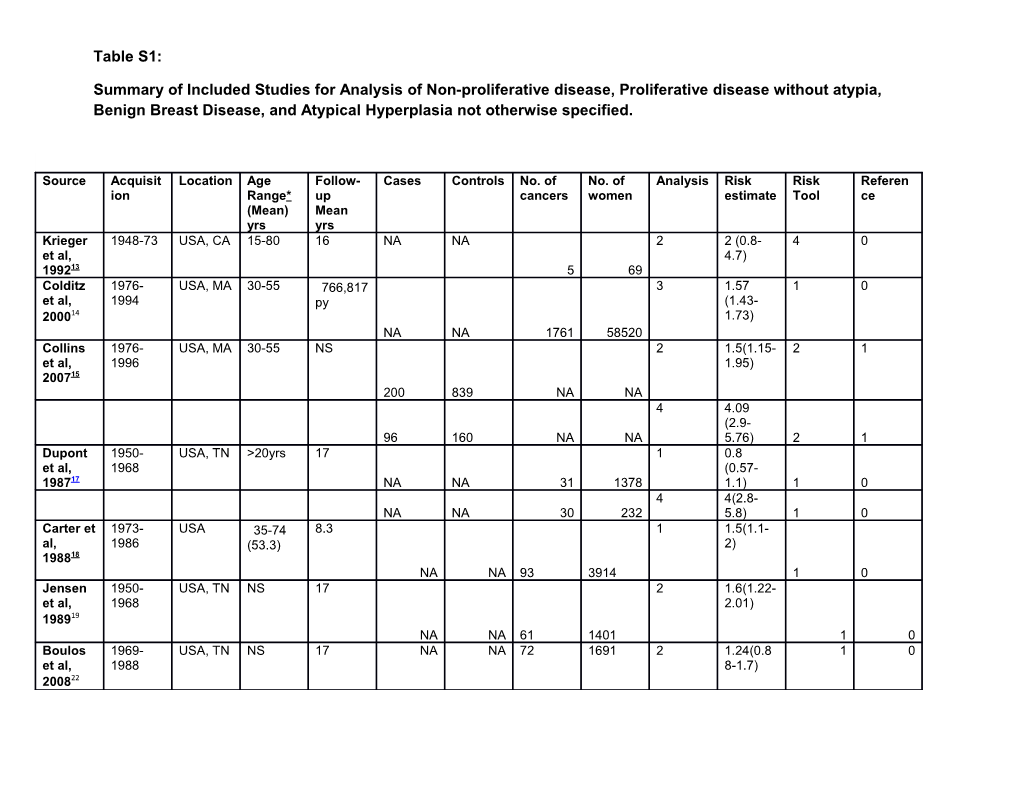
Table S1:
Summary of Included Studies for Analysis of Non-proliferative disease, Proliferative disease without atypia, Benign Breast Disease, and Atypical Hyperplasia not otherwise specified.
Source Acquisit Location Age Follow- Cases Controls No. of No. of Analysis Risk Risk Referen ion Range* up cancers women estimate Tool ce (Mean) Mean yrs yrs Krieger 1948-73 USA, CA 15-80 16 NA NA 2 2 (0.8- 4 0 et al, 4.7) 199213 5 69 Colditz 1976- USA, MA 30-55 766,817 3 1.57 1 0 et al, 1994 py (1.43- 200014 1.73) NA NA 1761 58520 Collins 1976- USA, MA 30-55 NS 2 1.5(1.15- 2 1 et al, 1996 1.95) 200715 200 839 NA NA 4 4.09 (2.9- 96 160 NA NA 5.76) 2 1 Dupont 1950- USA, TN >20yrs 17 1 0.8 et al, 1968 (0.57- 198717 NA NA 31 1378 1.1) 1 0 4 4(2.8- NA NA 30 232 5.8) 1 0 Carter et 1973- USA 35-74 8.3 1 1.5(1.1- al, 1986 (53.3) 2) 198818 NA NA 93 3914 1 0 Jensen 1950- USA, TN NS 17 2 1.6(1.22- et al, 1968 2.01) 198919 NA NA 61 1401 1 0 Boulos 1969- USA, TN NS 17 NA NA 72 1691 2 1.24(0.8 1 0 et al, 1988 8-1.7) 200822 Table S1:
Summary of Included Studies for Analysis of Non-proliferative disease, Proliferative disease without atypia, Benign Breast Disease, and Atypical Hyperplasia not otherwise specified.
