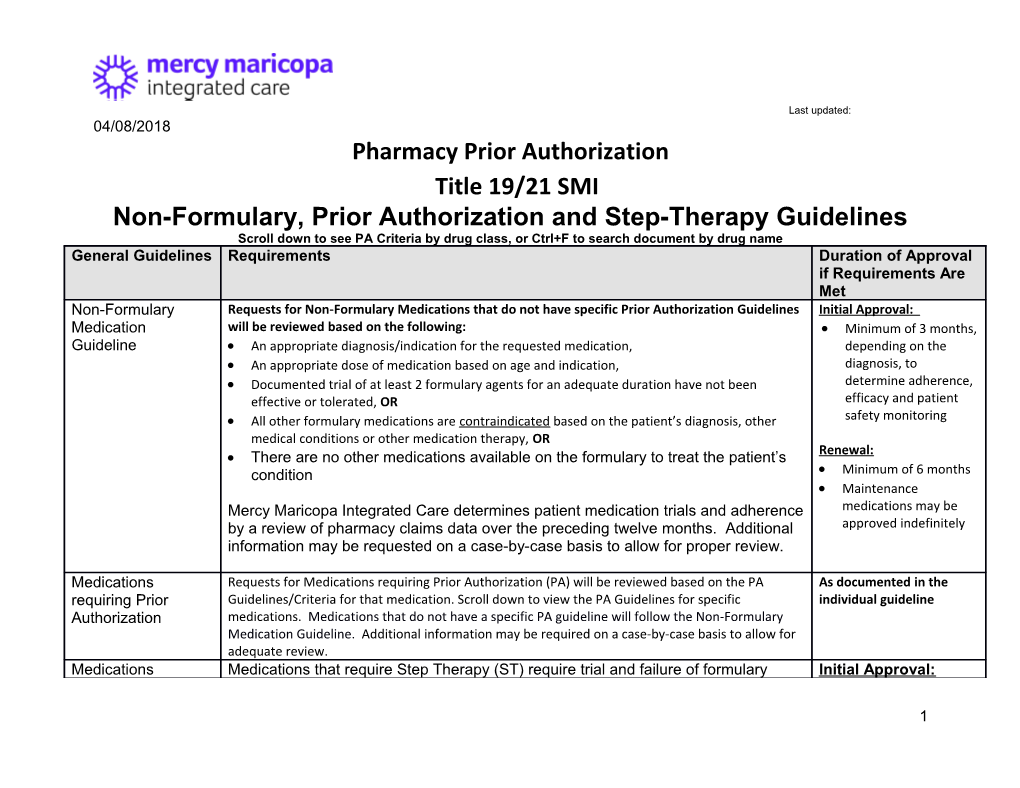
Last updated: 04/08/2018 Pharmacy Prior Authorization Title 19/21 SMI Non-Formulary, Prior Authorization and Step-Therapy Guidelines Scroll down to see PA Criteria by drug class, or Ctrl+F to search document by drug name General Guidelines Requirements Duration of Approval if Requirements Are Met Non-Formulary Requests for Non-Formulary Medications that do not have specific Prior Authorization Guidelines Initial Approval: Medication will be reviewed based on the following: Minimum of 3 months, Guideline An appropriate diagnosis/indication for the requested medication, depending on the An appropriate dose of medication based on age and indication, diagnosis, to Documented trial of at least 2 formulary agents for an adequate duration have not been determine adherence, effective or tolerated, OR efficacy and patient All other formulary medications are contraindicated based on the patient’s diagnosis, other safety monitoring medical conditions or other medication therapy, OR There are no other medications available on the formulary to treat the patient’s Renewal: condition Minimum of 6 months Maintenance Mercy Maricopa Integrated Care determines patient medication trials and adherence medications may be by a review of pharmacy claims data over the preceding twelve months. Additional approved indefinitely information may be requested on a case-by-case basis to allow for proper review.
Medications Requests for Medications requiring Prior Authorization (PA) will be reviewed based on the PA As documented in the requiring Prior Guidelines/Criteria for that medication. Scroll down to view the PA Guidelines for specific individual guideline Authorization medications. Medications that do not have a specific PA guideline will follow the Non-Formulary Medication Guideline. Additional information may be required on a case-by-case basis to allow for adequate review. Medications Medications that require Step Therapy (ST) require trial and failure of formulary Initial Approval:
1 Last updated: 04/08/2018 requiring Step agents prior to their authorization. If the prerequisite medications have been filled Indefinitely Therapy within the specified time frame, the prescription will automatically process at the pharmacy. Prior Authorization will be required for prescriptions that do not process automatically at the pharmacy. Brand Name Mercy Maricopa Integrated Care requires use of generic agents that are considered Initial Approval: Medication therapeutically equivalent by the FDA. For authorization of a brand name Indefinitely Requests medication, please submit a copy of the FDA MedWatch form detailing trial and failure of, or intolerance/adverse side effect to generic formulations made by 2 different manufacturers. The completed form should also be submitted to the FDA. The FDA MedWatch form is available at: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Safety/MedWatch/HowToReport/DownloadForms/UC M082725.pdf
Specialist Prescriber Some medications are covered when prescribed by a Specialist provider. If the Initial Approval: Medication medication is prescribed by the appropriate Specialist, the prescription will Indefinitely Requests automatically process at the pharmacy. Prior Authorization will be required for prescriptions that do not process automatically at the pharmacy. In those cases, authorization will be given upon receipt of a Specialist Consult or after trial and failure of 2 formulary medications. Behavioral Health Primary care providers, within the scope of their practice, who wish to provide psychotropic N/A Medications medications and medication adjustment and monitoring services may do so for members diagnosed with Attention Deficit Disorder/Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, depressive (including postnatal depression) and/or anxiety disorders. AHCCCS provides guidance in two appendices, Appendix E for children and adolescents and Appendix F for adults. For each of the three named diagnoses there are clinical guidelines that include assessment tools and algorithms. The clinical guidelines are to be used by the PCPs as an aid in treatment decisions. http://www.azahcccs.gov/shared/Downloads/MedicalPolicyManual/Chap300.pdf For treatment of other behavioral or mental health conditions, members will be referred to the Regional Behavioral Health Authority (RBHA). Behavioral Health Requirements Duration of Approval Guidelines if Requirements Are
2 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Met Non-Formulary Guidelines for Approval: Hospital Discharge: Behavioral Health 1. The patient must have a diagnosis for which the requested medication is FDA approved for 60 days Medications or the requested medication is included in treatment guidelines. 2. The patient has previously tried and had an inadequate response, experienced adverse Initial Approval: reactions, or developed breakthrough symptoms with at least 2 other formulary mediations in 12 months the same class at maximum tolerated doses. 3. The dose of the requested medication must not be greater than the FDA recommended Initial Approval for High- maximum daily dosage. Dose: a. If the dose requested exceeds the FDA recommended maximum, documentation to 3 months support the following must also be submitted: Renewal: a.i. The dosing requested must be supported by peer-reviewed literature. 12 months a.ii. The Behavioral Health Medical Provider (BHMP) has evaluated and determined that medication non-adherence is not the reason for the dose escalation. a.iii. Supporting documentation indicates that use of the medication at a lower dose (or within the plan quantity limit) has been ineffective and a clinically significant trial was completed. a.iv. The BHMP has ruled out a non-response due to an unrecognized or under- treated co-morbid disorder. a.v. The treatment plan must include ongoing safety monitoring.
Brand Name FDA Approved Indication: Hospital Discharge: For adults, BHR has a diagnosis for which requested medication is an FDA approved treatment 60 days Behavioral Health indication. For individuals under the age of 18, the BHR must have a diagnosis for which the Medications requested medication meets the community standard of care. Initial Approval Indefinite Aplenzin Guidelines for Approval: Edluar 1. Documentation of intolerance, nonresponse or non-adherence to a formulary generic equivalent formulation of the requested medication at maximal tolerated doses for at least 4 Emsam weeks. Fanapt Gralise 2. Documentation of intolerance, nonresponse or non-adherence to a formulary generic
3 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Horizant pharmaceutical alternative formulation of the requested medication at maximal tolerated Intermezzo SL doses for at least 4 weeks. Intuniv 3. Documentation of intolerance, non-adherence, or non-response to at least two generic Lamictal XR formulary medications in the same medication class at maximal tolerated doses for at least 4 Pexeva weeks. Quillivant XR Saphris Guidelines for Exceptions: 1. Documentation of intolerance/contraindication to other formulary medications (including Seroquel XR documentation of the risk of metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes), and documentation for Silenor the reason why the requested medication will ameliorate the risks Suboxone Film Viibryd 2. Documentation that the individual has responded to a generic immediate release formulary Zolpimist medication, but requires the brand name extended release formulation to maintain adherence. Additional Requirements: If BHR preference interferes with compliance to generic equivalent formulation or generic pharmaceutical alternative formulation, brand name request will be reviewed on a case by case basis.
If a BHR has been stabilized in another setting on a brand only medication for which there is no generic equivalent or generic pharmaceutical alternative formulation, then the brand name medication will be approved.
Coverage is Not Authorized for: 1. Indications that have not received FDA approval.
2. Doses greater than FDA recommended maximum daily dosage without meeting prior authorization guidelines for exceeding maximum daily dosage. References: 1. ADHS/DBHS: Provider Manual Section 3.15: Psychotropic Medication: Prescribing and Monitoring 2. Manufacturer Product Information Antidepressants Approved Behavioral Health Indications: Hospital Discharge: with CYP450 60 days mediated drug Treatment Resistant Depression interactions Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (clomipramine with fluvoxamine) Initial Approval:
4 Last updated: 04/08/2018 TCA with fluoxetine 6 months (strong 2D6 inhibitor) Guidelines for Approval: TCA with paroxetine Renewal: 1. Approval will be granted when a member is transitioning from one (strong 2D6 1 year inhibitor) TCA with medication to another. bupropion 2. Evidence of adequate trials of at least three (3) individual formulary (moderate 2D6 antidepressants, from at least two (2) different therapeutic classes, for 4-6 inhibitor) TCA with weeks at maximum tolerated doses. duloxetine a.Fa Brilueare kis t hdruoeu gto:h symptoms or an inadequate response at maximum (moderate 2D6 tolerated doses, or inhibitor) b. Adverse reaction(s) TCA with sertraline (moderate-weak And 2D6 inhibitor) 3. Documentation confirming that trials of at least two (2) Clomipramine with evidenced based augmentation strategies have been tried for an fluvoxamine (strong adequate trial and failed, resulted in significant side effects, or arec 1A2 inhibitor) ontraindicated. Examples of augmentation strategies include lithium, thyroid hormone, bupropion, mirtazapine, quetiapine, or aripiprazole. Bupropion, Failure is due to: clomipramine, a. Inadequate response at maximum tolerated doses, b. Adverse reaction(s), or duloxetine, c. Break through symptoms fluoxetine, 4. Initial TCA treatment should be initiated at the lowest possible dosage. fluvoxamine, paroxetine, 5. Supporting clinical documentation must be provided with the initial sertraline, tricyclic These parameters include the following: prior authorization request. antidepressants a. Assessment showing there is no evidence of cardiovascular conduction delays, b. Heart rate, c. Blood pressure and d. TCA levels.
5 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Additional Requirements: 1. Provider must provide supporting documentation that: a. Adherence to the treatment regimen is not a contributing factor to the inadequate response to the medication trials,
Coverage is No t A u t h o r i z e d for: 1. Members with known hypersensitivity to the requested medication(s). 2. Prior Authorization Requests that do not meet the above stated criteria. 3. Members currently taking an MAOI medication.
References: 1. ADHS/DBHS: P r o v id e r M a nu a l S e c t i o n 3 .1 5 : P s y ch o t r o pic M e di c at i on : P r e s c ri b i n g a n d Mo n i t o r i n g 2. American Psychiatric Association Practice Guideline for the Treatment rd of patients with Major Depressive Disorder, 3 edition. American Psychiatric Association; October 2010. h t tp :/ / p s y ch i a t r y o n l i n e . o r g / c o n te n t . a s p x ? b oo k i d =2 8 & s e c t i o n i d =166748 5 accessed 7/2/13 3. Preskorn, Sheldon H. The Potential for Clinically Significant Drug- Drug Interactions involving the CYP 2D6 system: Effects with Fluoxetine and Paroxetine versus Sertraline. Journal of Psychiatric Practice. Jan 2007: (1527- 4160), 13(1) 5. 4. Spina E; Trifiro G; Caraci F. Clinically Significant Drug Interactions with Newer Antidepressants. CNS Drugs. 2012 Jan 1;26(1):39-67 5. Indiana University Division of Clinical Pharmacology P450 Drug Interaction Table. h tt p : //me di c i n e .i u p u i. e d u / cl i n p h a r m/ ddi s /ta bl e . a s p x A cc e ss e d 7 / 2 / 1 3 6. Wagner W; Vause EW; Fluvoxamine: A Review of Global Drug-Drug Interaction Data. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1995;29 Suppl 1:26-31; discussion 31
6 Last updated: 04/08/2018 —2 Sequenced Treatment Alternatives to Relieve Depression (STAR*D) 7. Study Rush AJ; Trivedi MH; Stewart JW; et al. Combining Medications to 8. Enhance Depression Outcomes (CO-MED): Acute and Long-Term Outcomes of a Single-Blind Randomized Study. Am J Psychiatry 2011; 168:689-701. 9. Trivedi MH, Fava M, Wisniewski SR, et al. Medication augmentation the failure of SSRIs for depression. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(12):1243- after 52.
Concomitant Approved Indication: Hospital Discharge: Antidepressant Treatment Resistant Depression 60 days Treatment Special Considerations: Initial Approval: Cross tapers may be approved for up to 60 days per each RBHA’s policy. For 2 SSRIs 60 days for cross greater than 60 days, Providers must submit a prior authorization request for taper an SSRI in continued utilization of concomitant use of two (2) antidepressants for the combination with an following: 6 months for non- SNRI 1. Two SSRIs cross taper 2 SNRIs 2. An SSRI in combination with an SNRI 3. Two SNRIs 2 Tricyclics (TCAs) 4. Two Tricyclics (TCAs) Renewal: Guidelines for Approval: 1. Approval will be granted when a member is transitioning from one 1 year medication to another. 2. Evidence of adequate trials of at least three (3) individual formulary antidepressants, from at least two (2) different therapeutic classes, for 4-6 weeks at maximum tolerated doses.
7 Last updated: 04/08/2018
a.Failure An in isad deuque atto:e response at maximum tolerated doses, b. Adverse reaction(s), or c. AndBr eak through symptoms. 3. Documentation confirming that trials of at least four (4) evidenced based augmentation strategies have been tried for an adequate trial and failed, resulted in significant side effects, or are contraindicated. Examples of bupropion, augmentation strategies include lithium, thyroid hormone, mirtazapine, quetiapine, or aripiprazole). Failure is due to: a. Inadequate response at maximum tolerated doses, b. Adverse reaction(s), or c. B reak through symptoms Additional Requirements: 1. Provider must provide supporting documentation that: a. Adherence to the treatment regimen is not a contributing factor to the inadequate response to the medication trials, b. Appropriataned c sliynmicptal ommosn oitof rsienrgo ofto ntainrg seynt sdyrommeptom, adhes, adrevncerese t or eactions treincatmeludingn ts, isgnsuic ide risk, heart rate, blood pressure, and weight has been completed, and c. Appropriate clinical monitoring has been completed for TCAs, which includes but is not limited to, pupillary reactive response, thyroid function, liver function, abdominal girth, TCA levels and an ECG at baseline and follow up. Coverage is No t A u t h o r i z ed for: 1. Members with known hypersensitivity to the requested agent(s). 3.2. Members cunotrr meetently itnagk itnhge aanbo MvAOe stateI medd cicriatetiorina.
