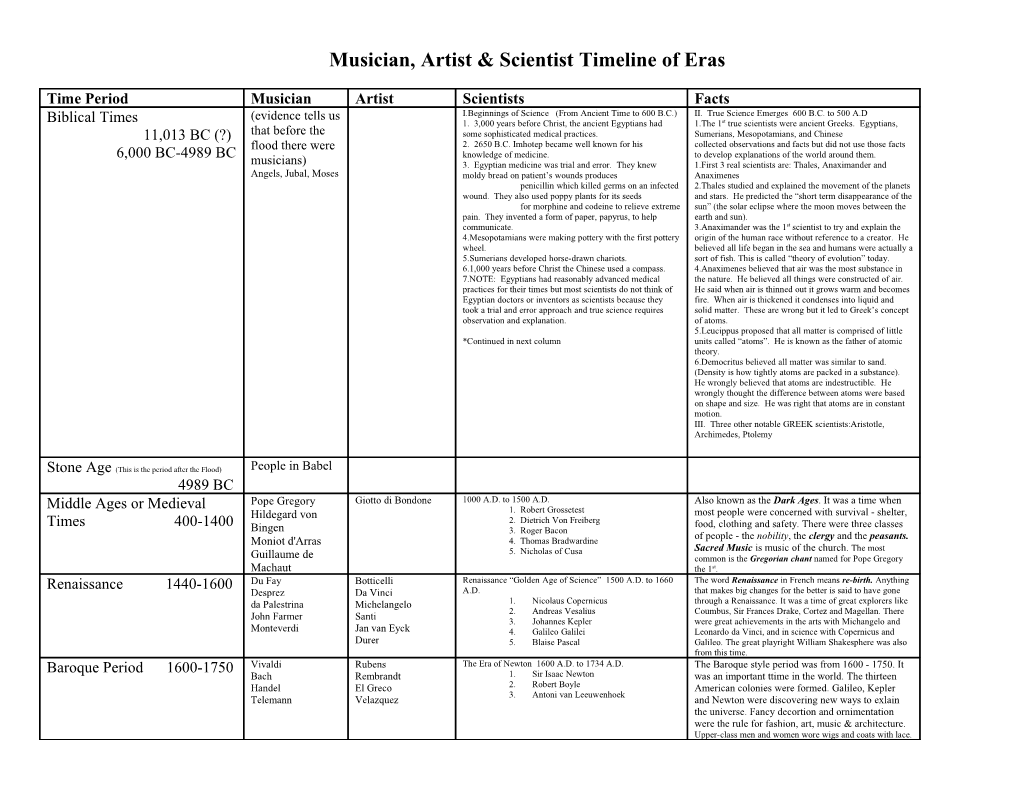
Musician, Artist & Scientist Timeline of Eras
Time Period Musician Artist Scientists Facts (evidence tells us I.Beginnings of Science (From Ancient Time to 600 B.C.) II. True Science Emerges 600 B.C. to 500 A.D Biblical Times 1. 3,000 years before Christ, the ancient Egyptians had 1.The 1st true scientists were ancient Greeks. Egyptians, 11,013 BC (?) that before the some sophisticated medical practices. Sumerians, Mesopotamians, and Chinese flood there were 2. 2650 B.C. Imhotep became well known for his collected observations and facts but did not use those facts 6,000 BC-4989 BC knowledge of medicine. to develop explanations of the world around them. musicians) 3. Egyptian medicine was trial and error. They knew 1.First 3 real scientists are: Thales, Anaximander and Angels, Jubal, Moses moldy bread on patient’s wounds produces Anaximenes penicillin which killed germs on an infected 2.Thales studied and explained the movement of the planets wound. They also used poppy plants for its seeds and stars. He predicted the “short term disappearance of the for morphine and codeine to relieve extreme sun” (the solar eclipse where the moon moves between the pain. They invented a form of paper, papyrus, to help earth and sun). communicate. 3.Anaximander was the 1st scientist to try and explain the 4.Mesopotamians were making pottery with the first pottery origin of the human race without reference to a creator. He wheel. believed all life began in the sea and humans were actually a 5.Sumerians developed horse-drawn chariots. sort of fish. This is called “theory of evolution” today. 6.1,000 years before Christ the Chinese used a compass. 4.Anaximenes believed that air was the most substance in 7.NOTE: Egyptians had reasonably advanced medical the nature. He believed all things were constructed of air. practices for their times but most scientists do not think of He said when air is thinned out it grows warm and becomes Egyptian doctors or inventors as scientists because they fire. When air is thickened it condenses into liquid and took a trial and error approach and true science requires solid matter. These are wrong but it led to Greek’s concept observation and explanation. of atoms. 5.Leucippus proposed that all matter is comprised of little *Continued in next column units called “atoms”. He is known as the father of atomic theory. 6.Democritus believed all matter was similar to sand. (Density is how tightly atoms are packed in a substance). He wrongly believed that atoms are indestructible. He wrongly thought the difference between atoms were based on shape and size. He was right that atoms are in constant motion. III. Three other notable GREEK scientists:Aristotle, Archimedes, Ptolemy
Stone Age (This is the period after the Flood) People in Babel 4989 BC Middle Ages or Medieval Pope Gregory Giotto di Bondone 1000 A.D. to 1500 A.D. Also known as the Dark Ages. It was a time when Hildegard von 1. Robert Grossetest most people were concerned with survival - shelter, Times 400-1400 2. Dietrich Von Freiberg food, clothing and safety. There were three classes Bingen 3. Roger Bacon of people - the nobility, the clergy and the peasants. Moniot d'Arras 4. Thomas Bradwardine 5. Nicholas of Cusa Sacred Music is music of the church. The most Guillaume de common is the Gregorian chant named for Pope Gregory Machaut the 1st. Renaissance 1440-1600 Du Fay Botticelli Renaissance “Golden Age of Science” 1500 A.D. to 1660 The word Renaissance in French means re-birth. Anything Desprez Da Vinci A.D. that makes big changes for the better is said to have gone da Palestrina Michelangelo 1. Nicolaus Copernicus through a Renaissance. It was a time of great explorers like 2. Andreas Vesalius Coumbus, Sir Frances Drake, Cortez and Magellan. There John Farmer Santi 3. Johannes Kepler were great achievements in the arts with Michangelo and Monteverdi Jan