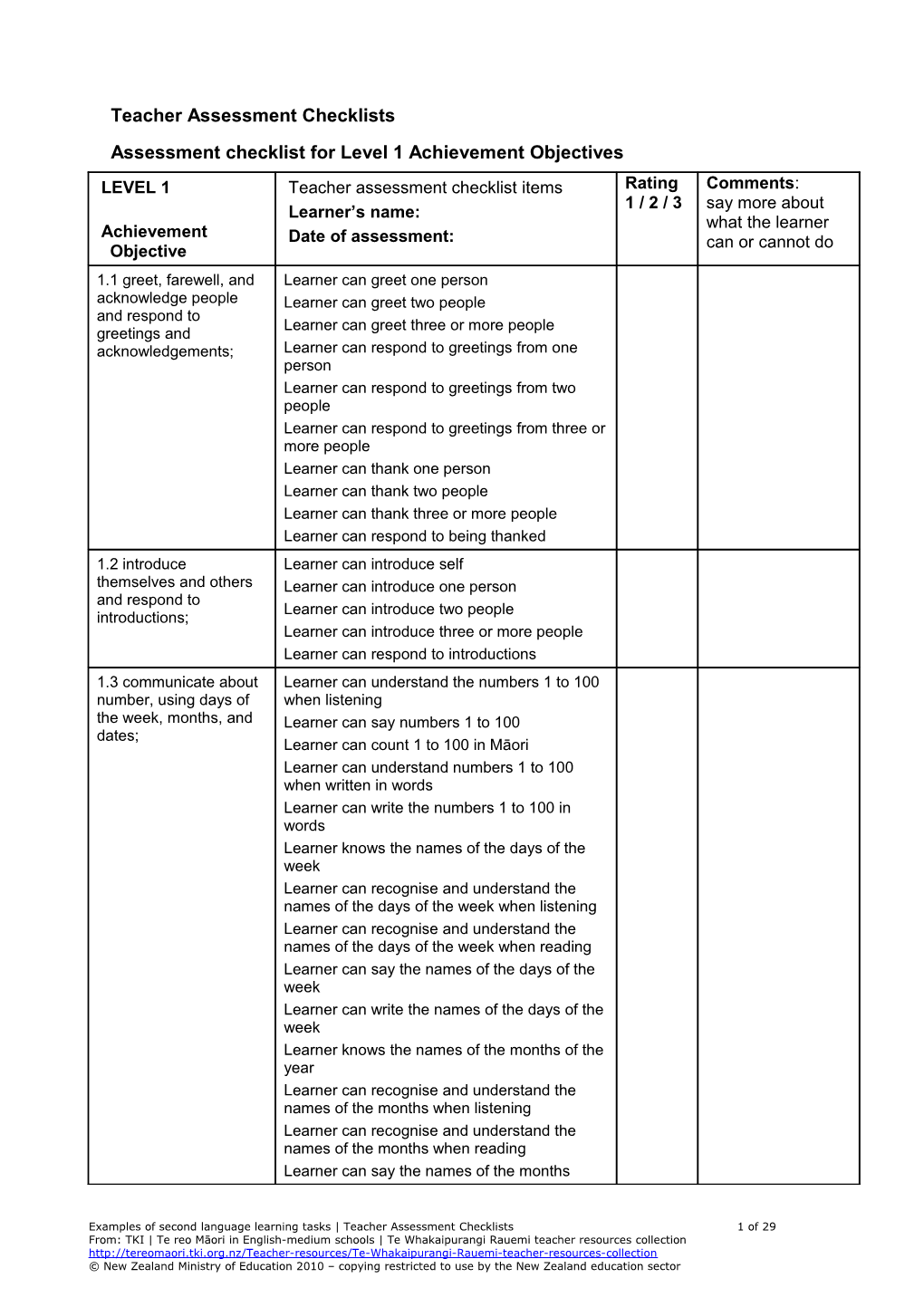
Teacher Assessment Checklists Assessment checklist for Level 1 Achievement Objectives
LEVEL 1 Teacher assessment checklist items Rating Comments: 1 / 2 / 3 say more about Learner’s name: what the learner Achievement Date of assessment: can or cannot do Objective 1.1 greet, farewell, and Learner can greet one person acknowledge people Learner can greet two people and respond to Learner can greet three or more people greetings and acknowledgements; Learner can respond to greetings from one person Learner can respond to greetings from two people Learner can respond to greetings from three or more people Learner can thank one person Learner can thank two people Learner can thank three or more people Learner can respond to being thanked 1.2 introduce Learner can introduce self themselves and others Learner can introduce one person and respond to Learner can introduce two people introductions; Learner can introduce three or more people Learner can respond to introductions 1.3 communicate about Learner can understand the numbers 1 to 100 number, using days of when listening the week, months, and Learner can say numbers 1 to 100 dates; Learner can count 1 to 100 in Māori Learner can understand numbers 1 to 100 when written in words Learner can write the numbers 1 to 100 in words Learner knows the names of the days of the week Learner can recognise and understand the names of the days of the week when listening Learner can recognise and understand the names of the days of the week when reading Learner can say the names of the days of the week Learner can write the names of the days of the week Learner knows the names of the months of the year Learner can recognise and understand the names of the months when listening Learner can recognise and understand the names of the months when reading Learner can say the names of the months
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 1 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector Learner can write the names of the names of the months Learner knows that numbers and the names of days and months are combined to make dates Learner can understand dates while listening Learner can understand dates while reading Learner can say the date Learner can write the date in words and numerals Learner can interpret dates from a diary or calendar in Māori 1.4 communicate about Learner can understand his or her own name personal information, when listening such as name, iwi, Learner can understand other names when hapū, mountain and listening river; or hometown and Learner can read his or her own name when it place of origin; is written Learner can read familiar names Learner can say his or her own name Learner can say the names of people he or she knows Learner can write his or her own name Learner can understand age information when listening Learner can understand age information when reading Learner can tell others their own age Learner can speak about the age of other people and things Learner can write down his or her age in words Learner can write about the age of other people and things Learner can understand information about where people are from when listening Learner can read and understand information about where people are from Learner can say where people are from Learner can write where people are from Learner knows the Māori names for personally relevant places in New Zealand Learner knows the Māori names of personally relevant countries 1.5 communicate about Learner can understand basic information on location; location in space when listening Learner can understand basic information on location in space when reading Learner can convey basic information on location in space when speaking Learner can convey basic information on location in space when writing Learner can understand and convey simple information about where people and things are currently located
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 2 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector 1.6 understand and use Learner can understand simple politeness simple politeness conventions when listening conventions (for Learner can understand simple politeness example, ways of conventions when reading (eg the greetings / acknowledging people, mihi in a letter or an invitation) expressing regret, and Learner can use simple politeness conventions complimenting people); when speaking Learner can use simple politeness conventions when writing (eg in a simple personal letter) Learner can thank people at a basic level Learner knows how to apologise at a basic level Learner knows how to excuse themselves at a simple level from a situation or for a mistake or poor behaviour Learner knows how to pay simple compliments 1.7 use and respond to Learner can understand simple classroom simple classroom statements when listening language (including Learner can understand basic classroom asking for the word to instructions when listening express something in te Learner can understand simple classroom reo Māori). statements when reading Learner can understand basic classroom instructions when reading Learner can express simple classroom statements when speaking Learner can express basic classroom instructions when speaking Learner can express simple classroom statements when writing Learner can express basic classroom instructions when writing Learner can understand simple requests for information in the classroom Learner can respond to requests for basic information in the classroom context Whakarongo – Learner can identify the sounds of the Listening consonants and vowels of Māori when listening By the end of level 1, learners can: Learner can recognise the difference between short and long vowels when listening identify the sounds of letters of the Māori Learner can recognise consonant and single alphabet, letter vowel sequences when listening (eg ka, ko, ki) combinations, Learner can identify sound combinations when intonation, and stress listening (eg syllables, vowel combinations: patterns; whā, whai, ngau, hea, kua, pau) recognise and Learner can distinguish minimal pairs when understand simple, listening (eg: tai, tae; hou, hau) familiar spoken words, Learner can recognise different intonation phrases, and patterns when listening sentences. Learner can recognise word stress when listening Learner can recognise phrase and utterance or sentence stress when listening