Refere1.nces: ADHS/DBHS: P r o v id e r M a nu a l Secti o n 3 .1 5 : P s y ch o t r o pic M e di c at i on :
8 Last updated: 04/08/2018 P r e s c ri b i n g a n d Mo n ito r i n g 2. American Psychiatric Association Practice Guideline for the Treatment of rd patients with Major Depressive Disorder, 3 edition. American Psychiatric Association; October 2010. h tt p: //p s y c h i a t r y o n l i n e .o r g / c o n t e nt . a s p x ? boo k i d = 2 8 & s e c t i o n i d = 166748 5 accessed 7/2/13 3. Sequenced Treatment Alternatives to Relieve Depression (STAR*D) Study Rush AJ; Trivedi MH; Stewart JW; et al. Combining Medications to 4. Enhance Depression Outcomes (CO-MED): Acute and Long-Term Outcomes of a Single-Blind Randomized Study. Am J Psychiatry 2011; 168:689-701 5. Trivedi MH, Fava M, Wisniewski SR, et al. Medication augmentation after the failure of SSRIs for depression. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(12):1243- 52. 6. Debonnel G; Saint-Andre E; Hebert C; et al. Differential Physiological Effects of a Low Dose and High Doses of Venlafaxine in Major Depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007 Feb; 10(1):51-61
Concomitant Approved Indications: Hospital Discharge: Antipsychotic Treatment Refractory 60 days Treatment 1. Schizophrenia spectrum disorders or 2. Bipolar disorder, with psychosis and/or severe symptoms Initial Approval: 60 days for cross Special Considerations: taper Cross tapers will automatically be approved for 60 days. Providers must submit a prior authorization request for continued utilization of concomitant use of any 2 6 months for non- antipsychotics beyond the 60 days allowed for cross tapering. cross taper
9 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Guidelines for Approval for refractory schizophrenia spectrum disorder: Renewal: 1. Evidence of adequate trials of at least three (3) individual formulary 1 year antipsychotics, one of which is clozapine, 4-6 weeks of maximum tolerated doses, and failure due to: a. Inadequate response to maximum tolerated dose b. Adverse reaction(s), c. Break through symptoms
Guidelines for Approval for refractory bipolar disorder with psychosis and/or severe symptoms: 1. Evidence of adtehqeu eapisodete trials t yofp ea.t Tleriaastls f omuary ( 4inc) eluvdeide lintcheiu bma,s deidv atrlpeatmroex,en att opypitcioanl s adnetpipesnydcehnot tuicp mono notherapy, carbamazepine, haloperidol, lamotrigine, lithium + an anticonvulsant, lithium + an antipsychotic, or an anticonvulsant + an antipsychotic. Trials should be 4-6 weeks of maximum tolerated doses, with failure due to:
b.a. AIndavdeersequ atreae rcetiospon(sn)se, to maximum tolerated dose c. Break through symptoms
Additional Requirements:
Provider must provide supporting documentation that adherence to the treatment regimen has not been a contributing factor to the lack of response in the medication trials.
Coverage is No t A u t h o r i z e d for: 1. Members with known hypersensitivity to requested medication(s). 2. Prior Authorization Requests not meeting the above stated criteria.
References: 1. ADHS/DBHS: P r o v i d e r M a nu a l S e c ti o n 3 . 15: Psy c h o tr o p ic M e d i c a ti o n:
10 Last updated: 04/08/2018 P r es c ri b ing a nd M o ni t o ring 2. Correll CU, Rummel-Kluge C, Corves C, et al. Antipsychotic combinations vs monotherapy in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 2009;35:443-457. 3. Essock SM, Schooler NR, Stroup TS, et al. Effectiveness of switching from antipsychotic polypharmacy to monotherapy. Am. J. Psychiatry, 2011;168:702-708. 4. Tandon R, Belmaker RH, Gattaz WF, et al. World Psychiatric Association Pharmacopsychiatry Section statement on comparative effectiveness of antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 2008;100:20-38. 5. Tsutsumi C, Uchida H, Suzuki T, et al. The evolution of antipsychotic switch and polypharmacy in natural practice- A longitudinal perspective. Schizophr. Res. 2011;130:40-46. 6. Zink M., Englisch S, Meyer-Lindberg A. Polypharmacy in schizophrenia. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry, 2010;23:103- 111.s 7. Yatham LN, Kennedy SH, Schaffer A, et al, Canadian Network for Mood and Anxaiendty IntTreaerntmatieontsna l( SocCANMAiety fTo)r Bipolar Disorders (ISBD) collaborative update of CANMAT guidelines for the management of patients with bipolar disorder: update 2009. Bipolar Disorder. 2009 May;11(3):225-55. 8. Hirschfeld R., Bowden C., Gitlin M, et al. Practice Guideline for the Treatment for Patients With Bipolar Disorder (Revision). Am J Psychiatry. 2003: 1(1) 64-110. 9. Crimson, L., Argo T., Bendele S., Suppes T., Texas Medication Algorithm Project Procedural Manual- Bipolar Disorder Algorithms. Texas Department of State Health Services. Web httadd p ://wress w: w. pb h c a r e .o r g / p u bdoc s / u p l o ad / d oc um e nt s /T IMABDm a n2007 . pd f Accessed July 15, 2013.
Injectable FDA Approved Indication: Hospital Discharge: 11 Last updated: 04/08/2018 antipsychotics BHR has a diagnosis for which the requested medication has an approved 60 days Abilify Maintenna FDA indication. These medications are not approved for use in individuals Invega Sustenna under the age of 18. Initial Approva: 6 months Guidelines for Approval: 1. BHR must demonstrate sustained clinical improvement and tolerability Renewal: on the short acting form of the requested Brand Name Long Acting agent, and 1 year 2. Documentation of noncompliance on oral medications, and/or documentation supporting the benefit of long acting medication in achieving clinical stability.
Additional Requirements: Prior Authorization for medications covered under this guideline will not continue beyond 60 days for members receiving oral antipsychotics concomitantly with Brand Name Long Acting Injectable Antipsychotics
Initial Prior Authorization for Abilify Maintena and Invega Sustenna will be for 6 months. Subsequent Prior Authorization frequency may be determined by the (T)RBHA, and will be contingent upon evidence of clinical efficacy and appropriate clinical monitoring.
Coverage is No t A u t h o r i z e d for: 1. Doses greater than FDA recommended maximum daily dosage without meeting prior authorization guidelines for exceeding maximum daily dosage. 2. Concomitant use of cytochrome p450 inducers (eg, carbamazepine) 3.and AbiliIndifyv Midauianlste nunader the age of 18
References: 1. ADHS/DBHS: P r o v id e r M a nu a l S e c t i o n 3 .1 5 : P s y ch o t r o pic M e di c at i on : P r e s c ri b i n g a n d Mo n i t o r i n g
12 Last updated: 04/08/2018 2. Manufacturer Product Information
Vivitrol Patient must have a diagnosis of alcohol or opioid use disorder and either: Initial Approval: a. Patient has failed a trial of oral medication indicated for alcohol or opioid use disorder; or 3 months b. The patient’s clinical status indicates instability or non-adherence such that oral medication will not be taken consistently or a trial will likely fail. Renewal: 12 months
Physical Health Authorization Guidelines/Criteria Guidelines Somatostatin Octreotide, Sandostatin LAR, Signifor, Signifor LAR Analogs See Detailed document: https://www.mercymaricopa.org/providers/mmic/pharmacy
Growth Hormone See Detailed document on pharmacy website Antagonist Somavert Afinitor may be authorized when the following criteria are met: Afinitor Initial Approval: 1 year i Prescribed by an oncologist Last reviewed: 10/22/2015 Patient has ONE of the following diagnoses: Renewal: 3 years o Recurrent or stage IV hormone receptor positive (ER/PR +) breast cancer For members with stable that progressed or recurred while on letrozole or anastrozole: disease (tumor size . Patient is postmenopausal OR premenopausal and has had within 25% of baseline). ovarian ablation/suppression . Must be used in combination with exemestane Discontinuation is o Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNET) that are locally advanced, metastatic or unresectable appropriate when there o Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) with ONE of the following is evidence of disease manifestations: progression. . Renal angiomyolipoma
13 Last updated: 04/08/2018 . Subependymal giant cell tumor that is unresectable o Relapsed or stage IV, unresectable, renal cell carcinoma (RCC) of predominant clear cell histology following treatment with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (i.e., Sutent, Nexavar, Inlyta, or Votrient) o Relapsed or stage IV, unresectable, renal cell carcinoma (RCC) of non- clear cell histology Afinitor Disperz may be authorized when the following criteria are met: Prescribed by an oncologist Pediatric patient at least 1 year old Diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) with s ubependymal giant cell tumor that is unresectable
Ampyraii May be approved when the following criteria are met: Initial Approval: Last reviewed: 10/22/2015 Prescribed by, or in consultation with a neurologist 2 months Patient is between 18 and 70 years old Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis with impaired walking ability defined as a Renewal: baseline 25-ft walking test between 8 and 45 seconds OR Expanded 1 year Disability Status Scale (EDSS) between 4.5 and 6.5 Requires: Patient is stabilized on disease modifying therapy for MS (i.e., no recent At least 20% exacerbations) improvement in timed Patient is NOT wheelchair-bound walking speeds on 25- Patient does not have a history of seizures ft walk within 4 weeks Patient does not have moderate to severe renal impairment (Crcl < 50 of starting medication ml/min) Note: Less than 50% of patients respond to treatment
Antidementia For Patients who meet all of the following: Initial Approval: Drugs Indefinitely
14 Last updated: 04/08/2018 donepezil Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease 5mg,10mg, -ODT, Potential causes for cognitive dysfunction. (eg, cerebrovascular disease, galantamine, -ER, cobalamin [vitamin B-12] deficiency, syphilis, thyroid disease) has beeen Namenda, ruled out. rivastigmine Cognitive assessment to evaluate for the presence of dementia; capsules o Mini-Mental Status Exam (MMSE) score below 22
OR
o Mini-Cog score of ≤ 2 and abnormal CDT (clock drawing test)
o Age restriction: must be at least 18 years old
ARBs For patients who meet the following: Initial Approval: Benicar Prescribed by a cardiologist OR Indefinite Edarbi 2 fills of a first-line agent (or any combination of first-line agents) in the last 130 days OR Documented intolerance to formulary ARBs Age restriction o Benicar – must be at least 6 years old and weigh at least 20 kg o Edarbi – must be at least 18 years old First-line Agents include: ACE inhibitors Formulary ARBs: o Losartan, losartan/HCTZ o Irbesartan, irbesartan/HCTZ o Valsartan, valsartan/HCTZ o Amlodipine/valsartan, amlodipine/valsartan/HCTZ Diabetes medication
15 Last updated: 04/08/2018
Botulinum Toxins Botox, Myobloc, Dysport, Xeomin
See Detailed document: https://www.mercymaricopa.org/providers/mmic/pharmacy
Cambia[ii] May be authorized for patients who meet the following criteria: Initial Approval: Last reviewed: 10/21/2015 Diagnosis of migraine headaches Indefinite 18 years of age or older Tried and failed at least 2 formulary triptans (e.g., sumatriptan, naratriptan) or Limit of 9 packets (1 has a contraindication to triptans box per month) Tried and failed at least 2 formulary NSAIDs (e.g., Ibuprofen, naproxen, diclofenac)
Capecitabineiii May be authorized when prescribed by an oncologist for patients who are at least 18 Initial Approval: 1 year Last reviewed: 1/19/2016 years old who have ANY of the following indications: Metastatic colorectal cancer Renewal: 3 years based Adjuvant (post-surgery) treatment of Dukes’ C colon cancer on therapeutic response. Metastatic breast cancer that is refractory to both paclitaxel and an anthracycline- containing chemotherapy regimen Required: Metastatic breast cancer that is refractory to paclitaxel when the patient is not Crcl >30mL/min appropriate for anthracycline therapy neutrophils >1 × Metastatic breast cancer that has progressed on an anthracycline-containing 109/L chemotherapy when used in combination with docetaxel platelets >50 × 109/L Locally advanced anal/rectal cancer when used in combination with radiation Pancreatic cancer when used in combination with radiation HER2 positive advanced/recurrent or metastatic breast cancer: o Disease has progressed after receiving prior therapy with an anthracycline (doxorubicin, daunorubicin, epirubicin, idarubicin), a taxane (paclitaxel, docetaxel), AND
16 Last updated: 04/08/2018 trastuzumab (Herceptin) o Must be used in combination with Tykerb
Note: Capecitabine is contraindicated in severe renal impairement (Crcl <30mL/min). Note: Patients with baseline neutrophil counts of <1.5 × 109/L or platelet counts of <100 × 109/L should not be treated with capecitabine
Caprelsaiv May be authorized for adults when the following criteria are met: Initial: 1 year Renewal: 3 years Last reviewed: 10/22/15 Prescribed by an oncologist Patient is at least 18 years old No history of congenital long QT syndrome (Black Box Warning) Patient meets ONE of the following: o Diagnosis of locally recurrent or metastatic differentiated thyroid carcinoma (including papillary, follicular, and Hurthle cell) after surgical resection that is progressive or symptomatic AND is refractory to radioactive iodine treatment AND Nexavar or Lenvima o Diagnosis of medullary thyroid cancer and one of the following: . Local disease progression or recurrence after surgery which is unresectable . Symptomatic disease progression or recurrence after surgery with distant metastases . Asymptomatic disease progression or recurrence after surgery with distant metastases that is unresectable
Celecoxib[iii] May be authorized for patients who meet the following criteria: Initial Approval: Last reviewed: 09/09/2015 Patient meets ONE of the following: Indefinite o Was unable to achieve clinical benefit with 3 formulary NSAIDs o Has a history of NSAID-induced gastritis confirmed by EGD o Is at high-risk for adverse GI events (e.g., >65 years of age, concomitant corticosteroid or anticoagulant use, or history of GI bleed, PUD, GERD, or
17 Last updated: 04/08/2018 gastritis) AND not currently taking a daily aspirin No recent history (in the past 6 months) of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) or CABG Age >2 years old for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) OR >18 years old for all other indications Dose does not exceed FDA recommended maximum for indication o OA: 200 mg/day o RA, acute moderate pain, dysmenorrhea, moderate to severe pain associated with orthopedic surgery, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis: 400 mg/day o JRA: . >25 kg: 100mg BID . 10-25 kg: 50mg BID Cialis for BPH For patients that meet all of the following: Initial Approval: Diagnosis of BPH 3 months Trial and failure of all of the following: o Doxazosin Renewal: o Alfuzosin 3 months o Tamsulosin Requires demonstration of improvement in BPH symptoms Colony-Stimulating Granix, Leukine, Neupogen, Neulasta, Zarxio Factors (CSF) See Detailed document: https://www.mercymaricopa.org/providers/mmic/pharmacy
Cometriqv May be authorized when the following criteria are met: Initial: 1 year Last reviewed: 10/22/2015 Prescribed by an oncologist Recommended dose: Patient is at least 18 years old 140 mg ORALLY once
18 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Documented diagnosis of medullary thyroid cancer AND ONE of the following: daily o Local disease progression or recurrence after surgery which is unresectable Renewal: 3 years o Symptomatic disease progression or recurrence after surgery with distant Discontinuation is metastases appropriate upon o Asymptomatic disease progression or recurrence after surgery with disease progression or distant metastases that is unresectable drug toxicity No evidence of moderate or severe hepatic impairment Patient is not currently taking a strong CYP3A4 inducer or inhibitor Compounds Compounds are not a covered benefit with the following exceptions: Initial Approval: If each active ingredient is FDA-approved (non-bulk chemicals aka Active Pharmaceutic • For market shortages: 3 Ingredient “API” ) months If each active ingredient is used for an indication that is FDA-approved or compendia supported • All others: 1 year The final route of administration of the compound is the same as the FDA-approved or compendia supported route of administration of each active ingredient. (i.e., oral baclofen Renewals: tablets should not be covered for topical use) • For market shortages: 3 months Patient meets ONE of the following: o Has an allergy and requires a medication to be compounded without a certain • All others: 1 year active ingredient (e.g. dyes, preservatives, fragrances). This situation requires submission of an FDA MedWatch form consistent with DAW1 guidelines. o Cannot consume the medication in any of the available formulations and the medication is medically necessary. o Commercial prescription product is unavailable due to a market shortage (or discontinued) and it is medically necessary. o Request is for 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate (even if bulk ingredients are used) for the prevention of preterm birth in women who are pregnant with a singleton pregnancy and have history of a prior spontaneous preterm birth. o Request is for a formulary antibiotic or anti-infective for injectable use
19 Last updated: 04/08/2018 NOTE: All compounds will require authorization and clinical review if total submitted cost exceeds $200.
