HANDOUT 5-2
Form 1112-5 UNITED STATES (May 2001) DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR BUREAU OF LAND MANAGEMENT RISK MANAGEMENT WORKSHEET
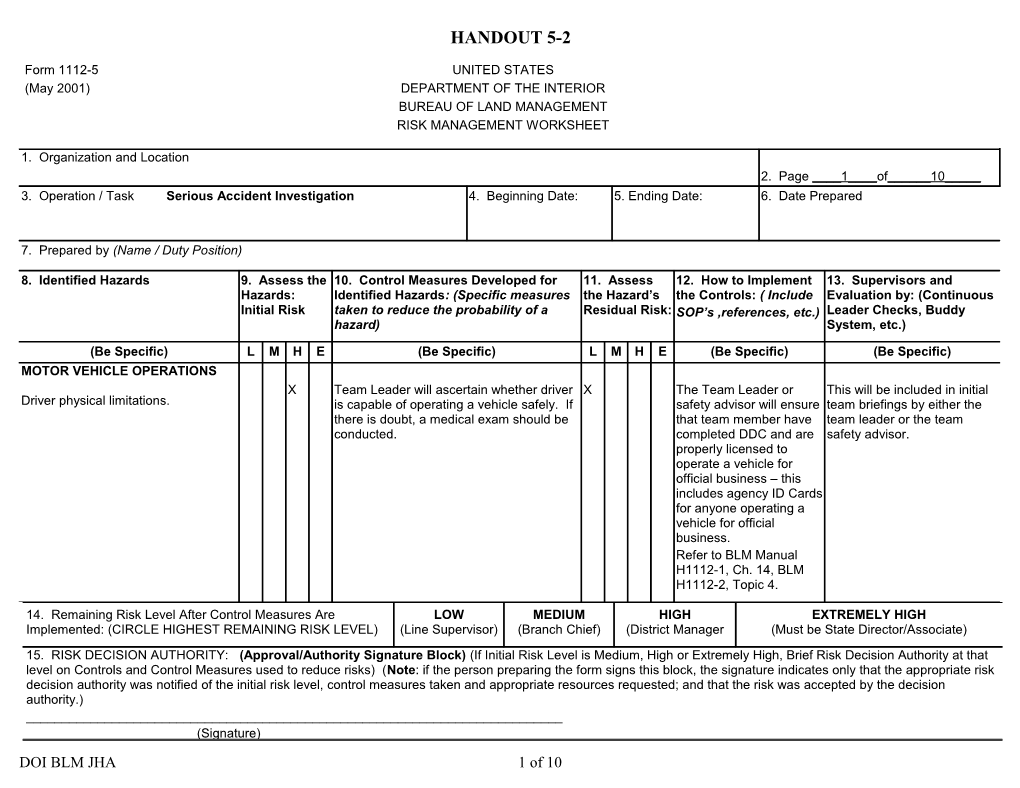
1. Organization and Location 2. Page ____1____of______10_____ 3. Operation / Task Serious Accident Investigation 4. Beginning Date: 5. Ending Date: 6. Date Prepared
7. Prepared by (Name / Duty Position)
8. Identified Hazards 9. Assess the 10. Control Measures Developed for 11. Assess 12. How to Implement 13. Supervisors and Hazards: Identified Hazards: (Specific measures the Hazard’s the Controls: ( Include Evaluation by: (Continuous Initial Risk taken to reduce the probability of a Residual Risk: SOP’s ,references, etc.) Leader Checks, Buddy hazard) System, etc.)
(Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) (Be Specific) MOTOR VEHICLE OPERATIONS X Team Leader will ascertain whether driver X The Team Leader or This will be included in initial Driver physical limitations. is capable of operating a vehicle safely. If safety advisor will ensure team briefings by either the there is doubt, a medical exam should be that team member have team leader or the team conducted. completed DDC and are safety advisor. properly licensed to operate a vehicle for official business – this includes agency ID Cards for anyone operating a vehicle for official business. Refer to BLM Manual H1112-1, Ch. 14, BLM H1112-2, Topic 4.