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 3 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector Learner can recognise and understand simple, familiar spoken words Learner can recognise and understand simple, familiar phrases Learner can recognise and understand simple, familiar sentences Pānui – Reading Learner can identify the letters of the Māori By the end of level 1, alphabet when reading learners can: Learner can identify letter and sound identify letters of the combinations when reading Māori alphabet Learner can distinguish minimal pairs when (arapū), letter reading (eg: tai, tae; hou, hau) combinations, basic Learner can recognise basic written language written language conventions conventions, and Learner can use basic punctuation such as simple punctuation; macrons, commas, full stops and question recognise and marks, capital and lower case letters understand simple, Learner can recognise and understand simple, familiar written words, familiar written words phrases, and sentences Learner can recognise and understand simple, familiar written phrases Learner can recognise and understand simple, familiar written sentences Mātakitaki – Viewing Learner can recognise the communicative By the end of level 1, significance of particular facial expressions learners can: and other body language recognise the Facial expressions and body language communicative introduced: significance of ...... particular facial ...... expressions and other Learner can interpret meanings that are body language; conveyed in combinations of words and interpret meanings images or symbols. that are conveyed in Visual texts introduced: combinations of words ...... and images or ...... symbols Kōrero – Speaking Learner can produce the sounds of individual By the end of level 1, Māori consonants and vowels when speaking learners can: Learner can produce the difference between imitate the short and long vowels when speaking pronunciation, Learner can produce consonant and single intonation, stress, and vowel sequences when speaking (eg ka, ko, rhythm of Māori ki) words, phrases, and Learner can produce sound combinations sentences; when speaking (eg syllables, vowel respond appropriately combinations) to simple, familiar Learner can distinguish minimal pairs when instructions, and speaking (eg tai, tae; hou, hau) simple questions; Learner can produce different intonation ask simple questions; patterns at a basic level when speaking initiate spoken Learner can produce simple, familiar spoken encounters in te reo words Māori, using simple Learner can produce simple, familiar spoken greetings, questions,
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 4 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector and statements. words, with appropriate word stress Learner can produce familiar phrases Learner can produce simple, familiar utterances or sentences Learner can produce familiar phrases and utterances with appropriate stress when speaking Learner can ask simple questions Learner can produce simple greetings Learner can produce simple statements Learner can issue simple instructions Learner can respond to simple, familiar instructions Learner can respond to simple, familiar questions Tuhituhi – Writing Learner can write down the letters of the Māori By the end of level 1, alphabet (eg when these are spoken) learners can: Learner can write vowels with macrons write letters and Learner can write letter combinations and numbers; words, including macrons, to produce familiar write vowels with words, phrases, and sentences in familiar macrons; contexts Learner can write letter combinations and reproduce letter words, phrases, and sentences in familiar combinations and contexts using appropriate punctuation and punctuation for Māori accurate spelling words, phrases, and sentences in familiar Learner can write the numbers 1 to 100 in contexts; numerals (eg when these are read to them) write simple, familiar Learner can write the numbers 1 to 100 in words, phrases, and words sentences using the conventions of written language, such as appropriate spelling and punctuation. Whakaatu – Learner can use appropriate facial Presenting expressions, body language and images to By the end of level 1, convey messages (with and without learners can: accompanying verbal language) use appropriate facial Learner can use selected features of visual expressions, body language to add meaning to simple spoken language and images text to convey messages Features introduced: ...... (with and without ...... accompanying verbal ...... language); Learner can use selected features of visual use selected features language to add meaning to simple written text of visual language to Features introduced: add meaning to simple ...... written/oral text......
