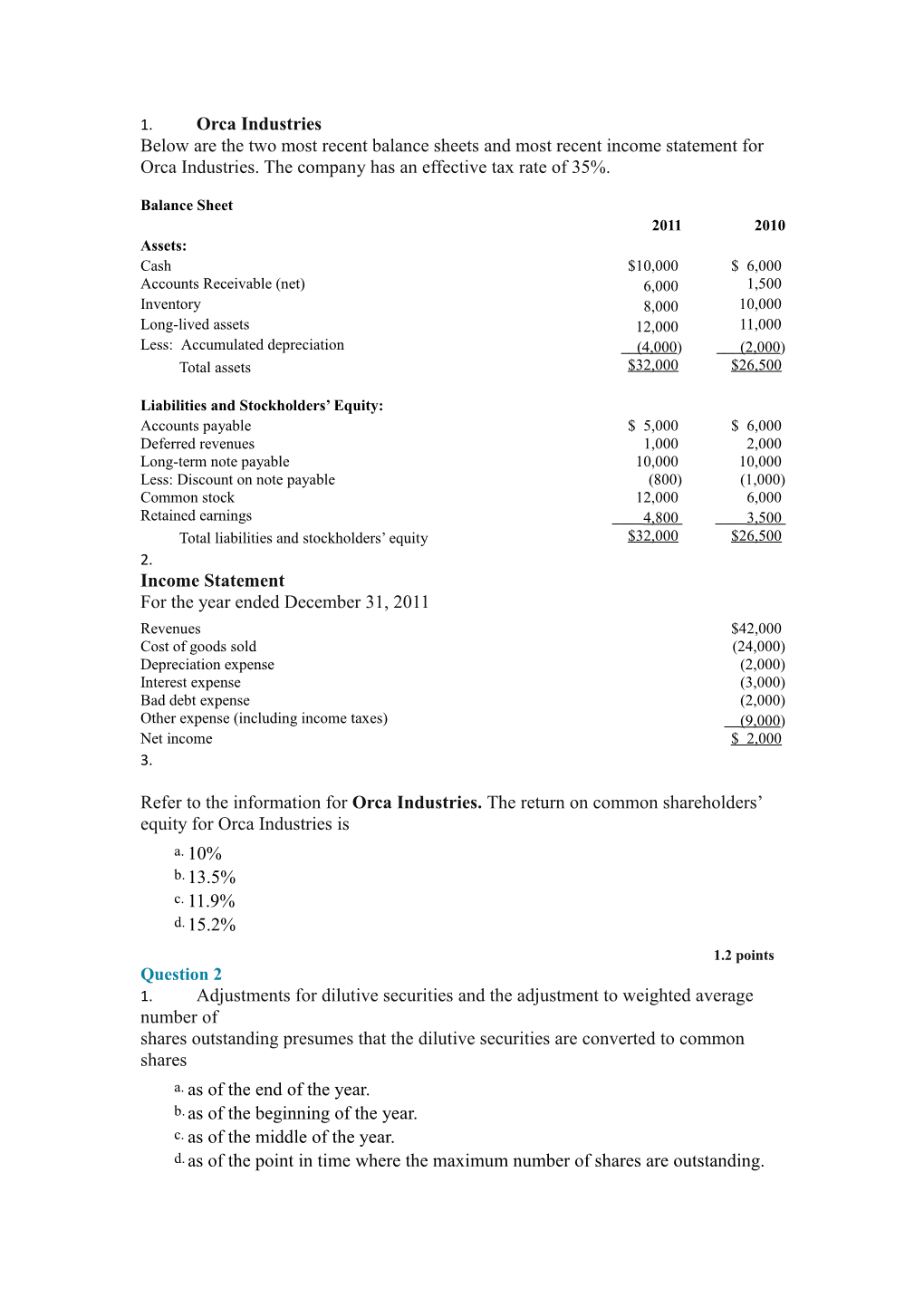
1. Orca Industries Below are the two most recent balance sheets and most recent income statement for Orca Industries. The company has an effective tax rate of 35%.
