Links to KS3 and KS4 National Curriculum Programmes of Study and exam specifications
SCIENCE
At a glance
11-14 curriculum links
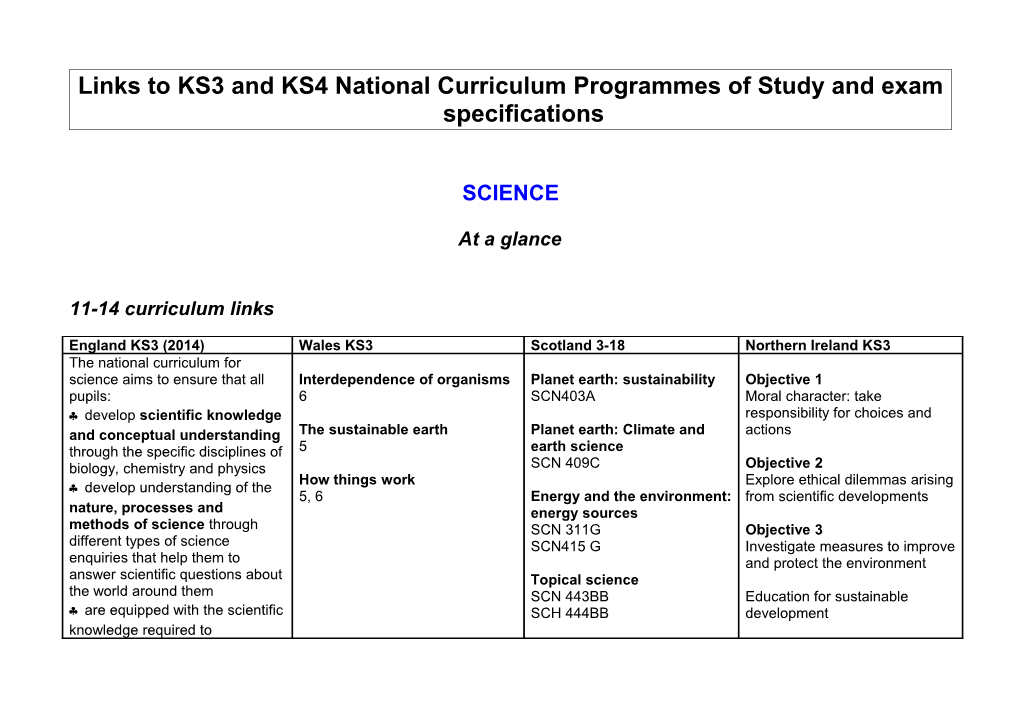
England KS3 (2014) Wales KS3 Scotland 3-18 Northern Ireland KS3 The national curriculum for science aims to ensure that all Interdependence of organisms Planet earth: sustainability Objective 1 pupils: 6 SCN403A Moral character: take . develop scientific knowledge responsibility for choices and and conceptual understanding The sustainable earth Planet earth: Climate and actions through the specific disciplines of 5 earth science biology, chemistry and physics SCN 409C Objective 2 How things work Explore ethical dilemmas arising . develop understanding of the 5, 6 Energy and the environment: from scientific developments nature, processes and energy sources methods of science through SCN 311G Objective 3 different types of science SCN415 G Investigate measures to improve enquiries that help them to and protect the environment answer scientific questions about Topical science the world around them SCN 443BB Education for sustainable . are equipped with the scientific SCH 444BB development knowledge required to understand the uses and implications of science, today and for the future.
