Sigma and Pi Bonds
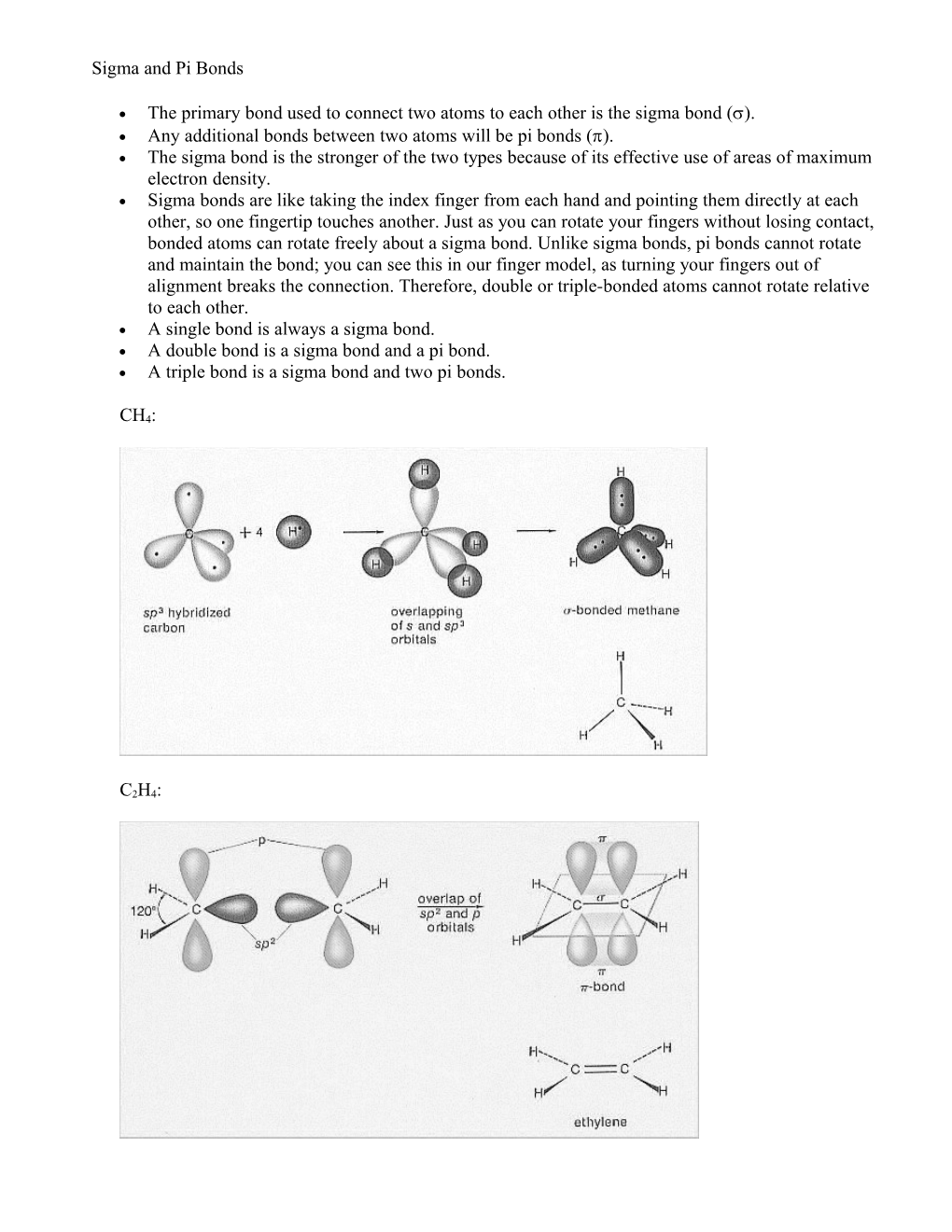
The primary bond used to connect two atoms to each other is the sigma bond (). Any additional bonds between two atoms will be pi bonds (). The sigma bond is the stronger of the two types because of its effective use of areas of maximum electron density. Sigma bonds are like taking the index finger from each hand and pointing them directly at each other, so one fingertip touches another. Just as you can rotate your fingers without losing contact, bonded atoms can rotate freely about a sigma bond. Unlike sigma bonds, pi bonds cannot rotate and maintain the bond; you can see this in our finger model, as turning your fingers out of alignment breaks the connection. Therefore, double or triple-bonded atoms cannot rotate relative to each other. A single bond is always a sigma bond. A double bond is a sigma bond and a pi bond. A triple bond is a sigma bond and two pi bonds.
CH4:
C2H4: C2H2:
How many sigma and pi bonds are in each molecule?
Example: CO2
2 sigma and 2 pi bonds (each double bond consists of 1 sigma and 1 pi bond)
bonds bonds