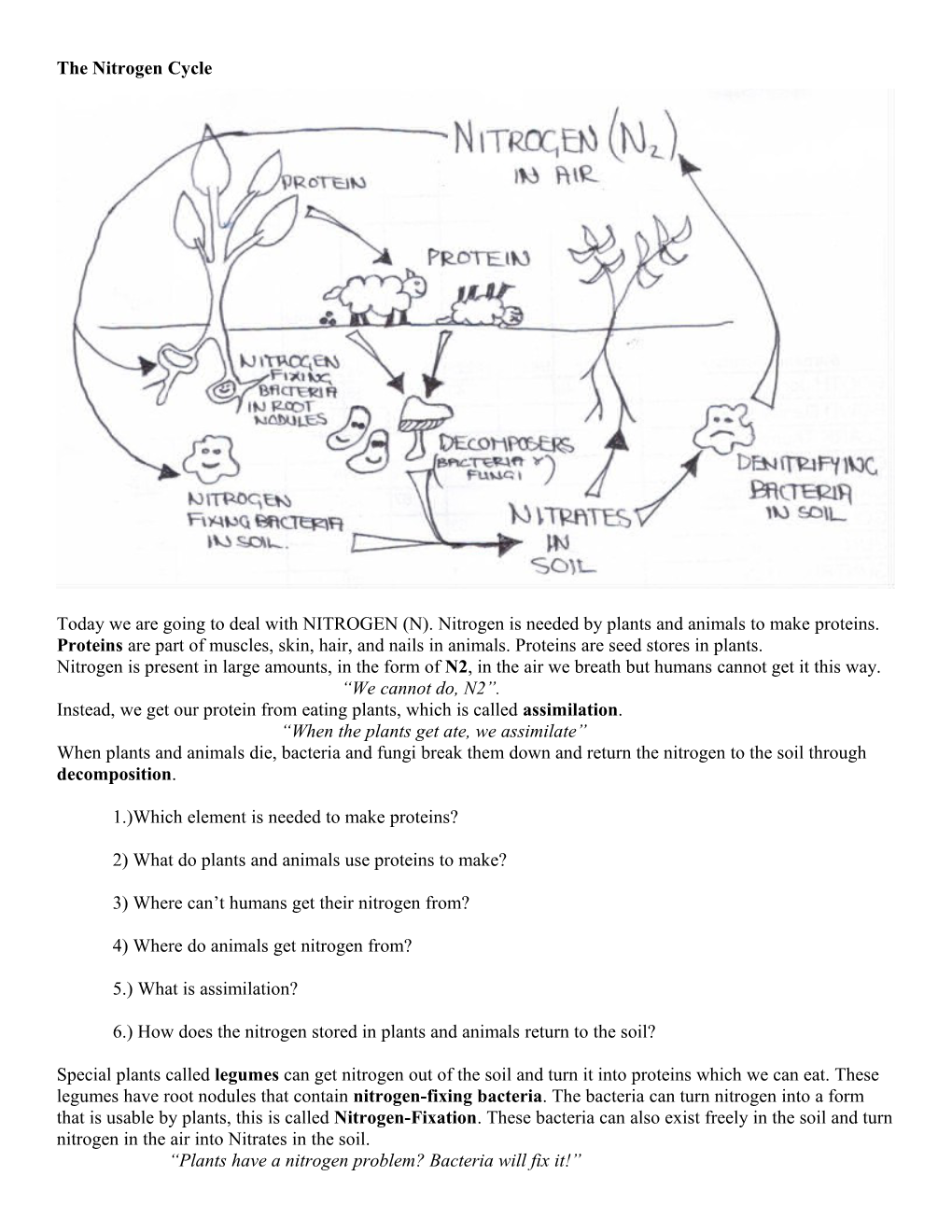
The Nitrogen Cycle
Today we are going to deal with NITROGEN (N). Nitrogen is needed by plants and animals to make proteins. Proteins are part of muscles, skin, hair, and nails in animals. Proteins are seed stores in plants. Nitrogen is present in large amounts, in the form of N2, in the air we breath but humans cannot get it this way. “We cannot do, N2”. Instead, we get our protein from eating plants, which is called assimilation. “When the plants get ate, we assimilate” When plants and animals die, bacteria and fungi break them down and return the nitrogen to the soil through decomposition.
1.)Which element is needed to make proteins?
2) What do plants and animals use proteins to make?
3) Where can’t humans get their nitrogen from?
4) Where do animals get nitrogen from?
5.) What is assimilation?
6.) How does the nitrogen stored in plants and animals return to the soil?
Special plants called legumes can get nitrogen out of the soil and turn it into proteins which we can eat. These legumes have root nodules that contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The bacteria can turn nitrogen into a form that is usable by plants, this is called Nitrogen-Fixation. These bacteria can also exist freely in the soil and turn nitrogen in the air into Nitrates in the soil. “Plants have a nitrogen problem? Bacteria will fix it!” Examples of legume plants are peas and beans. They are very important in the nitrogen cycle.
7) What type of plants can convert nitrogen in the soil into protein?
8.) What do these plants have that allow them to change nitrogen into a usable form?
9.) What is Nitrogen fixation?
10) Give two specific examples of a plant that fix nitrogen.
Nitrogen in the soil can be converted into N2 to enter the atmosphere, this called denitrification. The process is completed by denitrifying bacteria. “To make nitrogen fly, bacteria denitrify!” Nitrogen in the air can also change forms when struck by lightning.
11) How is nitrogen returned to the air to complete the cycle?
12) What is the chemical symbol for nitrogen in the air?
13.) What natural phenomenon can convert nitrogen in the air?