Balance Sheet 2011 2010 Assets: Cash $10,000 $ 6,000 Accounts Receivable (net) 6,000 1,500 Inventory 8,000 10,000 Long-lived assets 12,000 11,000 Less: Accumulated depreciation (4,000) (2,000) Total assets $32,000 $26,500
Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity: Accounts payable $ 5,000 $ 6,000 Deferred revenues 1,000 2,000 Long-term note payable 10,000 10,000 Less: Discount on note payable (800) (1,000) Common stock 12,000 6,000 Retained earnings 4,800 3,500 Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity $32,000 $26,500 2. Income Statement For the year ended December 31, 2011 Revenues $42,000 Cost of goods sold (24,000) Depreciation expense (2,000) Interest expense (3,000) Bad debt expense (2,000) Other expense (including income taxes) (9,000) Net income $ 2,000 3.
Refer to the information for Orca Industries. The return on common shareholders’ equity for Orca Industries is a. 10% b. 13.5% c. 11.9% d. 15.2% 1.2 points Question 2 1. Adjustments for dilutive securities and the adjustment to weighted average number of shares outstanding presumes that the dilutive securities are converted to common shares a. as of the end of the year. b. as of the beginning of the year. c. as of the middle of the year. d. as of the point in time where the maximum number of shares are outstanding. 1.2 points Question 3 1. Orca Industries Below are the two most recent balance sheets and most recent income statement for Orca Industries. The company has an effective tax rate of 35%.
Balance Sheet 2011 2010 Assets: Cash $10,000 $ 6,000 Accounts Receivable (net) 6,000 1,500 Inventory 8,000 10,000 Long-lived assets 12,000 11,000 Less: Accumulated depreciation (4,000) (2,000) Total assets $32,000 $26,500
Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity: Accounts payable $ 5,000 $ 6,000 Deferred revenues 1,000 2,000 Long-term note payable 10,000 10,000 Less: Discount on note payable (800) (1,000) Common stock 12,000 6,000 Retained earnings 4,800 3,500 Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity $32,000 $26,500 2. Income Statement For the year ended December 31, 2011 Revenues $42,000 Cost of goods sold (24,000) Depreciation expense (2,000) Interest expense (3,000) Bad debt expense (2,000) Other expense (including income taxes) (9,000) Net income $ 2,000 3.
Refer to the information for Orca Industries. Orca’s accounts receivable turnover is (assume that Orca makes all sales on account) a. 10 b. 7.0 c. 11.2 d. .53 1.2 points Question 4 1. Mobile Company Mobile Company manufactures computer technology devices. Selected financial data for Mobile is presented below, use the information to answer the following questions:
Current Assets As of Dec. 31, 2010 Dec. 31, 2009 Cash and short-term investments $1,267,038 $ 616,604 Accounts Receivable (net) 490,816 665,828 Inventories 338,599 487,505 Prepaid Expenses and other current assets 292,511 291,915 Total Current Assets $2,388,964 $2,061,852
Current Liabilities Short-term borrowings $ 25,190 $ 38,108 Current portion of long-term debt 182,295 210,090 Accounts payable 296,307 334,247 Accrued liabilities 941,912 743,999 Income taxes payable 203,049 239,793 Total Current Liabilities 1,648,753 1,566,237 2. Selected Income Statement Data - for the year ending December 31, 2010: Net Sales $4,885,340 Cost of Goods Sold 2,542,353 Operating Income 733,541 Net Income 230,101 3. Selected Statement of Cash Flow Data - for the year ending December 31, 2010: Cash Flows from Operations $1,156,084 4.
