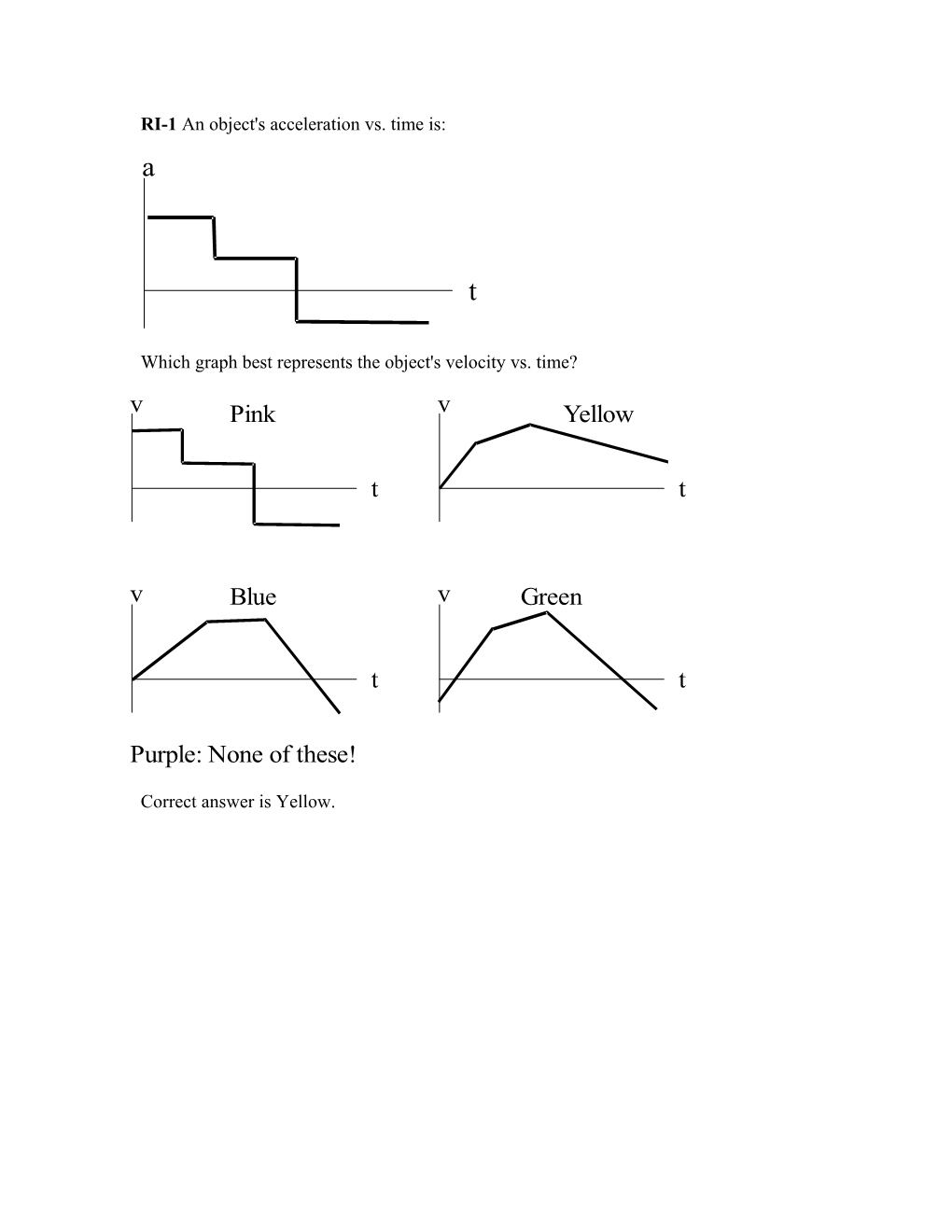
RI-1 An object's acceleration vs. time is:
a
t
Which graph best represents the object's velocity vs. time? v v Pink Yellow
t t
v Blue v Green
t t
Purple: None of these!
Correct answer is Yellow. RI-2 A student is asked the following question on an exam: A car is moving at 90mph and suddenly brakes with a constant acceleration a = -2g to a full stop. How many second does the car take to stop?
Which equation can be used to answer the question:
1 2 Yellow: x xo vo t 2 a t
Blue: v vo at 2 2 Green: v vo 2a(x xo )
Answer: v vo a t . We know the initial velocity vo, the final speed (v=0) and the acceleration a. We seek the time t. RI-3 Consider the vector A
y Which equation is correct?
Yellow: A x A cos
Blue: A x A cos
x Green: A x A sin Pink: A A sin x
A
Answer: A x A sin RI-4 The "multiflash photograph" below shows a ball rolling along a surface. The camera flashed once a second, and the time is shown above each image.
Which graph below best represents the ball's velocity as a function of time?
Correct answer is Purple. RI-5 What is the direction of vector C A B?
Ax = 1, Ay = 1
Bx = -2, By = 2
y
Blue Pink
x Green Yellow
Purple if along x or y axes.
Correct answer is Blue. Cx = Ax + Bx = +1 - 2 = -1, Cy = Ay + By = +1 + 2 = +3. The vector C points to the upper left, in the second quandrant. RI-6. A particle is moving with constant acceleration. Its velocity vector at two different times is shown below. What is the direction of the acceleration? y V 1 Blue Purple: None of these!
Green Yellow V 2 Pink x
Answer: The direction of the acceleration is the same as the v2 direction of v , which is up. Remember the vector v is the vector you vector-add to vector v1 to get vector v2. v
v1
Australia!
g V 2 V 1 RI-7.
A projectile is fired at an initial speed of vo at an angle of above the horizontal. Which of the following expressions could possibly be the correct expression for the range of the projectile? (Hint: check the units).
2 Pink : x 2 g v0 tan Yellow : x 2 g vo sin(2) v 2 g Green : x o sin 2 Blue : x sin 2 2 g vo
v2 Answer: Only the equation x o sin2 has the dimensions of length on both sides of g the equation. RI-8. A car moves around a figure-eight track at a constant speed in the direction shown. Over which part of the track is the magnitude of the car's acceleration smallest? B D
C A
Blue: from A to B Green: from C to D Yellow: Neither.
Answer: Neither! When moving along the straight portions of the track (B to C or D to A) the acceleration is zero. RI-9. An elevator is going up at a constant speed. Near the top floor, it starts to slow to a stop. During the period that it is slowing down, its acceleration is
BLUE: downward
YELLOW: upward.
PINK: in some other direction.
Answer: Acceleration is downward even though the velocity is upward. Use the "delta-v" argument to see this. RI-10 A bucket containing a brick is swung in a circle at constant speed in a vertical plane as shown. The bucket is swung fast enough that the brick does not fall out.
The net force on the brick as it is swung has T maximum magnitude at position. Pink: Top. Green:Bottom. Yellow: Right Purple: The net force has the same magnitude at all positions. N R
Answer: The net force has the same magnitude at all positions. Since this is circular motion with constant speed, the magnitude of the acceleration (a=v2/R) is B constant and so is Fnet=ma.
Consider the normal force exerted on the brick by the bucket when the bucket is at the three positions shown: R, T, B. The magnitude of the normal force is a minimum at position... Pink: Top. Green:Bottom. Yellow: Right Purple: The normal force has the same magnitude at all positions.
T Answer: The normal force is minimum at position T(top). At both positions B and T, the normal force N vector added to the weight mg mg N is the net force Fnet. Since Fnet and mg are constant in magnitude, N is minimum when it Ffric points in the same direction as mg .
R N N mg
B mg