bee Animated Math Models Activity: Lucy Goosey iTools: Base Ten Blocks Literature: Doubles Fun on the Farm iTools: Counters Literature: Game Time iTools: Number Charts Literature: Bennie, Bessie, and The Blueberries iTools: Number Lines Game: Caterpillar Chase Personal Math Trainer Game: On the Ferris Wheel Math on the Spot Videos
Additional Resources for Chapter 3 Operations in Algebraic Thinking 1 Operations in Algebraic Thinking 2 Operations in Algebraic Thinking 4 Mastering the Basic Facts in Addition and Subtraction: Chapter 2: Plus 1 and Plus 2 Mastering the Basic Facts in Addition and Subtraction: Chapter 3: Adding 0 Mastering the Basic Facts in Addition and Subtraction: Chapter 4: Adding 10 Mastering the Basic Facts in Addition and Subtraction: Chapter 5: Doubles Mastering the Basic Facts in Addition and Subtraction: Chapter 6: Making 10 Mastering the Basic Facts in Addition and Subtraction: Chapter 7: Using 10s Mastering the Basic Facts in Addition and Subtraction: Chapter 8: Using Doubles CGI – Addition and Subtraction Story Bank Blue Square Game
Des Moines Public Schools 2014-2015 Math Curriculum Guides Page | 4 Grade 2 – Chapter 3