Refer to the information for Mobile Company. Mobile's quick ratio changed by what percentage from 2009 to 2010? a. 82% b. 107% c. 25% d. 30% 1.2 points Question 5 1. Mobile Company Mobile Company manufactures computer technology devices. Selected financial data for Mobile is presented below, use the information to answer the following questions:
Current Assets As of Dec. 31, 2010 Dec. 31, 2009 Cash and short-term investments $1,267,038 $ 616,604 Accounts Receivable (net) 490,816 665,828 Inventories 338,599 487,505 Prepaid Expenses and other current assets 292,511 291,915 Total Current Assets $2,388,964 $2,061,852
Current Liabilities Short-term borrowings $ 25,190 $ 38,108 Current portion of long-term debt 182,295 210,090 Accounts payable 296,307 334,247 Accrued liabilities 941,912 743,999 Income taxes payable 203,049 239,793 Total Current Liabilities 1,648,753 1,566,237 2. Selected Income Statement Data - for the year ending December 31, 2010: Net Sales $4,885,340 Cost of Goods Sold 2,542,353 Operating Income 733,541 Net Income 230,101 3. Selected Statement of Cash Flow Data - for the year ending December 31, 2010: Cash Flows from Operations $1,156,084 4.
Refer to the information for Mobile Company. Mobile's days accounts payable outstanding at the end of 2010 is a. 45.51 days b. 50 days c. 7.53 days d. 48.09 days 1.2 points Question 6 1. Ramos Company Ramos Company included the following information in its annual report: 2011 2010 2009 Sales $178,400 $162,500 $155,500 Cost of goods sold 115,000 102,500 100,000 Operating expenses 50,000 50,000 45,000 Net income 13,400 10,000 10,500 2.
Refer to the information for Ramos Company. In a common size income statement for 2009, the cost of goods sold are expressed as: a. 64.3% b. 40.0% c. 103% d. 87 % 1.2 points Question 7 1. Multiples of EPS to value firms are referred to as. a. ROCE b. price-earnings ratios c. Weighted average number of common shares outstanding d. ROA 1.2 points Question 8 1. Extreme Sports Company and All Sports Corporation Below is financial information for two sporting goods retailers. Extreme Sports Company operates a retail business and franchising business. At the end 2011, Extreme Sports had 263 Company-owned and 120 franchise-operated retail stores. Extreme’s stores are located in suburban, strip mall and regional mall locations, the company operates in 32 states. All Sports Corporation sells sporting goods and related products at over 2,500 Company-operated retail stores. Selected Data for All Sports and Extreme Sports (amounts in millions) All Sports Extreme Sports Sales $5,320 $1,344 Cost of Goods Sold 3,897 887 Interest Expense 138 43 Net Income 212 33 Average Inventory 998 286 Average Fixed Assets 1,163 130 Average Total Assets 2,472 662 Average Tax Rate 40% 40% 2.
Refer to the information for Extreme Sports Company and All Sports Corporation. What is the return on assets for All Sports? a. 9.2% b. 8.6% c. 11.9% d. 10.8% 1.2 points Question 9 1. Here are several ratios calculated from Midas Company's financial statements: Days in Receivables = 43 Days in Payables = 38 Days in Inventory = 31
How many days of working capital financing does Midas need to obtain from other sources? a. 36 days b. 56 days c. 26 days d. 112 days 1.2 points Question 10 1. Mobile Company Mobile Company manufactures computer technology devices. Selected financial data for Mobile is presented below, use the information to answer the following questions:
Current Assets As of Dec. 31, 2010 Dec. 31, 2009 Cash and short-term investments $1,267,038 $ 616,604 Accounts Receivable (net) 490,816 665,828 Inventories 338,599 487,505 Prepaid Expenses and other current assets 292,511 291,915 Total Current Assets $2,388,964 $2,061,852
Current Liabilities Short-term borrowings $ 25,190 $ 38,108 Current portion of long-term debt 182,295 210,090 Accounts payable 296,307 334,247 Accrued liabilities 941,912 743,999 Income taxes payable 203,049 239,793 Total Current Liabilities 1,648,753 1,566,237 2. Selected Income Statement Data - for the year ending December 31, 2010: Net Sales $4,885,340 Cost of Goods Sold 2,542,353 Operating Income 733,541 Net Income 230,101 3. Selected Statement of Cash Flow Data - for the year ending December 31, 2010: Cash Flows from Operations $1,156,084 4.
