REDOX REACTIONS
OXIDATION The LOSS of electrons. An increase of the oxidation number. Group one and two metals oxidize spontaneously. Transition metals are oxidized by metals below them on table J. Active non-metals can only be oxidized by an industrial process called electrolysis. All oxidations must balance for MASS and CHARGE, in this case there is one Ca on each side. Use the algebra bubble (wiener) to balance charge. ALWAYS add electrons to the more positive side of the oxidation to balance charge.
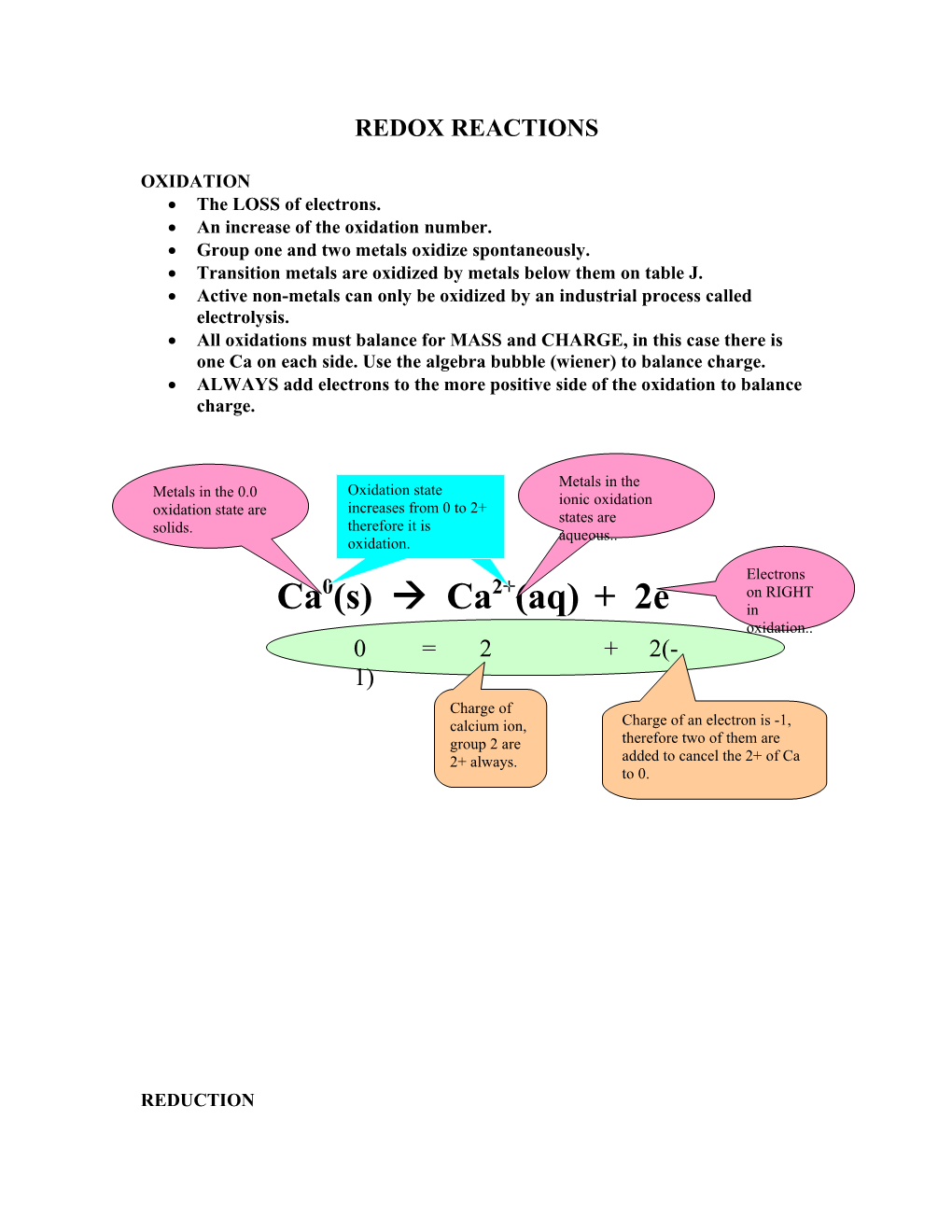
Metals in the Oxidation state Metals in the 0.0 ionic oxidation increases from 0 to 2+ oxidation state are states are therefore it is solids. aqueous.. oxidation.
Electrons 0 2+ - on RIGHT Ca (s) Ca (aq) + 2e in oxidation.. 0 = 2 + 2(- 1) Charge of calcium ion, Charge of an electron is -1, group 2 are therefore two of them are 2+ always. added to cancel the 2+ of Ca to 0.
REDUCTION The GAIN of electrons. A decrease (reduction) of the oxidation number. Halogens reduce spontaneously. Transition metals are reduced by metals above them on table J. Active metals can only be reduced by an industrial process called electrolysis. All reductions must balance for MASS and CHARGE, on each side. Use the algebra bubble (wiener) to balance charge. ALWAYS add electrons to the more positive side of the reduction to balance charge.
Oxidation state Cl in the 0.0 decreases from 0 to 1- Electrons on the oxidation state is therefore it is left in reduction a gas. reduction.
0 - - Cl2 (g) + 2e 2 Cl 2(0) + 2(-1) = 2(-1) Oxidation state of each Cl is 0, HONClBrIF
You need 2 electrons to make the left -2, ad to the o state if the Cl 2. Charge of a halogen . ion is usually 1- when it is free in solution.