14. Remaining Risk Level After Control Measures Are LOW MEDIUM HIGH EXTREMELY HIGH Implemented: (CIRCLE HIGHEST REMAINING RISK LEVEL) (Line Supervisor) (Branch Chief) (District Manager (Must be State Director/Associate) 15. RISK DECISION AUTHORITY: (Approval/Authority Signature Block) (If Initial Risk Level is Medium, High or Extremely High, Brief Risk Decision Authority at that level on Controls and Control Measures used to reduce risks) (Note: if the person preparing the form signs this block, the signature indicates only that the appropriate risk decision authority was notified of the initial risk level, control measures taken and appropriate resources requested; and that the risk was accepted by the decision authority.) ______(Signature) DOI BLM JHA 1 of 10 HANDOUT 5-2
8. Identified Hazards 9. Assess 10. Control Measures Developed for 11. Assess 12. How to Implement 13. Supervisors and the Identified Hazards: (Specific the Hazard’s the Controls: ( Include Evaluation by: (Continuous Hazards: measures taken to reduce the Residual SOP’s, references, Leader Checks, Buddy Initial Risk probability of a hazard) Risk: etc.) System, etc.) (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) (Be Specific) Driver proficiency. X -Driver must possess a valid state X -Supervisor will Supervisor checks of driver’s license. physically view driver’s employee driving activities. license, contact safety office for training info.
Fatigue X -Adequate rest stops/stretch breaks, X -Refer to BLM Manual Supervisor check of time driver rotation. H1112-1, Ch. 14, BLM recovery to ensure driving/rest -Drivers will not exceed 8 hours driving H1112-2, Topic 4. schedules are being followed. time within a 16 hour duty period. Pre-trip briefing. -At least 8 consecutive hours of rest are required before any duty period requiring driving.
Vehicle malfunction. X -Thoroughly inspect vehicle monthly; X -Vehicle manager will Supervisor will spot check for fluids, lights, wipers, washers, brakes, perform. performance. belts, and tires.
- Daily pre-trip “walk-around” inspections - Driver will perform. of tires, lights, glass, fluid leaks. Refer to BLM Manual H1112-1, Ch. 14, BLM H1112-2, Topic 4. Collision. X -Seat belt worn at all times when vehicle X -Defensive Driver Supervisor will spot check for is in motion. Training will be performance. -3 second rule following distance, and provided other defensive driving techniques. -Reduce speed. -Increase following distance/time to 4 seconds+. -Insure proper tire inflation as per info on tire. -Vehicles will carry: Warning flags or reflectors Essential emergency repair tools First Aid kit, w/BBP barriers
DOI BLM JHA 2 of 10 HANDOUT 5-2
8. Identified Hazards 9. Assess 10. Control Measures Developed for 11. Assess 12. How to Implement 13. Supervisors and the Identified Hazards: (Specific the Hazard’s the Controls: ( Include Evaluation by: (Continuous Hazards: measures taken to reduce the Residual SOP’s, references, Leader Checks, Buddy Initial Risk probability of a hazard) Risk: etc.) System, etc.) (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) (Be Specific) Wet, icy, or loose pavement X -Reduce speed X -Defensive Driver Supervisor will spot check for -Increase following distance/time to 4 Training will be performance. seconds provided. -Insure proper tire inflations as per info on tire Vehicle Emergency X -Reduce speed, stay calm, maintain X -Vehicle manager or attention and firm control, and pull off primary driver. roadway slowly.
Backcountry driving, gravel and/or X -Reduce speed. X -Team new employees -Supervisor will spot check for mountainous roads. Increase following distance/time to 4 with employees performance. seconds. experienced with local -Supervisor will spot check for conditions for initial compliance. * Poor traction X -Insure proper tire inflations as per info X trips. -Crew chief, supervisor safety on tire. -Safety meeting briefings. reminders, briefings. -Buddy System with crew members. * Tire puncture X -Ensure that spare tire and necessary tools are prepared prior to departure. X
* Dust/mud obscured visibility X -Utilize windshield cleaner, increase X following distance to 4 seconds.