Refer to the information for Mobile Company. Mobile's days receivables outstanding at the end of 2010 was a. 45.25 days b. 8.50 days c. 43.20 days d. 40.50 days 1.2 points Question 11 1. Below is selected information from Marker’s 2012 financial statements:
As of Dec. 31, 2012 Dec. 31, 2011 Cash and short-term investments $ 958,245 $ 745,800 Accounts Receivable (net) 125,850 135,400 Inventories 195,650 175,840 Prepaid Expenses and other current assets 45,300 30,860 Total Current Assets $1,325,045 $1,087,900 Plant, Property and Equipment, net 1,478,320 1,358,700 Intangible Assets 125,600 120,400 Total Assets $2,928,965 $2,567,000
Short-term borrowings $ 25,190 $ 38,108 Current portion of long-term debt 45,000 40,000 Accounts payable 285,400 325,900 Accrued liabilities 916,722 705,891 Income taxes payable 125,400 115,600 Total Current Liabilities $1,397,712 $1,225,499 Long-term Debt 450,000 430,000 Total Liabilities $1,847,712 $1,655,499 Shareholders' Equity $1,081,253 $ 911,501 Total Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity $2,928,965 $2,567,000
Selected Income Statement Data - for the year ending December 31, 2012: Net Sales $3,210,645 Cost of Goods Sold (2,310,210) Operating Income $ 900,435 Net Income $ 324,850
Selected Statement of Cash Flow Data - for the year ending December 31, 2012: Cash Flows from Operations $584,750 Interest Expense 42,400 Income Tax Expense 114,200 2.
Marker’s Liabilities to Assets Ratio for 2012 is a. 63.1% b. 78.3% c. 105.1% d. 100.0% 1.2 points Question 12 1. The best indicator for assessing a firm's long-term solvency risk is its ability to generate what over a period of years? a. Positive cash flows b. Income from continuing operations c. Sales d. Earnings 1.2 points Question 13 1. Which of the following might an analyst not want to eliminate from past earnings when using past earnings to forecast future earnings? a. revenue from the sale of inventory. b. nonrecurring restructuring charges. c. nonrecurring gains from the sale of assets. d. unusual asset impairment charges. 1.2 points Question 14 1. Net Devices Inc. The following balance sheets and income statements are for Net Devices Inc., a manufacturer of small electronic devices, including calculators, personal digital assistants and mp3 players. For purposes of these questions assume that the company has an effective tax rate of 35%.