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 5 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector Assessment checklist for Level 2 Achievement Objectives
LEVEL 2 Teacher assessment checklist items Rating Comments: 1 / 2 / 3 say more about Learner’s name: what the learner Achievement Objective Date of assessment: can or cannot do 2.1 communicate about Learner can describe his or her kin relationships between relationship to members of own family people; Learner knows kin vocabulary for key family relationships Learner can talk about the key family relationships of other people 2.2 communicate about Learner can express what he or she owns possessions; (eg using nāku / nōku, or, ko tāku X tēnei) Learner can express what others own (eg using nā / nō wai, or, ko tāna X tēnei, ko āna X ērā) Learner can express what is for self and other people to have (eg using mā / mō wai, māku, māu, māna) Learner can express who currently has something (eg using kei a wai, kei a au, kei a kōrua, kei a rātou) 2.3 communicate about Learner can express his or her likes and likes and dislikes, giving preferences reasons where appropriate; Learner has a range of ways of expressing his or her likes and preferences Learner can give reasons for liking something or someone Learner can express dislikes Learner has a range of ways of expressing his or her dislikes Learner can give reasons for disliking something or someone 2.4 communicate about Learner can tell the time in Māori time, weather, and Learner can use a simple time phrase seasons; (adverbial of time) to locate an event in time (eg i nanahi, i nāianei, i tērā wiki, ā te Rāmere) Learner can describe the daily weather at a basic level Learner knows the words for the seasons Learner can give basic information about the seasons 2.5 communicate about Learner can describe what someone or physical characteristics, something looks like at a simple level personality, and feelings. Learner has a wider range of ways of describing physical appearance Learner can describe some personality traits Learner has a wider range of ways of describing personality traits Learner can describe what he or she, or
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 6 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector someone else is feeling Learner has a wider range of ways of describing feelings Whakarongo –Listening Learner can identify the sounds of Māori, By the end of level 2, and sound combinations when listening learners can: Learner can identify intonation, and stress identify sounds of letters patterns of the Māori alphabet, Learner can recognise and understand letter combinations, familiar spoken words in familiar contexts intonation, and stress Learner can recognise and understand patterns; familiar spoken words in some unfamiliar recognise and contexts understand familiar Learner can understand a range of short spoken words even in spoken texts containing familiar phrases some unfamiliar contexts; and sentences understand a range of Learner can get the gist of slightly more short oral texts containing complex or less familiar spoken phrases familiar phrases and and sentences sentences; get the gist of slightly more complex or less familiar te reo Māori phrases and sentences. Pānui – Reading Learner can identify letters of the Māori By the end of level 2, alphabet, letter combinations, and simple learners can: punctuation identify letters of the Learner can recognise and understand Māori alphabet, letter simple, familiar written words, phrases, and combinations, and simple sentences punctuation; Learner can understand short written texts recognise and consisting of familiar Māori words, phrases, understand simple, and sentences familiar written words, Learner can get the gist of slightly more phrases, and sentences; complex or less familiar Māori phrases and sentences. understand short written texts consisting of familiar reo Māori words, phrases, and sentences; get the gist of slightly more complex or less familiar reo Māori phrases and sentences. Mātakitaki – Viewing Learner can respond appropriately to By the end of level 2, meanings conveyed through selected learners can: visual texts Visual texts introduced: respond appropriately to ...... meanings conveyed ...... through selected visual texts; Learner can understand and respond to combinations of visual and verbal language understand and respond in selected texts to combinations of visual Visual texts introduced: and verbal language in ...... selected texts......
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 7 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector Kōrero – Speaking Learner is beginning to use pronunciation By the end of level 2, for emphasis and to distinguish meaning learners can: Learner is beginning to use intonation for begin to use emphasis and to distinguish meaning pronunciation, intonation, Learner is beginning to use stress and stress, and rhythm for rhythm for emphasis and to distinguish emphasis and to clarify meaning meaning; Learner can respond appropriately to respond appropriately to simple, familiar instructions simple, familiar Learner can respond to simple questions instructions and simple Learner can ask simple questions questions; Learner can give simple information ask simple questions and give simple information; Learner can initiate simple conversations initiate simple conversations in te reo Māori. Tuhituhi – Writing Learner can write simple, familiar words, By the end of level 2, phrases, and sentences using spelling and learners can: punctuation conventions write simple, familiar Learner can convey simple messages in words, phrases, and writing sentences using spelling Learner can write a series of sentences and punctuation describing the appearance of something. conventions; Learner can write a series of sentences write simple te reo Māori describing the characteristics of something. messages; Learner can also write the following: write a series of ...... sentences in te reo Māori ...... describing the ...... appearance or ...... characteristics of ...... something. Whakaatu – Presenting Learner can produce visual texts to present By the end of level 2, information learners can: Learner can produce visual texts to present produce visual texts to ideas present information Learner can combine visual and verbal and/or ideas; language to present information combine visual and Learner can combine visual and verbal verbal language to language to present ideas present information Visual texts produced by this learner: and/or ideas......