* Brake failure X -Avoid riding breaks on long or steep X downhill grades: utilize low gears as much as possible to reduce speed.
HELICOPTER OPERATIONS Get safety briefing as required prior to assignment. X Team briefings Team Safety Advisor will Flying objects, particulates, dust, X ensure PPE is available and etc. Wear appropriate PPE. i.e. flight suits or worn and required briefings fire nomex shirts and pants, helmets or X PPE will be worn IAW are performed. Noise and other flight related X hardhats, leather or nomex flight gloves, flight safety hazards and hearing protection. requirements DOI BLM JHA 3 of 10 HANDOUT 5-2
8. Identified Hazards 9. Assess 10. Control Measures Developed for 11. Assess 12. How to Implement 13. Supervisors and the Identified Hazards: (Specific the Hazard’s the Controls: ( Include Evaluation by: (Continuous Hazards: measures taken to reduce the Residual SOP’s, references, Leader Checks, Buddy Initial Risk probability of a hazard) Risk: etc.) System, etc.) (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) (Be Specific)
WALKING AND HIKING Falling objects X Approved hardhats will be worn when X Safety Advisor will Team Safety Advisor will there are overhead hazards; including ensure that everyone ensure PPE is available and walking in wooded areas. Hazard trees has a hardhat and worn and required briefings will be identified and noted. wears it as required. are performed.
Unimproved walking surfaces. X Safety briefings will be performed and X The Safety briefing will - tripping hazards appropriate boots will be worn by all be conducted on site - snags personnel. Snags and other hazards will and general and - steep rough terrain be identified to members walking to help specific safety issues will be covered. The Team Leader will ensure proper Fatigue X work/rest cycles. Team members who X Work rest schedules will are not accustomed to working at be developed and arduous duties should be identified and adhered to by the team. actions taken to ensure that they do not overextend themselves.
The Team Safety Advisor will ensure that The Team Leader will Weather X appropriate attire, sunscreen, raingear, X ensure that equipment - sun etc., will be made available for the team is available and used. - cold as appropriate. Any vehicle operations - wind during inclement weather will require a - raid formal Risk Assessment approved by the - snow/ice Team Leader. The Safety Advisor will coordinate with the local Local safety personnel will provide the safety person to Other hazards X team an overview of other hazards the X ascertain the hazards Entry into areas will not be - poisonous plants team may be exposed to and offer the team may be made until routine and know - inspects/animals remedies that routinely help ensure that exposed to. non-routine hazards are - illegal drug activities local employees are not exposed to Involvement of the local identified and the risks - hostile people these hazards. safety person may mitigated. Noted hazards will Law enforcement will be used as include safety briefings be briefed to all team appropriate and be provided by the local to the team as well as members. unit. coordination for law enforcement.
DOI BLM JHA 4 of 10 HANDOUT 5-2
8. Identified Hazards 9. Assess 10. Control Measures Developed for 11. Assess 12. How to Implement 13. Supervisors and the Identified Hazards: (Specific the Hazard’s the Controls: ( Include Evaluation by: (Continuous Hazards: measures taken to reduce the Residual SOP’s, references, Leader Checks, Buddy Initial Risk probability of a hazard) Risk: etc.) System, etc.) (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) (Be Specific) Security/Safety X Establish building evacuation procedures X The Team Safety Team Leader will ensure that for work area being utilized; make sure Advisor will develop this is complete and briefed to all employees are aware of exits and Emergency Plans as the team. safety meeting area. necessary for the team to include sign-in/out Inform team members of the process to procedures. report any accidents or injuries.
Provide all team members with incident emergency phone numbers and the process to follow for rapid notification in the event of an emergency.
Check-out/check-in systems (such as a sign out board) shall be located and utilized for team use.
Advise the appropriate person(s) on the accident investigation team of travel plans with expected times of arrival and return when traveling to and from the investigation site or isolated locations. Ensure vehicles are operating properly and are equipped for the specific task. Travel in pairs where warranted.
