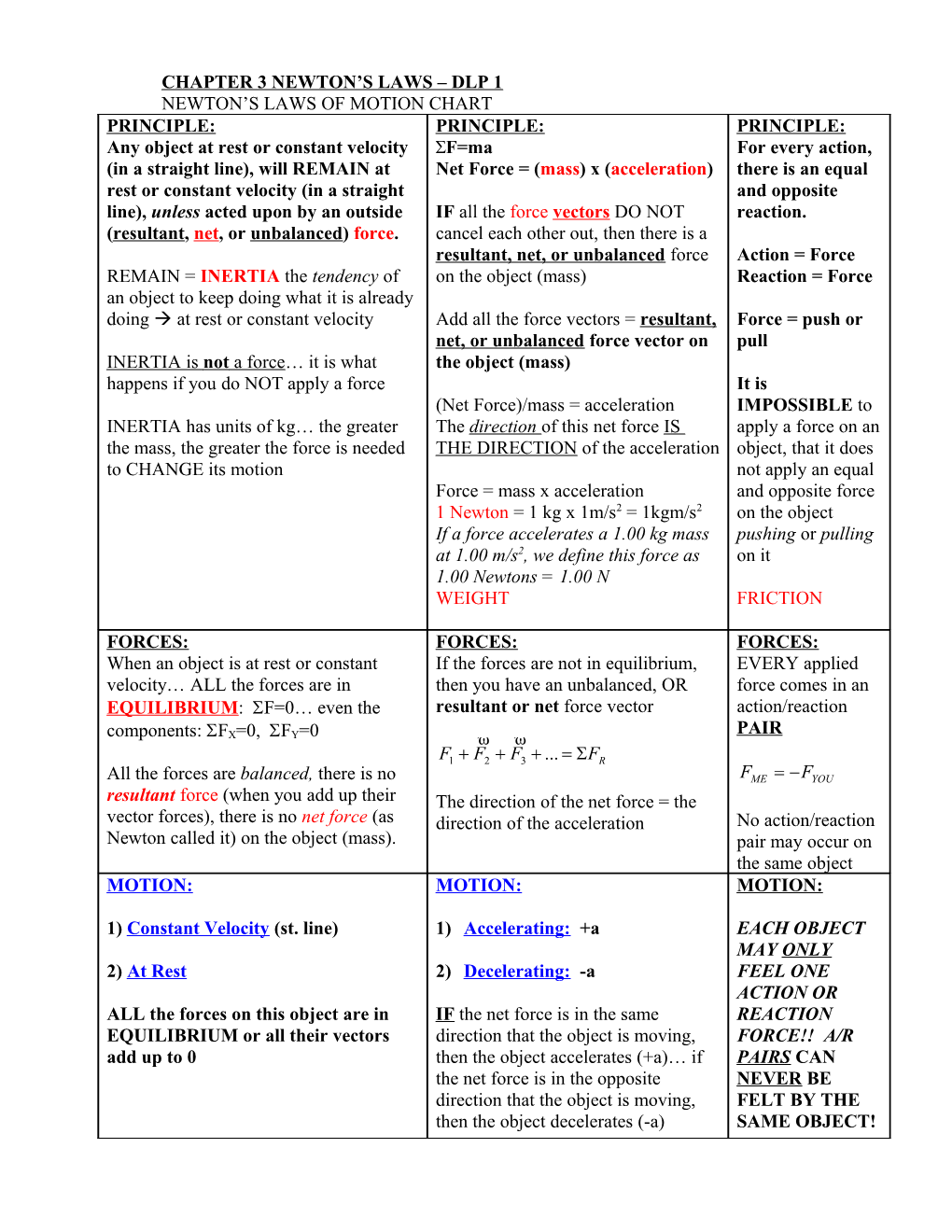
CHAPTER 3 NEWTON’S LAWS – DLP 1 NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION CHART PRINCIPLE: PRINCIPLE: PRINCIPLE: Any object at rest or constant velocity F=ma For every action, (in a straight line), will REMAIN at Net Force = (mass) x (acceleration) there is an equal rest or constant velocity (in a straight and opposite line), unless acted upon by an outside IF all the force vectors DO NOT reaction. (resultant, net, or unbalanced) force. cancel each other out, then there is a resultant, net, or unbalanced force Action = Force REMAIN = INERTIA the tendency of on the object (mass) Reaction = Force an object to keep doing what it is already doing at rest or constant velocity Add all the force vectors = resultant, Force = push or net, or unbalanced force vector on pull INERTIA is not a force… it is what the object (mass) happens if you do NOT apply a force It is (Net Force)/mass = acceleration IMPOSSIBLE to INERTIA has units of kg… the greater The direction of this net force IS apply a force on an the mass, the greater the force is needed THE DIRECTION of the acceleration object, that it does to CHANGE its motion not apply an equal Force = mass x acceleration and opposite force 1 Newton = 1 kg x 1m/s2 = 1kgm/s2 on the object If a force accelerates a 1.00 kg mass pushing or pulling at 1.00 m/s2, we define this force as on it 1.00 Newtons = 1.00 N WEIGHT FRICTION
FORCES: FORCES: FORCES: When an object is at rest or constant If the forces are not in equilibrium, EVERY applied velocity… ALL the forces are in then you have an unbalanced, OR force comes in an EQUILIBRIUM: F=0… even the resultant or net force vector action/reaction PAIR components: FX=0, FY=0 F1 F2 F3 ... FR All the forces are balanced, there is no FME FYOU resultant force (when you add up their The direction of the net force = the vector forces), there is no net force (as direction of the acceleration No action/reaction Newton called it) on the object (mass). pair may occur on the same object MOTION: MOTION: MOTION:
1) Constant Velocity (st. line) 1) Accelerating: +a EACH OBJECT MAY ONLY 2) At Rest 2) Decelerating: -a FEEL ONE ACTION OR ALL the forces on this object are in IF the net force is in the same REACTION EQUILIBRIUM or all their vectors direction that the object is moving, FORCE!! A/R add up to 0 then the object accelerates (+a)… if PAIRS CAN the net force is in the opposite NEVER BE direction that the object is moving, FELT BY THE then the object decelerates (-a) SAME OBJECT! NEWTONIAN TERMS
INERTIA
FRICTION
FORCE
NET FORCE
RESULTANT FORCE
NORMAL FORCE
FRICTIONAL FORCE
APPLIED FORCE
GRAVITY FORCE
CONTACT FORCES
WEIGHT
POUND
NEWTON
GRAVITY
KILOGRAM
ACCELERATION
MASS
EQUILIBRIUM