The following compounds are examples of preparations that Aetna considers to be experimental and investigational, because there is inadequate evidence in the peer- reviewed published medical literature of their effectiveness. Bioidentical hormones and implantable estradiol pellets Nasal administration of nebulized anti-infectives for treatment of sinusitis Topical Ketamine, Muscle Relaxants, Antidepressants, NSAIDS, and Anticonvulsants products typically use for pain Proprietary bases: PCCA Lipoderm Base, PCCA Custom Lipo-Max Cream, Versabase Cream, Versapro Cream, PCCA Pracasil Plus Base, Spirawash Gel Base, Versabase Gel, Lipopen Ultra Cream, Lipo Cream Base, Pentravan Cream/Cream Plus, VersaPro Gel, Versatile Cream Base, PLO Transdermal Cream, Transdermal Pain Base Cream, PCCA Emollient Cream Base, Penderm, Salt Stable LS Advanced Cream, Ultraderm Cream, Base Cream Liposome, Mediderm Cream Base, Salt Stable Cream.
Cystic Fibrosis Pulmozyme will be authorized for patients that meet the following: Initial Approval: (pulmonary) Age >/= 5 years (Per label: Pulmozyme was studied in patients 3 months to 5 Kalydeco/Orkambi: Medications years of age; while clinical trial data are limited in patients <5 years, the use of 3 months Last reviewed: Pulmozyme should be considered for pediatric patients with CF who may 4/22/15 experience potential benefit in pulmonary function or who may be at risk of All others : indefinite respiratory tract infection. Pulmozyme Diagnosis of moderate to severe cystic fibrosis OR Renewal Bethkis Diagnosis of mild cystic fibrosis after failure of inhaled hypertonic saline (Kalydeco/Orkambi): Cayston 6 months Kalydeco Kitabis and Bethkis are the preferred formulary agents and may be authorized Orkambi when the following are met: Requires Diagnosis of cystic fibrosis documentation to support response to
20 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Age >/= 6 years therapy including
FEV1 between 25-80% predicted current lab results to Sputum cultures positive for P.aeruginosa support ALT/AST and NOT colonized with Burkholderia cepacia bilirubin levels (for Tobi Podhaler and tobramycin inhaled solution are non-formulary and require Orkambi) trial and failure of Kitabis AND Bethkis
Cayston will be authorized for patients that meet the following: Diagnosis of cystic fibrosis Age >/= 7 years
FEV1 between 25-75% predicted Sputum cultures positive for P.aeruginosa NOT colonized with Burkholderia cepacia Contraindication/intolerance to tobramycin
Kalydeco can be recommended for approval for patients who meet the following: Diagnosis of cystic fibrosis with one of the following CFTR gene mutations: G551D, G1244E, G1349D, G178R, G551S, S1251N, S1255P, S549N, S549R, or R117H NOT homozygous for the F508del mutation in the CFTR gene Age >/=2 years Note: all reviews must be sent to MDR for final decision
Orkambi can be recommended for approval for patients who meet the following: Prescribed by a pulmonologist Member is 12 years of age and older Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis and lab results to support homozygous F508Del at the CFTR gene. (If the patient’s genotype is unknown, an FDA-cleared CF
21 Last updated: 04/08/2018 mutation test should be used to detect the presence of the F508del mutation on both alleles of the CFTR gene) Current lab results to support normal ALT/AST and bilirubin NOT taking strong CYP3A inducers such as rifampin, rifabutin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, and St. John’s wort NOTE: Patients should be on other CF agents to manage and control symptoms (i.e., dornase alpha, tobramycin, hypertonic saline, or Cayston) Note: all reviews must be sent to MDR for final decision
Daliresp For patients who meet all of the following: Initial Approval: Last reviewed: Adult 40 years of age or older 6 months 06/15/15 Prescribed by or in consultation with a pulmonologist Diagnosis of severe COPD with chronic bronchitis with FEV1<50% predicted based Renewals: on post-bronchodilator FEV1 Indefinite; requires Documented symptomatic exacerbations within the last year while compliant with improvement in the dual long-acting bronchodilator treatment [long-acting beta-agonist (LABA) plus long-acting number of COPD muscarinic antagonist (LAMA)] for at least 3 months exacerbations Daliresp will be used in conjunction with a LABA and LAMA unless contraindicated/intolerant Will not be used in combination with theophylline Direct Renin For patients that meet the following: Initial Approval: Inhibitors Treatment of HTN Indefinite Last reviewed: At least 18 years old 06/15/15 Inadequate response or inability to tolerate a trial of a formulary ARB and Tekturna ACE inhibitor and at least one other formulary antihypertensive agent from a Tekturna HCT different class: Tekamlo o Thiazide-type diuretic Amturnide o Calcium channel blocker o Beta-blocker Will not be used in combination with an ACE inhibitor or an ARB
22 Last updated: 04/08/2018
Note: The long-term benefit on major cardiovascular or renal outcomes with direct renin inhibitors in the treatment of HTN has not been established, therefore it is recommended to use medications from other classes first. Duavee Duavee can be approved for adult women who have an intact uterus and who Initial Approval: Last reviewed: meet ONE of the following: 4/22/15 Treatment of vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause (VMS): 5 years o Patient has failed (or has contraindication/intolerance to) at least 2 formulary estrogen/progestin products (e.g., estradiol tablets/patch, Prempro, Estrace) Prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis: o Patient is at significant risk of osteoporosis Patient has tried and failed (or has contraindication/intolerance to) raloxifene and alendronate (non-estrogen medication is preferred) Elidel Elidel is covered for patients between 2 and 10 years of age. For other age Initial Approval: (pimecrolimus) groups, Elidel requires step therapy with topical corticosteroids. Indefinitely If patient has filled 2 topical corticosteroids in the last 60 days, the prescription Protopic will automatically process at the pharmacy. (tacrolimus) Prior Authorization will be required for prescriptions that do not process automatically at the pharmacy. In those cases, Elidel will be reviewed based upon the affected area being treated: o Body/extremities - after trial and failure or intolerance to at least 2 different formulary topical corticosteroids. o Face – after trial and failure of one formulary low-potency topical corticosteroid o Eyelid or other sensitive area – Elidel will be approved without trial and failure of topical corticosteroids
Protopic is covered after trial and failure of Elidel Anti-TNFS
23 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Enbrel, Humira, Remicade, Cimzia, Simponi
See Detailed document: https://www.mercymaricopa.org/assets/pdf/providers/pharmacy/PA %20Guidelines/Anti-TNFs-MMIC.PDF
Erythropoiesis- Epogen, Procrit, Aranesp Stimulating Agents = See Detailed document: https://www.mercymaricopa.org/providers/mmic/pharmacy
GnRH Analogs For patients who meet the following based on diagnosis: Initial Approval: Last reviewed: 7/1/15 Central Precocious Endometriosis Puberty Leuprolide acetate (Lupron Depot, Synarel, Zoladex [3.6 mg dose only]) Supprelin LA: Lupron Depot Prescribed by or in consultation with a gynecologist or obstetrician 12 months Lupron Depot-PED 18 years of age or older All others: 6 Eligard Trial and failure of at least one formulary hormonal cycle control agent months Trelstar (such as Portia, Ocella, Previfem), medroxyprogesterone, or Danazol Vantas Patient is not pregnant or breastfeeding Endometriosis Synarel 6 months Supprelin LA Uterine Leiomyoma (fibroids) Zoladex (Lupron Depot, Synarel, Zoladex [3.6 mg dose only]) Uterine Leiomyoma Prescribed by or in consultation with a gynecologist or obstetrician (fibroids) 18 years of age or older 6 months Prescribed to improve anemia and/or reduce uterine size for 3-6 Dysfunctional uterine months prior to planned surgical intervention bleeding Patient is not pregnant or breastfeeding 2 months
24 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Prostate/Breast Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding Cancer (Zoladex [3.6mg dose only]) 2 years Prescribed by or in consultation with a gynecologist or obstetrician 18 years of age or older Renewal: Prescribed to thin endometrium prior to planned endometrial ablation Central Precocious or hysterectomy within the next 4-8 weeks Puberty Patient is not pregnant or breastfeeding 6 months - 1 year (up to age Central Precocious Puberty (CPP) 11 for females (Lupron Depot-PED, leuprolide acetate solution, Synarel, Supprelin LA) and age 12 for Prescribed by, or in consultation with an Endocrinologist males) MRI or CT Scan has been performed to rule out lesions Requires clinical Onset of secondary sexual characteristics earlier than 8 years in response to females and 9 years in males treatment (i.e., Response to a GnRH stimulation test (or if not available, other labs pubertal slowing to support CPP such as luteinizing hormone levels, estradiol and or decline, testosterone level) height velocity, Bone age advanced 1 year beyond the chronological age bone age, LH, or estradiol and Baseline height and weight testosterone Age restriction (leuprolide acetate solution for injection [once daily level) regimen]): must be at least 1 year old Age restriction (Lupron Depot-Ped [1-month or 3-month regimen]): Endometriosis must be at least 2 years old Retreatment Lupron only Advanced Prostate Cancer (treatment with (Lupron Depot, Leuprolide acetate solution, Eligard, Zoladex,Vantas Trelstar) Synarel and Prescribed by, or in consultation with oncologist or urologist Zoladex not Age restriction: must be at least 18 years old recommended beyond 6
25 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Advanced Breast Cancer months): 6 (Zoladex [3.6mg dose only]) months Prescribed by, or in consultation with oncologist Requires: Age restriction: must be at least 18 years old o Bone mineral density within normal limits o Use in combination with norethindron e acetate
Uterine Leiomyoma (fibroids) or Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding Long-term use is not recommended Retreatment may be considered on a case by case basis
Growth Hormone Genotropin, Humatrope, Norditropin, Nutropin, Omnitrope, Saizen, Tev-Tropin, Zorbtive
See Detailed document: https://www.mercymaricopa.org/providers/mmic/pharmacy
26 Last updated: 04/08/2018
Hepatitis C Agents Sovaldi and Harvoni are the preferred agents Initial Approval Please click here for full Policy: Full course/ treatment http://mercymaricopa.org/assets/pdf/providers/pharmacy/Hepatitis_C_Treatment_Cr duration dependent iteria_MMIC.pdf upon genotype
Hetlioz For patients that meet all of the following: Initial Approval Last reviewed: At least 18 years old Indefinite 4/22/15 Diagnosis of non-24 sleep-wake disorder Completely blind with NO light perception History of at least 3 months of difficulty initiating sleep, difficulty awakening in the morning, or excessive daytime sleepiness No other concomitant sleep disorder (i.e., sleep apnea, insomnia)
Hyaluronic Acid Injection: Euflexxa, Hyalgan, Synvisc, Synvisc-ONE, Orthovisc, Supartz Agents Topical agents: See detailed document posted separately on website. Intial Approval: Topical: Bionect, Burns or dermatitis: HyGel, Hylira,XClair When used for treatment of burns, dermal ulcers, wounds, radiation 3 fills of generic dermatitis: agent Prescriber must be a dermatologist Xerosis: Patient must be at least 18 years old Up to 1,000 grams of When used for treatment of xerosis: equivalent Prescriber must be a dermatologist generic agent Trial and failure of ammonium lactate or a topical corticosteroid per 30 days for Patient must be at least 18 years old three months Renewal: 3 months Hyperlipidemia Crestor can be approved when the following criteria are met: Initial Approval:
27 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Medications Patient is at least 10 years old; AND PSCK9 inhibitors: 3 months Last reviewed: 6/15/15 Patient has failed to achieve LDL goal on a compliant regimen of maximum Juxtapid, Kynamro: 3 tolerated dose of atorvastatin; OR months Crestor Patient requires a high intensity statin (i.e., diagnosis of familial All others: 6 months hypercholesterolemia or high ASCVD risk per provider evaluation) AND Zetia patient had a trial and failure of atorvastatin Renewal: PSCK9 inhibitors: 6 months Lovaza Zetia requires step therapy: Juxtapid, Kynamro: 6 Vascepa If member has filled 2 prescriptions for 2 different statins (specifically months Epanova All others: indefinite atorvastatin, simvastatin or Crestor) within the last 130-days, the prescription will automatically process at the pharmacy. Repatha Renewals require Prior Authorization will be required for prescriptions that do not process Praluent improvement in fasting automatically at the pharmacy. lipids and Juxtapid In those cases, Zetia will be authorized upon receipt of documentation to documentation of Kynamro support the diagnosis of hyperlipidemia and failure of, or contraindication to recommended safety atorvastatin, simvastatin, and Crestor. monitoring parameters (such as liver Non-formulary medications for hypertriglyceridemia (Lovaza, Vascepa, and Epanova) can be enzymes) approved when the following criteria are met: Patient is at least 18 years old Drug will be used as an add-on to lifestyle interventions to include diet and exercise Treatment of severe hypertriglyceridemia (triglyceride level greater than or equal to 500 mg/dL) Trial and failure of OTC fish oil and at least ONE other formulary medication such as fenofibrate, fenofibric acid, gemfibrozil, or niacin or contraindication to all formulary agents PCSK9 Inhibitors (Repatha and Praluent) can be approved when ALL of the following criteria are met: Lab results support an LDL ≥300 mg/dL (within the past 90 days)
28 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Failure of a compliant, 60 day trial of 2 different high potency statins* (atorvastatin and Crestor) at maximum tolerated doses used in combination with Zetia, niacin, or a bile acid sequestrant The PCSK9 will be used in combination with maximum tolerated doses of a statin* in combination with Zetia, niacin, or a bile acid sequestrant In addition for diagnosis of Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH): o Patient has tried and failed or is not a candidate for LDL apheresis In addition for diagnosis of Primary Hypercholesterolemia non FH: o Chart notes support evidence of ASCVD or high CVD risk (i.e., history of AMI, MI, PCI, or CABG) NOTE: All requests must be forwarded to MDR for final approval
Juxtapid and Kynamro can be approved when ALL of the following criteria are met: Diagnosis of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia with a documented LDL of >300 mg/dl (within the past 90 days) Failure of a compliant, 60 day trial of 2 different high potency statins* (atorvastatin and Crestor) at maximum tolerated doses used in combination with Zetia, niacin, or a bile acid sequestrant Juxtapid or Kynamro will be used in combination with maximum tolerated doses of a statin* in combination with Zetia, niacin, or a bile acid sequestrant AND lifestyle interventions to include diet and exercise (low-fat diet recommended, <20% of calories from fat) Patient has tried and failed or is not a candidate for LDL apheresis Patient is at least 18 years old Recommended baseline labs are submitted: Fasting lipid panel, ALT, AST, alk phos, total bili, and negative pregnancy test (if applicable) Patient does not have moderate to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B or C) or active liver disease NOTE: All requests must be forwarded to MDR for final approval
29 Last updated: 04/08/2018 * Exception to statin therapy trials requires documentation of intolerance to at least 2 statins (at least one trial being a moderate to high potency statin). Documentation will include chart notes supporting skeletal muscle related symptoms that resolved when statin therapy was discontinued; and documentation the member has been rechallenged at a lower dose or with a different statin.