Ensure that communications equipment is operating properly and replacement batteries are available for hand-held radios.
Bloodborne Pathogen Program X All employees shall receive HIV/AIDS X The Safety Advisor will Team Leader will ensure that education training. For employees ensure this is this is complete and briefed to whose jobs put them at risk for an completed. The team the team. occupational exposure, training shall may use the local BBP cover the major elements of the OSHA program to accomplish bloodborne pathogens regulation. this.
Exposure to Diseases X To further minimize employee risk, all X The Safety Advisor will Team Leader will ensure that DOI BLM JHA 5 of 10 HANDOUT 5-2
8. Identified Hazards 9. Assess 10. Control Measures Developed for 11. Assess 12. How to Implement 13. Supervisors and the Identified Hazards: (Specific the Hazard’s the Controls: ( Include Evaluation by: (Continuous Hazards: measures taken to reduce the Residual SOP’s, references, Leader Checks, Buddy Initial Risk probability of a hazard) Risk: etc.) System, etc.) (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) (Be Specific) employees, regardless of job ensure this is this is complete and briefed to classification or duties, shall observe completed. The team the team. universal precautions at all times. may use the local BBP Observing universal precautions is an program to accomplish approach to infection control in which this. human blood and human body fluids are treated as if known to be infectious for HIV, HBV, or other bloodborne pathogens.
Working in Hot Conditions X Individual differences in heat tolerance X The Safety Advisor will All team members will use the - Fatigue are related to fitness, hydration, illness, monitor heat indexes buddy system to ensure heat - Weather drugs and medication, and fatigue. and ensure that injuries do not affect the teams identified control work. Heat stress occurs when the body's core measures are temperature rises beyond safe limits. implemented. All team Evaporation of sweat is the body's main members will monitor line of defense against heat. As sweat not only their own evaporates, it cools the body. When condition but that of water lost by sweating is not replaced, their team mates. the body's heat controls break down and body temperature climbs dangerously. Three factors that can contribute to heat The team leader will stress are low or poor physical fitness, ensure that water is excess weight, and hypertension. made available for all team members, that Schedule the hardest work during the rest breaks are cooler hours of the day. Set a moderate scheduled, and that the work pace. As the temperature team is aware of heat increases, stop for frequent rest periods indexes and warnings. of at least 15 minutes. Always have an adequate supply of water available and ensure that employees are getting needed liquids.
Plan ahead for drinking water; don't allow water supplies to run out. To prevent dehydration:
DOI BLM JHA 6 of 10 HANDOUT 5-2
8. Identified Hazards 9. Assess 10. Control Measures Developed for 11. Assess 12. How to Implement 13. Supervisors and the Identified Hazards: (Specific the Hazard’s the Controls: ( Include Evaluation by: (Continuous Hazards: measures taken to reduce the Residual SOP’s, references, Leader Checks, Buddy Initial Risk probability of a hazard) Risk: etc.) System, etc.) (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) (Be Specific) Drink 8 to 16 ounces of water before work.
Take frequent drinks during each hour of work (1 quart or 1 liter per hour).
Drink as much water as possible at lunch and the evening meal.
Continue replacing fluids throughout the evening.
Limit caffeine drinks, such as coffee or cola.
Avoid alcoholic drinks.
Provide well-planned meals and healthy snacks that are vital to maintain work capacity and to avoid heat disorders through adequate replacement of water, salt, and potassium. Carbohydrate/electrolyte beverages are recommended.
Wear hardhats; they protect your head and keep you cooler.
Prevent sunburn by wearing lightweight, light-colored, loose clothing, which allows air to circulate and sweat to evaporate, and offers protection from direct sun. Bare skin absorbs the sun's radiant heat and raises body temperature.