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 8 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector Assessment checklist for Level 3 Achievement Objectives
LEVEL 3 Teacher assessment checklist items Rating Comments: 1 / 2 / 3 say more about Learner’s name: Achievement what the learner Objective Date of assessment: can or cannot do 3.1 communicate, Learner can describe habits including comparing and Learner can describe routines contrasting, about habits, Learner can compare and contrast habits routines and customs; Learner can compare and contrast routines
3.2 communicate about Learner can relate information about events events and where they he or she has been involved in take place; Learner can relate information about events he or she is currently involved in Learner can relate events he or she plans to be involved in Learner can relate information about events others have been involved in Learner can relate information about where events take place 3.3 give and follow Learner can give simple directions to a directions; location Learner can give more complex directions to a location Learner can use a map to give directions to a location Learner can give simple directions to complete a task Learner can give more complex directions to complete a task Learner can follow simple directions to a location Learner can follow more complex directions to a location Learner can use a map to follow directions to a location Learner can follow simple directions to complete a task Learner can follow more complex directions to complete a task 3.4 communicate, Learner can convey information about how including comparing and he or she travels to familiar destinations contrasting, about how Learner can convey information about how people travel; others travel to familiar destinations Learner knows relevant vocabulary for modes of transport Learner can express comparisons and contrasts about how people travel Learner can provide information based on timetables and brochures Learner can interpret information from timetables and brochures
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 9 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector 3.5 communicate about Learner can convey information about what immediate past activities. he or she has just done, or done recently Learner can convey information about what others have just done, or done recently Whakarongo – Learner can understand specific detail in Listening familiar contexts when listening By the end of level 3, Learner can understand overall meaning in learners can: familiar contexts when listening understand specific Learner can understand specific detail in detail and overall some unfamiliar contexts when listening meaning in familiar Learner can understand overall meaning in contexts and in some some unfamiliar contexts when listening unfamiliar contexts; Learner can understand a range of short understand a range of spoken texts consisting mainly of familiar short oral texts language consisting mainly of Types of spoken texts familiar to this familiar language; learner: get the gist of short ...... oral texts that contain ...... some unfamiliar ...... language...... Learner can get the gist of short spoken texts that contain some unfamiliar language Pānui – Reading Learner can understand specific detail in a By the end of level 3, range of short written texts consisting learners can: mainly of familiar language understand specific Learner can understand overall meaning in detail and overall a range of short written texts consisting meaning in a range of mainly of familiar language short written texts Types of written texts familiar to this learner: consisting mainly of ...... familiar language; ...... get the gist of short ...... written texts that ...... contain some Learner can get the gist of short written unfamiliar language. texts that contain some unfamiliar language
Mātakitaki – Viewing Learner can identify and respond to some By the end of level 3, visual and verbal features of texts, and the learners can: ways these features interact for particular purposes identify and respond to some visual and verbal Learner can understand and respond to a features of texts, and range of features in selected visual texts. the ways these Visual texts introduced: features interact for ...... particular purposes; ...... understand and ...... respond to a range of features in selected visual texts. Kōrero – Speaking Learner can initiate short conversations By the end of level 3, Learner can sustain short conversations learners can: Learner can give short prepared talks on initiate and sustain familiar topics
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 10 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector short conversations; Learner can use generally appropriate give short prepared pronunciation, stress, rhythm, and talks on familiar topics; intonation use generally Learner can express simple original ideas appropriate Learner can describe familiar events pronunciation, stress, Learner can describe familiar people rhythm, and intonation; Learner can describe familiar things. express simple original ideas; describe familiar events, people, and things. Tuhituhi – Writing Learner can use resources (eg dictionaries By the end of level 3, and glossaries) to experiment with some learners can: new language in writing and to check spelling use resources (for example, dictionaries Resources used by this learner: and glossaries) to ...... experiment with some ...... new language in ...... writing and to check spelling; Learner can prepare and write short texts on familiar topics prepare and write short Familiar topics for this learner: texts on familiar topics; ...... write simple personal ...... letters and emails; ...... use appropriate writing Learner can write simple personal letters conventions. Learner can write simple personal emails Learner can use appropriate writing conventions Learner can also write the following: ...... Whakaatu – Presenting Learner can present texts in which visual By the end of level 3, and verbal features interact to produce learners can: particular meanings and effects present texts in which Learner can present or perform a legend visual and verbal that pays attention to visual language features interact to features produce particular Learner can present or perform a meanings and effects; whakataukī that pays attention to visual present/perform a language features kōrero pūrakau, Learner can present or perform a pepeha whakataukī, pepeha or that pays attention to visual language waiata making effective features use of visual language Learner can present or perform a waiata features. that pays attention to visual language features Visual texts produced by this learner: ......
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 11 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector Assessment checklist for Level 4 Achievement Objectives
LEVEL 4 Teacher assessment checklist items Rating Comments: 1 / 2 / 3 say more about Learner’s name: Achievement what the learner Objective Date of assessment: can or cannot do 4.1 request, offer, accept, Learner can make requests and decline things, Learner can make offers invitations, and Learner can accept things, invitations, suggestions; suggestions Learner can decline things, invitations, suggestions 4.2 communicate about Learner can express what he or she is plans for the immediate about to do future; Learner can express his or her plans for the immediate future 4.3 communicate about Learner can express his or her obligations obligations and Learner can express his or her responsibilities; responsibilities Learner can express what others are obliged to do Learner can express what others are responsible for 4.4 give and seek Learner can give permission to others permission or agreement; Learner can ask for permission 4.5 communicate about Learner can convey information about the the quality, quantity, and quality of things cost of things. Learner can convey information about general quantity Learner can convey information about specific quantities Learner can convey information about the general cost of things Learner can convey information about the specific cost of things using money expressions (dollars and cents) Whakarongo – Listening Learner can make use of context and By the end of level 4, familiar language when listening, to work learners can: out meaning of less familiar items make use of context and Learner can make use of context and familiar language to work familiar language when listening, to work out meaning and out relationships between things, events, relationships between and ideas things, events, and Learner can understand specific details in ideas; spoken contexts that may contain some understand specific unfamiliar language details in contexts that may contain some unfamiliar language. Pānui – Reading Learner can understand a range of short By the end of level 4, written texts that consist mainly of familiar learners can: language understand a range of Written texts understood by this learner:
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 12 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector short written texts that ...... consist mainly of familiar ...... language; ...... understand overall Learner can understand overall meaning meaning and specific and specific detail in contexts that may detail in contexts that contain some unfamiliar language may contain some Learner can guess the meanings of unfamiliar language; unfamiliar words and phrases used in guess the meanings of familiar contexts unfamiliar words and Familiar contexts for this learner: phrases used in familiar ...... contexts...... Mātakitaki – Viewing Learner can identify particular features of By the end of level 4, visual language learners can: Learner can understand particular visual identify particular features and their significance in features of visual communicating information and ideas to language and specific audiences understand their Learner can understand combinations of significance in visual and verbal language communicating information and ideas to Learner can respond to combinations of specific audiences; visual and verbal language understand and respond Learner can understand the significance of to combinations of visual visual language in communicating and verbal language and information and ideas to specific audiences their significance in Learner can respond to the significance of communicating visual language in communicating information and ideas to information and ideas to specific audiences specific audiences. Typical audiences for this learner: ...... Kōrero – Speaking Learner can initiate short personal By the end of level 4, conversations learners can: Learner can respond in short personal engage in short personal conversations conversations Learner can sustain short personal make plans with friends, conversations face-to-face, and by Learner can make plans with friends face- telephone to-face initiate and sustain short Learner can make plans with friends on the conversations that telephone involve polite social interactions (such as Learner can initiate short conversations declining invitations) including polite social conventions, such as declining invitations or making excuses give short prepared talks Learner can sustain short conversations on familiar topics including polite social conventions, such as use generally declining invitations or making excuses appropriate Learner can give short prepared talks on pronunciation, stress, familiar topics rhythm, and intonation. Learner can use generally appropriate pronunciation, stress, rhythm and intonation
Tuhituhi – Writing Learner can use resources (eg dictionaries By the end of level 4,
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 13 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector learners can: and glossaries) to experiment with new use resources (for language example, dictionaries Typical resources used by this learner: and glossaries) to ...... experiment with new ...... language and to review ...... writing for accuracy; Learner can use resources to review writing write short texts on for accuracy familiar topics; Learner can write short texts on familiar plan longer written texts topics and write parts of these; Topics familiar to this learner: ...... use appropriate writing ...... conventions; ...... send text and email Learner can plan longer written texts and messages. write parts of these Learner can use appropriate writing conventions Learner can send text messages Learner can send email messages Learner can also write the following: ...... Whakaatu – Presenting Learner can communicate information By the end of level 4, through texts in which visual and verbal learners can: features interact to produce particular communicate meaning and effects information, ideas or Learner can communicate ideas through narrative through texts in texts in which visual and verbal features which visual and verbal interact to produce particular meaning and features interact to effects produce particular Learner can communicate a narrative meaning and effects; through texts in which visual and verbal present or perform features interact to produce particular traditional or modern meaning and effects cultural items in selected Learner can present or perform traditional settings. aspects of the culture in selected settings Learner can present or perform modern aspects of the culture in selected settings Visual texts produced by this learner: ......
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 14 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector Assessment checklist for Level 5 Achievement Objectives
LEVEL 5 Teacher assessment checklist items Rating Comments: 1 / 2 / 3 say more about Achievement what the learner Objective Learner’s name: can or cannot do Date of assessment: 5.1 communicate about Learner can communicate about his or her past activities and events; past activities Learner can communicate about others’ past activities Learner can communicate about past events he or she was involved in Learner can communicate about past events they were not involved in 5.2 communicate about Learner can communicate about present present and past states, states feelings, and opinions; Learner can communicate about past states Learner can communicate about present feelings Learner can communicate about past feelings Learner can communicate about present opinions Learner can communicate about past opinions 5.3 communicate about Learner can communicate about past habits past habits and routines; Learner can communicate about past routines 5.4 describe, compare, Learner can describe people and contrast people, Learner can compare and contrast people places, and things. Learner can describe places Learner can compare and contrast places Learner can describe things Learner can compare and contrast things Whakarongo – Learner can make use of context and Listening familiar language when listening to work out By the end of level 5, meaning learners can: Learner can make use of context and make use of context familiar language when listening to work out and familiar language relationships between things to work out meaning Learner can make use of context and and relationships familiar language when listening to work out between things, relationships between events events, and ideas; Learner can make use of context and understand specific familiar language when listening to work out details in contexts that relationships between ideas may contain some Learner can understand specific details in unfamiliar language; spoken contexts that may contain some distinguish between unfamiliar language past and present Learner can distinguish between past and actions and states. present actions when listening
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 15 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector Learner can distinguish between past and present states when listening Typical listening contexts for this learner: ...... Pānui – Reading Learner can make use of context and By the end of level 5, familiar language to work out meaning when learners can: reading make use of context Learner can make use of context and and familiar language familiar language when reading to work out to work out the relationships between things relationships between Learner can make use of context and things, events, and familiar language when reading to work out ideas; relationships between events understand specific Learner can make use of context and details in contexts that familiar language when reading to work out may contain some relationships between ideas unfamiliar language; Learner can understand specific details in distinguish between written contexts that may contain some past and present unfamiliar language actions and states. Learner can distinguish between past and present actions when reading Learner can distinguish between past and present states when reading Mātakitaki – Viewing Learner can understand information and By the end of level 5, ideas encountered in a variety of visual learners can: texts understand and Learner can respond to information and respond to information ideas encountered in a variety of visual and ideas encountered texts in a variety of visual Learner can identify particular features of texts; visual language in communicating identify particular information to a specific audience for a features of visual specific purpose, on their own and in language and combinations with verbal language understand their Learner can understand the significance of significance in particular features of visual language in communicating communicating information to a specific information to a audience for a specific purpose, on their specific audience for a own and in combinations with verbal specific purpose when language used on their own and also in combinations with verbal language. Kōrero – Speaking Learner can initiate short conversations By the end of level 5, Learner can sustain short conversations learners can: Learner can give short talks on familiar initiate and sustain topics in a range of contexts in the past short conversations; Learner can give short talks on familiar give short talks on topics in a range of contexts in the present familiar topics in a Learner can discuss topics of mutual range of contexts, past interest with a friend and present; Learner can discuss topics of mutual discuss topics of interest with a teacher mutual interest; Learner can discuss topics of mutual
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 16 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector use appropriate interest in a group pronunciation, stress, Typical topics for this learner: rhythm, and intonation...... Learner can use appropriate pronunciation, stress, rhythm, and intonation Tuhituhi – Writing Learner can use resources to experiment By the end of level 5, with new language learners can: Learner can use resources to review writing use resources such as for accuracy dictionaries and Learner can write information on familiar glossaries to topics in a range of contexts in the past experiment with new Learner can write information on familiar language and review topics in a range of contexts in the present writing for accuracy; Learner can use appropriate writing write information on conventions familiar topics in a Learner can write an expository text range of contexts, past and present; Learner can write a recount text use appropriate writing Learner can write a narrative text conventions; Learner can also write the following: ...... write a range of text ...... types, for a range of ...... purposes and ...... audiences...... Whakaatu – Presenting Learner can communicate information By the end of level 5, through texts in which visual and verbal learners can: features interact to produce particular meanings and effects communicate information, ideas or Learner can communicate ideas through narrative through texts texts in which visual and verbal features in which visual and interact to produce particular meanings and verbal features interact effects to produce particular Learner can communicate a narrative meanings and effects; through texts in which visual and verbal present or perform a features interact to produce particular variety of visual texts meanings and effects for a range of purposes Learner can present or perform a variety of and audiences. visual texts Learner can present or perform a variety of visual texts for a range of purposes Learner can present or perform a variety of visual texts for a range of audiences Visual texts produced by this learner: ......