Idiopathic Non-formulary use of Esbriet or Ofev can be approved when the following are Initial Approval: 3 Pulmonary met: months Fibrosis Agents Diagnosis of mild to moderate idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Last reviewed: 06/16/15 o Confirmed by high resolution computed tomography (HRCT), lung Renewal: 6 months biopsy, or bronchoscopy Esbriet o Interstitial lung disease cannot be attributed to another cause (i.e., Criteria for renewal: Ofev rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, systemic sclerosis, asbestos exposure, or Documentation of hypersensitivity pneumonitis) stable FVC o Forced vital capacity (FVC) between 50 and 80% predicted (recommended to Documentation of baseline liver function tests (LFT’s) prior to initiating discontinue if there treatment is a >10% decline Patient age must be 18 years or greater in FVC over a 12 Patient is not a current smoker month period) Attestation that LFT’s Prescribed by, or in consultation with, a pulmonologist are being monitored
Note: There is no conclusive evidence to support the use of any drugs to increase the survival of people with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Imatinibvi Can be authorized for patients who meet the following: Approval Duration: Prescribed by an oncologist Last reviewed: 10/22/2015 GIST, CML, ASM, or Prescribed to treat one of the following FDA-approved or NCCN compendium listed indications: HES/CEL: Yearly o Primary treatment of Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ In the presence of CML) disease progression or o Newly diagnosed Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL) in combination with a demonstrated
30 Last updated: 04/08/2018 chemotherapy or corticosteroids insufficient response o Relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL) to therapy, a dose o Myelodysplastic / myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD) associated with PDGFR increase may be (platelet-derived growth factor receptor) gene rearrangements in adults considered in the o Aggressive systemic mastocytosis (ASM) absence of severe o Adults with Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and / or chronic eosinophilic leukemia adverse reactions (CEL) and/or cytopenias. o Unresectable, recurrent and / or metastatic dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) in adults o Soft tissue sarcoma – Desmoid tumors o Recurrent bone cancer- chordoma o Unresectable, recurrent, or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) o Kit (CD117) positive gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) after surgical resection Indications other *This list is not inclusive. All off-label use will be reviewed in nationally recognized than GIST, CML, ASM, compendia for the determination of medically-accepted indications. or HES/CEL: Yearly as long as there is no evidence of progressive disease or unacceptable toxicity.
Increlex For patients that meet the following: Initial Approval: Last reviewed: Prescribed by or in consultation with pediatric endocrinologist 6 months 4/22/15 Patient is ≥ 2 years old No evidence of epiphyseal closure Renewal: No evidence of neoplastic disease 6 months if at Documentation supports a diagnosis of Severe, Primary IGF-1 deficiency least doubling of o Height standard deviation score less than or equal to −3 pretreatment growth velocity o Basal IGF-1 standard deviation score less than or equal to −3 1 year if growth
31 Last updated: 04/08/2018 o Normal or elevated growth hormone (GH) levels velocity ≥ 2.5 o No evidence of secondary forms of IGF-1 deficiency, such as GH cm/yr and deficiency, malnutrition, hypothyroidism, or chronic treatment with epiphyses are pharmacologic doses of corticosteroids. open OR Documentation supports diagnosis of GH gene deletion and development of neutralizing antibodies to GH Initial: 1 year Inlytavii May be authorized when the following criteria are met: Patient is 18 years of age or older Last reviewed: 1/19/2016 Prescribed by an oncologist Renewal: 3 years with Patient does not have uncontrolled blood pressure evidence of stable disease Patient is not taking a strong CYP3A4 inducer or inhibitor (tumor size within 25% of Patient has relapsed or stage IV, unresectable, renal cell carcinoma (RCC) of predominant clear cell histology and has failed treatment with a formulary tyrosine baseline) kinase inhibitor (Nexavar, Sutent, or Votrient). Note: the formulary TKI’s require PA.
QLL: #120 tablets per 30 days Integrin Receptor This guideline describes the criteria for use of Tysabri and Entyvio in inflammatory bowel Initial Approval: Antagonists for diseases. To see the criteria for use in of Tysabri in MS, refer to the section titled, “MS Agents.” 3 months Inflammatory Bowel Diseases[ii] General Criteria: First Renewal: Last reviewed: 10/22/2015 Prescribed by a gastroenterologist 3 months 18 years of age or older Requires at Tysabri Will be used as monotherapy and NOT in combination with antineoplastic, least 20% symptom Entyvio immunosuppressive, or immunomodulating agents (e.g., azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine improvement cyclosporine, methotrexate, TNF-inhibitors) Additional Renewals: Additional Criteria for Inducing Remission in Crohn’s Disease: (Tysabri or Entyvio) 6 months
32 Last updated: 04/08/2018 STEROID-DEPENDENT CROHN’S : (if patient is Patient meets ONE of the following: responding) o Relapse occurs within three months of stopping glucocorticoids o Glucocorticoids cannot be tapered to <10 mg/day within three months NOTE: If member is unable to taper off of without symptom recurrence steroids in the first 6- Patient has failed a compliant, 3-month trial of ONE of the following: months, d/c Tysabri o 6-mercaptopurine(6-MP) or azathioprine (AZA) o Methotrexate (for patients with a contraindication to 6-MP and AZA) Patient has failed a compliant, 3-month trial of ONE formulary anti-TNF
STEROID-REFRACTORY CROHN’S: Inadequate response to IV glucocorticoids within 7-10 days (NOTE: it is recommended to switch to IV glucocorticoids for patients who are not responding to oral glucocorticoids) Patient has failed a compliant, 3-month trial of ONE formulary anti-TNF
Additional Criteria for Steroid-Dependent Ulcerative Colitis: (Entyvio) Relapse occurs within three months of stopping glucocorticoids OR tapering prednisone to <10 mg/day Patient has failed a compliant, 3-month trial of ONE of the following: o 6-mercaptopurine(6-MP) or azathioprine (AZA) o Sulfasalazine 4-6g per day, mesalamine 4.8g per day, or balsalazide 6.75g per day (if patient has a contraindication to 6-MP and AZA) Patient has failed a 3-month trial of ONE formulary anti-TNF
Additional Criteria for Steroid-Refractory Ulcerative Colitis: (Entyvio) Inadequate response to IV glucocorticoids within 7-10 days (NOTE: it is recommended to switch to IV glucocorticoids FIRST for patients who are not responding to oral glucocorticoids)
33 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Patient meets ONE of the following: o Patient had a previous failure on 6-MP and AZA or a contraindication to both medications and is therefore not a candidate for treatment with these agents for current episode o Patient has symptoms after surgical intervention o Patient is not a surgical candidate or refuses surgery AND had an inadequate response to cyclosporine (NOTE: Switching to anti-TNF’s after cyclosporine failure is NOT recommended by clinical practice guidelines) o Patient has a contraindication to cyclosporine (NOTE: cyclosporine is used as a bridge therapy for patients who will be started on the slower acting 6- MP or AZA) Patient has failed a 3-month trial of ONE formulary anti-TNF
IL-17 Antagonistsviii May be authorized for Plaque Psoriasis when the following criteria is met: Initial Approval: Last reviewed:10/22/2015 Patient is at least 18 years old 6 months Prescribed by a dermatologist Cosentyx Patient is up to date with all recommended vaccinations Renewal: Patient has been screened for latent TB 2 years, with clinical Symptoms are not controlled with topical therapy notes documenting an Disease has a significant impact on physical, psychological or social wellbeing improvement (e.g., Patient has failed a 3-month compliant trial with MTX or cyclosporine or has a reduction in PASI, true contraindication to both decreased Psoriasis is severe and extensive (for example, more than 10% of body surface swollen/painful joints) area affected or a PASI score of more than 10) Phototherapy has been ineffective, cannot be used or has resulted in rapid relapse (rapid relapse is defined as greater than 50% of baseline disease severity within 3 months) Patient has failed a compliant, 3-month trial of BOTH Enbrel and Humira or has contraindications to both
34 Last updated: 04/08/2018
Anticoagulants Fragmin, fondaparinux, and enoxaparin should pay at the point of sale for an Initial Approval: -Injectable[i] initial duration of 21days without a PA. Prophylaxis post Last reviewed: 10/21/2015 ortho surgery) For prescriptions of enoxaparin, fondaparinux, and Fragmin that do not pay Up to 35 days Enoxaparin at the point of sale, prior authorization requests can be authorized for the Fondaparinux following indications: Prophylaxis (non-ortho Fragmin All 3 agents: Iprivask surgery and major o VTE prophylaxis in patients undergoing hip or knee replacement or hip trauma) fracture surgery Up to 14 days o VTE treatment in patients who are taking warfarin until the INR is in therapeutic range for 2 days Prophylaxis (post- o Bridge therapy for perioperative warfarin discontinuation surgery with CA) o Prophylaxis or treatment of thrombotic complications in a high risk 4 weeks pregnancy VTE prophylaxis in patients with restricted mobility during acute illness o VTE treatment, bridge Treatment of superficial vein thrombosis (SVT) of the lower limb of at o therapy, acute illness least 5 cm in length 10 days or as o Treatment of acute upper-extremity DVT (UEDVT) that involves the requested axillary or more proximal veins Fragmin and enoxaparin only: High risk pregnancy o VTE treatment after trial and failure of warfarin or for patients who are Until 6 weeks not candidates for warfarin after delivery o VTE treatment in patients who have cancer (EDC required o VTE prophylaxis in cancer patients with solid tumors who are at high for risk of thrombosis (i.e., previous VTE, immobilization, hormonal authorization) therapy, angiogenesis inhibitors, thalidomide, and lenalidomide) o VTE prophylaxis in patients with AFib undergoing cardioversion (up to Prophylaxis in cancer 3 weeks before and 4 weeks after) 6 months o VTE prophylaxis in patients with acute ischemic stroke and restricted
35 Last updated: 04/08/2018 mobility Upper extremity DVT o VTE prophylaxis in patients undergoing general and abdominal-pelvic 3 months surgery who are at moderate to high risk for VTE o VTE prophylaxis in patients with major trauma Lower-limb SVT 45 days Iprivask may be authorized if all the following criteria are met: VTE prophylaxis in patients undergoing hip replacement surgery VTE treatment for Patient had therapeutic failure or intolerance to enoxaparin or Fragmin and warfarin failure or in fondaparinux cancer OR 6 months Patient has contraindication to enoxaparin, fondaparinux, and Fragmin (i.e., allergic to pork, history of heparin induced thrombocytopenia) Renewal: Length of renewal authorization based on anticipated length of therapy, indication and/or recent INR if on warfarin Injectable Forteo, zoledronic acid, Prolia Osteoporosis Agents See Detailed document: https://www.mercymaricopa.org/assets/pdf/providers/pharmacy/PA %20Guidelines/Injectable-OP-Agents-MMIC.PDF
Insulin Pens Note: Insulin Pens will process without PA for members age <19 Initial Approval: Humalog Pen Adults: Indefinite Humalog Mix For patients who meet the following: Children: through PenHumulin o Patient is a school-aged child requiring multiple daily injections of insulin 18 years of age 500U/M Pen Lantus OR
36 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Solostar Pen o Patient is unable to effectively use insulin vials and syringes to self- Levemir Pen administer insulin due to at least one of the following: o Member has uncorrectable visual disturbances (e.g., macular degeneration, retinopathy, vision uncorrectable by prescription glasses) OR o Member is a brittle diabetic or has a physical disability or dexterity problems due to stroke, peripheral neuropathy, trauma, or other physical condition AND o Member does not have a caregiver who can administer insulin using vials and syringes. Interferonsix Chronic Hepatitis B Infection: (Intron A, Pegasys) Hairy cell leukemia: Last reviewed: 10/22/2015 Patient has HBeAg-positive or HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B (HBsAg positive for 6 months more than six months) α-Interferon Prescribed by, or in consultation with an infectious disease physician, HIV specialist, Condylomata Infergen gastroenterologist, hepatologist, or transplant physician acuminate: Intron A Patient has compensated liver disease (e.g., normal bilirubin, albumin within normal 3 weeks Pegasys limits, no cytopenias) Pegintron All other indications: Sylatron There is evidence of viral replication (HBeAg titer and/or HBV DNA levels >20,000 IU/mL for HBeAg-positive patients and >2000 IU/mL for HBeAg-negative patients) 1 year β-Interferon There is evidence of liver inflammation (e.g., elevated ALT, inflammation or fibrosis on Renewal: See Multiple liver biopsy) Sclerosis Agents Age restriction (Pegasys): Must be at least 18 years old Age restriction (Intron A): Must be at least 1 year old Hepatitis B: Intron A: additional γ-Interferon 16 weeks if still Actimmune AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma: (Intron A [powder for solution ONLY]) Prescribed by, or in consultation with an infectious disease physician or HIV specialist HBeAg-positive Not being used for the treatment of visceral AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma associated Intron A: up to 2 with rapidly progressive disease years for HBeAg- Patient must be at least 18 years old negative patients
37 Last updated: 04/08/2018
Hairy-cell Leukemia: (Intron A) Osteopetrosis: Prescribed by, or in consultation with a hematologist/oncologist 1 year if no Patient has demonstrated less than complete response to cladribine or pentostatin or has evidence of disease relapsed within 1 year of demonstrating a complete response progression Patient has indications for treatment such as: o Systemic symptoms – fatigue, weakness, weight loss, fever, night sweats, recurrent CGD: infection 1 year if number o Symptomatic splenomegaly or adenopathy and/or severity of o Significant cytopenias – hemoglobin < 12 g/dL, platelets < 100,000/mcL, or ANC < infections has 1000/mcL decreased Patient is at least 18 years old Condylomata Malignant Melanoma: (Intron A, Sylatron) acuminate: Prescribed by, or in consultation with a hematologist/oncologist 16 weeks Patient has undergone surgical resection AND is at high risk for recurrence (e.g., primary tumor > 4 mm thick, presence of ulceration, lymph node involvement) All other indications: Patient is at least 18 years old 1 year
Chronic Granulomatous Disease: (Actimmune) Prescribed by, or in consultation with an immunologist or infectious disease specialist Patient is also receiving antifungal and antibacterial prophylaxis (such as itraconazole and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole) Patient is at least 1 year old
Malignant Osteopetrosis: (Actimmune) Prescribed by, or in consultation with a hematologist/oncologist Prescribed for the treatment of severe, malignant osteopetrosis Patient is at least 1 year old
38 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Condylomata acuminata (genital or venereal warts): (Intron A, Alferon N-HPV) Patient at least 18 years old For intralesional use Lesions are small and limited in number Trial and failure of topical treatments or surgical technique ( ie imiquimod cream, Condylox, cryotherapy, laser surgery, electrodessication, surgical excision)