During periods of continued extreme temperatures (90 oF or above), ensure that supervisors monitor employees and DOI BLM JHA 7 of 10 HANDOUT 5-2
8. Identified Hazards 9. Assess 10. Control Measures Developed for 11. Assess 12. How to Implement 13. Supervisors and the Identified Hazards: (Specific the Hazard’s the Controls: ( Include Evaluation by: (Continuous Hazards: measures taken to reduce the Residual SOP’s, references, Leader Checks, Buddy Initial Risk probability of a hazard) Risk: etc.) System, etc.) (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) (Be Specific) that employees watch each other for signs of heat-stress disorders, including heat cramps, heat exhaustion, and heatstroke.
Heat cramps are identified by muscular pains and cramps, with leg and abdominal muscles usually affected first. Remedies include stretching and gently massaging cramped muscles and applying a heating pad or hot water bottle to help relieve muscle spasms.
Heat exhaustion is characterized by fatigue, weakness, and collapse. The skin becomes pale, cool, and clammy. Individuals experience nausea, dizziness, a throbbing headache, breathing problems, and diarrhea. Recommended actions include moving to a cool, shady place, lying with the feet raised 8 to 12 inches above the head, loosening clothing, and applying cool compresses to the skin. If there is no improvement quickly, seek medical attention at once.
Heatstroke is a medical emergency. Unaclimatized employees are especially prone to heatstroke. Symptoms are confusion, high body temperature, hot (often dry) skin, rapid pulse, convulsions, loss of consciousness, and coma. Lack of sweating is one sign of imminent heatstroke. Do not delay treatment. Cool the body down immediately. Administer fluids and transport the victim to a medical facility as quickly as possible. DOI BLM JHA 8 of 10 HANDOUT 5-2
8. Identified Hazards 9. Assess 10. Control Measures Developed for 11. Assess 12. How to Implement 13. Supervisors and the Identified Hazards: (Specific the Hazard’s the Controls: ( Include Evaluation by: (Continuous Hazards: measures taken to reduce the Residual SOP’s, references, Leader Checks, Buddy Initial Risk probability of a hazard) Risk: etc.) System, etc.) (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) (Be Specific)
Lightning and Thunderstorms X Heavy rain, hail, and lightning occur only X The team will avoid The Safety Advisor will ensure in the mature stage of a thunderstorm. working in the field that the team is aware of Keep informed; know what the storm is during periods of adverse weather conditions doing. extreme weather. If and takes the appropriate lightning is seen, the actions. When there is no shelter, avoid tall team will seek objects such as lone trees. If only appropriate shelter. isolated trees are nearby or if you are in open country, the best protection is to make yourself as small a target as possible. Drop to your knees, bend forward with your hands resting on your knees, and keep a distance of twice the height of the nearest tree between you and the tree. To minimize the flow of the current, keep your feet together. Keep away from wire fences, telephone lines, electrically conductive objects, and railroad tracks.
Advise team members that if they feel an electrical charge, if their hair stands on end, or their skin tingles, a lightning strike may be imminent.
Solar Radiation X Keep exposed skin covered by wearing a X Team members should Safety Advisor will ensure that hat, a bandanna, and a long-sleeved ensure they bring the team is properly outfitted shirt (with sleeves rolled down and collar appropriate personal and equipped for all turned up). items such as sun operations. glasses with UV Wear sunglasses that filter out 100 protection, sunscreen, percent of the UV rays. The use of non- etc., are brought and UV protected sunglasses or photo grey used as required. glasses can increase the chance of UV damage to the retina and are not recommended. DOI BLM JHA 9 of 10 HANDOUT 5-2
8. Identified Hazards 9. Assess 10. Control Measures Developed for 11. Assess 12. How to Implement 13. Supervisors and the Identified Hazards: (Specific the Hazard’s the Controls: ( Include Evaluation by: (Continuous Hazards: measures taken to reduce the Residual SOP’s, references, Leader Checks, Buddy Initial Risk probability of a hazard) Risk: etc.) System, etc.) (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) L M H E (Be Specific) (Be Specific)
Provide and use protective sunscreen lotion, cream, oil, and lip balm as identified in the JHA.
When possible, stay indoors during the peak exposure time in the summer or find worksites that are shady.
Alter work schedules where appropriate to avoid peak summer exposure.
DOI BLM JHA 10 of 10