14-16 examination specification links
OCR Edexcel AQA WJEC CCEA Scotland Standard Grade and 3-18
21st Century 360 Science Science A/B Science Science Double Topic 3 Science Additional C1b 7 11.8 Chemistry 1.6, 1.7 (A/B) 1, 3, 4, 5 A P1a 9, 10 12.3 Physics 1.1, 1.3, 1.4, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6 C5.1, P5.1, 5.5 12.6 1.5 Topic 4 360 Additional 13.2 Biology 1.5, 1.7 Science Double 1, 4, 5 Gateway Science Science 13.3 (Revised) B B2 3, 4 13.4 B1.10 3-18: C1 d, g, h P2 12 C2.4 P1 a, b, c P1.8, 1.9, 1.19 Planet earth: P2 a, b, c, d P2.10, 2.11 sustainability SCN403A Gateway Additional Science Planet earth: Climate B and earth science C3 c SCN 409C B4 h Energy and the environment: energy sources SCN 311G SCN415 G Topical science SCN 443BB SCH 444BB In detail
Sections Learning Objectives of Links with National Curriculum KS3 Links with National Curriculum KS4 Website Programme of Study Programme of Study (2009)
Climate To understand the change global nature of the Pay attention to objectivity and concern 1 c how explanations of many phenomena can be world's climate system for accuracy, precision, repeatability and developed using scientific theories, models and To comprehend the in- reproducibility ideas terconnectedness of Understand that scientific methods and cause and effect be- theories develop as earlier explanations 4 b to consider how and why decisions about sci- tween places ence and technology are made, including those are modified to take account of new To appreciate the ef- that raise ethical issues, and about the social, evidence and ideas, together with the fect of climate change economic and environmental effects of such deci- on the Arctic and the importance of publishing results and sions consequences of the peer review change The properties of the different states of 4 c how uncertainties in scientific knowledge and To understand that matter (solid, liquid and gas) in terms of scientific ideas change over time and about the there can be both posi- the particle model, including gas role of the scientific community in validating tive and negative out- pressure these changes. comes of climate The composition of the atmosphere change The production of carbon dioxide by 5 a organisms are interdependent and adapted to human activity and the effect on climate their environments Waves on water as undulations which 7 c radiations can transfer energy travel through water with transverse motion Conservation of material and of mass, 8 a the effects of human activity on the environ- and reversibility, in melting, freezing, ment can be assessed using living and non-living evaporation, sublimation, condensation indicators and dissolving Changes in the environment may leave in- 8 b the surface and the atmosphere of the Earth dividuals within a species, and some en- have changed since the Earth’s origin and are tire species, less well adapted to compete changing at present successfully and reproduce, which in turn may lead to extinction Sections Learning Objectives of Links with National Curriculum KS3 Links with National Curriculum KS4 Website Programme of Study Programme of Study (2009)
Living on the To investigate why How scientific ideas have developed his- 2 a plan to test a scientific idea, answer a scientif- edge people live in the Arctic torically ic question, or solve a scientific problem To undertake an en- The content of a healthy human diet. quiry into the changing The consequences of an imbalance in 2 b collect data from primary or secondary nature of living in the diet, particularly deficiency diseases sources, including using ICT sources and tools Arctic The seasons and the earth’s tilt, day To understand the im- length at different times of the year 3 b use both qualitative and quantitative plications of climate Human activity and natural processes can approaches change on the lives of lead to changes in the environment. people in the Arctic 4 h Explore contemporary and historical scientific developments and how they have been communicated.
