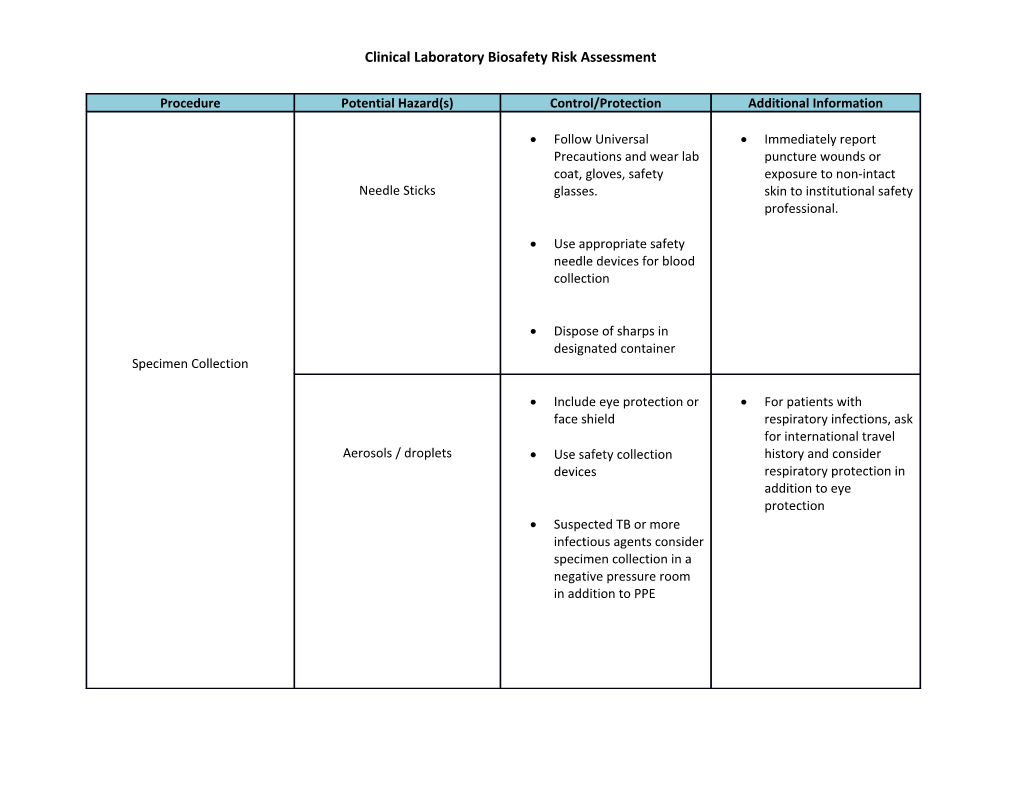
Clinical Laboratory Biosafety Risk Assessment
Procedure Potential Hazard(s) Control/Protection Additional Information
Follow Universal Immediately report Precautions and wear lab puncture wounds or coat, gloves, safety exposure to non-intact Needle Sticks glasses. skin to institutional safety professional.
Use appropriate safety needle devices for blood collection
Dispose of sharps in designated container Specimen Collection
Include eye protection or For patients with face shield respiratory infections, ask for international travel Aerosols / droplets Use safety collection history and consider devices respiratory protection in addition to eye protection Suspected TB or more infectious agents consider specimen collection in a negative pressure room in addition to PPE Clinical Laboratory Biosafety Risk Assessment
Procedure Potential Hazard(s) Control/Protection Additional Information Do not use pneumatic Know location of nearest tube system for spill kit or number to specimens suspected of reach environmental containing highly services for accidents in infectious agents common areas.
