BASIC PROPERTIES AND BEHAVIOR OF WAVES NOTES
Standard 8.P.3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the properties and behaviors of waves.
Performance Indicator8.P.3A.2: Develop and use models to exemplify the basic properties of waves (including frequency, amplitude, wavelength, and speed).
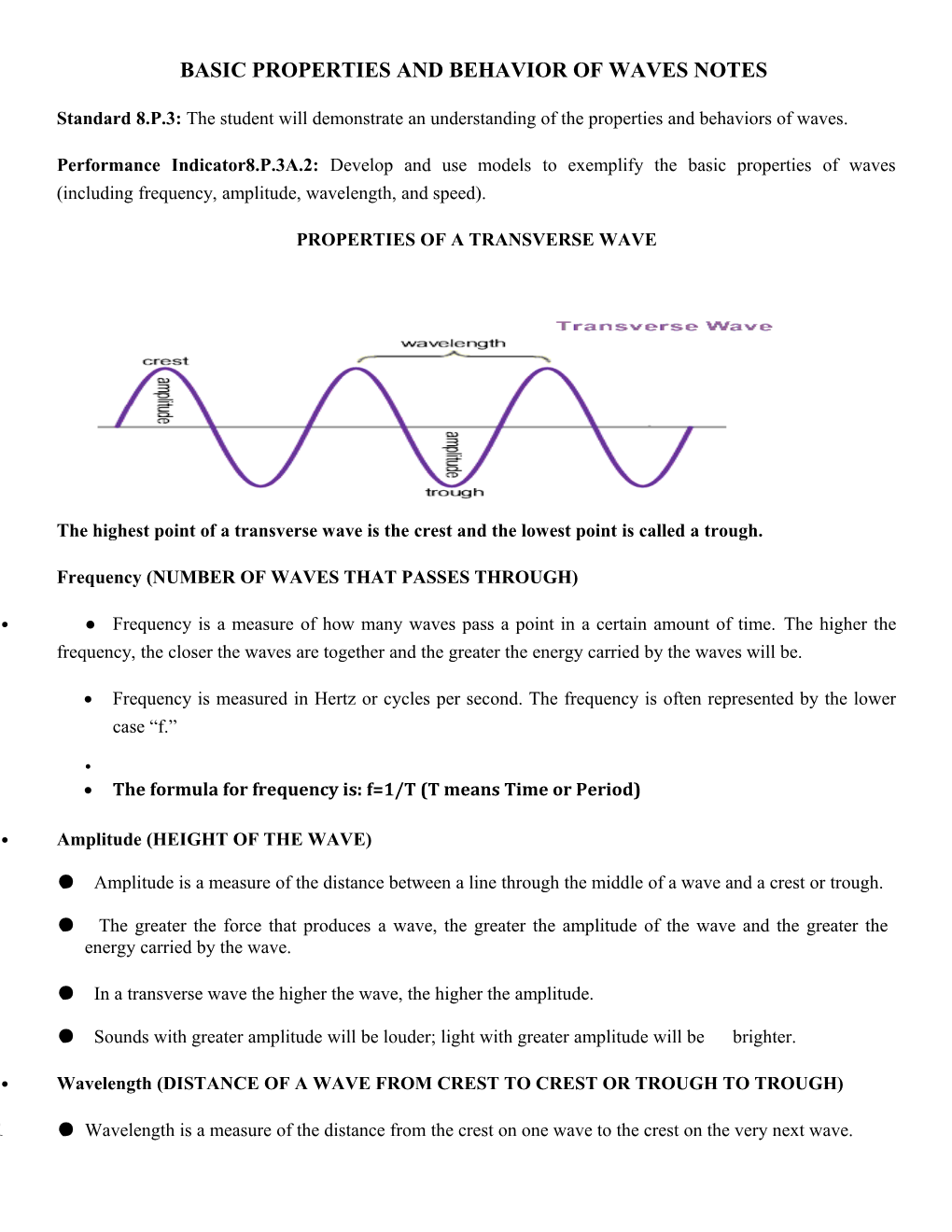
PROPERTIES OF A TRANSVERSE WAVE
The highest point of a transverse wave is the crest and the lowest point is called a trough.
Frequency (NUMBER OF WAVES THAT PASSES THROUGH)
• ● Frequency is a measure of how many waves pass a point in a certain amount of time. The higher the frequency, the closer the waves are together and the greater the energy carried by the waves will be.
Frequency is measured in Hertz or cycles per second. The frequency is often represented by the lower case “f.”
• The formula for frequency is: f=1/T (T means Time or Period)
• Amplitude (HEIGHT OF THE WAVE)
● Amplitude is a measure of the distance between a line through the middle of a wave and a crest or trough.
● The greater the force that produces a wave, the greater the amplitude of the wave and the greater the energy carried by the wave.
● In a transverse wave the higher the wave, the higher the amplitude.
● Sounds with greater amplitude will be louder; light with greater amplitude will be brighter.
• Wavelength (DISTANCE OF A WAVE FROM CREST TO CREST OR TROUGH TO TROUGH)
1 ● Wavelength is a measure of the distance from the crest on one wave to the crest on the very next wave. 2 ● Shorter wavelengths are influenced by the frequency.
3 ● A higher frequency causes a shorter wavelength and greater energy.
The wavelength is usually represented by the Greek letter lambda
4 Speed or Velocity of a Wave
5 ● Speed is a measure of the distance a wave travels in an amount of time.
6 ● The speed of a wave is determined by the type of wave and the nature of the medium.
7 ● As a wave enters a different medium, the wave’s speed changes. Waves travel at different speeds in different media. For example: sound travels at different speed in air than in water.
8 ● All frequencies of electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed in empty space.
The velocity can be found by multiplying the frequency by the wavelength.
RECAP- MOVEMENT OF TRANSVERSE VS. LONGITUDINAL WAVES LABEL THE CREST, TROUGH, AMPLITUDE AND WAVELENGTH OF THE TRANSVERSE WAVE
LABEL RAREFACTION, COMPRESSION AND WAVELENGTH ON THE COMPRESSIONAL/LONGITUDINAL WAVE