8 a the effects of human activity on the environ- ment can be assessed using living and non-living indicators
8 b the surface and the atmosphere of the Earth have changed since the Earth’s origin and are changing at present
8 c the solar system is part of the universe, which has changed since its origin and continues to show long-term changes. Sections Learning Objectives of Links with National Curriculum KS3 Links with National Curriculum KS4 Website Programme of Study Programme of Study (2009)
Arctic science To understand the im- Understand the properties and interac- 1 a how scientific data can be collected and ana- portance of the 2007- tions of matter in all its forms, and the re- lysed 2009 International Po- sources and means of transfer of energy lar Year as key determinants of all these interac- 1 b how interpretation of data, using creative To understand the na- tions thought, provides evidence to test ideas and de- ture of the Northern Understand that science is about working velop theories Lights objectively, modifying explanations to take To investigate some of account of new evidence and ideas and 2 a plan to test a scientific idea, answer a scientif- the research which is subjecting results to peer review ic question, or solve a scientific problem being undertaken in Make predictions using scientific knowl- the Arctic edge and understanding 2 b collect data from primary or secondary To undertake an en- Interpret observations and data and to sources, including using ICT sources and tools quiry into the pollutants draw conclusions and their effects in the How organisms affect and are affected by 4 c how uncertainties in scientific knowledge and Arctic their environment, including the accumula- scientific ideas change over time and about the tion of toxic materials role of the scientific community in validating Colours and different frequencies of light these changes. (for example in the Northern Lights) Earth’s magnetism, compass and naviga- 4 h Explore contemporary and historical tion scientific developments and how they have been The anomaly of ice-water transition communicated. 8 a the effects of human activity on the environ- ment can be assessed using living and non-living indicators
8 b the surface and the atmosphere of the Earth have changed since the Earth’s origin and are changing at present
8 c the solar system is part of the universe, which has changed since its origin and continues to show long-term changes. Sections Learning Objectives of Links with National Curriculum KS3 Links with National Curriculum KS4 Website Programme of Study Programme of Study (2009)
Hunter or To understand how an- Plants making carbohydrates in their 5 a understanding how organisms are hunted? imals adapt to living in leaves through photosynthesis interdependent and adapted to their environment. the Arctic Reproduction in plants To investigate a migra- The interdependence of organisms in an tory species, the bar- ecosystem, including food webs 8 a the effects of human activity on the environ- nacle goose ment can be assessed using living and non-living Differences between species To investigate the indicators The variation between species and fragility of the ecosys- tem between individuals of the same species 8 b the surface and the atmosphere of the Earth means some organisms compete more To undertake an en- have changed since the Earth’s origin and are quiry into the effects of successfully, which can drive natural se- changing at present climate change lection Changes in the environment may leave in- 8 c the solar system is part of the universe, which dividuals within a species, and some en- has changed since its origin and continues to tire species, less well adapted to compete show long-term changes. successfully and reproduce, which in turn
may lead to extinction The importance of maintaining biod- iversity and the use of gene banks to preserve hereditary material Postcard from To investigate the na- How organisms affect, and are affected 4 a use of contemporary scientific and the edge ture of the tourist in- by, their environment technological developments and their benefits, dustry in the Arctic The seasons and the Earth’s tilt, day drawbacks and risks To undertake an en- length at different times of the year. quiry of the effects of 8 a the effects of human activity on the environ- tourism on the Arctic ment can be assessed using living and non-living ecosystem and people indicators To understand eco- tourism and sustain- able tourism and the difference between them Sections Learning Objectives of Links with National Curriculum KS3 Links with National Curriculum KS4 Website Programme of Study Programme of Study (2009)
Troubled To learn about the na- Waves on water as undulations which waters ture and extent of sea travel through water with a transverse 1 c how explanations of many phenomena can be ice motion developed using scientific theories, models and To discover what it is ideas like to live and work on Earth’s magnetism, compass and the ice covered water navigation 4 b to consider how and why decisions about sci- To understand the ef- Pressure in liquids, increasing with depth, ence and technology are made, including those fect of climate change upthrust effects, floating and sinking that raise ethical issues, and about the social, on the sea ice extent economic and environmental effects of such deci- Forces as pushes or pulls, arising from sions the interaction between two objects 4 c how uncertainties in scientific knowledge and Atmospheric pressure, decreases with scientific ideas change over time and about the increase of height as weight of air role of the scientific community in validating above decreases with height these changes. 5 a organisms are interdependent and adapted to Forces being needed to cause objects their environments to start moving, stop or change direction 7 c radiations can transfer energy