Use less populated routes for intra-facility transport Transport accident resulting in for specimens suspected specimen break of containing highly infectious agents
Specimen Handling Specimens should be transported in leak-proof secondary container
Do not use pneumatic tube system for highly infectious specimens
Contain specimen in leak- proof secondary container Leaking / broken sample Place secondary container in BSC, remove specimen from bag if no broken glass and disinfect outside of leaking container. Clinical Laboratory Biosafety Risk Assessment
Procedure Potential Hazard(s) Control/Protection Additional Information
Ensure integrity of specimen container and sealed cap
Use micro-centrifuges inside BSC, making sure If a specimen breaks not to overload the inside centrifuge, wait 60 cabinet minutes for aerosols to settle before opening lid Specimen Handling Centrifugation and assessing the spill. Employ safety cups / sealed rotors. Follow manufacturer’s maintenance schedule If using counter top or full size centrifuge, load and unload sealed centrifuge rotors in BSC
Follow Universal Precautions and wear lab coat, gloves. Include eye protection. Consider Splashes / Spills respiratory protection based on organism risk group.
If a BSC is unavailable, work behind a plexi-glass shield with proper PPE Clinical Laboratory Biosafety Risk Assessment
Procedure Potential Hazard(s) Control/Protection Additional Information
Perform work in class II BSC
Allow slides to dry inside hood before removing for Direct Microscopic Examination Smear Preparation staining.
Do not flame slides, air dry or use a heat block prior to fixation.
Perform all set up in class II BSC with appropriate PPE
When a high consequence pathogen is Culture Set-up Blood culture- suspected suspected / AFB, use BSL- Highly infectious agent 3 practices in addition to BSC.
Do not perform viral cultures on avian influenza, SARS, Coronaviruses, Ebola Clinical Laboratory Biosafety Risk Assessment
Procedure Potential Hazard(s) Control/Protection Additional Information
AFB, viral cultures, highly High consequence infectious agents: pathogens include: Highly infectious agents perform in class II or III - Slow growing (24-48 Culture Work-up Vortexing BSC using BSL-3 practices hr)GNR or GNCB Centrifugation / sonication - Slow growth in blood Aerosol generating tests Parasitology: preserved culture bottles Pipetting stool manipulation - Growth only on performed in class II BSC chocolate agar or fume hood. Minimal - Flat, non-pigmented protection is provided irregular colonies using safety shield, face with ground glass shield or eye protection appearance. and mask. - GPR with boxcar shape with or without spores Aerosol generating procedures such as centrifugation, sonication, vortexing, must be performed in class II or III BSC. Use sealed rotor type centrifuge if unable to perform in BSC. Ensure correct balance of centrifuge and open sealed head rotor cups only in BSC. Clinical Laboratory Biosafety Risk Assessment
Procedure Potential Hazard(s) Control/Protection Additional Information
If specimen breaks inside Culture Work-up sealed rotor, place inside BSC and do not open for at least 30 minutes (allows aerosols to settle). Use mechanical device such as forceps to handle broken glass or sharp objects.
Perform Catalase test in BSC using covered petri dish or tube method
Use pipette tips with plugs to avoid contamination
Do not blow out the last drop of liquid from pipet.
Aerosol generating steps such as vortexing, pipetting, mixing should Centrifugation be performed in a class II Commercial / Rapid Tests Vortexing BSC. Splashes Pipetting
If BSC is not feasible, use Clinical Laboratory Biosafety Risk Assessment
Procedure Potential Hazard(s) Control/Protection Additional Information a safety shield or wear eye protection and respiratory protection.
AFB, Fungal: all work and culture manipulations are Identification to be performed in a class Report all suspected or AFB II or III BSC using BSL-3 confirmed exposures to Fungal Exposure practices. supervisor and Parasitology organization safety Viral Slides for professional. Highly pathogenic immunofluorescence organism staining should remain in class II or III BSC until fixed, after which they can be stained outside the BSC.
Use puncture proof sharps containers
Disinfect outside of waste Report all puncture container before wounds, exposures or Waste Handling Sharps removing from BSC. burns to supervisor and Contamination of outside of organization safety container professional. Burns- if autoclave
Wear appropriate PPE Clinical Laboratory Biosafety Risk Assessment
Procedure Potential Hazard(s) Control/Protection Additional Information and follow Universal Precautions when discarding infectious Segregate waste, waste including used PPE, from suspected Ebola specimens until testing is Allow autoclave to vent confirmed negative. before opening door. Waste Handling Stand behind door when opening.
Don liquid resistant apron, face shield and heat resistant gloves before removing items from autoclave.