This list is not inclusive. All off-label use will be reviewed in nationally recognized compendia for the determination of medically-accepted indications. Intravaginal For patients that meet the following: Initial Approval: Progesterone Prescribed by a provider of obstetrical care Approve as requested products Patient is not on Makena (17-hydroxyprogesterone) until 37 weeks Last reviewed: Patient is pregnant and has 1 of the following: gestation 4/22/15 o Patient has a short cervix OR progesterone Patient is at high risk for pregnancy loss based on other risk factors capsules, Crinone, First-progresterone suppositories Jakafix Criteria for the use in myelofibrosis: Initial: 6 months Last reviewed: 01/19/2016 Patient is at least 18 years old Prescribed by, or in consultation with, a hematologist/oncologist Renewal: 1 year; if Diagnosis of primary myelofibrosis, post-polycythemia vera myleofibrosis or post-essential benefit is demonstrated, thrombocythemia myelofibrosis as evidenced by spleen Intermediate or high risk disease defined as having two or more of the following risk factors size reduction (at least o Age > 65 years 35% decrease), symptom o Constitutional symptoms (weight loss > 10% from baseline or unexplained fever or improvement and excessive sweats persisting for more than 1 month) absence of disease o Hemoglobin < 10g/dL progression. o WBC count > 25 x 109/L
39 Last updated: 04/08/2018 o Peripheral Blood blasts > 1% Therapy should be Baseline complete blood count (CBC) with platelet count of at least 100 X 109/L prior to gradually tapered if initiating therapy patient fails to achieve at least 35% decrease from Criteria for the use in polycythemia vera: baseline in spleen Patient is at least 18 years old volume or experiences Prescribed by, or in consultation with, a hematologist/oncologist unacceptable toxicities Previous treatment failure with hydroxyurea Patient has splenomegaly and requires phlebotomy to control symptoms QLL: #60 tablets per 30 Baseline Hct of 40-45% days Long acting STEP criteria for Oxymorphone ER: Initial Approval: Opioids Oxycontin Treatment of chronic pain 1 year Butrans Patch At least 18 years old Exalgo Failed a minimum of 2 week trials of maximum tolerated doses of at least Renewal: Oxymorphone ER TWO formulary long-acting opioids (i.e., fentanyl patch, morphine sulfate ER, 1 year Zohydro ER methadone) OR have contraindications to all formulary agents. Xartemis XR Nucynta ER) Criteria for Oxycontin and other Non-Formulary Long-Acting Opioids: Treatment of malignant pain and pain due to sickle cell anemia (Oxycontin) OR Treatment of chronic non-malignant pain: o At least 18 years old o Failed a minimum of 2 week trials of maximum tolerated doses of at least THREE formulary long-acting agents (i.e., fentanyl patch, morphine sulfate ER, methadone, oxymorphone ER) one of which must be oxymorphone ER OR o Contraindication to all formulary long-acting agents
40 Last updated: 04/08/2018 OR Treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (Nucynta ER only): o At least 18 years old o Failed an adequate trial (at least 4 weeks at maximum tolerated doses) of duloxetine and tramadol and at least ONE additional formulary medication (i.e., gabapentin, amitriptyline, nortriptyline, or topical capsaicin) OR o Contraindications to all formulary agents
Lyrica[iv] Lyrica is authorized for members who are 18 years of age or older with a diagnosis Initial Approval: Last reviewed: 10/21/2015 of post herpetic neuralgia or partial onset seizures. Indefinite
Criteria for the diagnosis of fibromyalgia: Patient is 18 years of age or older Failure of a compliant 3-month trial of BOTH of the following: o Duloxetine at maximum tolerated doses o Gabapentin OR a tricyclic antidepressant (i.e., amitriptyline or nortriptyline) at maximum tolerated doses
Criteria for the diagnosis of neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, spinal cord injury, or cancer-related neuropathic pain: Patient is 18 years of age or older Trial and failure of a compliant 3-month trial of duloxetine AND at least 1 other generic formulary agent such as topical capsaicin, tricyclic antidepressants, tramadol, venlafaxine, or gabapentin at maximum tolerated doses
41 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Modafinil/Nuvigil[v] Modafanil is the preferred formulary agent, however still requires PA. Nuvigil is non- Initial Approval: Last reviewed: 10/21/2015 formulary and may be authorized if the patient meets criteria and also has a documented 6 months trial and failure of modafanil. Renewal: May be authorized for patients at least 17 years old for excessive daytime sleepiness 1 year associated with narcolepsy when the following is met: Requires a response to Diagnostic testing, such as multiple sleep latency test (MSLT) or polysomnography, supports treatment diagnosis of narcolepsy For OSA: patient must May be authorized for patients at least 17 years old for excessive daytime sleepiness be compliant with CPAP or BIPAP associated with Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) when the following is met: Prescribed by, or in consultation with, a sleep specialist For SWD: patient must Polysomnography has confirmed the diagnosis of OSA still be a shift-worker Patient remains symptomatic despite compliance with CPAP or BIPAP for at least 1 month CPAP or BIPAP will be continued after modafinil or Nuvigil is started The daytime fatigue is significantly impacting, impairing, or compromising the patient’s ability to function normally
May be authorized for patients at least 17 years old for excessive daytime sleepiness associated with Shift-Work Disorder (SWD) when the following is met: Prescribed by, or in consultation with, a sleep specialist Polysomnography has ruled out other types of sleep disorders Symptoms have been present for >3 months The sleepiness is significantly impacting, impairing, or compromising the patient’s ability to function normally
May be authorized for patients at least 17 years old for the treatment of excessive sleepiness associated with idiopathic hypersomnia when the following criteria is met: Prescribed by, or in consultation with, a sleep specialist
42 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Trial and failure of 2 formulary stimulants (e.g., amphetamine/dextroamphetamine, methylphenidate) Diagnosis is supported by polysomnography, MSLT, and clinical evaluation including the following: o Daily periods of irrepressible need to sleep or daytime lapses into sleep for at least three months o MSLT documents fewer than two sleep-onset rapid eye movement periods (SOREMPs), or no SOREMPs if the REM sleep latency on the preceding polysomnogram was ≤15 minutes o The presence of at least one of the following: . MSLT shows a mean sleep latency of ≤8 minutes . Total 24-hour sleep time is ≥660 minutes (typically 12 to 14 hours) on 24-hour polysomnography or by wrist actigraphy in association with a sleep log o Other causes of sleep disorder have been ruled out The sleepiness is significantly impacting, impairing, or compromising the patient’s ability to function normally
Multaq Multaq will be authorized when prescribed by, or in consultation with a Initial Approval: cardiologist. If not prescribed by or in consultation with a cardiologist, the Indefinite following must be met: Diagnosis is atrial fibrillation Patient has tried and failed amiodarone Age restriction: must be at least 18 years old
Multiple Sclerosis Aubagio, Avonex, Betaseron, Copaxone, Extavia, Gilenya, Glatopa, glatiramer, Lemtrada, Agents Mitoxantrone, Plegridy, Rebif, Tecfidera, Tysabri
See Detailed document:
43 Last updated: 04/08/2018 https://www.mercymaricopa.org/assets/pdf/providers/pharmacy/MS-Disease- Modifying-Agents-MMIC.pdf
Neumegaxi May be authorized for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced Initial Approval: Last reviewed: 10/22/2015 thrombocytopenia when the following are met: Up to 21 days’ Prescribed by a hematologist/oncologist supply Patient is at least 12 years old Refills if number Patient has a non-myeloid malignancy and is receiving myelosuppressive of cycles chemotherapy provided Patient is at high risk of severe thrombocytopenia or has experienced severe thrombocytopenia with a previous chemotherapy cycle Renewal: Administered 6 – 24 hours after the completion of chemotherapy Approval up to 1 NOT being used in the following situations: year Requires recent After myeloablative therapy o platelet count o Chemotherapy regimen longer than 5 days Concurrently with agents associated with delayed myelosuppression (e.g., nitrosoureas, mitomycin C)
Nexavarxii Nexavar, when prescribed by an oncologist for patients at least 18 years old, can be authorized Initial: 1 year for the following indications: Last reviewed: 1/19/2016 Treatment of relapsed or unresectable stage IV predominantly clear cell renal cell Renewal: 3 years if carcinoma (RCC) after treatment failure with Sutent or Votrient evidence of stable Treatment of relapsed or unresectable stage IV NON-clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) disease (tumor size after treatment failure with Sutent within 25% of baseline) Treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in a patient who is not a transplant candidate Treatment of metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma Treatment of differentiated thyroid carcinoma that is refractory to radioactive iodine treatment
44 Last updated: 04/08/2018
Note: Patients with advanced cardiac conditions should not receive Nexavar. Note: Nexavar should not be used in combination with a strong CYP3A4 inducer (e.g., dexamethasone, phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin, rifabutin, rifapentin, phenobarbital, St. John's Wort) unless there is no alternative to the CYP3A4 inducer
Non-Calcium For patients that meet all of the following: Initial Approval: Based Phosphate Treatment of hyperphosphatemia due to ESRD Indefinite Binders Receiving dialysis Last reviewed: At least 18 years old 4/22/15 Failed Renvela or Renagel (sevelamer) AND failed a calcium-based phosphate binder or has contraindications to both. (Note: Patients with elevated total serum calcium after correcting for albumin should not receive a calcium-based product) Fosrenol
Non-Formulary Diabetic Test Strip and Glucometer Quantity Limits: Initial Approval: Diabetic Supplies All diabetic test strips are limited to #150 per/30 days Indefinite Glucometers are limited to 1 glucometer/12 months Criteria to Receive Non-Formulary Diabetic Supplies Member with hematocrit level that is chronically less than 30% or greater than 55% Member with physical limitation (manual dexterity or visual impairment) that limits utilization of formulary product Member with an insulin pump that requires a specific test strip
Criteria to Receive >150 Test Strips Per Month Members newly diagnosed with diabetes or with gestational diabetes Children with diabetes (age ≤ 12 ) Members on insulin pump Members on high intensity insulin therapy with documentation of need to
45 Last updated: 04/08/2018 routinely test more than 4-5 times daily
Criteria to Receive >1 Glucometer Per Year Current glucometer is unsafe, inaccurate, or no longer appropriate based on patients medical condition o Current glucometer no longer functions properly, has been damaged, or was lost or stolen.
Northera For patients that meet all of the following: Initial Approval: Last reviewed: At least 18 years old 6 months 4/22/15 Patient has a diagnosis of symptomatic neurogenic orthostatic hypotension (NOH) caused by primary autonomic failure (e.g., Parkinson's disease, Renewal: multiple system atrophy, or pure autonomic failure), dopamine beta- Indefinite hydroxylase deficiency, or non-diabetic autonomic neuropathy Patient has tried and failed or has contraindication/intolerance to fludrocortisone and midodrine Onychomycosis Luzu can be approved as non-formulary for members who meet the following: Initial (Luzu): and Tinea Topical treatment of tinea pedis, tinea cruris, and tinea corporis. 30 days Last reviewed: At least 18 years old 4/22/15 Failure of OR contraindication to terbinafine cream Renewal (Luzu): Failure of at least 1 other formulary topical antifungal agents (ie clotrimazole, 30 days if responding ciclopirox, econazole, ketoconazole, miconazole, etc.) OR contraindication to to therapy Luzu all formulary agents Jublia Jublia or Kerydin: Kerydin Jublia or Kerydin can be approved as non-formulary for members who meet 48 weeks the following: Treatment of onychomycosis of the toenails with ONE of the following comorbidities: o Diabetes o HIV
46 Last updated: 04/08/2018 o Immunosuppression (i.e. receiving chemotherapy, taking long term oral corticosteroids, taking anti-rejection medications) o Peripheral vascular disease o Pain caused by the onychomycosis At least 18 years old Failure of 2 OR contraindication to all formulary antifungal agents indicated for onychomycosis (ie ciclopirox, griseofulvin, itraconazole and terbinafine tablets) Orenciaxiii General authorization criteria for all indications: Initial Approval: Last reviewed: 10/22/2015 Prescribed by a rheumatologist 4 months Patient is NOT on another biological DMARD Patient is up to date with all recommended vaccinations Renewals: Patient has been screened for latent TB and hepatitis B Indefinite
In addition, May be authorized for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) when the following are Renewals require at least met: 20% symptom Patient is at least 18 years old improvement If patient has COPD, the prescriber confirms that the benefit of using Orencia outweighs the risk in the patient Patient has moderate or high disease activity despite an adequate 3-month trial of BOTH of the following: o 2 different oral DMARD regimens (1 of which must include methotrexate (MTX) unless contraindicated) . Monotherapy: MTX, sulfasalazine (SSZ), or leflunomide (LEF) . Combination: MTX+SSZ+hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), MTX+HCQ, MTX+LEF, MTX+SSZ, SSZ+HCQ o Humira AND Enbrel (Note: these agents also require PA)
In addition, May be authorized for Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) when the following are met:
47 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Patient is at least 6 years old Request is for the IV formulation For SEVERE Polyarticular JIA: o Patient has failed an adequate 3-month trial with BOTH Humira and Enbrel For MODERATE Polyarticular JIA: o Patient has failed an adequate 3-month trial of MTX o Patient has failed an adequate 3-month trial of BOTH Enbrel and Humira For Systemic JIA: o Patient does NOT have currently ACTIVE systemic features (i.e., fever, evanescent rash, lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, or serositis) o Patient has continued synovitis in >1 joint despite treatment for 3 months with MTX or leflunomide AND both Humira and Enbrel
Otezla For moderate to severe psoriatic arthritis: Initial Approval: Last reviewed: Age is 18 years or older 3 months 4/22/15 Prescribed by or in consultation with a rheumatologist Trial and failure of methotrexate for three consecutive months (or Renewal: documentation showing contraindication) 12 months Trial and failure of Humira or Enbrel for three consecutive months (or documentation showing contraindication, non-responsiveness or diminished Requires: response over time) Patient experiencing For moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: positive response Age is 18 years or older to therapy. Prescribed by or in consultation with a dermatologist Patient is not Trial and failure of UVB or PUVA therapy or documentation showing experiencing contraindication) depression and/or Trial and failure of methotrexate for three consecutive months (or suicidal thoughts. documentation Patient has no