BALANCE SHEETS
ASSETS ($ in thousands)
Fiscal year end 2011 2010 2009 Cash $ 875,650 $ 571,250 $ 154,230 Marketable securities 6,560 0 0 Receivables 771,580 775,250 902,000 Inventories 1,320,150 1,254,600 1,418,500 Other current assets 249,000 231,200 229,900 Total current assets 3,222,940 2,832,300 2,704,630
Property, plant & equipment 1,118,750 1,100,300 1,122,400
Intangibles 263,050 241,000 215,600 Deposits & other assets 184,500 168,250 168,900 Total assets $4,789,240 $4,341,850 $4,211,530 2. LIABILITIES ($ in thousands)
Fiscal year end 2011 2010 2009 Accounts payable $1,178,540 $1,061,100 $1,138,250 Current long term debt 18,100 316,500 150,900 Accrued expenses 664,100 615,900 585,400 Income taxes payable 138,900 108,400 38,200 Other current liabilities 0 0 0 Total current liabilities 1,999,640 2,101,900 1,912,750
Long term debt 478,250 378,400 599,630 Other long term liabilities 13,350 0 0 Total liabilities 2,491,240 2,480,300 2,512,380
Preferred stock 850,000 850,000 550,000 Common stock net 4,000 3,950 3,800 Additional Paid-in Capital 869,000 758,000 689,500 Retained earnings 1,430,500 1,055,000 1,245,050 Treasury stock (855,500) (805,400) (789,200) Shareholders' equity 2,298,000 1,861,550 1,699,150
Total Liab. & Equity $4,789,240 $4,341,850 $4,211,530 3. INCOME STATEMENTS ($ in thousands)
Fiscal year end 2011 2010 Net sales $11,455,500 $11,082,100 Cost of Goods Sold (8,026,450) (7,940,065) Gross profit 3,429,050 3,142,035
Selling, general & admin. Exp. (1,836,400) (1,789,200) Income before deprec. & amort. 1,592,650 1,352,835
Depreciation & amortization (785,250) (757,250) Interest expense (46,19 (43,34 5) 0)
Income before tax 761,205 552,245 Provision for income taxes (157,725) (112,290) Minority interest -- --
Net income $ 603,480 $ 439,955
Outstanding shares (in thousands) 308,515 303,095 Preferred Dividends (in thousands) $85,000 $85,000 4.
Refer to the information for Net Devices Inc. What is Net Devices’ capital structure leverage ratio for 2011? a. 10.32 b. 3.71 c. 3.89 d. 1.68 1.2 points Question 15 1. Non-U.S. companies that list securities in the United States typically include a risk factors item in the: a. disaggregated ROCE b. Form 20-F c. MD&A d. 10-K 1.2 points Question 16 1. Economic theory teaches that differences in market returns must relate to differences in a. book value b. perceived risk c. price-earnings ratio d. bankruptcy risk 1.2 points Question 17 1. To calculate diluted EPS, the accountant does all of the following except: a. enters only the net incremental shares issued (shares issued under options minus assumed shares repurchased) in the computation of diluted EPS. b adds back any interest expense (net of taxes) on convertible bonds . c. adds back to net income any compensation expense recognized on the employee stock options d adds back any dividends on convertible preferred stock the firm subtracted in . computing net income to common shareholders. 1.2 points Question 18 1. The computation of the additional shares to be issued on the exercise of stock options assumes that the firm would repurchase common shares on the open market using an amount equal to the sum of all the following except: a. any cash proceeds from such exercise b any tax benefits that would be credited to additional paid-in capital . c. net incremental shares issued d any unamortized compensation expense on those options . 1.2 points Question 19 1. Critics of EPS as a measure of profitability point out that it does not consider: a. the deduction of preferred stock dividends from net income. b simple capital structures. . c. Adjustments for dilutive securities and the adjustment to weighted average number of shares outstanding for complex capital structures. d the amount of assets or capital required to generate a particular level of . earnings. 1.2 points Question 20 1. Which of the following is not a way a company can achieve a low-cost position a. outsourcing b. economies of scale c. production efficiency d. customer service 1.2 points Question 21 1. Common-size analysis requires the analyst to be aware that percentages can change because of all of the following except: a. changes in expenses in the numerator independent of changes in sales b changes in sales independent of changes in expenses . c. interaction effects between the numerator and denominator d All of these are possible explanations. . 1.2 points Question 22 1. All of the following are common international risks faced by companies except: a. exchange rate changes b. dependence on one or a few suppliers c. asset expropriation d. political unrest 1.2 points Question 23 1. Mobile Company Mobile Company manufactures computer technology devices. Selected financial data for Mobile is presented below, use the information to answer the following questions:
Current Assets As of Dec. 31, 2010 Dec. 31, 2009 Cash and short-term investments $1,267,038 $ 616,604 Accounts Receivable (net) 490,816 665,828 Inventories 338,599 487,505 Prepaid Expenses and other current assets 292,511 291,915 Total Current Assets $2,388,964 $2,061,852
Current Liabilities Short-term borrowings $ 25,190 $ 38,108 Current portion of long-term debt 182,295 210,090 Accounts payable 296,307 334,247 Accrued liabilities 941,912 743,999 Income taxes payable 203,049 239,793 Total Current Liabilities 1,648,753 1,566,237 2. Selected Income Statement Data - for the year ending December 31, 2010: Net Sales $4,885,340 Cost of Goods Sold 2,542,353 Operating Income 733,541 Net Income 230,101 3. Selected Statement of Cash Flow Data - for the year ending December 31, 2010: Cash Flows from Operations $1,156,084 4.