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 17 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector Assessment checklist for Level 6 Achievement Objectives
LEVEL 6 Teacher assessment checklist items Rating Comments: 1 / 2 / 3 say more about Learner’s name: Achievement what the learner Objective Date of assessment: can or cannot do 6.1 give and follow Learner can give instructions for a simple instructions; task Learner can follow instructions for a simple task Learner can give instructions for a more complex task Learner can follow instructions for a more complex task Learner can give instructions for a difficult task Learner can follow instructions for a difficult task 6.2 communicate about Learner can convey information about problems and solutions; problems at a simple level Learner can convey information about problems at a more complex level Learner can convey solutions to simple problems Learner can convey solutions to more complex problems 6.3 communicate about Learner can communicate about his or her immediate plans, hopes, immediate plans wishes, and intentions; Learner can communicate about his or her hopes Learner can communicate about his or her wishes Learner can communicate about his or her intentions 6.4 communicate in Learner can communicate in formal formal situations. situations Learner can communicate appropriately at a ...... Learner can communicate appropriately at a ...... List a series of formal situations that are relevant for your learners, such as: pōwhiri at school, pōwhiri on a marae, speaking competition, school assembly – and then turn these into assessment statements. You might also specify the communication role that the learner will perform, and a specific context, for example: Learner, as tangata whenua, can greet manuhiri during a school-based pōwhiri Learner, as manuhiri, can respond to formal greetings in the hongi line after a pōwhiri Learner can present a prepared speech in a school assembly
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 18 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector Learner can write an article for the local newspaper Learner can write invitations or posters for a major school event Learner can write a letter to a local business asking for sponsorship Learner can write a letter to his or her iwi rūnanga to apply for a scholarship Whakarongo – Learner can make use of context and Listening familiar language to understand instructions By the end of level 6, when listening in informal contexts learners can: Learner can make use of context and make use of context familiar language to understand instructions and familiar language when listening in formal contexts to understand Learner can make use of context and instructions and familiar language to understand information information in formal when listening in informal contexts and informal contexts; Learner can make use of context and understand specific familiar language to understand information details in contexts that when listening in formal contexts may contain some Learner can understand specific details unfamiliar language; when listening in contexts that may contain distinguish between some unfamiliar language past and present Learner can distinguish between past and actions and states. present actions when listening Learner can distinguish between past and present states when listening Pānui – Reading Learner can make use of context and By the end of level 6, familiar language to understand written learners can: instructions in informal contexts make use of context Learner can make use of context and and familiar language familiar language to understand written to understand written instructions in formal contexts instructions and Learner can understand specific details in information in formal written texts in contexts that may contain and informal contexts some unfamiliar language understand specific Learner can distinguish between past and details in contexts that present actions when reading may contain some Learner can distinguish between past and unfamiliar language present states when reading distinguish between past and present actions and states. Mātakitaki – Viewing Learner can understand various meanings, By the end of level 6, information and ideas encountered in visual learners can: texts understand and Learner can respond to various meanings, respond to various information and ideas encountered in visual meanings, ideas and texts effects in visual texts Learner can understand various meanings, for different purposes information and ideas encountered in visual and audiences texts for different purposes use appropriate Learner can respond to various meanings, terminology to describe information and ideas encountered in visual ways that visual and texts for different purposes verbal language
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 19 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector interact for specific Learner can understand various meanings, effects and purposes. information and ideas encountered in visual texts for different audiences Learner can respond to various meanings, information and ideas encountered in visual texts for different audiences Learner can use appropriate terminology to describe ways that visual and verbal language interact for specific effects Learner can use appropriate terminology to describe ways that visual and verbal language interact for specific purposes Kōrero – Speaking Learner can initiate more extended By the end of level 6, conversations in informal contexts learners can: Learner can sustain more extended initiate and sustain conversations in informal contexts more extended Learner can initiate more extended conversations in both conversations in formal contexts formal and informal Learner can sustain more extended contexts; conversations in formal contexts discuss projects and Learner can discuss projects and tasks in tasks in pairs or pairs eg when sharing peer feedback on groups, for example, writing when sharing peer feedback on writing; Learner can discuss projects and tasks in groups give short talks on familiar topics in Learner can give short talks on familiar familiar contexts that topics in familiar contexts, in the past relate to the past and Learner can give short talks on familiar present; topics in familiar contexts, in the present use appropriate Learner can use appropriate pronunciation, pronunciation, stress, stress, rhythm, and intonation rhythm, and intonation. Tuhituhi – Writing Learner can use resources to experiment By the end of level 6, with new language learners can: Learner can use resources to review writing use resources such as for accuracy dictionaries and Learner can write information on familiar glossaries to topics with past time reference experiment with new Learner can write information on familiar language and to review topics with present time reference writing for accuracy; Learner can write information on familiar write information on topics with future time reference familiar topics reffering to past, present, and Learner can write a range of text types and future time; more extended texts, eg: write a range of text Learner can write formal letters types and more Learner can write personal letters extended texts (for Learner can write blogs example, formal letters, Learner can write longer essays personal letters, blogs, longer essays, Learner can write longer descriptions descriptions, and Learner can write longer narratives narratives); Learner can write argument texts use a range of written Learner can write these texts too planning tools, such as ...... graphic organisers and ......