48 Last updated: 04/08/2018 showing contraindication) significant weight Trial and failure of Humira or Enbrel for three consecutive months (or loss. documentation showing contraindication, non-responsiveness or diminished response over time) Oral Platelet Effient or Brilinta can be approved for patients who meet the following: Initial Approval Inhibitors Diagnosis of ACS (unstable angina, STEMI, NSTEMI) (Effient and Brilinta): Last reviewed: 07/1/15 Failure or contraindication/intolerance to clopidogrel, including patients 12 months identified as CYP2C19 poor metabolizers Effient No active pathological bleeding, history of intracranial hemorrhage, or Indefinite approval can Brilinta planned CABG be given to patients Zontivity In addition, for Effient: with a history of stent 1. Age <75 unless patient is considered high thromboembolic risk thrombosis/restenosis 2. Taking concomitant 75-325mg/day aspirin 3. No history of TIA or stroke Initial Approval In addition, for Brilinta: (Zontivity): 1. Taking concomitant 75-100mg/day aspirin Indefinite 2. No severe hepatic impairment 3. No concomitant use with medications known to interact with Brilinta Renewals (Effient (i.e., potent CYP3A4 inhibitors/inducers and simvastatin or lovastatin and Brilinta): in doses >40mg/day) without provider documentation that benefit 12 months; requires outweighs the risk documentation from cardiologist that risk of Zontivity can be approved for patients who meet the following: thrombosis outweighs Prescribed for the secondary prevention of atherothrombosis in patients with bleeding risk with long- PAD or history of MI (drug NOT indicated for ACS) term use of Must be used with aspirin and/or clopidogrel according to the standard of antiplatelets care for the patient’s diagnosis No evidence of contraindications: history of stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), or intracranial hemorrhage (ICH); or active pathological bleeding Promacta Chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP): Initial Approval:
49 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Last reviewed: Patient is at least 18 years old 1 month 4/22/15 Patient had insufficient response to corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or splenectomy Renewal: Promacta is being used to prevent major bleeding (not in an attempt to achieve ITP and aplastic anemia: Indefinite platelet counts in the normal range i.e., 150,000-450,000/mm3) HCV: 1 year Interferon-induced thrombocytopenia : Patient is at least 18 years old Renewal Patient has chronic hepatitis C with severe thrombocytopenia which prevents requirements: initiation or ability to maintain interferon-based therapy Platelet count of at least 50,000/mm3 Severe aplastic anemia (response rates should Patient is at least 18 years old be seen at least 1 Patient has a diagnosis of severe aplastic anemia defined by at least 2 of the week after initiation of following: therapy with a o Neutrophil count < 0.5 x 109 /L maximum response o Platelet count <20 x 109/L seen at 2 weeks) 9 Severe aplastic o Reticulocyte count < 20 x 10 /L (value may be given as percent of RBCs) anemia response to Trial of or contraindication to first line treatment including allogeneic stem cell transplantation from an appropriate sibling donor or immunosuppressive treatment would be therapy with a combination of cyclosporine A and antithymocyte globulin indicated by (ATG) hematologic response in at least one lineage – platelets, RBC or WBC. Proton Pump Omeprazole OTC tablets, omeprazole rx capsules, First-omeprazole Initial Approval: Inhibitors (PPI) suspension, First-lansoprazole suspension, lansoprazole caps, and Adults: Aciphex, Nexium, pantoprazole are available on the formulary without priore authorization. indefinitely Dexilant Authorization of Non-Formulary Proton Pump Inhibitors requires trial and failure Children: 3-6 of 2 formulary PPIs. months
50 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Renewal: Children: 3-6 months at a time Pulmonary Arterial Adcirca, Adempas, epoprostenol, Letairis, Opsumit, Remodulin, Revatio (sildenafil), Hypertension Tracleer, Tyvaso, Ventavis, Uptravi (PAH) See Detailed Document: https://www.mercymaricopa.org/providers/mmic/pharmacy
Ranexa[vi] For patients age 18 years of age or older who meet all of the following: Initial Approval: Last reviewed: 10/22/2015 Diagnosis of chronic angina Indefinite Patient meets ONE of the following: - Ranexa is prescribed as ADD-on therapy after failure to achieve therapeutic benefit on at least 1 formulary agent from EACH of the following 3 drug classes: . Beta blockers: acebutolol, atenolol, carvedilol, metoprolol, nadolol, propranolol . Calcium channel blockers: amlodipine, diltiazem, felodipine, isradipine, nifedipine, nicardipine, verapamil . Long acting nitrates: Isosorbide dinitrate, isosorbide mononitrate, nitroglycerin patch - Has a documented contraindication or intolerance to beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, AND long-acting nitrates - Revlimidxiv May be authorized when prescribed by an oncologist for patients at least 18 years old for Initial Approval: 6 Last reviewed: 1/19/2016 any of the following diagnoses: months Multiple myeloma (MM) when used with dexamethasone Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) after relapse or progression with two prior therapies, one Renewal: of which includes Velcade®(bortezomib) MDS: 6 months if benefit Transfusion-dependent anemia associated with low- or intermediate-1 risk is demonstrated, as
51 Last updated: 04/08/2018 myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) POSITIVE for the del(5q) cytogenetic abnormality. evidenced by transfusion (Transfusion dependence is defined as having ≥ 2 units of red blood cells within 8 weeks independence within the of treatment) past two months. Transfusion-dependent anemia associated with low- or intermediate-1 risk MDS that is NEGATIVE for the del(5q) cytogenetic abnormality AND Multiple Myeloma, o serum EPO >500 mU/mL AND Mantle Cell Lymphoma: o Patient has any of the following characteristics: 3 years if benefit is . Age >60 years old demonstrated, as . >5% marrow blasts evidenced by absence of . Non-hypocellular marrow disease progression. . HLA-DR15 negative . PNH clone negative
Second Gleevec (a first generation TKI) is the preferred agent for CML and ALL (see Gleevec guideline for PA Initial: 1 year coverage criteria). Gleevec should NOT be used in patients who have had a treatment failure with a Renewal: 3 years Generation second generation TKI. Tasigna is the formulary preferred second generation TKI and is subject to approved as long as Tyrosine Kinase the PA criteria included below. there is no evidence of disease Inhibitors for CML Second Generation TKI’s when prescribed for adult patients (at least 18 years of age) by an progression or oncologist may be authorized when the following criteria are met: unacceptable toxicity. and ALL xv Patient has ONE of the following diagnoses: Last reviewed: 10/30/2015 o Philadelphia chromosome positive or BCR-ABL1 positive chronic myeloid leukemia Renewals should be Bosulif (Ph+ CML) in chronic phase or accelerated phase based on Iclusig o Relapsed, refractory Ph+ CML in blast phase when it is of lymphoid type (not documentation of Sprycel myeloid) major cytogenetic Tasigna o Relapsed, refractory Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL) o NOTE: The efficacy of TKI’s has not been evaluated in clinical trials for the treatment response (≤35% Ph+ of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) metaphases) and until In addition for Tasigna (formulary with PA) patient has ONE of the following: disease progression or o Intolerance, disease progression, or resistance to prior therapy with Gleevec death
52 Last updated: 04/08/2018 o Intolerance, disease progression, or resistance to prior therapy with a second generation TKI (Sprycel, Bosulif, or Iclusig) o Presence of any of the following mutations that are resistant to Gleevec: F317L/V/I/C, T315A, V299L In addition for Sprycel or Bosulif (non-formulary) patient has ONE of the following: o Intolerance, disease progression, or resistance to prior therapy with Gleevec AND Tasigna o Intolerance, disease progression, or resistance to prior therapy with a second generation TKI (Tasigna, Bosulif, Sprycel or Iclusig) o Presence of any of the following mutations that are resistant to Gleevec and Tasigna: Y253H, E255K/V, F359V/C/I In addition for Iclusig (non-formulary) patient has ONE of the following: o Intolerance, disease progression, or resistance to prior therapy with all other TKI’s (Gleevec, Tasigna, Sprycel, and Bosulif) Presence of the T315I mutation that is resistant to other TKI’s Stelaraxvi May be authorized for Plaque Psoriasis when the following criteria is met: Initial Approval: Last Patient is at least 18 years old 6 months reviewed:10/5/2015 Prescribed by a dermatologist Symptoms are not controlled with topical therapy Renewal: Disease has a significant impact on physical, psychological or social wellbeing 2 years, with clinical Patient has failed a 3-month compliant trial with MTX or cyclosporine or has a notes documenting an true contraindication to both improvement (e.g., Psoriasis is severe and extensive (for example, more than 10% of body surface reduction in PASI, area affected or a PASI score of more than 10) decreased Phototherapy has been ineffective, cannot be used or has resulted in rapid swollen/painful joints) relapse (rapid relapse is defined as greater than 50% of baseline disease severity within 3 months) NOTE: Safety and Patient has failed a compliant, 3-month trial of BOTH Humira and Enbrel efficacy of ustekinumab have not been May be authorized for Psoriatic Arthritis when the following criteria is met: established beyond 2
53 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Patient is at least 18 years old years of use Prescribed by a dermatologist or rheumatologist Patient is currently on an NSAID which will be continued when Stelara is initiated OR has a contraindication to NSAID use Patient meets ONE of the following: o Has active PsA despite a 3-month trial of adequate dose MTX (or leflunomide or sulfasalazine if MTX is contraindicated) o Patient has predominantly axial disease AND active PsA despite a 3- month trial of TWO different NSIADs at an adequate dose OR has a contraindication to NSAID use Patient has failed a compliant, 3-month trial of BOTH Humira and Enbrel
Sucraidxvii May be authorized when the following criteria is met: Initial Approval: 2 Last reviewed: 01/19/2016 Prescribed by a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, or genetic specialist months Member does not have secondary (acquired) disaccharidase deficiencies Documentation to support the diagnosis of congenital sucrose-isomaltase Renewal: 12 months deficiency has been submitted: o Diagnosis of congenital sucrose-isomaltase deficiency has been Requires: confirmed by low sucrose activity on duodenal biopsy and other Documentation to disaccharidases normal on same duodenal biopsy support a response to o If small bowel biopsy is clinically inappropriate, difficult, or inconvenient to treatment with Sucraid perform, the following diagnostic tests are acceptable alternatives (all (weight gain, must be performed and results submitted): decreased diarrhea, . Stool pH less than 6; AND increased caloric . Breath hydrogen increase greater than 10 ppm following fasting intake, decreased sucrose challenge; AND gassiness, abdominal . Negative lactose breath test pain).
Sutentxviii Can be authorized when prescribed by an oncologist for adult patients (at least 18 years old), for Initial: 1 year
54 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Last reviewed: 1/19/2016 the following indications: Treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) after disease progression on or Renewal: 3 years if intolerance to imatinib stable disease (tumor Treatment of relapsed or unresectable stage IV renal cell carcinoma (RCC) size within 25% of Treatment of progressive, well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET) in baseline) patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease in combination with or after disease progression on a somatostatin analog (i.e. octreotide, Sandostatin LAR) o Patients with an insulinoma do not require treatment with a somatostatin analog for approval
Note: Patients with advanced cardiac conditions should not receive Sutent. Note: Sutent should not be used in combination with a strong CYP3A4 inducer (e.g., dexamethasone, phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin, rifabutin, rifapentin, phenobarbital, St. John's Wort) unless there is no alternative to the CYP3A4 inducer Note: Patients receiving strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may require a lower dose to avoid toxicity.
Symlin For patients that meet all of the following: Initial Approval: Diagnosis of Type 1 or Type 2 DM Indefinite Prescribed by, or in consultation with an endocrinologist Patient is 18 years of age or older Patient is currently on mealtime bolus insulin (e.g., Novolog, Humalog) Patient failed to achieve desired glucose control with optimal insulin therapy Patient does not have any of the following: o Hypoglycemia unawareness or recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia o Gastroparesis o Poorly controlled diabetes (e.g., A1c > 9%) o Poor adherence to current insulin regimen
55 Last updated: 04/08/2018
Tarcevaxix When prescribed by an oncologist for patients at least 18 years old, can be authorized for the Initial: 1 year following indications: Last reviewed: 1/19/2016 Metastatic pancreatic cancer when used in combination with gemcitabine (Gemzar) in patients Renewal: 3 years if with a good performance status benefit (control of tumor Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that is positive for a sensitizing epidermal growth growth, or disease- factor receptor (EGFR) mutation [i.e., exon 19 deletions or exon 21 (L858R) substitution] related symptom Locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC after failure of at least one prior chemotherapy regimen improvement) Locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC that remains stable (no disease progression) after 4 to 6 cycles of platinum-based first-line chemotherapy since platinum-based chemotherapy is NOT Tx should be recommended beyond 6 cycles discontinued if any of the Treatment of relapsed or unresectable stage IV NON-clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) following occur: Interstitial Lung Note: Tarceva should not be used with PPI’s. If taken concomitantly with H2-receptor Disease (ILD) antagonists (i.e., ranitidine), Tarceva should be dosed 10 hours after and 2 hours before Severe hepatic taking the H2-receptor antagonist. toxicity that does not resolve Severe renal failure Severe bullous, blistering or exfoliating skin conditions Corneal perforation or severe ulceration
QLL (25mg tablets): #60 per 30 days QLL (100 and 150mg tablets): #30 per 30 days Thalomidxx May be authorized when prescribed by an oncologist for patients at least 12 years old for Initial Approval: 6
56 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Last reviewed: 1/19/2016 any of the following diagnoses: months Multiple myeloma (MM) when used with dexamethasone OR Erythema nodosum leprosum OR Renewal: Chronic or subacute cutaneous systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) after trial and 3 years if benefit is failure of topical corticosteroids AND 2 of the following for a duration of at least 12 demonstrated, as weeks: evidenced by absence of o Hydroxychloroquine disease progression. o Chloroquine o Methotrexate o Azathioprine o Cyclosporine o Cyclophosphamide o Mycophenolate Sulfasalazine Topical NSAIDs Criteria for Approval: Initial Approval: Last reviewed: 07/01/15 A. Age 18 or older Flector Patch: 1 month B History of or high risk for adverse GI effects associated with oral NSAID use AND All others: 1 year Voltaren gel trial and failure of celecoxib; OR Pennsaid C High risk for other adverse effects associated with oral NSAID use (i.e., CHF, Renewal: Flector patch renal failure, concomitant use of lithium); OR Flector Patch: 1 month D. Failure on TWO formulary NSAIDs All others: 1 year E. Diagnosis of OA of knee or hand for Voltaren gel F. Diagnosis of OA of knee for Pennsaid
Note: Flector patch is only FDA approved for acute pain. Requests for Flector patch for chronic pain should be denied. If patient meets all other criteria above, offer Voltaren Gel or Pennsaid as an alternative.