Refer to the information for Mobile Company. Mobile's 2010 Inventory Turnover ratio is a. 7.46 b. 11.83 c. 5.62 d. 6.16 1.2 points Question 24 1. Below is selected information from Marker’s 2012 financial statements:
As of Dec. 31, 2012 Dec. 31, 2011 Cash and short-term investments $ 958,245 $ 745,800 Accounts Receivable (net) 125,850 135,400 Inventories 195,650 175,840 Prepaid Expenses and other current assets 45,300 30,860 Total Current Assets $1,325,045 $1,087,900 Plant, Property and Equipment, net 1,478,320 1,358,700 Intangible Assets 125,600 120,400 Total Assets $2,928,965 $2,567,000
Short-term borrowings $ 25,190 $ 38,108 Current portion of long-term debt 45,000 40,000 Accounts payable 285,400 325,900 Accrued liabilities 916,722 705,891 Income taxes payable 125,400 115,600 Total Current Liabilities $1,397,712 $1,225,499 Long-term Debt 450,000 430,000 Total Liabilities $1,847,712 $1,655,499 Shareholders' Equity $1,081,253 $ 911,501 Total Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity $2,928,965 $2,567,000
Selected Income Statement Data - for the year ending December 31, 2012: Net Sales $3,210,645 Cost of Goods Sold (2,310,210) Operating Income $ 900,435 Net Income $ 324,850
Selected Statement of Cash Flow Data - for the year ending December 31, 2012: Cash Flows from Operations $584,750 Interest Expense 42,400 Income Tax Expense 114,200 2.
Marker’s 2012 Interest Coverage ratio is a. 4.35 b. 7.66 c. 11.35 d. 1.00 1.2 points Question 25 1. Below is selected information from Marker’s 2012 financial statements:
As of Dec. 31, 2012 Dec. 31, 2011 Cash and short-term investments $ 958,245 $ 745,800 Accounts Receivable (net) 125,850 135,400 Inventories 195,650 175,840 Prepaid Expenses and other current assets 45,300 30,860 Total Current Assets $1,325,045 $1,087,900 Plant, Property and Equipment, net 1,478,320 1,358,700 Intangible Assets 125,600 120,400 Total Assets $2,928,965 $2,567,000
Short-term borrowings $ 25,190 $ 38,108 Current portion of long-term debt 45,000 40,000 Accounts payable 285,400 325,900 Accrued liabilities 916,722 705,891 Income taxes payable 125,400 115,600 Total Current Liabilities $1,397,712 $1,225,499 Long-term Debt 450,000 430,000 Total Liabilities $1,847,712 $1,655,499 Shareholders' Equity $1,081,253 $ 911,501 Total Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity $2,928,965 $2,567,000
Selected Income Statement Data - for the year ending December 31, 2012: Net Sales $3,210,645 Cost of Goods Sold (2,310,210) Operating Income $ 900,435 Net Income $ 324,850
Selected Statement of Cash Flow Data - for the year ending December 31, 2012: Cash Flows from Operations $584,750 Interest Expense 42,400 Income Tax Expense 114,200 2.
Marker’s 2012 Long-term Debt to Long-Term Capital ratio is a. 29.4% b. 25.4% c. 31.4% d. 34.0%