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 20 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector mind maps; ...... use appropriate writing Learner can use a range of written planning conventions. tools, such as skeleton plans and mind maps Learner can use appropriate writing conventions for longer and more diverse texts Whakaatu – Presenting Learner can use visual language to By the end of level 6, communicate with different audiences learners can: Learner can use visual language to use visual language communicate for different purposes alone to communicate Learner can use combinations of visual and with different verbal language to communicate with audiences for different different audiences purposes; Learner can use combinations of visual and use combinations of verbal language to communicate for visual and verbal different purposes. language to Visual texts produced by this learner: communicate with ...... different audiences for ...... different purposes......
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 21 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector Assessment checklist for Level 7 Achievement Objectives
LEVEL 7 Teacher assessment checklist items Rating Comments: 1 / 2 / 3 say more about Learner’s name: Achievement what the learner Objective Date of assessment: can or cannot do 7.1 communicate about Learner can communicate about future future plans; plans 7.2 offer and respond to Learner can offer advice advice, warnings, and Learner can respond to advice suggestions; Learner can convey warnings Learner can respond to warnings Learner can make suggestions Learner can respond to suggestions 7.3 express and respond Learner can express approval to approval and Learner can respond to expressions of disapproval, agreement approval and disagreement; Learner can express disapproval Learner can respond to expressions of disapproval Learner can express agreement Learner can respond to expressions of agreement Learner can express disagreement Learner can respond to expressions of disagreement 7.4 offer and respond to Learner can offer information information and opinions, Learner can respond to information and giving reasons; offers of information Learner can offer opinions Learner can respond to opinions Learner can give reasons for their opinions Learner can give reasons for offering information, or for the nature of the information 7.5 read about and Learner can read about and understand recount actual or actual events in the past imagined events in the Learner can read about and recount actual past. events in the past Learner can read about and understand imagined events in the past Learner can read about and recount imagined events in the past Whakarongo – Learner can understand much of what other Listening speakers of Māori say about a range of By the end of level 7, topics learners can: List key topics for this learner here: understand much ...... of what other ...... speakers of te reo ...... Māori say about a ...... range of topics Learner can understand much of what other
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 22 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector across a range of speakers of Māori say across a range of spoken text types, spoken, informal text types formal and List key informal spoken text types for this informal; learner distinguish here: ...... between facts and ...... opinions and ...... recognise ...... intentions to Learner can understand much of what other persuade and speakers of Māori say across a range of influence. spoken, formal text types List key formal spoken text types for this learner here: ...... Learner can distinguish between facts and opinions when listening Learner can recognise intentions to persuade and influence when listening Pānui – Reading Learner can understand much of what is By the end of level 7, written in Māori about a range of topics learners can: Learner understand much of what is written understand much in Māori across a range of written text types: of what is written in Learner can understand narrative texts te reo Māori about Learner can understand expository texts a range of topics, Learner can understand persuasive texts across a range of written text types Learner can understand ...... texts intended for Learner can distinguish between facts and different purposes opinions when reading and audiences; Learner can recognise intentions to distinguish persuade and influence when reading between facts and opinions and recognise intentions to persuade and influence. Mātakitaki – Viewing Learner can understand visual texts that By the end of level 7, have been created for a range of purposes learners can: List purposes here for this understand and learner: ...... respond to visual ... texts that have ...... been created for a ...... range of purposes, ...... and audiences; Learner can understand visual texts that describe how have been created for different audiences visual and verbal List audiences here for this learner: features are ...... combined for ...... different purposes, ...... and audiences...... Learner can understand visual texts that have been created for different effects
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 23 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector List effects here for this learner: ...... Learner can understand visual texts that have been created for a range of purposes List purposes here for this learner: ...... Learner can describe how visual and verbal features are combined for different purposes Learner can describe how visual and verbal features are combined for different audiences Learner can describe how visual and verbal features are combined for different effects Kōrero – Speaking Learner can use Māori to entertain as well By the end of level 7, as to inform when speaking learners can: Learner can use Māori to entertain as well use te reo Māori to as to persuade when speaking entertain and Learner can initiate and sustain extended persuade as well conversations in Māori as to inform; Learner can give talks on a range of topics initiate and sustain List key topics here for this learner: conversations in te ...... reo Māori; ...... give talks on a ...... range of topics in a ...... range of contexts; Learner can give talks in a range of contexts use appropriate pronunciation, (eg: learner can give a three-minute intonation, rhythm, impromptu speech amongst classmates; and stress. learner can give an impromptu speech in the presence of manuhiri) List key contexts here for this learner: ...... Learner can use appropriate pronunciation, intonation, rhythm and stress Tuhituhi – Writing Learner can use resources to experiment By the end of level 7, with new language when writing learners can: Learner can use resources to review writing use resources for accuracy such as List key resources used by this learner: dictionaries and ...... glossaries to ...... experiment with ...... new language and ...... to review writing Learner can write in Māori about a range of for accuracy; topics
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 24 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector write in te reo List key topics here for this learner: Māori about a ...... range of topics, ...... using words and ...... expressions that ...... are appropriate for Learner can write in Māori using words and the purpose and expressions that are appropriate for the intended audience; purpose begin to use Learner can write in Māori using words and language to expressions that are appropriate for entertain and intended audience persuade as well Learner is beginning to use language to as to inform. entertain as well as inform Learner is beginning to use language to persuade as well as inform Learner comfortably uses language to entertain as well as inform Learner comfortably uses language to persuade as well as inform Whakaatu – Presenting Learner can use visual language in a range By the end of level 7, of texts for different audiences learners can: Learner can use visual language in a range use visual of texts for different purposes language effects in Learner can use visual language in a range a range of texts for of texts for different effects different audiences Learner can combine features of visual and and purposes; verbal language in a range of texts for combine features different audiences of visual and Learner can combine features of visual and verbal language in verbal language in a range of texts for a range of texts for different purposes different audiences Learner can combine features of visual and and purposes; verbal language in a range of texts for create new visual different effects texts to express Learner can create new visual texts to their own express their own information and ideas information and ideas. List key visual texts here for this learner: ......