The risk factors that correlate strongly to adverse GI effects of oral NSAID use are: History of GERD, GI bleed, or ulcer
57 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Chronic oral steroid use Current anticoagulant or antiplatelet use Age 65 or greater
Tranexamic acid For patients who meet all of the following: Initial Approval: (generic Lysteda) Premenopausal female with diagnosis of cyclic heavy menstrual bleeding (menstrual flow >7days) Indefinite Trial and failure, intolerance or contraindication to oral NSAIDs Maximum of 30 tablets - Trial and failure, intolerance or contraindication to oral hormonal cycle control agents per 30days or refuses oral hormonal cycle control agents Age restriction: 12 years of age or order
Tykerbxxi May be authorized when prescribed by an oncologist for patients at least 18 years old who have Initial: 1 year ONE of the following indications: Last reviewed: 1/19/2016 Hormone-receptor positive, HER2 positive metastatic breast cancer: Renewal: 3 years based o Used in combination with letrozole on therapeutic response o Patient is postmenopausal or until disease HER2 positive advanced/recurrent or metastatic breast cancer: progression or o Disease has progressed after receiving prior therapy with an anthracycline unacceptable toxicity (doxorubicin, daunorubicin, epirubicin, idarubicin), a taxane (paclitaxel, docetaxel), AND trastuzumab (Herceptin) Requires no evidence of: o Used in combination with capecitabine or Herceptin severe hepatotoxicity interstitial lung Note: Tykerb should not be given to patients with an abnormal LVEF. disease Note: Tykerb should not be used in combination with a strong CYP3A4 inducer (e.g., dexamethasone, phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin, rifabutin, rifapentin, phenobarbital, St. John's Wort) unless there is no alternative to the CYP3A4 inducer
Velphoro For patients that meet all of the following: Initial Approval: Diagnosis of hyperphosphatemia 1 year At least 18 years old Receiving dialysis Renewal:
58 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Failed at least 2 formulary phosphate binding agents such as calcium acetate 1 year capsules or tablets, sevelamer carbonate (Renvela), or Renagel
Viscosupplements Hyalgan, Gel-One, Euflexxa, Synvisc, Orthovisc
See Detailed document: https://www.mercymaricopa.org/assets/pdf/providers/pharmacy/Viscosupplements- MMIC.pdf
Votrientxxii Votrient can be authorized when prescribed by an oncologist for a patient at least 18 years old for Initial: 1 year any of the following indications: Last reviewed: 1/19/2016 Diagnosis of relapsed or unresectable stage IV predominantly clear-cell renal cell carcinoma Renewal: 3 years if (RCC) evidence of stable Diagnosis of advanced soft tissue sarcoma after treatment with a prior chemotherapy disease (tumor size within 25% of baseline) Note: Votrient should not be used in combination with a strong CYP3A4 inducer (e.g., and ALT is <8 times ULN. dexamethasone, phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin, rifabutin, rifapentin, phenobarbital, St. Patients with ALT John's Wort) unless there is no alternative to the CYP3A4 inducer between 3 and 8 times Note: Patients receiving strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may require a lower dose to avoid toxicity. ULN should have ALT monitored weekly until <3 times ULN
Weight Reduction For patients who meet all of the following: Initial Approval: Medications BMI ≥ 30 kg/m 2 (obese) 3 months Xenical OR Renewal: Belviq BMI ≥ 27kg/m2 (overweight) and one of the following obesity-related chronic Xenical and Belviq: Bontril diseases and risk factors: 3 months Didrex o Coronary heart disease Requires
59 Last updated: 04/08/2018 phentermine o Dyslipidemia: documentation of a Tenuate . HDL <35mg/dl or weight loss of at least Qsymia . LDL ≥ 160mg/dL, or 4 pounds per month Contrave . Triglycerides ≥ 400mg/dl o Controlled hypertension (less than> 140/90mm Hg) All others: o Type II diabetes mellitus Treatment beyond 3 o Sleep apnea months is not o Polycystic ovary syndrome recommended and is considered “off label” o OA For Xenical: no contraindications such as chronic malabsorption syndrome, Additional Renewal: cholestasis, hepatic disease, hypersensitivity to orlistat, pregnancy Xenical and Belviq: For Belviq: no contraindications such as pregnancy, concurrent use with 6 months to 1 year (no (SSRIs), (SNRIs), (MAOIs), triptans, bupropion, dextromethorphan, St. John’s more than 4 years) wort Requires documentation For Contrave: member has been abstinent from opioids for a minimum of 7 showing member continues – 10 days (up to 14 days if taking long-acting opioid) prior to starting weight loss plan and has naltrexone/bupropion, including treatment of alcohol dependence. maintained at least 67% of All others: no contraindications such as uncontrolled cardiovascular disease their initial weight loss to (cardiac arrhythmias, stroke, TIA, CHF, advanced artherosclerosis), date uncontrolled hypertension (>140/90), hyperthyroidism, psychiatric disorder (depression, schizophrenia, seizures), substance abuse, concurrent use or within 14 days of MAOI therapy, pregnancy No concurrent use of other weight loss medications Patient will be using the requested drug as an adjunct to caloric restriction and physical activity program Age restriction (phentermine, Bontril): must be at least 16 years old Age restriction (Xenical, Didrex): must be at least 12 years old Age restriction (Tenuate, Qsymia, Belviq, Contrave): must be at least 18 years old
60 Last updated: 04/08/2018 Xeljanzxxiii May be authorized for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) when the following are met: Initial Approval: Last reviewed: 10/22/2015 Patient is at least 18 years old 3 months Prescribed by a rheumatologist Patient is NOT on a biological DMARD or azathioprine or cyclosporine Renewal: Patient is up to date with all recommended vaccinations Indefinite Patient has been screened for latent TB and hepatitis B Patient has moderate or high disease activity despite an adequate 3-month trial Renewals require at of BOTH of the following: least 20% symptom o 2 different non-biologic DMARD regimens (1 of which must include improvement methotrexate (MTX) unless contraindicated) . Monotherapy: MTX, sulfasalazine (SSZ), or leflunomide (LEF) . Combination: MTX+SSZ+hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), MTX+HCQ, MTX+LEF, MTX+SSZ, SSZ+HCQ o BOTH Humira and Enbrel (Note: both Enbrel and Humira require PA) Xolair For the treatment of moderate-severe persistent asthma: Initial Approval: Last reviewed: 07/01/15 Prescribed by, or after consultation with a pulmonologist or Asthma: 6 months allergist/immunologist 12 years of age or older Chronic urticaria: 3 Baseline IgE levels between 30-700 IU/ml months Weight is less than 150 kg (330 lbs) Allergic sensitization demonstrated by positive skin testing or in vitro testing for allergen-specific IgE to an allergen that is present year round (a perennial Renewal: allergen), such as dust mite, animal dander, cockroach, or molds Asthma: 1 year Requires demonstration of Evidence of reversible disease (12% or greater improvement in FEV1 with at least a 200-ml increase or 20% or greater improvement in PEF as a result of clinical improvement (e.g., a short-acting bronchodilator challenge ↓ use of rescue Patient should be non-smoking or actively receiving smoking cessation medications or systemic treatment corticosteroids, ↑ in FEV1 from pre-treatment Patient has tried and failed conventional immunotherapy or immunotherapy is
61 Last updated: 04/08/2018 not indicated. (Immunotherapy has demonstrated efficacy against dust mites, baseline, ↓ in number of animal dander, and pollens but not against molds and cockroach allergies). ED visits or Asthma symptoms are not adequately controlled by high dose inhaled hospitalizations) and corticosteroids AND a long-acting beta agonist (LABA) for 6 months compliance with asthma o Inadequate control is defined as: controller medications, and . Requirement for systemic corticosteroids (oral, parenteral) to non-smoking status. treat asthma exacerbations OR Chronic urticaria: 6 months . Daily use of rescue medications (short-acting inhaled beta-2 Requires agonists) demonstration of adequate symptom OR control (e.g., ↓ itching) . 2 ED visits or 1 hospitalization for asthma in the last 12 months OR . 2-3 unscheduled office visits with documentation of intensive care for acute asthma exacerbation OR . Nighttime symptoms occurring more than once a week
For the treatment of chronic urticaria: Symptoms continuously or intermittently present for at least 6 weeks. Prescribed by an allergist/immunologist or dermatologist 12 years of age or older Currently receiving H1 antihistamine therapy Failure of a 4 week, compliant trial of at least two high dose H1 antihistamines AND Failure of a 4-week, compliant trial of at least one of the following medications (used in addition to H1 antihistamine therapy): o Leukotriene inhibitor (montelukast or zafirlukast) o H2 antihistamine (ranitidine or cimetidine)
62 Last updated: 04/08/2018 o Doxepin AND Failure of a 4 week, compliant trial of low dose cyclosporine (used in addition to H1 antihistamine therapy) or contraindication to cyclosporine.
NOTE: Anti-inflammatory medications (dapsone, sulfasalazine, or hydroxychloroquine) may be useful in treating urticaria, however the evidence is limited
**Note: Off-label and not covered for diagnosis of Allergic Rhinitis or food allergy**
63 i Afinitor References: 1. Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled phase III trial. The Lancet. 2008 2. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Kidney Cancer. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/kidney.pdf Version 3.2015. Accessed September 8, 2015. 3. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Breast Cancer. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf. Version 3.2015. Accessed September 8, 2015. 4. Besalga J, Campone M, Piccart M, et al. Everolimus in postmenopausal hormone-receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012 Feb 9;366(6):520-9. 5. National Guideline Clearinghouse (NGC). Guideline summary: Guidelines on renal cell carcinoma. In: National Guideline Clearinghouse (NGC). http://www.guideline.gov/content.aspx? id=45321&search=advanced+renal+cell+carcinoma#Section420. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ); cited 2015 August 10. Available: http://www.guideline.gov. 6. Owens, James. Tuberous sclerosis complex: Management. In UpToDate, Post TW (Ed.), Waltham, MA, (accessed on August 10,2015). 7. Torres, Vicente. Renal angiomyolipomas. In UpToDate, Post TW (Ed.), Waltham, MA, (accessed on August 10, 2015). 8. Chan Ang, Jennifer. Metastatic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and poorly differentiated gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine carcinomas: Systemic therapy options to control tumor growth and symptoms of hormone hypersecretion. In UpToDate, Post TW (Ed.), Waltham, MA, (accessed August 10, 2015). 9. Ellis, Matthew. Treatment approach to metastatic hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: Endocrine therapy. In UpToDate, Post TW (Ed.), Waltham, MA, (accessed August 10, 2015). 10. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Neuroendocrine Tumors. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/neuroendocrine.pdf. Version 1.2015. Accessed September 8, 2015. ii Ampyra References 1. Drug Facts and Comparisons on-line. (www.drugfacts.com), Wolters Kluwer Health, St. Louis, MO. Updated periodically 2. National Multiple Sclerosis Society Disease Management Consensus Statement-Recommendations from the MS Information Sourcebook; 2007 Update. National Multiple Sclerosis Society. Available at: http://www.nationalmssociety.org/For- Professionals/Clinical-Care/Managing-MS. Accessed on Sept 2, 2014
[ii][ii] Cambia References 1. Cambia [full prescribing information]. Newark, CA: Depomed Inc.; Revised 01/2014. 2. Marmura MJ, Silberstein SD, Schwedt TJ. The Acute Treatment of Migraines in Adults: The American Headache Society Evidence Assessment of Migraine Pharmacotherapies. Headache. 2015;55:3-20. iii Xeloda References 1. Xeloda [capecitabine] prescribing information. South San Francisco, CA: Genentech, inc. Updated: March, 2015. 2. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Colon Cancer. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/colon.pdf. Version 2.2016. Accessed December 17, 2015. 3. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Anal Carcinoma. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/anal.pdf. Version 2.2015. Accessed November 4, 2015. 4. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Brest Cancer. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf. Version 1.2016. Accessed December 17, 2015. 5. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/pancreatic.pdf. Version 2.2015. Accessed December 17, 2015. iv Caprelsa References 1. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Thyroid Carcinoma. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/thyroid.pdf. Version 2.2015. Accessed September 8, 2015. 2. Aetna CPB: Antineoplastics Accessed August 2015 3. Vandetanib. In: Clinical Pharmacology Online. Atlanta, GA: Elsevier / Gold Standard; [Updated 7/30/2014;Accessed August 2015] http://clinicalpharmacology-ip.com/Forms/Monograph/monograph.aspx?cpnum=3722&sec=monindi&t=0
[iii][iii] Celecoxib References 1. Standard, G. (2013, May 13). Celebrex. Tampa, Florida, USA. Retrieved August 27, 2015from http://www.clinicalpharmacology-ip.com/Forms/Monograph/monograph.aspx?cpnum=689&sec=monindi&t=0 v Cometriq References 1. Cabozantinib. [Prescribing Information]. Exelixis. San Francisco, CA. November 2012. 2. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Thyroid Carcinoma. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/thyroid.pdf. Version 2.2015. Accessed September 8, 2015. 3. Medullary thyroid cancer: management guidelines of the American Thyroid Association, accessed September 2015 4. American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force, Kloos RT, Eng C, Evans DB, Francis GL, Gagel RF, Gharib H, Moley JF, Pacini F, Ringel MD, Schlumberger M, Wells SA Jr. Thyroid. 2009;19(6):565. vi Imatinib References 1. Demetri, D George MD. Morgan, Jeffrey MD. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy for advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. In UpToDate, Post TW (ed.), Waltham, MA (accessed on August 31, 2015). 2. Imatinib: Drig Information. In UpToDate, Post TW (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA. (Accessed on August 31, 2015. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/imatinib-drug-information? source=search_result&search=gleevec&selectedTitle=1%7E128. 3. National Guideline Clearinghouse (NGC). Guideline summary: The role of cytotoxic therapy with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: update of the 2006 evidence-based review. In National Guideline Clearinghouse (NGC). http://www.guideline.gov/content.aspx?id=36630&search=imatinib. Rockville (MD): Agnecy for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ); cited 2015 August 31. Available : http://www.guideline.gov. 4. Gleevec [full prescribing information]. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis U.S.; Revised 02/2013 5. NCCN Drugs and Biologics Compendium http://www.nccn.org/professionals/drug_compendium/MatrixGenerator/Matrix.aspx?AID=18 accessed 3/18/2010, 3/24/11, 3/27/12 6. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Practice Guidelines in Oncology – Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia, Version 1.2016 09/17/2015. 7. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Practice Guidelines in Oncology – Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, Version 1.2015 09/17/2015 8. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Practice Guidelines in Oncology – Bone Cancer, Version 1.2015 09/17/2015 9. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Practice Guidelines in Oncology – Soft Tissue Sarcoma, Version 1.2015 09/17/2015. 10. Alvarado Y, Apostolidou E, Swords R, Giles FJ. Emerging therapeutic options for Philadelphia-positive acute lymphocytic leukemia. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2007 Mar;12(1):165-79 11. National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE). Imatinib for the treatment of unresectable and/or metastatic gastro-intestinal stromal tumours. London (UK): National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE); 2004 Oct. 38 p. 12. Pardanani A, Ketterling RP, Brockman SR, et al: CHIC2 deletion, a surrogate for FIP1L1-PDGFRA fusion, occurs in systemic mastocytosis associated with eosinophilia and predicts response to imatinib mesylate therapy. Blood 2003 Nov 1; 102(9): 3093-6 13. McArthur G. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: Recent Clinical Progress. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007 Jul 24 14. Fletcher S, Bain B. Diagnosis and treatment of hypereosinophilic syndromes. Curr Opin Hematol. 2007 Jan;14(1):37-42 vii Inlyta References: 1. Inlyta (axitinib) [package insert]. NY, NY; Pfizer: Revised January 2012. 2. Rini BI, Escudier B, Tomczak P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of axitinib versus sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): a randomized phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011;378:1931-39. 3. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Kidney Cancer. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/kidney.pdf Version 3.2015. Accessed September 8, 2015. 4. Inlyta. In: Clinical Pharmacology online. Gold Standard: [Updated June 24, 2015; Accessed August 26, 2015]. http://www.clinicalpharmacology-ip.com/Forms/Monograph/monograinph.aspx? cpnum=3751&sec=mondesc&t=0
[ii][ii] Integrin Receptor Antagonist References 1. Terdiman JP, Gruss CB, Heidelbaugh JJ, Sultan S, Falck-Ytter YT. American gastroenterological association institute guideline on the use of thiopurines, methotrexate, and anti–TNF-a biologic drugs for the induction and maintenance of remission in inflammatory crohn’s disease. Gastroenterol. 2013;145:1459–1463. 2. The Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Ulcerative colitis practice guidelines in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:501-523. 3. Farrell RJ, Peppercorn MA. Overview of the medical management of severe or refractory Crohn disease in adults. Waltham, MA: UpToDate; Last modified June 10, 2015. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-the-medical- management-of-severe-or-refractory-crohn-disease-in-adults? source=search_result&search=crohns&selectedTitle=2%7E150. Accessed October 1, 2015 4. Cohen RD., Stein AC. Approach to adults with steroid-refractory and steroid-dependent ulcerative colitis. Waltham, MA: UpToDate; Last modified July 2015. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/approach-to-adults-with-steroid- refractory-and-steroid-dependent-ulcerative-colitis?source=see_link. Accessed August 11, 2015. 5. Peppercorn MA., Farrell RJ. Management of severe ulcerative colitis. Waltham, MA: UpToDate; Last modified July 2015. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/management-of-severe-ulcerative-colitis? source=search_result&search=ulcerative+colitis&selectedTitle=2%7E150. Accessed August 11, 2015 viii IL-17 Antagonist References: 1. Cosentyx (secukinumab) [package insert]. East Hanover, NJ; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; January 2015. 2. Feldman SR. Treatment of psoriasis. Waltham, MA: UptoDate; Last modified July 13, 2015. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-of-psoriasis? source=search_result&search=psoriasis&selectedTitle=1%7E150#H42. Accessed September 25, 2015. 3. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). Psoriasis: the assessment and management of psoriasis. London (UK): National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE); 2012 Oct. 61 p. (NICE clinical guideline; no. 153).