8 a the effects of human activity on the environ- ment can be assessed using living and non-living indicators
8 b the surface and the atmosphere of the Earth have changed since the Earth’s origin and are changing at present Sections Learning Objectives of Links with National Curriculum KS3 Links with National Curriculum KS4 Website Programme of Study Programme of Study (2009)
Resources To discover the tradi- Changes in the environment may leave 1 b How interpretation of data, using creative from the edge tional resources that individuals within a species, and some thought, provides evidence to test ideas and have been used for entire species, less well adapted to develop theories. hundreds of years in compete successfully and reproduce, 2 b collect data from primary or secondary the Arctic Region and which in turn may lead to extinction sources, including using ICT sources and tools the changes that are 4 b to consider how and why decisions about occurring The importance of maintaining biodiver- To understand the rich science and technology are made, including those sity and the use of gene banks to pre- variety of resources that raise ethical issues, and about the social, available in the sea serve hereditary material. economic and environmental effects of such and on the land The properties of metals and non-metals decisions. To explore how climate Earth as a source of limited resources and the efficacy of recycling 6 d The properties of a material determine its change is affecting the uses exploitation of these resources Sections Learning Objectives of Links with National Curriculum KS3 Links with National Curriculum KS4 Website Programme of Study Programme of Study (2009)
Arctic To define the Arctic re- Changes in the environment may leave 3 b use both qualitative and quantitative Circumpolar gion individuals within a species, and some approaches Governance To understand the entire species, less well adapted to complexities of Arctic compete successfully and reproduce, governance which in turn may lead to extinction 3 c ability to present information, develop an The importance of maintaining biodiver- argument and draw a conclusion, using scientific, To understand why sity and the use of gene banks to pre- technical and mathematical language, there is a need for serve hereditary material. conventions and symbols and ICT tools. change in Arctic gover- Make predictions using scientific knowl- nance, particularly in light of climate change edge and understanding 4 a use of contemporary scientific and techno- Earth as s source of limited resources logical developments and their benefits, draw- backs and risks
8 a The surface and the atmosphere of the Earth have changed since the Earth’s origin and are changing at present. Sections Learning Objectives of Links with National Curriculum KS3 Links with National Curriculum KS4 Website Programme of Study Programme of Study (2009)
Snow, water, To investigate the See the connections between biology, 1 c how explanations of many phenomena can be ice and cryosphere chemistry and physics developed using scientific theories, models and permafrost Build up extended specialist vocabulary ideas To research the The properties of the different states of changes facing the re- matter 4 b to consider how and why decisions about sci- gion, and described Waves on water as undulations which ence and technology are made, including those many impacts which travel through water with a transverse that raise ethical issues, and about the social, were based on obser- motion economic and environmental effects of such deci- vations and research. sions To understand how the Conservation of material and mass, and 4 c how uncertainties in scientific knowledge and effects of climate reversibility, in melting, freezing, scientific ideas change over time and about the change will impact on evaporation, sublimation, condensation role of the scientific community in validating the environment and dissolving these changes.
5 a organisms are interdependent and adapted to their environments
7 c radiations can transfer energy
8 a the effects of human activity on the environ- ment can be assessed using living and non-living indicators
8 b the surface and the atmosphere of the Earth have changed since the Earth’s origin and are changing at present Sections Learning Objectives of Links with National Curriculum KS3 Links with National Curriculum KS4 Website Programme of Study Programme of Study (2009)
Adapting to To learn more about To understand the social and economic 3 b use both qualitative and quantitative change the UK’s Policy Frame- implications of science, using different approaches work and the UK’s in- contexts to maximize pupils’ engagement terest in the Arctic. with and motivation to study science To show how the UK See the connections between biology, 3 c ability to present information, develop an will work with the Arctic chemistry and [physics argument and draw a conclusion, using scientific, States and the wider Show how scientific ideas have developed international com- technical and mathematical language, historically and reflecting on modern conventions and symbols and ICT tools. munity. science To identify the expert- Make predictions using scientific ise that the UK can of- knowledge and understanding 4 a use of contemporary scientific and techno- fer to help meet some logical developments and their benefits, draw- of the long-term chal- Earth’s magnetism, compass and backs and risks lenges facing the re- navigation gion. Many of these 8 a The surface and the atmosphere of the challenges have Earth have changed since the Earth’s origin and already been identified are changing at present. in other sections of the site.