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 25 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector Assessment checklist for Level 8 Achievement Objectives
LEVEL 8 Teacher assessment checklist items Rating Comments: 1 / 2 / 3 say more about Learner’s name: Achievement what the learner Objective Date of assessment: can or cannot do 8.1 communicate about Learner can communicate about certainty certainty and uncertainty, Learner can communicate about uncertainty possibility and probability; Learner can communicate about possibility Learner can communicate about probability 8.2 develop an argument Learner can develop an argument or point or point of view, with of view, giving reasons reasons; 8.3 recount a series of Learner can recount a series of events to events to inform, inform persuade, or entertain; Learner can recount a series of events to persuade Learner can recount a series of events to entertain 8.4 communicate the Learner can communicate the same same information in information in different ways to suit different different ways for different contexts audiences; List key contexts here for this learner: ...... 8.5 respond to selected, Learner can respond to selected and and adapted texts in te adapted texts about Māori language reo Maori that are about Learner can respond to selected and te reo and tikanga Maori adapted texts about Māori culture (for example, texts from recorded speeches, literature, film, newspapers, magazines, television, video, DVD, and radio). Whakarongo – Learner can understand much of what other Listening speakers of Māori say about a range of By the end of level 8, topics learners can: List key spoken topics here for this learner: understand much ...... of what other ...... speakers of te reo ...... Māori say about a ...... range of topics; Learner can distinguish between facts, distinguish opinions, and hypotheses when listening between facts, Learner can recognise intentions to opinions, and persuade and influence in different spoken hypotheses and contexts recognise List key spoken contexts here for this intentions to learner: persuade and ...... influence in ......
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 26 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector different contexts...... Pānui – Reading Learner can understand much of what is By the end of level 8, written by other users of Māori about a learners can: range of topics understand much List key spoken topics here for this learner: of what is written ...... by other users of ...... Māori about a ...... range of topics; ...... distinguish Learner can distinguish between facts, between facts, opinions, and hypotheses while reading opinions, and Learner can recognise intentions to hypotheses and persuade and influence in different contexts recognise List key written contexts here for this intentions to learner: persuade and ...... influence in ...... different contexts...... Mātakitaki – Viewing Learner can understand the ways in which By the end of level 8, artists, speakers and writers combine visual learners can: and verbal features to present ideas in a range of genres and settings understand the ways in which Learner can understand the ways in which artists, speakers artists, speakers and writers combine visual and writers and verbal features to present information in combine visual a range of genres and settings and verbal Learner can understand the ways in which features to present artists, speakers and writers combine visual ideas and and verbal features to achieve particular information to effects in a range of genres and settings achieve particular Learner can understand and respond to effects for a range visual features used to present information of purposes and for particular effects in a range of genres audiences; and settings understand and Learner can understand and respond to respond to visual visual features used to present ideas for features used to particular effects in a range of genres and present settings information and List key genres here for this learner: ideas for particular ...... effects for a range ...... of purposes and ...... audiences...... List key settings here for this learner: ...... Kōrero – Speaking Learner can initiate and sustain By the end of level 8, conversations in a range of contexts learners can: Learner can give talks on a range of topics initiate and sustain in a wide range of contexts conversations; List key contexts here for this learner: give talks on a ......
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 27 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector range of topics in a ...... wide range of ...... contexts; ...... produce a wide Learner can produce a wide range of range of spoken informal spoken text types text types, formal List key informal spoken text types here for and informal; this learner: adapt spoken texts ...... to suit different ...... audiences and ...... purposes; ...... use te reo Māori to Learner can produce a wide range of formal entertain and to spoken text types persuade as well List key formal spoken text types here for as to inform. this learner: ...... Learner can adapt spoken texts to suit different audiences Learner can adapt spoken texts to suit different purposes Learner can use Māori to entertain as well as to inform Learner can use Māori to persuade as well as to inform Tuhituhi – Writing Learner can use resources to experiment By the end of level 8, with new language and to review writing for learners can: accuracy use resources Learner can write about a range of topics such as across a wide range of text types, selecting dictionaries and words and expressions that are appropriate glossaries to for the purpose and intended audience experiment with Learner can adapt written texts to suit new language and different audiences and purposes to review writing Learner can write Māori to entertain and to for accuracy; persuade as well as to inform write about a List key written text types or genre here for range of topics this learner: across a wide ...... range of text types, ...... selecting words ...... and expressions ...... that are List key written topics here for this learner: appropriate for the ...... purpose and ...... intended audience; ...... adapt written texts ...... to suit different audiences and purposes; use te reo Māori to entertain and to persuade as well as to inform.
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 28 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector Whakaatu – Presenting Learner can combine visual and verbal By the end of level 8, features to present ideas and information to learners can: achieve particular effects in a range of genres and settings combine visual and verbal Learner can use visual language in a range features to present of genres for different audiences, purposes ideas and and effects information to Learner can create new visual texts to achieve particular express their own information and ideas effects for a range List key genres here for this learner: of purposes and ...... audiences; ...... use visual ...... language in a ...... range of text types List key written settings here for this learner: for different ...... audiences, ...... purposes and ...... effects; ...... create new visual Visual texts produced by this learner: texts to express ...... their own ...... information and ...... ideas......
Examples of second language learning tasks | Teacher Assessment Checklists 29 of 29 From: TKI | Te reo Māori in English-medium schools | Te Whakaipurangi Rauemi teacher resources collection http://tereomaori.tki.org.nz/Teacher-resources/Te-Whakaipurangi-Rauemi-teacher-resources-collection © New Zealand Ministry of Education 2010 – copying restricted to use by the New Zealand education sector