[i][i] Injectable Anticoagulants References 1. Drug Facts and Comparisons on-line. (www.drugfacts.com), Wolters Kluwer Health, St. Louis, MO. Updated periodically 2. Clinical Pharmacology [Internet database]. Gold Standard Inc. Tampa, FL. Updated periodically. 3. PL Detail-Document, Comparison of Injectable Anticoagulants. Pharmacist’s Letter/Prescriber’s Letter. August 2012,26(9):260902 4. Kahn SR., Lim W., Dunn AS., et al. Prevention of VTE in nonsurgical patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines), Chest 2012; 141 (Suppl 2): e195S-e226S 5. Gould MK., Garcia DA., Wren SM,, et al. Prevention of VTE in Nonorthopedic Surgical Patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012; 141 (Suppl 2): e227S-e277S 6. Falck-Ytter Y., Francis CW., Johanson NA,, et al. Prevention of VTE in Orthopedic Surgery Patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012; 141 (Suppl 2): e278S-e325S 7. Douketis JD., Spyropoulos AC., Spencer FA., et al. Perioperative Management of Antithrombotic Therapy: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence- Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012; 141 (Suppl 2): e326S-e350S 8. Kearon C., Akl EA., Comerota AJ., et al. Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2_suppl):e419S-e494S. 9. You JJ., Singer DE., Howard PA., et al. Antithrombotic Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2_suppl):e531S-e575S 10. Lansberg MG., O’Donnell MJ., Khatri P., et al. Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy for Ischemic Stroke: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence- Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2_suppl):e601S-e636S. 11. Bates SM., Greer IA., Middeldorp S., et al. VTE, Thrombophilia, Antithrombotic Therapy, and Pregnancy: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence- Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2_suppl):e691S-e736S. ix Interferon References: 1. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. (2014, August 11). Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C. Retrieved September 13, 2014, from American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Infectious Diseases Society of America: http://www.hcvguidelines.org/fullreport 2. Gold Standard, Inc. (2013, October 13). Interferon Gamma-1b. Clinical Pharmacology. Tampa, FL, USA. Retrieved September 13, 2014, from http://www.clinicalpharmacology-ip.com 3. Gold Standard, Inc. (2014, April 22). Interferon Alfa-2b. Clinical Pharmacology. Tampa, FL, USA. Retrieved from http://www.clinicalpharmacology-ip.com 4. Gold Standard, Inc. (2014, April 22). Interferon Alfacon-1. Clinical Pharmacology. Tampa, FL, USA. Retrieved from http://www.clinicalpharmacology-ip.com 5. Gold Standard, Inc. (2014, August 18). Peginterferon Alfa-2b. Clinical Pharmacology. Tampa, FL, USA. Retrieved September 13, 2014, from http://www.clinicalpharmacology-ip.com 6. Lok, A. S., & McMahon, B. J. (2009, September). Chronic Hepatitis B: Update 2009. Retrieved September 14, 2014, from American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: www.aasld.org 7. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. (2014, April 22). Melanoma. Retrieved September 13, 2014, from NCCN Guidelines: http://www.nccn.org 8. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. (2014, August 22). Non-Hodgkin's Lymphomas. Retrieved September 13, 2014, from NCCN Guidelines : http://www.nccn.org 9. Rosenzweig, S. D., & Holland, S. M. (2014, January 24). Chronic granulomatous disease: Treatment and prognosis. Retrieved September 13, 2014, from Up To Date: http://www.uptodate.com 10. Schering Corporation. (2014, August). Infergen. Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA. 11. Sosman, J. A. (2014, June 10). Adjuvant immunotherapy for melanoma. Retrieved September 13, 2014, from Up To Date: http://www.uptodate.com 12. Tallman, M. S. (2014, February 13). Treatment of hairy cell leukemia. Retrieved September 13, 2014, from Up To Date: http://www.uptodate.com 13. The NIH Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center. (2012, December). Osteopetrosis Overview. Retrieved from http://www.niams.nih.gov/health_info/bone/ 14. Thomson Micromedex. (2014, August 08). DRUGDEX System. Retrieved September 13, 2014, from Interferon Gamma: http://www.thomsonhc.com x Jakafi References 1. Jakafi™(ruxolitinib) tablets prescribing information. Incyte, Corp. Greenville, NC; June, 2012. 2. Cervantes F, Dupriez B, Pereira A, et al. New prognostic scoring system for primary myelofibrosis based on a study of the International Working Group for Myelofibrosis Research and Treatment. Blood 2009;113:2895-2901. 3. Harrison C, Kiladjian J-J, Al-Ali HK, et al. JAK inhibition with ruxolitinib versus best available therapy for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med 2012;366:787-98. 4. Verstovsek S, Mesa RA, Gotlib J, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ruxolitinib for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med 2012;366:799-807. 5. Tefferi A. Prognosis and treatment of polycythemia vera. Waltham, MA: UptoDate; Last modified April 2, 2015. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/prognosis-and-treatment-of-polycythemia-vera? source=search_result&search=polycythemia+vera&selectedTitle=2%7E116#H3815834. Accessed October 30, 2015. 6. Tefferi A. Prognosis and treatment of primary myelofibrosis. Waltham, MA: UptoDate; Last modified September 9, 2015. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/prognosis-and-treatment-of-primary-myelofibrosis? source=search_result&search=myelofibrosis&selectedTitle=2%7E75#H6939591. Accessed October 30, 2015.
[iv][iv] Lyrica References 1. Decker, J. E., & Hergenroeder, A. C. (2012, September 21). Overview of cervical spinal cord and cervical peripheral nerve injuries in the child or adolescent athlete. Retrieved from Up To Date: http://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-cervical-spinal-cord-and-cervical-peripheral-nerve-injuries-in-the- child-or-adolescent-athlete? source=preview&search=pain+due+to+spinal+cord+injury&selectedTitle=7%7E150&language=en- US&anchor=H2#H13 2. Gold Standard, Inc. (2012, June 21). Pregabalin. Retrieved September 13, 2014, from Clinical Pharmacology: http://www.clinicalpharmacology-ip.com 3. Gold Standard, Inc. (2013, May 09). Gabapentin. Retrieved September 13, 2014, from http://www.clinicalpharmacology-ip.com 4. Portenoy, R. K., Ahmed, E., & Keilson, Y. Y. (2014, July 30). Cancer pain management: Adjuvant analgesics (coanalgesics). Retrieved September 13, 2014, from Up To Date: http://www.uptodate.com/contents/cancer-pain- management-adjuvant-analgesics-coanalgesics? source=machineLearning&search=neuropathic+pain+treatment&selectedTitle=3%7E150§ionRank=1&anchor= H18#H21 5. Thomson Micromedex. (2014, September 11). Duloxetine. DRUGDEX System. Greenwood Village, CO. Retrieved September 13, 2014, from DRUGDEX System: http://www.thomsonhc.com 6. Thomson Micromedex. (2014, September 10). Gabapentin. Greenwood Village, CO. Retrieved September 13, 2014, from http://www.thomsonhc.com 7. Thomson Micromedex. (2014, September 10). Pregabalin. Greenwood Village, CO. Retrieved September 13, 2014, from http://www.thomsonhc.com 8. Goldenberg D.L. (July 2015 ). Initial treatment of fibromyalgia in adults. UpToDate. (P.H. Schur, P.L. Romain, Eds.) Waltham, MA. Retrieved August 27, 2015, from http://www.uptodate.com/contents/initial-treatment-of-fibromyalgia- in-adults?source=search_result&search=fibromyalgia&selectedTitle=2%7E136#H352171909
[v][v] Modafinil/Nuvigil 1. Gold Standard, Inc. Clinical Pharmacology [database online]. Available at: http://www.clinicalpharmacology.com. Accessed .August 2015 2. Fosnocht, KM. Approach to the adult patient with fatigue. In: UpToDate, Fletcher, RH (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA. (Accessed on August 15, 2014.) 3. Escalante, CP. Cancer-related fatigue: Treatment. In: UpToDate, Hesketh, PJ (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA. (Accessed on August 15, 2014.) 4. Lavault, S., Dauvilliers, Y., Drouot, X., Leu-Semenescu, S., Golmand, J.-L., Lecendreux, M., et al. (2011). Benefit and risk of modafinil in idiopathic hypersomnia vs. narcolepsy. Sleep Medicine, 550-556. 5. Bruera E, Y. S. (2014, May 8). Palliative care: Overview of fatigue, weakness, and asthenia. Retrieved September 15, 2014, from Uptodate: http://www.uptodate.com 6. Chevrin R, C. (2014, April 23). Idiopathic hypersomnia. Retrieved September 15, 2014, from Up To Date: http://www.uptodate.com. 7. Nuvigil prescribing information. Cephalon, Inc. July 2008. 8. Provigil prescribing information. Cephalon, Inc. March 2008. 9. Stankoff B, Waubant E, Confavreux C,, et al. Modafinil for fatigue in MS: a randomized placebo-controlled double- blind study. Neurology. 2005;64(7):1139-1143. xi Neumega References 1. Neumega. . In: DRUGDEX System (Micromedex 2.0). Greenwood Village, CO: Truven Health Analytics; c1974-2014. http://nv- ezproxy.roseman.edu:3305/micromedex2/librarian/ND_T/evidencexpert/ND_PR/evidencexpert/CS/B11C95/ND_AppProduct/ evidencexpert/DUPLICATIONSHIELDSYNC/2B8F26/ND_PG/evidencexpert/ND_B/evidencexpert/ND_P/evidencexpert/PFAction Id/evidencexpert.IntermediateToDocumentLink? docId=1757&contentSetId=31&title=OPRELVEKIN&servicesTitle=OPRELVEKIN. (Accessed on April 9, 2015). xii Nexavar References 1. Nexavar prescribing information. Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals Inc;Wayne, NJ: Updated July 2015. 2. Bukowski R, Cella D, Gondek K, et al. Effects of sorafenib on symptoms and quality of life: results from a large randomized placebo-controlled study in renal cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 2007 Jun;30(3):220-7 3. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Hepatobiliary Cancers. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/hepatobiliary.pdf. Version 2.2015. Accessed October 30, 2015. 4. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Thyroid Carcinoma. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/thyroid.pdf. Version 2.2015. Accessed October 30, 2015. 5. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Kidney Cancer. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/kidney.pdf. Version 1.2016. Accessed October 30, 2015. xiii Orencia References: 1. Orencia (abatacept) [package insert]. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; Revised June 2015. 2. Singh JA, Furst DE, Bharat A, et al. 2012 update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2012;64(5):625-639. 3. Ringold S, Weiss PF, Beukelman T, et al. 2013 update of the 2011 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: recommendations for the medical therapy of children with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and tuberculosis screening among children receiving biologic medications. Arthritis Care Res. 2013;65(10):1551-1563. 4. Weiss PF. Polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Clinical manifestations and diagnosis. Waltham, MA: UptoDate; Last modified September 29, 2015. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/polyarticular-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-treatment? source=search_result&search=juvenile+arthritis&selectedTitle=8%7E150 Accessed October 5, 2015. [vi][vi] Ranexa References 1. Fihn SD, G. J. (December 2012). 2012 American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association/American College of Physicians/American Association for Thoracic Surgery/Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association/Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions/Socie. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, Volume 60 Issue 24. 2. Gold Standard, Inc. (2013, Decemember 25). Ranexa. Retrieved August 25, 2015, from ClinicalPharmacology: http://www.clinicalpharmacology.com 3. Kannam, J. e. (201, August 12). Stable ischemic heart disease: Overview of care . Retrieved August 25, 2015, from Up to Date: http://www.uptodate.com. 4. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Management of stable angina. NICE Clinical Guideline 126 (July 2011). From https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg126/chapter/1-Guidance#anti-anginal-drug-treatment Accessed September 17, 2015. xiv Revlimid References 1. Revlimid® (lenalidomide) prescribing information. Celgene Corp., June 2013. 2. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Multiple Myeloma. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/myeloma.pdf. Version 2.2016. Accessed December 10, 2015. 3. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Myelodysplastic Syndrome. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/mds.pdf. Version 1.2016. Accessed December 10, 2015. xv Second Generation TKI References 1. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/cml.pdf. Version 1.2015. Accessed September 8, 2015. 2. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/all.pdf. Version 1.2015. Accessed September 8, 2015. 3. Bosulif [full prescribing information]. New York, NY: Pfizer U.S.; Revised 09/2013. 4. Gleevec [full prescribing information]. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis U.S.; Revised 02/2013. 5. Cortes JE, et al, Bosutinib Versus Imatinib in Newly Diagnosed Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Results From the BELA Trial. J Clin Oncol, 2012;30(28):3486-3492. 6. Cortes JE, et al, Safety and efficacy of bosutinib (SKI-606) in chronic phase Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia patients with resistance or intolerance to imatinib. Blood. 2011;118(17): 4567-4576. 7. Khoury HJ, et al, Bosutinib is active in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia after imatinib and dasatinib and/or nilotinib therapy failure. Blood, 2012;119(15)3403-3412. 8. Shieh MP, Mitsuhashi M, LillyM. Moving on up: Second-Line Agents as Initial Treatment for Newly-Diagnosed Patients with Chronic Phase CML. Clin Med Insights Oncol, 2011;5:185-199. 9. Antineoplastics - Pharmacy Clinical Policy Bulletins Aetna Non-Medicare Prescription Drug Plan. Aetna Clinical Pharmacy Bulletins xvi Stelara References: 4. Ustekinumab. (2015) In Clinical Pharmacology online. Retrieved from http://www.clinicalpharmacology- ip.com/Forms/drugoptions.aspx?cpnum=3586&n=Stelara&t=0. 5. Stelara (ustekinumab) [package insert]. Horsham, PA: Janssen Biotech, Inc. 2014 March.; 6. Feldman SR. Treatment of psoriasis. Waltham, MA: UptoDate; Last modified July 13, 2015. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-of-psoriasis? source=search_result&search=psoriasis&selectedTitle=1%7E150#H42. Accessed September 25, 2015. 7. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). Psoriasis: the assessment and management of psoriasis. London (UK): National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE); 2012 Oct. 61 p. (NICE clinical guideline; no. 153). xvii Sucraid References 4. Kellermayer, Richard, Shulman, Robert J. Overview of the causes of chronic diarrhea in children. In: UpToDate, Klish, William J (Ed), Hoppin, Alison G (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA, Dec 16, 2015. 5. Sucraid [package insert]. Vero Beach, FL: QOL Medical, LLC; November, 2014. 6. US National Library of Medicine. Congenital sucrase-isomaltase deficiency. Genetics Home Reference. July 2008; http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/congenital-sucrase-isomaltase-deficiency. Accessed 12/16/2015. 7. NASPGHAN and NASPGHAN Foundation for Children’s Digestive Health and Nutrition. Recognition and management of dietary carbohydrate-induced diarrhea in pediatric patients. Monographs. October 2011; www.naspghan.org//files/documents/pdfs/medical-resources/nutrition/Disaccharide Newsletter_11-17- 11.pdf. Accessed 12/16/2015. 8. International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders, Inc. (2015, January 26). Congenital Sucrase-Isomaltase Deficiency (CSID). Retrieved December 16, 2015, from International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: http://www.iffgd.org xviii Sutent References 1. Sutent prescribing information. Pfizer Inc.;New York, NY; Updated 5/2015. 2. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Kidney Cancer. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/kidney.pdf. Version 1.2016. Accessed October 30, 2015. 3. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Neuroendocrine Tumors. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/neuroendocrine.pdf. Version 1.2015. Accessed October 30, 2015. 4. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Soft Tissue Sarcoma. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/sarcoma.pdf. Version 1.2015. Accessed October 30, 2015. xix Tarceva References 1. Tarceva® (erlotinib) prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.: South San Francisco, CA. Updated: May, 2015. 2. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Kidney Cancer. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/kidney.pdf. Version 1.2016. Accessed October 30, 2015. 3. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/pancreatic.pdf. Version 2.2015. Accessed December 15, 2015. 4. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf. Version 2.2016. Accessed December 15, 2015. xx Thalomid References 9. Thalomid® (thalidomide) prescribing information. Celgene Corp., Updated 8/2015. 10. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Multiple Myeloma. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/myeloma.pdf. Version 2.2016. Accessed December 10, 2015. 11. Clarke J. Management of refractory discoid lupus and subacute cutaneous lupus. Waltham, MA: UptoDate; Last modified October 22, 2015. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/management-of-refractory-discoid-lupus-and-subacute- cutaneous-lupus?source=search_result&search=thalidomide&selectedTitle=15%7E150#H1088110. Accessed December 15, 2015. 12. Schur PH, Moschella SL. Mucocutaneous manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Waltham, MA: UptoDate; Last modified April 16, 2014. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/mucocutaneous-manifestations-of-systemic- lupus-erythematosus?source=search_result&search=sle&selectedTitle=5%7E150#H18. Accessed December 15, 2015. 13. Scollard D, Stryjewska B. Treatment and prevention of leprosy. Waltham, MA: UptoDate; Last modified December 7, 2015. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-leprosy? source=search_result&search=erythema+nodosum+leprosum&selectedTitle=2%7E11#H89888451. Accessed December 15, 2015. xxi Tykerb References 1. Tykerb [lapatinib] Prescribing Information. GlaxoSmithKline. Updated: March, 2015. 2. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Brest Cancer. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf. Version 1.2016. Accessed December 17, 2015. xxii Votrient References 6. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Kidney Cancer. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/kidney.pdf. Version 1.2016. Accessed October 30, 2015. 7. NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guideline in Oncology: Soft Tissue Sarcoma. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/sarcoma.pdf. Version 1.2015. Accessed October 30, 2015. xxiii Xeljanz References: 1. Xeljanz (tafacitinib citrate) [package insert]. NJ, NJ; Pfizer Labs; Revised November 2012. 2. Singh JA, Furst DE, Bharat A, et al. 2012 update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2012;64(5):625-639.