van Eyck 4. Galileo Galilei Leonardo da Vinci, and in science with Copernicus and Durer 5. Blaise Pascal Galileo. The great playright William Shakesphere was also from this time. Baroque Period 1600-1750 Vivaldi Rubens The Era of Newton 1600 A.D. to 1734 A.D. The Baroque style period was from 1600 - 1750. It Bach Rembrandt 1. Sir Isaac Newton was an important ttime in the world. The thirteen Handel El Greco 2. Robert Boyle American colonies were formed. Galileo, Kepler 3. Antoni van Leeuwenhoek Telemann Velazquez and Newton were discovering new ways to exlain the universe. Fancy decortion and ornimentation were the rule for fashion, art, music & architecture. Upper-class men and women wore wigs and coats with lace. Classical Period 1750-1825 Haydn The “Enlightment” and the Industrial Revolution Many world changes occured during the Classical Period. Boccherini 1735 A.D. to 1819 A.D. The French Revoluation and the Napoleonic Wars changed Mozart 1. Immanuel Kant used the term enlightment to Europe forever. The American Revolution and the Constitution changed the new world. It became possible for Beethoven describe the change in the underlying assumptions more Europeans to find leasure time and attend concerts. Schubert of science. The patronage system - where a composer or musician was 2.Carrolus Linnaeus paid a salary by a church or wealthy family to compose or 3.Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier perform for them - was very popular at this time. 4.John Dalton 5.Industrial Revolution (up until now most all work was done by hand but inventions started to come around to decrease the hours of labor Romantic Period 1825-1910 Rossini de Goya The rest of the Nineteenth Century 1820 A.D. to The Romantic period represented a time of change. Mendelssohn Constable 1899 A.D. It was a time of Mark Twain novels and telegraphs. Chopin Turner 1. Charles R. Darwin It was the time of the U.S. Civil war and a time Schumann Delzcroix 2. Louis Pasteur when Alexander Grahm Bell invented the telephone. Gounnod Bonheur 3. Sir Charles Lyell It was the time of changing from the strict structure Strauss Courbet 4. Gregor Mendel of the Classical Period to the flowing ideas, Brahms Manet 5. Michael Farady emotions and impressions of composers and artists Saint-Saens Monet 6. James Clerk Maxwell Bizet Renoir 7. James Joule The Romantic period , because individual Tchaikovsky Cassatt expression was so important to composers, the types Dvorak Cezanne of pieces had a great deal of variety. No longer were Grieg van Gogh there restrictions on the length of a piece or what Mussorgsky instruments could be used. Richard Wagner (VOG- Schubert ner) wrote operas that lasted 6 hours! Beethoven's Rimsky-Korsakov Ninth Symphony used an oversized orchestra, a full Sousa choir as well as vocal soloists. Puccini Williams 20th Century 1900-2000 Debussy Kollwitz Modern Science 1900 A.D. to Present Melodies in the 20th Century are very different than Rachmaninoff Matisse 1. Max Planck those of of previous periods. Melodies by some Sousa Picasso 2. Albert Einstein composers use ancient scales or scales form the Elgar Chagall 3. Niels Bohr Middle Ages and others use melodies that have large Britten Homer leaps and sue only a few notes. Dvorak Easkins Ives Bellows Chance Music - In chance music the composer leaves a lot Kodaly Hopper up to the performer. Impressionism - this music is an Stravinsky O’Keeffe offshoot of Romantic Program Music. Neo-Classical music Bernstein Bearden can sound very modern, but follows the structure of the Still Wyeth Classical Period. Twelve Tone Music - In twelve tone Prokofiev Moore music the composer uses the twelve notes that make up an Copeland Hepworth octave of music in a row determined by the composer. Electronic Music - In Electronic Music, composers use Calder computers, synthesizers and other tecnological devices to create music. Contemporary 2000-Present