4 3.24(1.6- NA NA 10 108 6.5) 1 0 Wrensc 1972- USA, CA (43) 21-grp 1 2 2.0 (1.5- h 1991 9 -grp 2 2.8) et al, 200144 NA NA 77 940 1 0 4 2.1(1.1- NA NA 12 109 3.9) 1 0 Hill et al, 1983- USA, CA <40 NS 3 1.9(1.5- 200229 1988 2.4) 269 180 NA NA 2 0 Worsha 1981- USA, MI >18 10.3 2 1.75(1.1 m 1994 3-2.42) et al, 200942 125 349 NA NA 2 0 4 4.56(2.4 29 31 NA NA 6-8.47) 2 0 Hartman 1967- USA, MN (51.4 ) 15 3 1.56(1.4 n 1991 18-85 5-1.68) et al, 200527 NA NA 707 9087 1 0 Lewis et 1967- USA, MN (51.4 ) 16 1 1.28(1.1 al, 1991 18-85 6-1.42) 200633 NA NA 383 6053 1 0 2 1.9(1.66- NA NA 232 2308 2.16) 1 0 4 4.17(3.1- NA NA 50 267 5.5) 1 0 Ashbeck 1992- USA, 30-89 6.8 2 2.13(1.7- et al, 2000 New 2.69) 200720 Mexico NA NA 74 2,279 5 0 4 4.4(2.73- NA NA 17 319 7.09) 5 0 Table S1:
Summary of Included Studies for Analysis of Non-proliferative disease, Proliferative disease without atypia, Benign Breast Disease, and Atypical Hyperplasia not otherwise specified. Bodian 1930- USA, NY (42.6) 20.6 1 1.6(1.0- et al, 1982 17-88 2.6) 199321 NA NA 18 278 1 0 2 2.1(1.7- NA NA 94 1095 2.6) 1 0 3.0(1.5- NA NA 8 70 4 6.0) 1 0 Helmric 1976- USA, <70yrs NS 3 2.7(2.2- h 1980 Canada, (52) 3.3) et al, Israel 198328 216 271 NA NA 1 0 McDivitt 1980-82 USA-6 20-54 NS 1 1.5(1.3- et al, states: 1.9) 199234 GA, CN, IO, WA, MI, CA 227 154 NA NA 2 0 2 1.8(1.3- 124 68 NA NA 2.4) 2 0 3 1.7(1.5- 417 248 NA NA 2.0) 2 0 4 2.6(1.6- 66 26 NA NA 4.1) 2 0 Kabat et 1980- CAN,UK, 40-59 T, 15.4 2 1.44(1.1 al, 1988 USA 18-77 L, 1-1.87) 201031 Toronto 18-85 P (T), 1946- 1984 London (L), 1970- 1994 Portland (P) 393 362 NA NA 2 1 Table S1:
Summary of Included Studies for Analysis of Non-proliferative disease, Proliferative disease without atypia, Benign Breast Disease, and Atypical Hyperplasia not otherwise specified. 4 4.73(2.1 32 12 NA NA 1-10.61) 2 1 Dorjgoc 1996-98, Shangha (49.6) NS 3 1.7(1.5- hoo et 2002-05 i, China 47.2- 1.8) al, 51.6 200823 1472 1049 NA NA 2 1 Shaaban 1979- UK, 49.39 5.6 1 0.8(0.66- et al, 1999 Liverpool mdn 0.96) 200240 and (18.03- Broad- 86.65) green 62 248 NA NA 1 0 2 1.53(1.1- 38 79 NA NA 2.13) 1 0 Goldacr 1963- UK 40.1 10.7 3 2.3(2.2- e 1999 2.5) et al, 2010 ORLS26 NA NA 850 4442 1 0 Goldacr 1963- UK 43.9 3.3 3 3.2(3.0- e 1999 3.3) et al, 2010 EnHES26 NA NA 1812 17338 4 0 Palli et 1975- Italy, NS NS 2 1.2(0.5- al, 1987 Florence 3.2) 199138 6 31 NA NA 1 1 4 10(3.4- 11 7 NA NA 29.9) 1 1 1972- Japan 45.9 8 1 0.75(0.0 Nomura 1987 8-6.68) et al, 199336 NA NA 1 285 1 0 Table S1:
Summary of Included Studies for Analysis of Non-proliferative disease, Proliferative disease without atypia, Benign Breast Disease, and Atypical Hyperplasia not otherwise specified. 2 4(0.34- NA NA 2 109 9.85) 1 0 3 3.5(1.03- NA NA 7 428 11.9) 1 1 4 25.2(3.6 8- NA NA 4 34 172.78) 1 1 Minami 1978- Japan 44.1 7.6 1 0.93(0.1 et al, 1991 1-7.66) 199935 NA NA 5 256 1 0 2 7.26(2.1 NA NA 8 114 7-24.26) 1 0 3 3.26(1.0 NA NA 15 387 8-9.83) 1 0 4 16.03(3. 34- NA NA 2 17 76.87) 1 0 * - Age Range of cases, py-person years, yrs-years, grp-group, T-Toronto, Canada; L-London, UK; Portland, USA
Analysis: 1=Nonproliferative disease, 2=Proliferative disease without atypia (ProlifNat), 3-BBD (Benign Breast Disease), 4=Atypical Hyperplasia Not otherwise specified (AH NOS),
Risk tool: 1=RR, 2=OR, 3=SIR, 4=Rate ratio, 5=HR, 6=IRR (RR=Relative Risk, OR=Odds Ratio, SIR= Standardized incidence ratios, HR=Hazard Ratio, IRR-incidence rate ratio)
Reference: 0=designated reference population, 1=BBD
1. Krieger N, Hiatt RA. Risk of Breast Cancer after Benign Breast Diseases. American Journal of Epidemiology. March 15, 1992 1992;135(6):619-631. 2. Colditz GA, Rosner B. Cumulative Risk of Breast Cancer to Age 70 Years According to Risk Factor Status: Data from the Nurses' Health Study. American Journal of Epidemiology. November 15, 2000 2000;152(10):950-964. 3. Collins LC, Baer HJ, Tamimi RM, Connolly JL, Colditz GA, Schnitt SJ. Magnitude and laterality of breast cancer risk according to histologic type of atypical hyperplasia. Cancer. 2007;109(2):180-187. Table S1:
Summary of Included Studies for Analysis of Non-proliferative disease, Proliferative disease without atypia, Benign Breast Disease, and Atypical Hyperplasia not otherwise specified. 4. Dupont WD, Page DL. BREAST CANCER RISK ASSOCIATED WITH PROLIFERATIVE DISEASE, AGE AT FIRST BIRTH, AND A FAMILY HISTORY OF BREAST CANCER. American Journal of Epidemiology. May 1, 1987 1987;125(5):769-779. 5. Carter CL, Corle DK, Micozzi MS, Schatzkin A, Taylor PR. A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF BREAST CANCER IN 16,692 WOMEN WITH BENIGN BREAST DISEASE. American Journal of Epidemiology. September 1, 1988 1988;128(3):467-477. 6. Jensen RA, Page DL, Dupont WD, Rogers LW. Invasive breast cancer risk in women with sclerosing adenosis. Cancer. 1989;64(10):1977- 1983. 7. Boulos FI, Dupont WD, Simpson JF, et al. Histologic associations and long-term cancer risk in columnar cell lesions of the breast. Cancer. 2008;113(9):2415-2421. 8. Wrensch MR, Petrakis NL, Miike R, et al. Breast Cancer Risk in Women With Abnormal Cytology in Nipple Aspirates of Breast Fluid. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. December 5, 2001 2001;93(23):1791-1798. 9. Hill DA, Preston-Martin S, Ross RK, Bernstein L. Medical radiation, family history of cancer, and benign breast disease in relation to breast cancer risk in young women, USA. Cancer Causes and Control. 2002;13(8):711-718. 10. Worsham M, Raju U, Lu M, et al. Risk factors for breast cancer from benign breast disease in a diverse population. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 2009;118(1):1-7. 11. Hartmann LC, Sellers TA, Frost MH, et al. Benign Breast Disease and the Risk of Breast Cancer. New England Journal of Medicine. 2005;353(3):229-237. 12. Lewis JT, Hartmann LC, Vierkant RA, et al. An Analysis of Breast Cancer Risk in Women With Single, Multiple, and Atypical Papilloma. The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 2006;30(6):665-672. 13. Ashbeck, RD R, Stauber PM KC. Benign breast biopsy diagnosis and subsequent risk of breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. . 2007 Mar 2 2007 16(3):467-472. 14. Bodian CA, Perzin KH, Lattes R, Hoffmann P, Abernathy TG. Prognostic significance of benign proliferative breast disease. Cancer. 1993;71(12):3896-3907. 15. Helmrich SP, Shapiro S, Rosenberg L, et al. RISK FACTORS FOR BREAST CANCER. American Journal of Epidemiology. January 1, 1983 1983;117(1):35-45. 16. McDivitt RW, Stevensm JA, Lee NC, Wingo PA, Rubin GL, Gersell D. Histologic types of benign breast disease and the risk for breast cancer. Cancer. 1992;69(6):1408-1414. 17. Kabat, JG J, N O, et al. A multi-center prospective cohort study of benign breast disease and risk of subsequent breast cancer. Cancer Causes Control. 1/19/2010 2010, Jun;21(6):821-828. 18. Dorjgochoo T, Deming S, Gao Y-T, et al. History of benign breast disease and risk of breast cancer among women in China: a case–control study. Cancer Causes and Control. 2008;19(8):819-828. 19. Shaaban AM, Sloane JP, West CR, et al. Histopathologic Types of Benign Breast Lesions and the Risk of Breast Cancer: Case-Control Study. The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 2002;26(4):421-430. Table S1:
Summary of Included Studies for Analysis of Non-proliferative disease, Proliferative disease without atypia, Benign Breast Disease, and Atypical Hyperplasia not otherwise specified. 20. Goldacre MJ, Abisgold JD, Yeates DGR, Vessey MP. Benign breast disease and subsequent breast cancer: English record linkage studies. Journal of Public Health. December 1, 2010;32(4):565-571. 21. Palli D, Turco MRD, Simoncini R, Bianchi S. Benign breast disease and breast cancer: A case-control study in a cohort in italy. International Journal of Cancer. 1991;47(5):703-706. 22. Nomura Y, Tashiro H, Katsuda Y. Benign Breast Disease as a Breast Cancer Risk in Japanese Women. Cancer Science. 1993;84(9):938-944. 23. Minami Y, Ohuchi N, Taeda Y, et al. Risk of Breast Cancer in Japanese Women with Benign Breast Disease. Cancer Science. 1999;90(6):600-606.